Method for recovering copper and nickel nitrate by electrolysis of electroplating waste water
A technology for electroplating wastewater and electrolysis recovery is applied in the field of preparation technology of copper and nickel nitrate, which can solve the problems of cumbersome process and high extraction cost, and achieve the effects of simple and convenient process, low recovery cost, good economic benefits and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
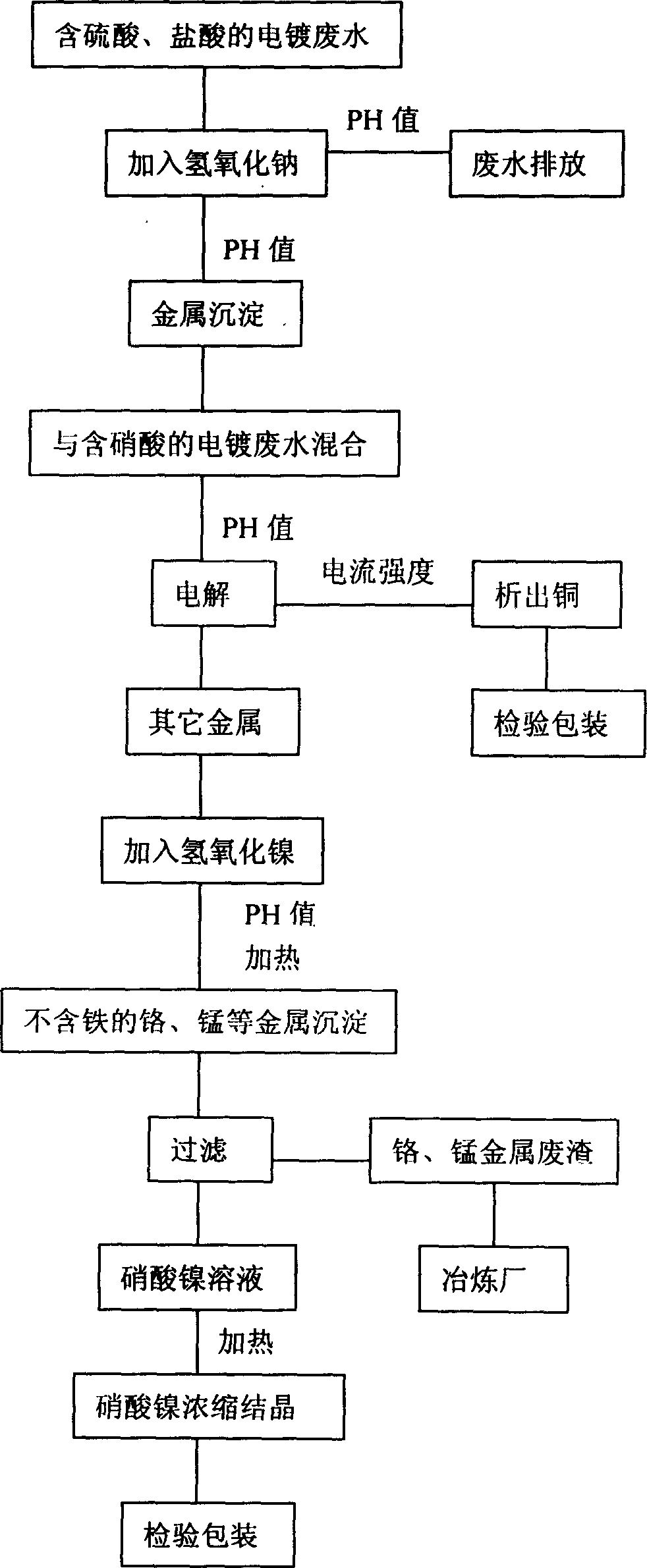
[0022] see figure 1 In this embodiment, sodium hydroxide is added to the electroplating wastewater containing at least one of sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, and through a chemical reaction, its pH value reaches 6-8, that is, the amount of sodium hydroxide added to achieve the pH requirement is At this time, all kinds of metals in the wastewater are precipitated, and the wastewater can be discharged if it reaches the standard; of course, it is best to have a pH value of 7, because at this time the pH is just neutral, that is, the acid-base content of the wastewater is just neutralized.
[0023] Then, mix the precipitated metal with the electroplating wastewater containing nitric acid, and all the metals are dissolved in the nitric acid wastewater. At this time, the pH value is controlled between 1-3, preferably between 2-2.5, and then directly electrolyzed. The current intensity is controlled between 150-200 amperes, so that the copper is completely precipitated during th...
Embodiment 2
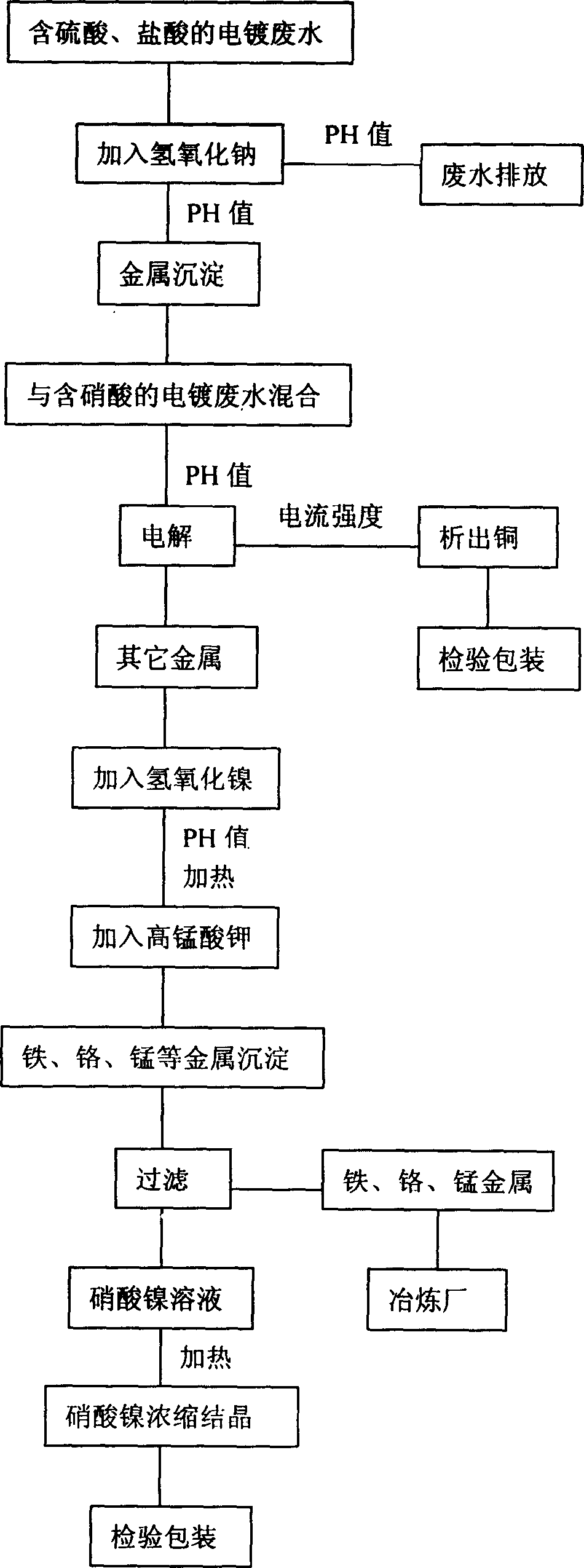
[0028] see figure 2 , in this embodiment, the first two steps are the same as in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated.
[0029] After the electrolytic copper is obtained by electrolysis, since the nitric acid liquid containing metal also contains iron, nickel hydroxide is added, and the pH value is 4-5, preferably 4-4.5, and then heated. The heating temperature is controlled between 95°C-98°C, preferably 97°C. After that, potassium permanganate needs to be added to make the iron in the solution precipitate together with chromium, manganese and other metals. It should be noted that the amount of potassium permanganate added is generally determined according to the weight of iron in the solution. If there is 0.1-0.2 kg of iron in the solution, 0.5 kg of potassium permanganate needs to be added. To increase or decrease the weight, the amount of potassium permanganate added needs to be increased or decreased in proportion.
[0030] Finally, the precipitated iron, chromium, ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com