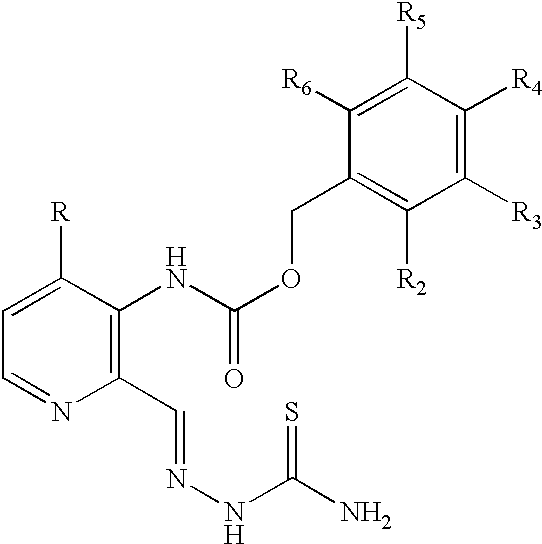
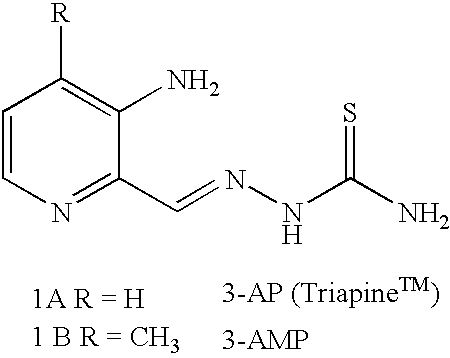
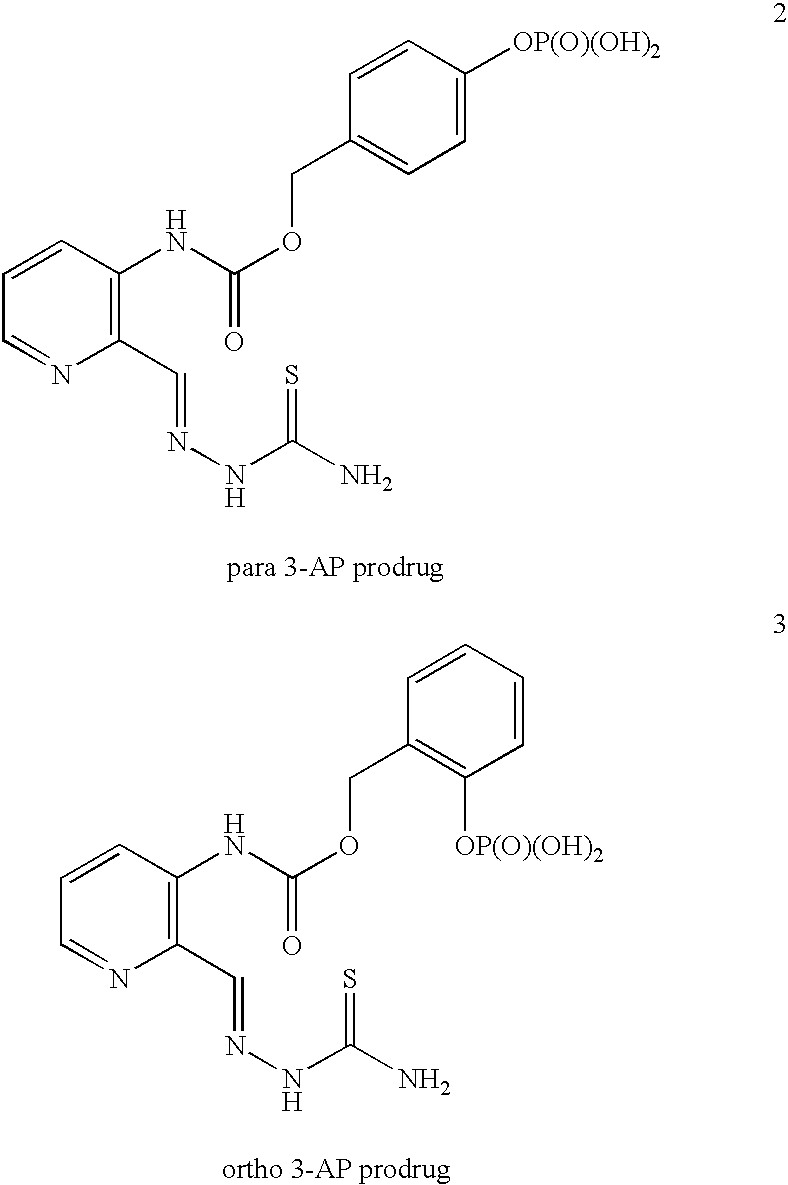
Modified prodrug forms of AP/AMP
a technology of prodrug and modified form, which is applied in the direction of biocide, group 5/15 element organic compounds, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of limited therapeutic potential of this compound, achieve favorable pharmacokinetic parameters, maximize the intended effect of compound, and maximize the beneficial effect effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-3
General Procedures for Preparation of the Nicotinic Acid (20)
example 1
Preparation of 2-chloronicotinic acid methyl ester (18)
[0063] To a mixture of 2-chloronicotinic acid (Aldrich, 100.0 g, 0.63 mol) in 1,4-dioxane (500 mL) was added thionyl chloride (70 mL, 0.96 mol). The suspension was heated under reflux for 22 h with a gas trap to absorb hydrogen chloride gas. After evaporation of the solvent, the residue was dissolved in methanol (300 mL). To the solution was added dropwise triethylamine (TEA, 120 mL, 1.26 mol) at 0.degree. C. over 2 h. The solvents were evaporated and the residue was suspended in ethyl acetate. The precipitate was removed by filtration. The filtrate was concentrated to afford the ester 18 (92.3 g, 86%) as an oil:
[0064] Rf (1:5 v / v ethyl acetate-hexane) 0.38.
[0065] .sup.1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl.sub.3) .delta. 88.53 (dd, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (dd, 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (dd, 7.7 Hz, 1H) and 3.97 (s, 3H).
[0066] .sup.13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl.sub.3) .delta. 164.5, 151.6, 149.6, 140.0, 126.4, 121.9 and 52.5.
example 2
Preparation of 2-styrylnicotinic acid methyl ester (19)
[0067] To a solution of the ester 18 (48.8 g, 0.28 mol) in DMF (450 mL) was added styrene (165 mL, 1.42 mol), palladium acetate (6.5 g, 30 mmol), sodium acetate (47 g, 0.57 mol) and triphenyl phosphine (30 g, 0.11 mol). The mixture was heated under reflux for 22 h. The palladium-catalyst was removed by filtration through a Celite pad. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in a minimum amount of ethyl acetate. To the above solution was added hexane. After removal of the precipitate by filtration, the filtrate was concentrated. The resulting crude material was purified by FCC (1:1 v / v ethyl acetate-hexane) to afford the ester 19 (55.0 g, 81%) as a light yellow oil:
[0068] Rf (1:5 v / v ethyl acetate-hexane) 0.41.
[0069] .sup.1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl.sub.3) .delta. 8.70 (dd, 1H), 8.10 (dd, 1H), 8.16 (d, 1H), 7.94 (d, 1H), 7.64 (d, 2H), 7.4-7.3 (m, 3H), 7.18 (dd, 1H) and 3.94 (s, 3H).
[0070] .su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com