Method for inhibiting chloride ion corrosion in recirculated cooling water
A technology of chloride ion corrosion and circulating cooling water, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, descaling and water softening, etc., and can solve the problem of increasing the investment of chemicals, water and sewage, and heat exchanger holes Corrosion, waste of water resources and other issues, to achieve excellent results, lower requirements, and low prices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
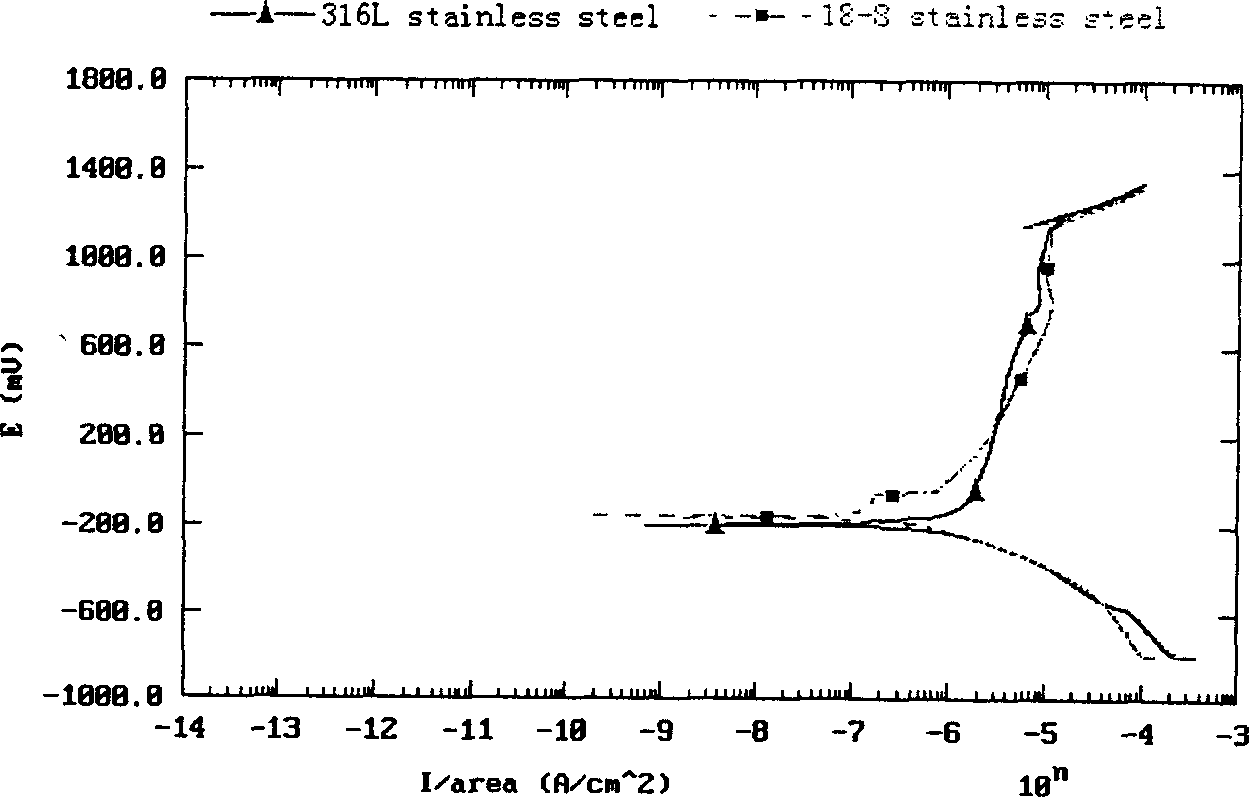
[0026] In this example, 18-8 stainless steel was used for corrosion test.
[0027] Test instrument: American EG&G PARC M352 comprehensive corrosion tester. The working electrode is the sample, the reference electrode is the saturated calomel electrode, and the auxiliary electrode is the platinum electrode.
[0028] Test sample: 18-8 stainless steel. Epoxy sealed sample, exposed 1cm 2The test surface is polished to 600 step by step with metallographic sandpaper # , washed with water and ethanol. Polished sample in 25% HNO at 50°C 3 Medium passivation treatment for 1 hour.
[0029] Test conditions: temperature 30±2°C; scanning speed 1mv / s; retrace current density 0.1mA / cm 2 , the solution does not deoxygenate.
[0030] Test water quality: 1 / 2 Beijing tap water + 1 / 2 deionized water was used as the basic water quality of the test. The main water quality is shown in Table 1. Test results such as figure 2 shown.
[0031] project
[0032] figure 2 for Cl - W...
example 2
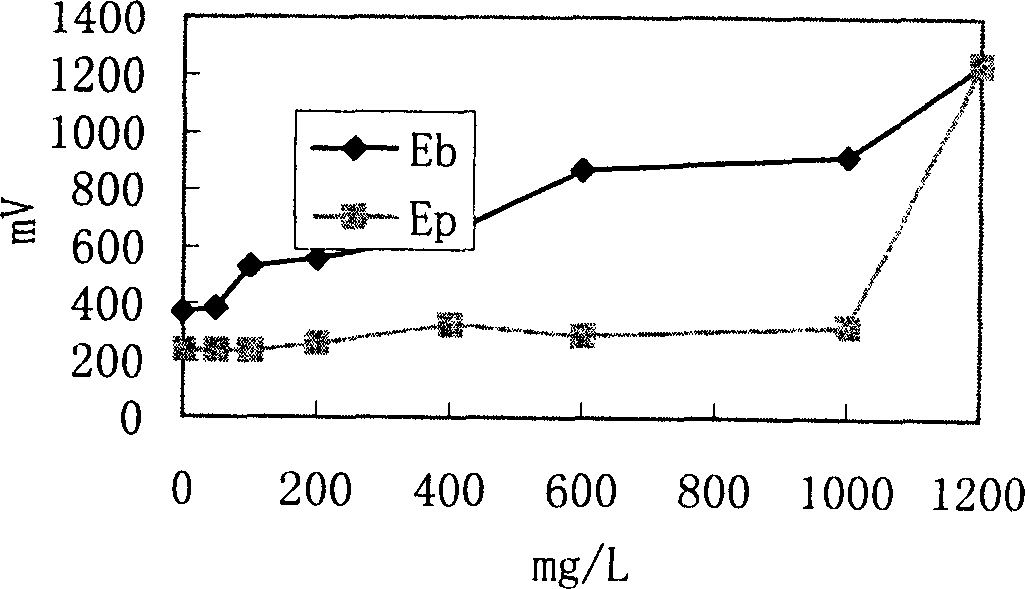
[0034] In this example, 18-8 stainless steel was used for corrosion test.
[0035] Test condition and water quality are the same as example 1, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0036] serial number
[0037] Table 2 Description, SO 4 2- The presence of SO greatly improves the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. 4 2- When chlorine ions below 400mg / L were added to 600mg / L experimental water, the pitting potential of 18-8 stainless steel was above 1247mV, and no pitting corrosion occurred. but no SO 4 2- When it exists, even if only 100mg / L chloride ion is added to the water, the pitting potential of 18-8 stainless steel will drop to 556mV.
example 3
[0039] This example uses 20 # Carbon steel was subjected to corrosion tests.
[0040] The test water quality is the same as Example 1, the test conditions refer to HG / T215991, the test temperature is 50°C, the speed is 75 rpm, the operation is 72 hours, and the pH is 7.5-7.6.
[0041] Add 20 mg / L of hydroxyethylidene diphosphonic acid, 30 mg / L of polyol phosphonate, 50 mg / L of terpolymer of acrylic acid, AMPS and maleic anhydride, 15 mg / L of zinc salt and different concentrations of SO 4 2- with Cl - (respectively with analytically pure Na 2 SO 4 and NaCl preparation). The test results are shown in Table 3.
[0042] serial number
[0043] The results in Table 3 show that when no water treatment agent is added, at high concentrations of Cl - and SO 4 2- Presence under 20 # Carbon steel is severely corroded, and the corrosion rate is as high as 1.4320mm / a. After adding the water treatment agent, the corrosion rate is below 0.0653mm / a, indicating that the wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com