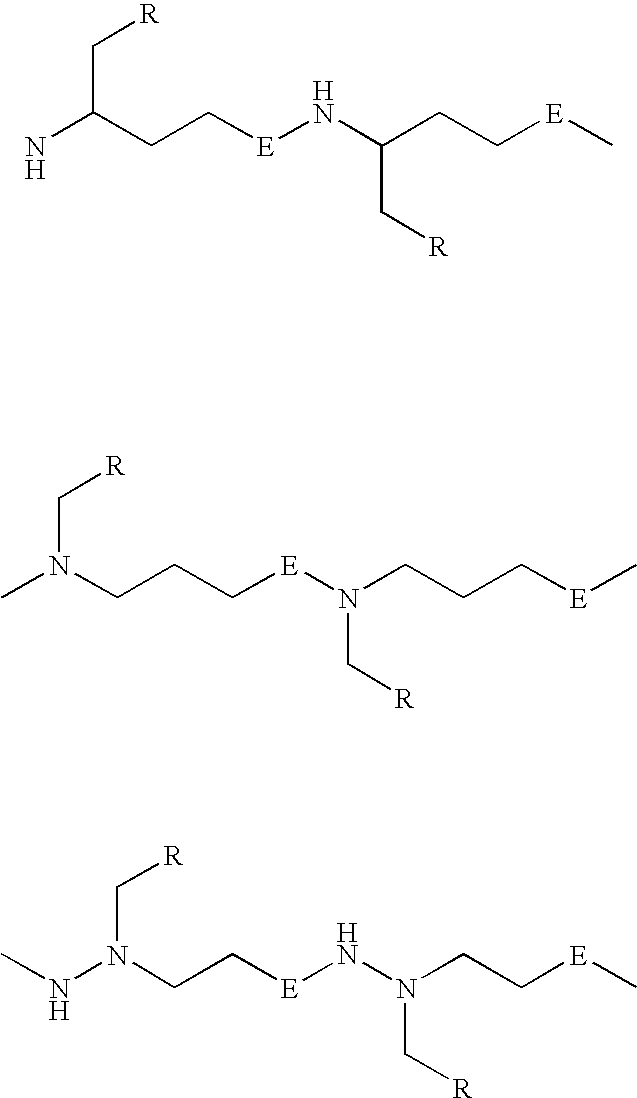
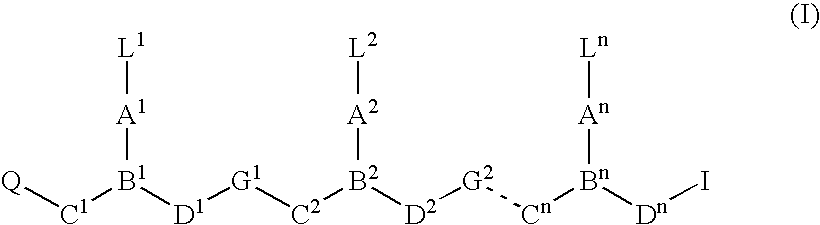
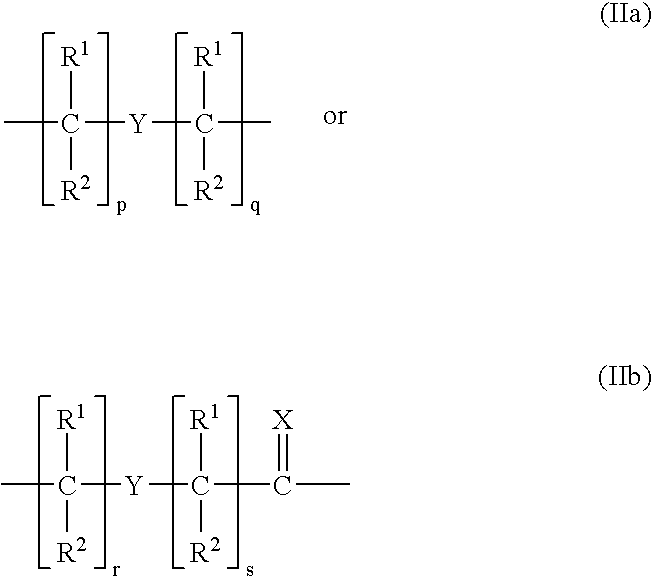Peptide nucleic acids and synthetic procedures therefor
a technology of oligobonucleotides and nucleic acids, applied in the field of peptide nucleic acids, can solve the problems of difficult preparation in more than a few minutes, less routine chemical synthesis of oligobonucleotides, and unphysiologically high ionic strength and low ph
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
tert-Butyl 4-nitrophenyl carbonate
[0182] Sodium carbonate (29.14 g; 0.275 mol) and 4-nitrophenol (12.75 g; 91.6 mmol) were mixed with dioxane (250 ml). Boc-anhydride (20.0 g; 91.6 mmol) was transferred to the mixture with dioxane (50 ml). The mixture was refluxed for 1 h, cooled to 0.degree. C., filtered and concentrated to 1 / 3, and then poured into wat 0.82 ml; 82.6 mmol) and a suspension of N.sup.4-benzyloxycarbonyl-cytosine (9, 21.0 g; 82.6 mmol) and potassium carbonate (11.4 g; 82.6 mmol) in dry DMF (900 ml). The mixture was stirred vigorously overnight, filtered, and evaporated to dryness, in vacuo. Water (300 ml) and 4 N hydrochloric acid (10 ml) were added, the mixture was stirred for 15 minutes at 0.degree. C., filtered, and washed with water (2.times.75 ml). The isolated precipitate was treated with water (120 ml), 2N sodium hydroxide (60 ml), stirred for 30 min, filtered, cooled to 0.degree. C., and 4 N hydrochloric acid (35 ml) was added. The title compound was isolated b...
example 9
N.sup.4-Benzyloxycarbonyl-N.sup.1-carboxymethyl-cytosine pentafluorophenyl ester (11)
[0183] N.sup.4-Benzyloxycarbonyl-N.sup.1-carboxymethyl-cytosine (10, 4.00 g; 13.2 mmol) and pentafluorophenol (2.67 g; 14.5 mmol) were mixed with DMF (70 ml), cooled to 0.degree. C. with ice-water, and DCC (3.27 g; 15.8 mmol) was added. The ice bath was removed after 3 min and the mixture was stirred for 3 h at room temperature. The precipitated DCU was removed by filtration, washed with DMF, and the filtrate was evaporated to dryness, in vacuo (0.2 mmHg). The solid residue was treated with methylene chloride (250 ml), stirred vigorously for 15 min, filtered, washed twice with diluted sodium hydrogen carbonate and once with saturated sodium chloride, dried over magnesium sulfate, and evaporated to dryness, in vacuo. The solid residue was recrystallized from 2-propanol (150 ml) and the crystals were washed thoroughly with ether.
[0184] Yield 3.40 g (55%). M.p. 241-245.degree. C. Anal. for C.sub.20H.su...
example 10
N.sup.4-Benzyloxycarbonyl-1-Boc-aeg-cytosine (12)
[0185] To a solution of (N-Boc-2-aminoethyl)glycine (2) in DMF, prepared as described above, was added triethyl amine (7.00 ml; 50.8 mmol) and N.sup.4-benzyloxycarbonyl-N.sup.1-carboxymethyl-cytosine pentafluorophenyl ester (11, 2.70 g; 5.75 mmol). After stirring the solution for 1 h at room temperature, methylene chloride (150 ml), saturated sodium chloride (250 ml), and 4 N hydrochloric acid to pH .about.1 were added. The organic layer was separated and washed twice with saturated sodium chloride, dried over magnesium sulfate, and evaporated to dryness, in vacuo, first with a water aspirator and then with an oil pump. The oily residue was treated with water (25 ml) and was again evaporated to dryness, in vacuo. This procedure then was repeated. The oily residue (2.80 g) was then dissolved in methylene chloride (100 ml), petroleum ether (250 ml) was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight. The title compound was isolated by filt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ionic strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com