Conversion of high purity silicon powder to densified compacts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
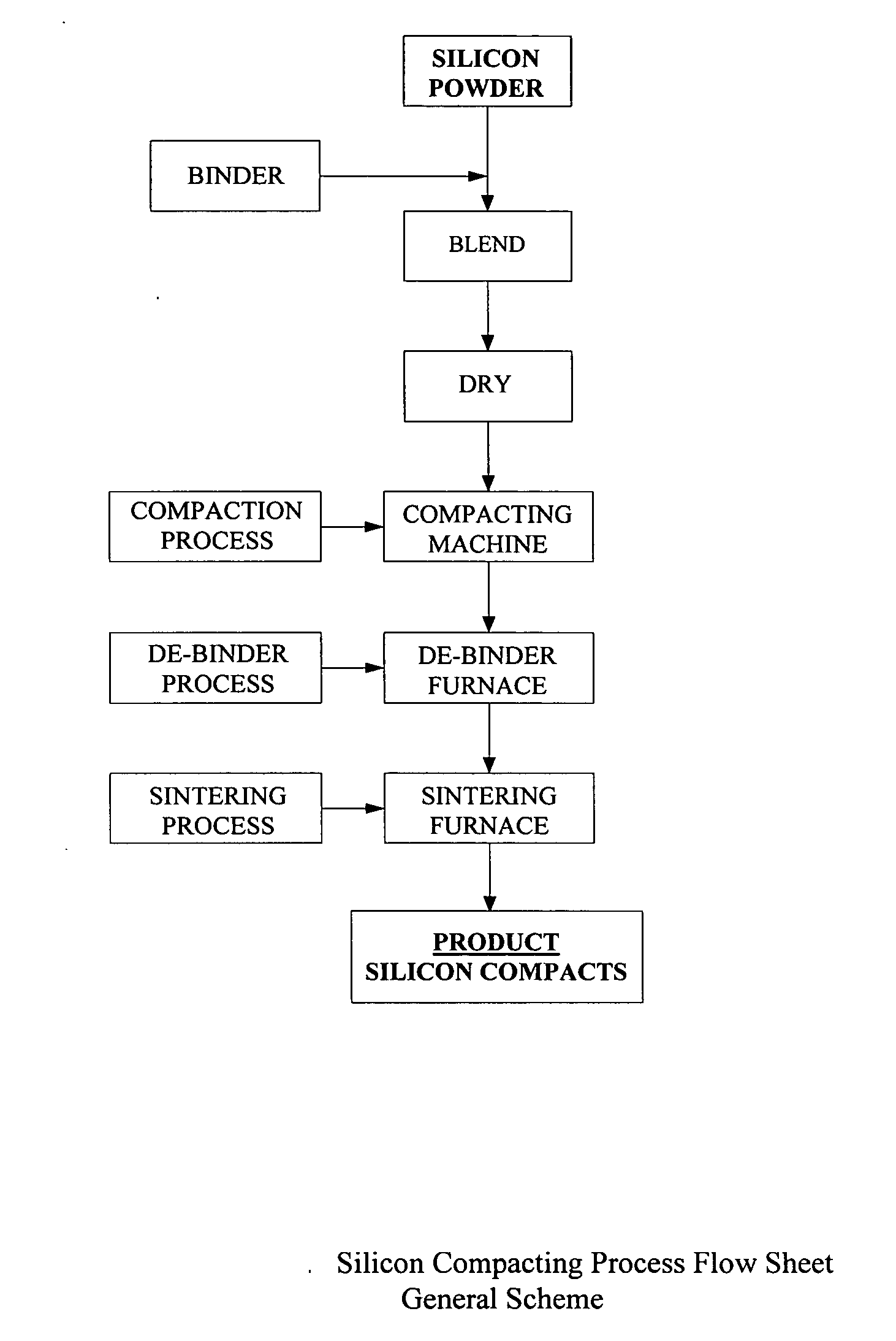
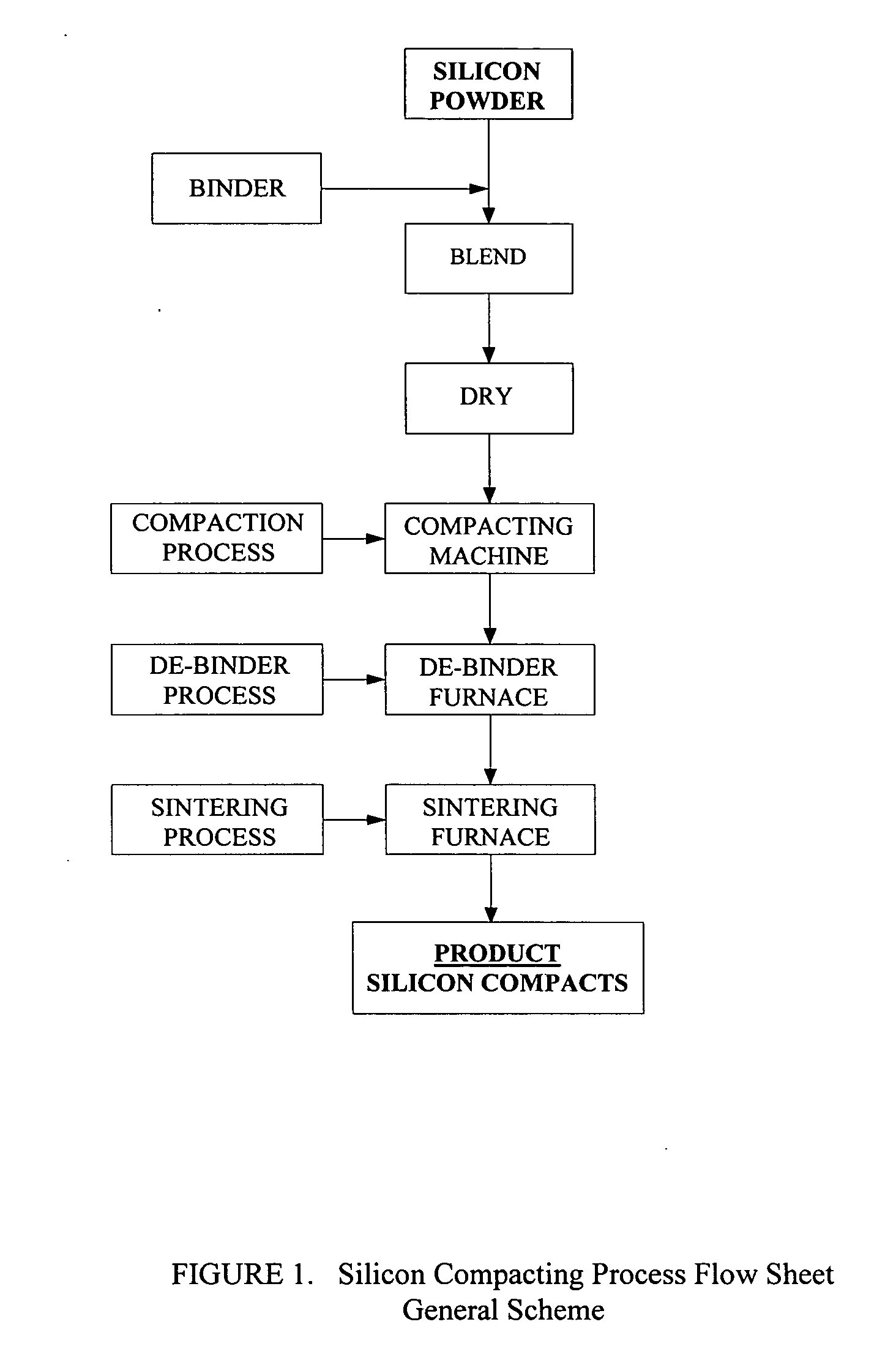
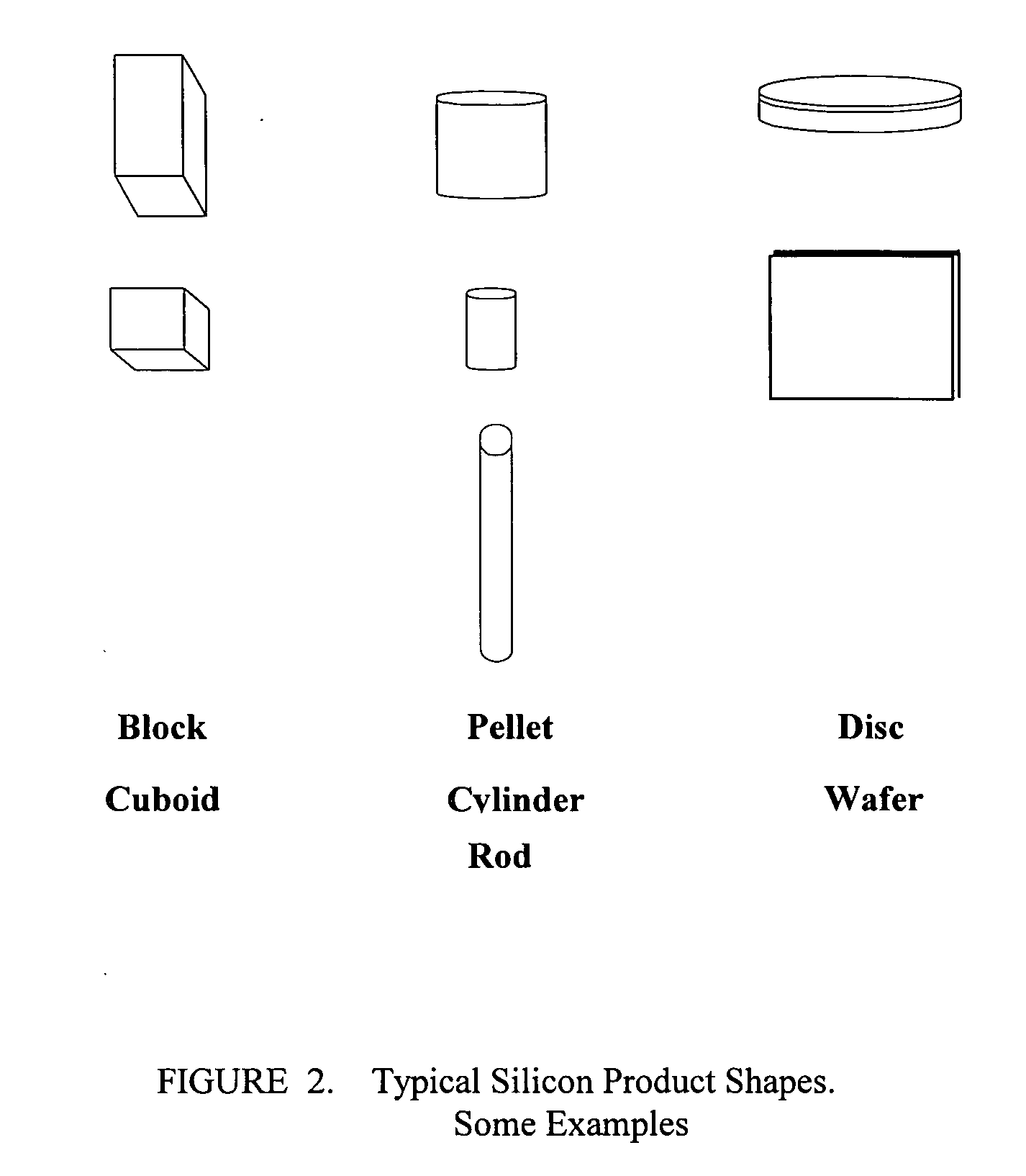
[0040] High purity Silicon powder is mixed with high purity fumed silica as a binder. Typically, the fumed silica is in the range 0.01-5 weight percent of the silicon powder, preferably in the range 0.05-0.2 weight percent. When added to the silicon powders, fumed silica aids powder flow, by forming a layer on the silicon surface and acts like a lubricant, aiding flow and compression. Due to the hydrophilic nature of the fumed silica it absorbs water off the surface of the particles and prevents caking. The mix is well blended, then formed into compacts or pellets / tablets of required shape. The compacted shape is then sintered in an inert gas or reducing gas such as hydrogen in inert gas or vacuum environment at 1000-1350 C. to produce the compacted densified final product.
[0041] During the sintering operation the fumed silica binder reacts with the silicon matrix to form SiO gas, which vaporizes from the compact. The residual oxygen in the sintered silicon compact is expected to b...
example 2
[0042] High purity Silicon powder is mixed with high purity colloidal silica as a binder. The high purity colloidal silica is nominally 40-50% by weight SiO2 in isopropyl alcohol or toluene. Typically, the colloidal silica is in the range 0.01-5 weight percent of the silicon powder, preferably in the range 0.05-0.2 weight percent. When added to the silicon powders, colloidal silica aids powder agglomeration and particle bonding. The mix is well blended, then dried to remove essentially all carrier solvent, then formed into compacts or pellets / tablets of required shape. The compacted shape is then sintered in an inert gas or reducing gas such as hydrogen in inert gas or vacuum environment at 1000-1350 C. to produce the compacted densified final product.
[0043] During the run up to the sintering temperature any remaining carrier solvent is removed from the compact (FIG. 3). During sintering the silica content of the binder reacts with the silicon matrix to form SiO gas, which vaporize...
example 3
[0044] High purity Silicon powder is mixed with high purity ethyl silicate 40 (polydiethoxysiloxane with 40% SiO2) as a binder. Typically, the ethyl silicate 40 is in the range 0.01-5 weight percent of the silicon powder, preferably in the range 0.05-0.5 weight percent. The mix is well blended, then formed into compacts or pellets / tablets of required shape. The use of ethyl silicate 40 binder requires a de-binder step prior to sintering. Ethyl silicate 40 decomposes completely at >300 C. to silica and ethyl alcohol. The latter boils off the compacted body without any significant reaction with silicon.
[0045] After binder removal the compacted shape is then sintered in an inert gas or reducing gas such as hydrogen in inert gas or vacuum environment at 1000-1350 C. to produce the compacted densified final product. During the sintering step all volatile decomposition products of ethyl silicate 40 will be released completely from the compact. The silica will react with silicon to form s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com