Tin-zinc base plumbum-free solder alloy and its preparing technology
A lead-free solder and preparation process technology, applied in manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of no large-scale commercial application, high raw material cost, complex process, etc., and achieve good cost performance and practicability , good development potential, simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
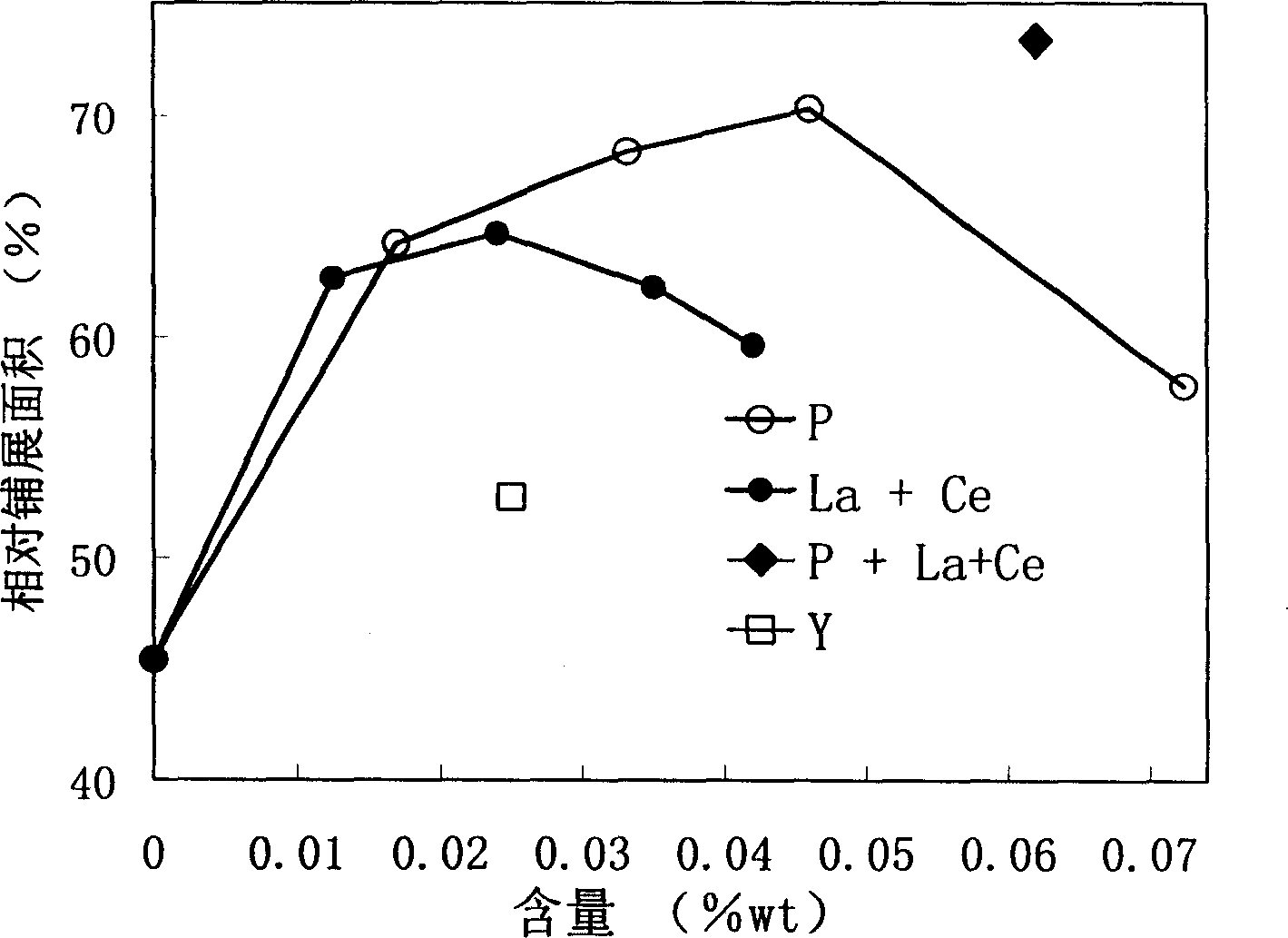
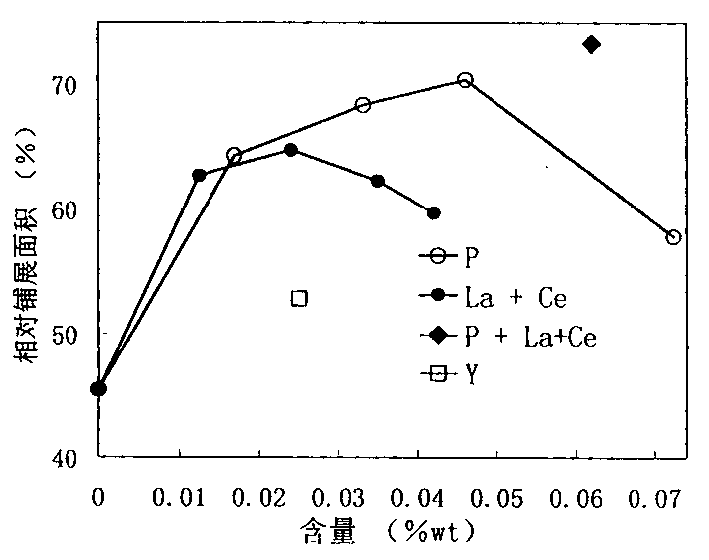
[0024] A preparation process of a tin-zinc-based lead-free solder alloy, wherein a tin-zinc-based lead-free solder alloy base material is melted and prepared in a resistance furnace with a graphite crucible, wherein the zinc content is 9.0% of the total weight of the alloy, and the surface is protected by graphite; The melting point of the prepared base metal was measured to be 198°C. The alloy was prepared by melting in a vacuum induction furnace; 100 grams of the base metal was melted in a corundum crucible in a resistance furnace and heated to 370°C, the red phosphorus powder was covered with tin foil, and the melt was quickly pressed into the melt and stirred. After holding for 10 minutes, the temperature was lowered to 300 ℃, cast into a round bar of φ20mm with an iron mold.
[0025] A series of tin-zinc-based alloys with different phosphorus contents were fused according to the above method for wettability measurement; the zinc content of the conventional tin-lead solder...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A preparation process of a tin-zinc-based lead-free solder alloy, wherein a tin-zinc-based lead-free solder alloy base material is fused in a resistance furnace with a graphite crucible, wherein the zinc content is 9.0% of the total weight of the alloy, and the surface is protected by graphite; The melting point of the prepared base metal was measured to be 198°C. Add single or mixed lanthanum and cerium in a vacuum induction furnace, and smelt to prepare a master alloy; melt 100 grams of base metal in a resistance furnace with a corundum crucible and heat it up to 350 °C, quickly press into the melt and stir, and keep it for 10 minutes. Cool down to 290°C, and cast it into a round bar of φ20mm with an iron mold
[0029] A series of tin-zinc-based alloys with different phosphorus contents were fused according to the above method for wettability measurement; the zinc content of the conventional tin-lead solder alloy for comparison was 37% of the total weight of the tin-l...
Embodiment 3
[0030] A preparation process of a tin-zinc-based lead-free solder alloy, wherein a tin-zinc-based lead-free solder alloy base material is melted and prepared in a resistance furnace with a graphite crucible, wherein the zinc content is 9.0% of the total weight of the alloy, and the surface is protected by graphite; The melting point of the prepared base metal was measured to be 198°C. Add single or mixed lanthanum and cerium in a vacuum induction furnace, smelt to prepare a master alloy, melt 100 grams of base metal in a resistance furnace with a corundum crucible and heat it up to 370 ° C, wrap the master alloy with tin foil, and quickly press into the melt And stir, and then wrap red phosphorus powder with tin foil, quickly press into the melt and stir, keep warm for 10 minutes, cool down to 290 ° C, and cast it into a φ20mm round rod with an iron mold.
[0031] According to the above method, a tin-zinc-based alloy with a phosphorus content of 0.009% by weight and a 1:1 weig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com