Method for preparing large yellow tea polysaccharide through ultrahigh pressure and application of large yellow tea polysaccharide
A technology of ultra-high pressure and big tea, which is applied in food science and other fields, can solve the problems of changing the primary structure and composition of polysaccharides and enhancing their biological activity, and achieve the effects of liver damage protection, simple preparation method and improved liver protection activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Ultra-high pressure extraction of yellow tea polysaccharides
[0020] Step 1: Mix Huangdacha and absolute ethanol in a ratio of 1:10, soak in a 60°C water bath for 12 hours, remove the ethanol, dry, pulverize and pass through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain Huangdacha dry powder.
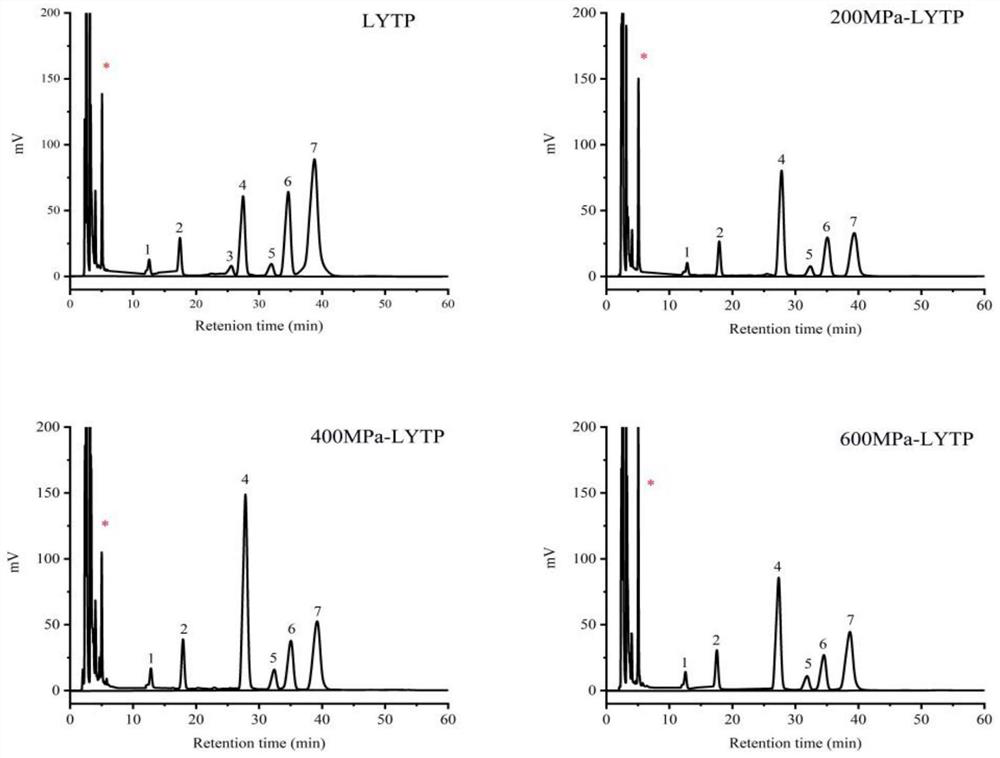
[0021] Step 2: Add the dried yellow tea powder obtained in step 1 into distilled water according to the ratio of material to liquid 1:10, put it into ultra-high pressure equipment after vacuum packaging, set the pressure to 200, 400 and 600MPa, hold the pressure for 5min, and extract the temperature to 25 ℃, the obtained extract is subjected to solid-liquid separation, reduced pressure concentration, alcohol precipitation and freeze-drying to obtain the yellow tea polysaccharide UHP-LYTP.
[0022] Step 3: Determination of chemical composition of LYTP and UHP-LYTP. The total sugar content was determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method with glucose as the standard; the protein content...
Embodiment 2
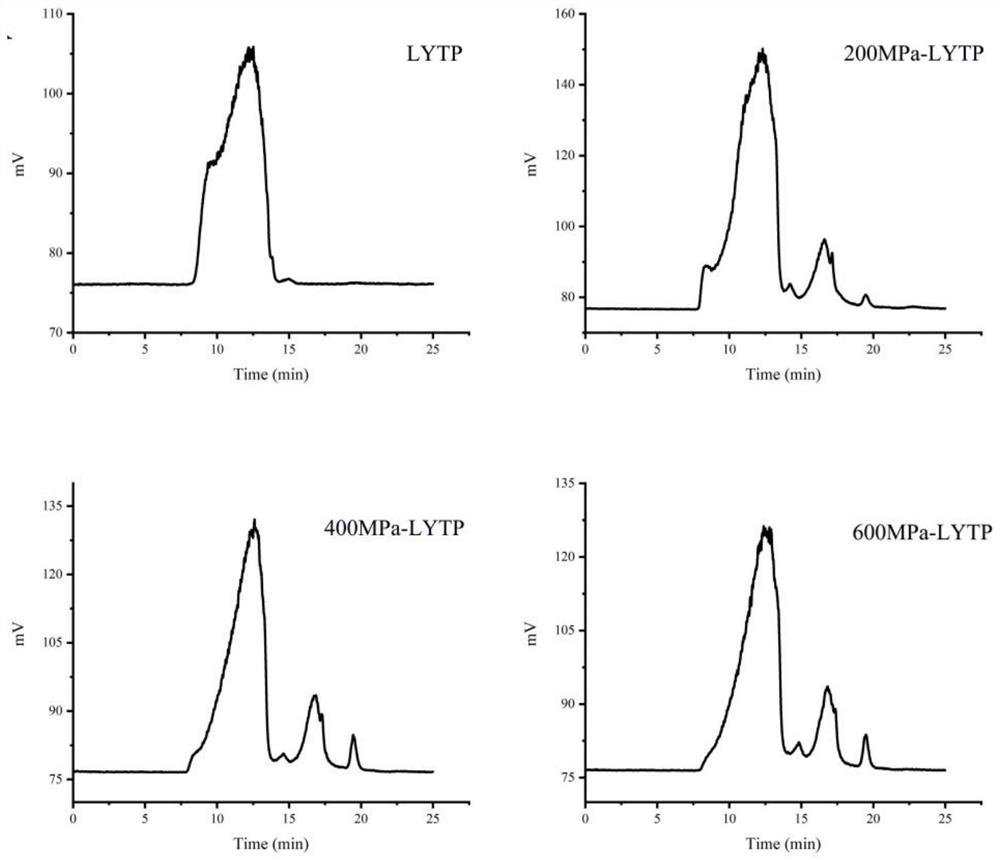
[0026] Example 2: LYTP and UHP-LYTP monosaccharide composition and molecular weight determination
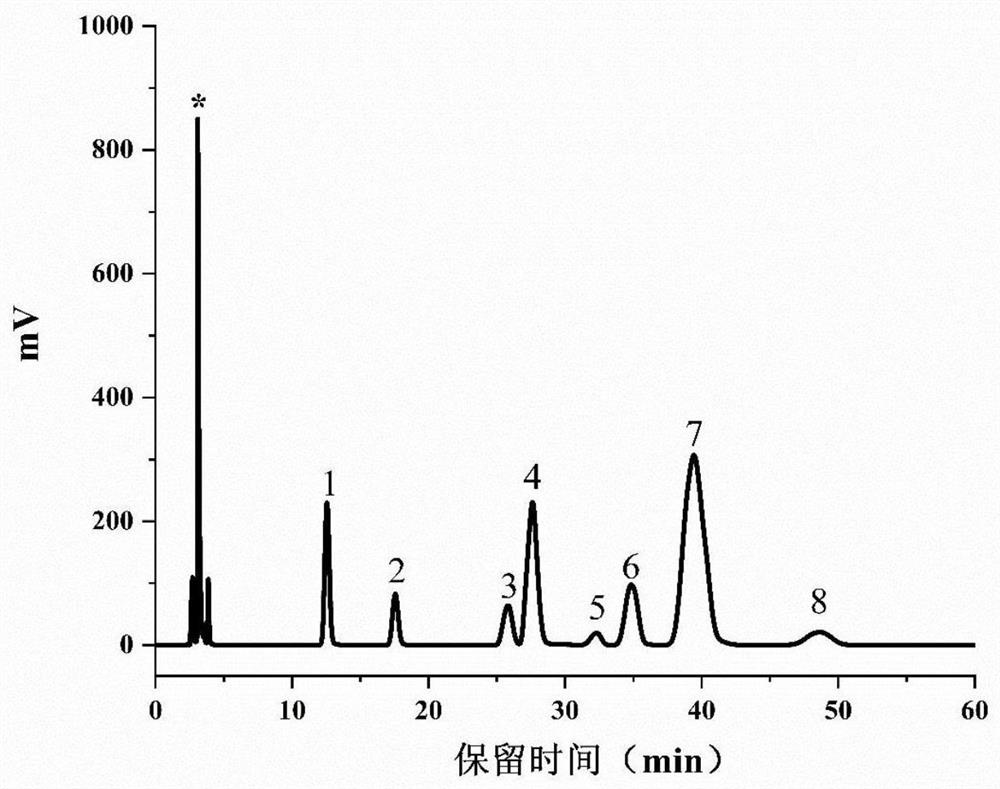
[0027] Step 1: Monosaccharide composition analysis of LYTP and UHP-LYTP The samples were treated by acid hydrolysis-pre-column PMP derivatization method, and analyzed and determined by high performance liquid chromatography. LYTP and UHP-LYTP (5 mg) were weighed and dissolved in 5 mL of 2 mol / L trifluoroacetic acid, sealed with nitrogen, and fully hydrolyzed in an oil bath at 110 °C for 8 h. Rotate out the water with a rotary evaporator, add an appropriate amount of deionized water, and repeat the rotary evaporation until the pH of the solution is neutral, add 1 mL of distilled water, and set aside.
[0028] Step 2: Add 50 μL, 0.5 mol / LPMP methanol solution and 50 μL, 0.3 mol / L NaOH solution to the standard monosaccharide and the hydrolyzed sample solution, react in a water bath at 70 °C for 30 min for PMP pre-column derivatization, and then use 50 μL of .3mol / L HCl to neutrali...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Determination of hepatoprotective activity of LYTP and UHP-LYTP
[0038] Step 1: Grouping of experimental animals
[0039] After a week of adaptive feeding, 56 mice were randomly divided into 7 groups (n=8), which were the blank control group (NC), the bifendate control group (PC), and the hot water extraction yellow tea group. (LYTP), 200MPa extraction of yellow tea polysaccharide group (200MPa-LYTP), 400MPa extraction of yellow tea polysaccharide group (400MPa-LYTP), 600MPa extraction of yellow tea polysaccharide group (600MPa-LYTP). The gavage amount was uniformly 400 mg / Kg·d per day, and the blank group was given the corresponding normal saline. All mice except the blank group were given ethanol to induce alcoholic liver injury (0.025mL / 10g, 2 days; 0.05mL / 10g, 3 days; 0.08mL / 10g, 5 days; 0.10mL / 10g, 7 days; 0.12mL / 10g, 10 days; 0.14mL / 10g, 1 day) for four weeks, weighing once a week.
[0040] Step 2: Determination of mouse serum biochemical indicator...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com