Photo-acoustic functional brain imaging method and device
A brain function and imaging technology, which is applied in medical science, sensors, vaccination and ovulation diagnosis, etc., can solve the problems of inability to capture dynamic changes in brain function, high price, low time resolution, etc., and achieve fast and non-destructive brain function imaging with low cost , easy to apply and promote the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
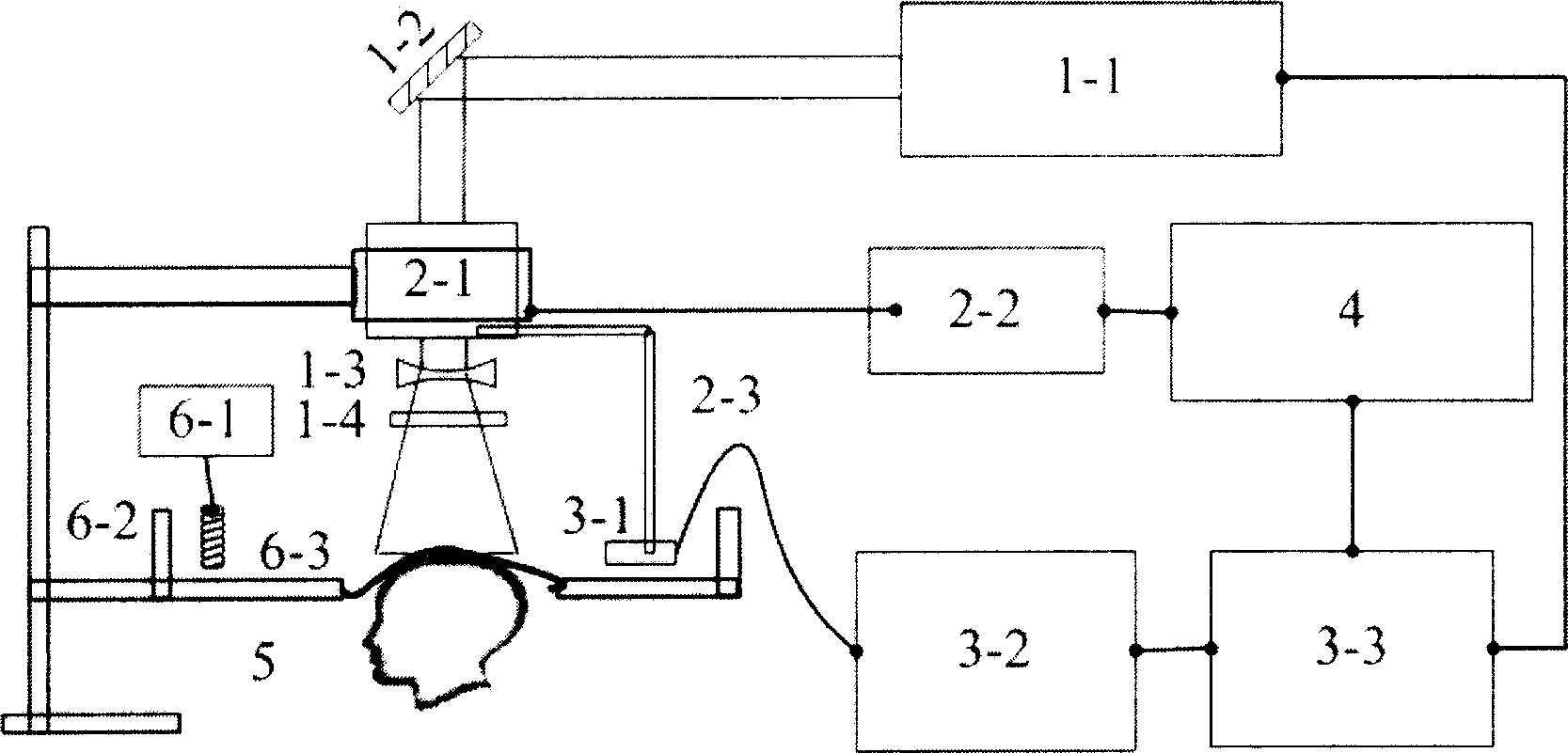
[0047] A five-week-old Kunming mouse weighing about 30 g was tested with the device of the present invention. Before the test, the hair on the head of the mice was depilated with a self-made depilatory solution (8% sodium sulfide glycerin paste), without damaging the epidermis and cranium of the brain. Anesthetize the mouse intravenously with 2% sodium pentobarbital at a dose of 30 mg / kg, then place the mouse on a three-dimensional lifting frame, fix the head with a fixer, and place it under the polyethylene film in the middle of the acoustic coupling pool , calibrate the scanning plane of the ultrasound probe so that it is on the same plane as the mouse brain.
[0048] In the experiment, a 532nm pulsed laser was selected, with a pulse width of 10ns, a repetition rate of 15Hz, and an output pulse energy density of 8mJ / cm 2 . The photoacoustic signal of the brain received by the ultrasonic detector is sent to the digital oscilloscope after being amplified. In the experiment,...
Embodiment 2
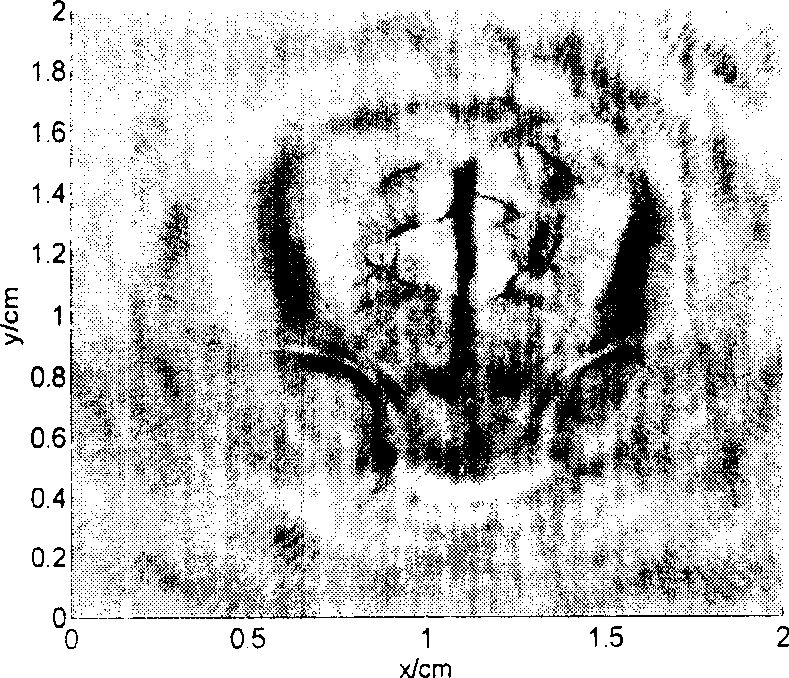
[0050] The device of the present invention is used to test a brain injury model mouse. Before the experiment, the mice were anesthetized by intravenous injection, the hair on the scalp was removed, and then a needle was artificially used to pierce the scalp and skull on the lower left side of the mouse's head, and inserted into the surface of the cerebral cortex to create a model of intracerebral injury and bleeding. After the mouse was fixed, according to the method of Example 1, a 1064nm pulsed laser was selected, with a pulse width of 10ns, a repetition rate of 15Hz, and an output pulse energy density of 8mJ / cm 2 , scan and collect the photoacoustic signal of the brain to obtain a photoacoustic tomographic image of the brain, as shown in FIG. 3( a ). After the experiment, the mice were sacrificed and dissected, and the anatomical diagram is shown in Figure 3(b). It can be seen from Fig. 3(a) that the area of brain injury, the situation of blood vessel destruction, and th...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A drug-stimulated mouse was tested with the device of the present invention. The drug is acetazolamide (Acetazolamide), which is an isocyclic sulfonamide, is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, can make cerebral vasodilators, and is used for cerebral blood perfusion SPECT imaging to evaluate cerebral vascular reserve function. It is affirmed and called "ACZ Brain Stress Test", which can increase cerebral blood flow and dilate cerebral blood vessels. In the test, the same mouse was used to perform photoacoustic scanning according to the method of Example 1 before and after feeding the drug, and the resulting images were compared and compared. Feed it to mice with a dose of 25ul / g, and it will start to take effect after 30 minutes, and the drug effect will reach the peak after 2 hours. Thirty minutes after the experiment, the mice were awake and recovered. Figure 4(a) is the brain image before drug administration, and Figure 4(b) is the brain image after drug administration...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com