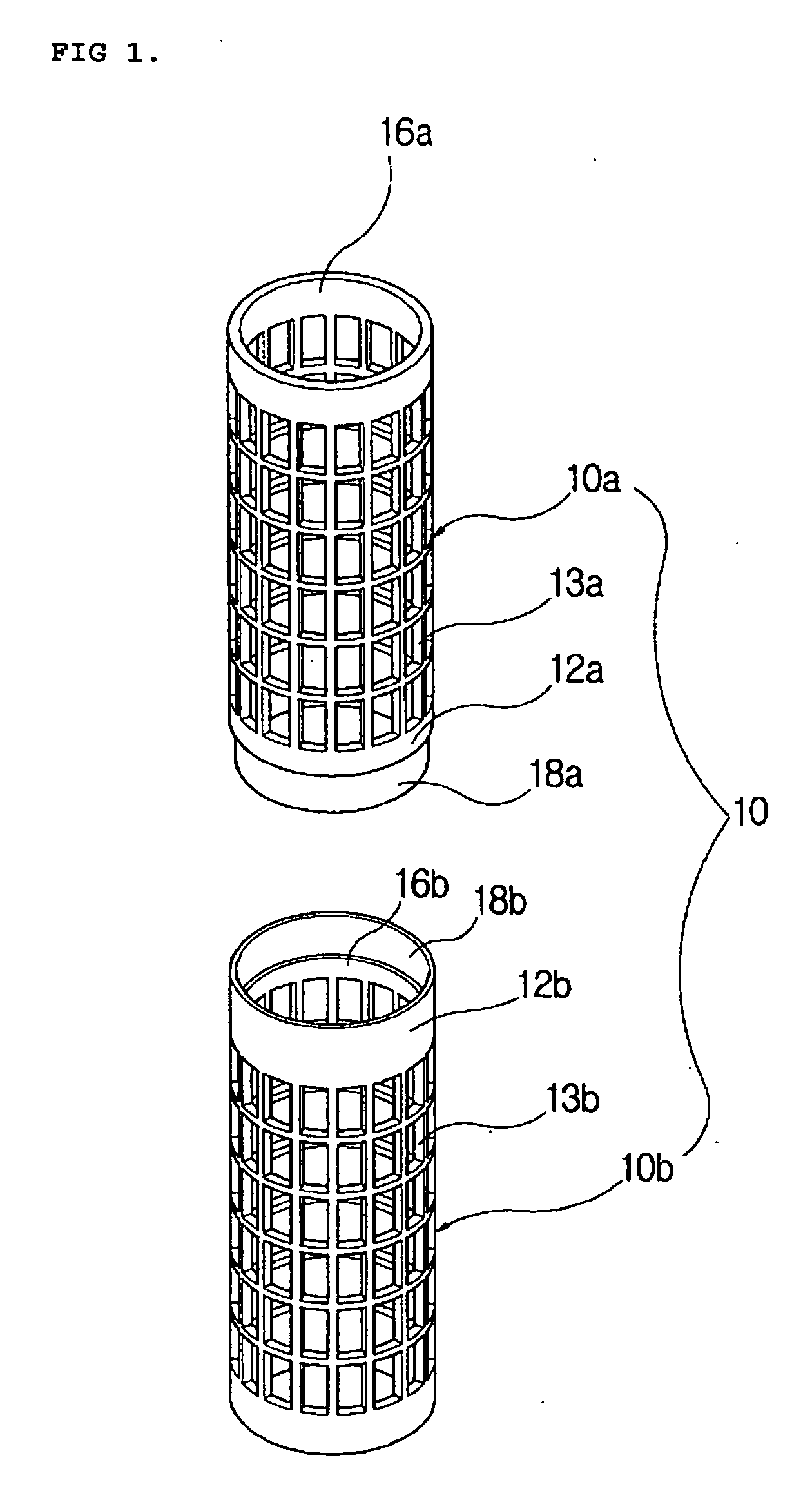
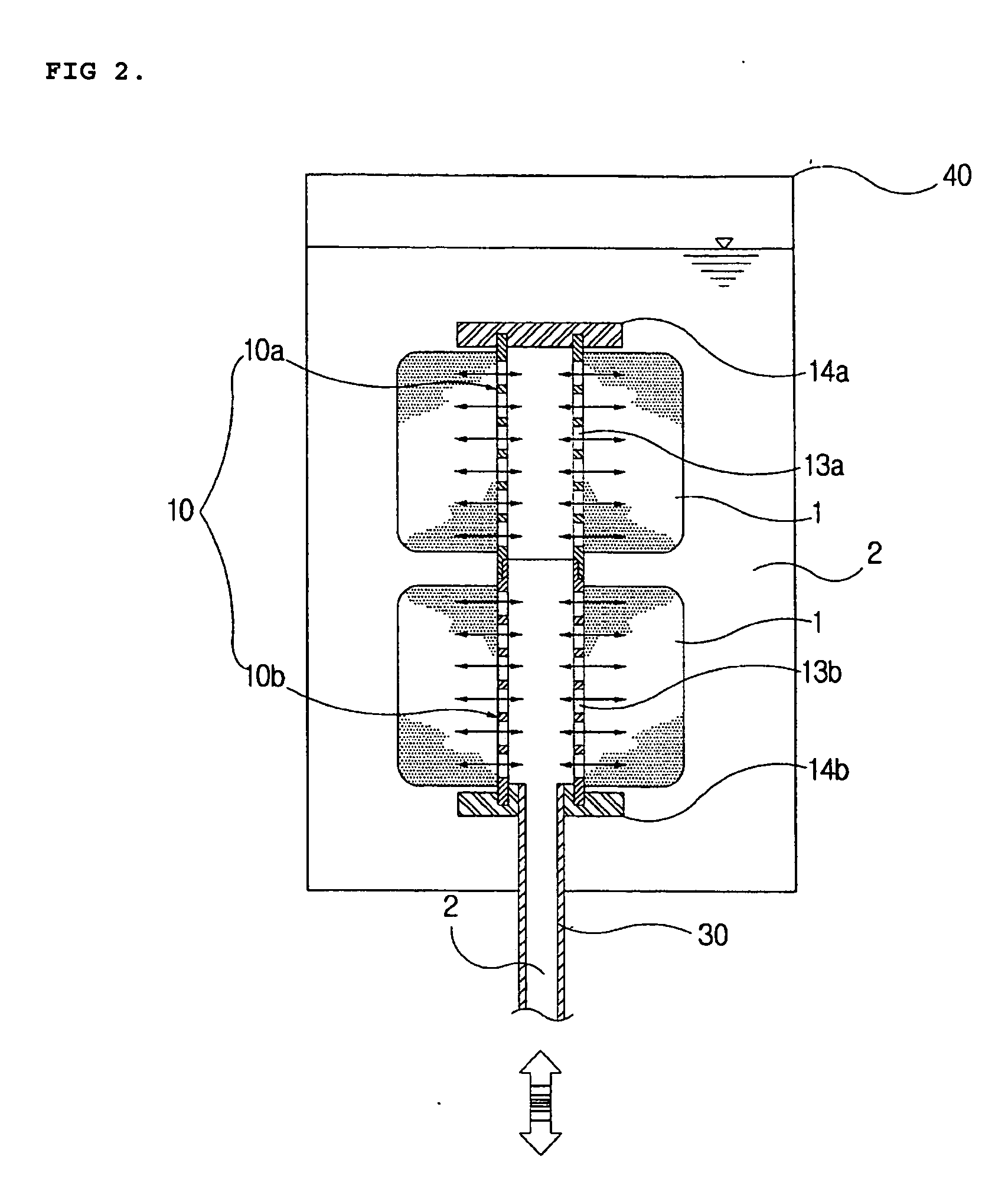
Crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol fiber and method for producing the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0072] PVA was used in a powder form with a degree of saponification of 99.9 mol % and a degree of polymerization of 2,000, and methyl alcohol and DMSO were used in a purified solvent mixture form with a water content of less than 100 ppm. To prepare the solvent mixture, DMSO and methyl were mixed such that the content of methyl alcohol content in the solvent was 5% by volume. PVA was dissolved in the solvent mixture such that it was 22 wt % relative to a PVA spinning dope. Next, the PVA solution was produced into a PVA fiber by a dry and wet spinning technique, using gel spinning. In this spinning process, a circular nozzle with a nozzle hole number of 500, a nozzle hole diameter of 0.5 mm and a L / D ratio of 5 was used. Also, air-gap was 50 mm, and methanol was used as a solvent in a coagulation bath. At this time, the coagulation bath was maintained at a solvent / methanol mixing ratio of 20 / 80 and a temperature of 0° C. After passing through an extraction tank, the PVA fiber must b...
examples 2 and 3
[0073] The ratio between terephthaldicarboxaldehyde, acetic acid and methanol was adjusted to a ratio given in Table 1, and the resulting raw cord was crosslinked and then measured for its physical properties, including tenacity and fatigue resistance.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Linear density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com