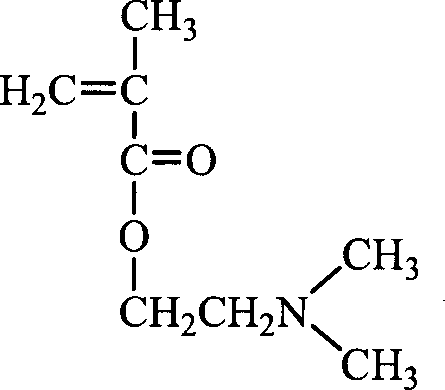
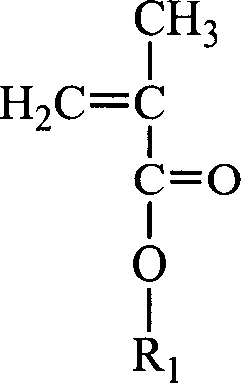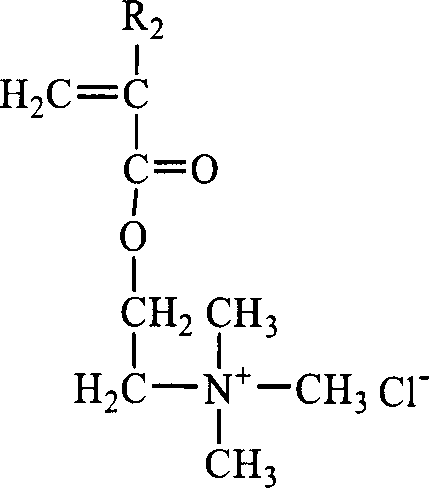Random and copolymer cation macromolecular emulsion and its preparation
A technology of macromolecular emulsifier and random copolymerization, which is applied in the field of copolymers to achieve the effects of high conversion rate, migration prevention, and low requirements for reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Poly(SMA-co-DMAEMA) (1:9, molar ratio) and its preparation
[0043] (1) Preparation of reaction monomers and initiators: 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate is used with activated basic Al 2 o 3 Column treatment, and then vacuum distillation for later use; octadecyl methacrylate was used directly; AIBN was recrystallized with absolute ethanol for later use.
[0044] (2) Preparation of polymer: Weigh 3.8g (0.01mol) of hydrophobic monomer octadecyl methacrylate (SMA), hydrophilic monomer 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) 16.0g (0.09mol); Initiator AIBN 0.2g (weighed by 1.2% of the total monomer molar weight); Measure 1mL of n-dodecanethiol, be dissolved in 127mL (measured by 20% solid content) After stirring evenly, pour it into a 250mL four-necked bottle equipped with a stirrer, a reflux condenser, a thermometer and a nitrogen conduit, and pass N 2 , stirring at a stirring speed of 350r / min, rapidly raising the temperature to 70°C, and maintaini...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: Poly(SMA-co-DMAEMA) (2:8, molar ratio) and its preparation
[0048] (1) Preparation of reaction monomers and initiators: same as step [1] of embodiment one.
[0049] (2) Preparation of polymer: Weigh 7.0 g (0.02 mol) of hydrophobic monomer octadecyl methacrylate (SMA); hydrophilic monomer 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) 12.6g (0.08mol); Initiator AIBN 0.2g (take by weighing 1.2% of total monomer molar weight); Measure 1mL n-dodecanethiol, be dissolved in 127ml (take by solid content 20%) After stirring evenly, pour it into a 250mL four-necked bottle equipped with a stirrer, a reflux condenser, a thermometer and a nitrogen conduit, and pass N 2 , stirring at a stirring speed of 350r / min, rapidly raising the temperature to 70°C, and maintaining this temperature and stirring speed, reacting for 3h, cooling and discharging.
[0050] (3) Purification of polymer: Rotate the reaction product in (2) at 60-70°C to remove the solvent and some unreacted ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Poly(SMA-co-DMAEMA) (1:9, molar ratio) and its preparation
[0053] (1) Preparation of reaction monomer and initiator: carry out by the method of embodiment one (1).
[0054] (2) Preparation of polymer: Weigh 0.39 g (1.15 mmol) of hydrophobic monomer octadecyl methacrylate (SMA); hydrophilic monomer 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) 1.63g (10.3mmol); Initiator AIBN 0.19g (take by weighing 10% of total monomer molar weight), be dissolved in the dehydrated alcohol of 17mL (measure by solid content 13%), after stirring , pour it into a 250mL four-necked bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser, thermometer and nitrogen conduit, and pass through N 2 , stirring at a stirring speed of 350r / min, rapidly raising the temperature to 70°C, and maintaining this temperature and stirring speed, reacting for 6.5h, cooling and discharging.
[0055] (3) Purification of polymer: carry out by the method for embodiment one (3).
[0056] (4) Characterizatio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Critical micelle concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Critical micelle concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Relative molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com