Expandable biodegradable polymeric stents for combined mechanical support and pharmacological or radiation therapy
a biodegradable polymer and combined technology, applied in the field of stents, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory current stent and catheter technology, unsatisfactory delivery of medicine to the lesion site either locally or systemically, and still present potential vessel injury problems of metal stents, etc., to avoid chronic mechanical disturbance of the vessel wall, avoid residual stress, and gradual absorption over time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
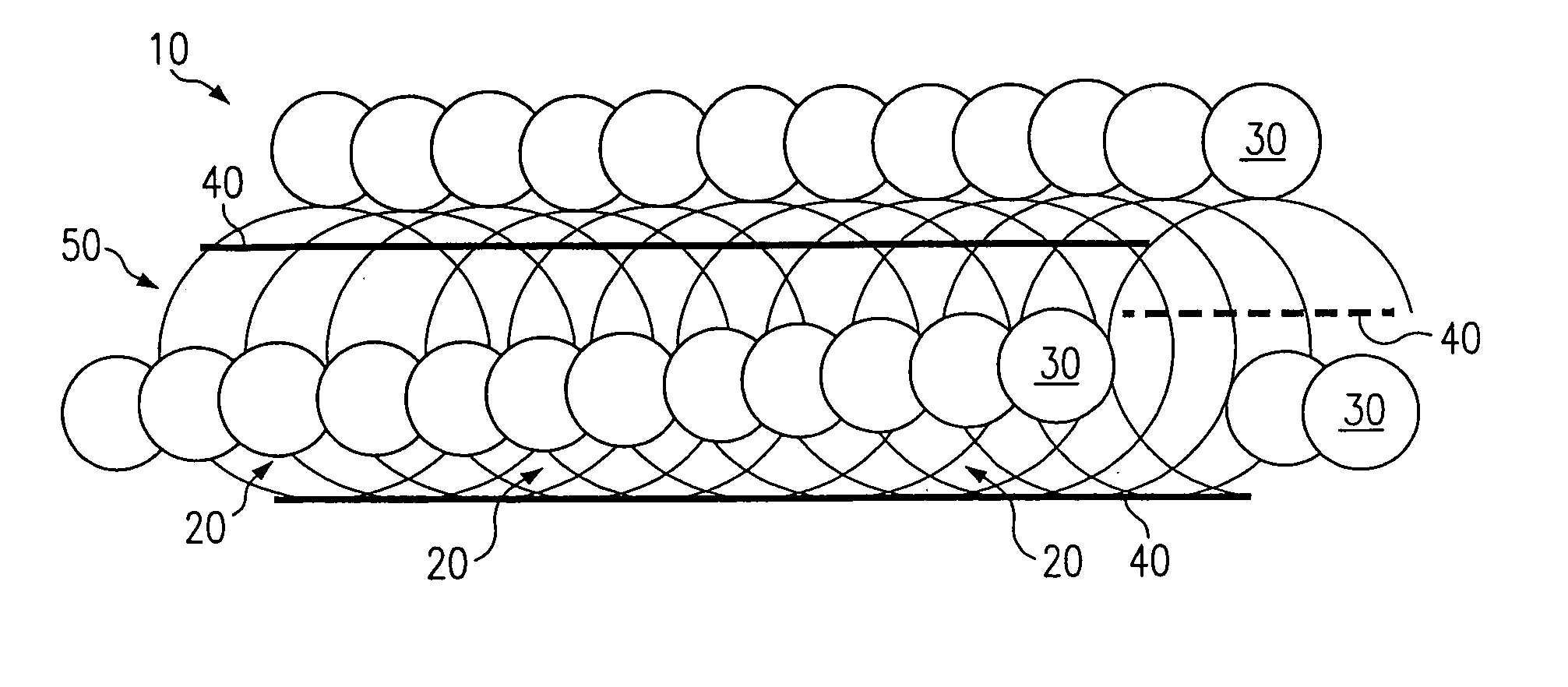
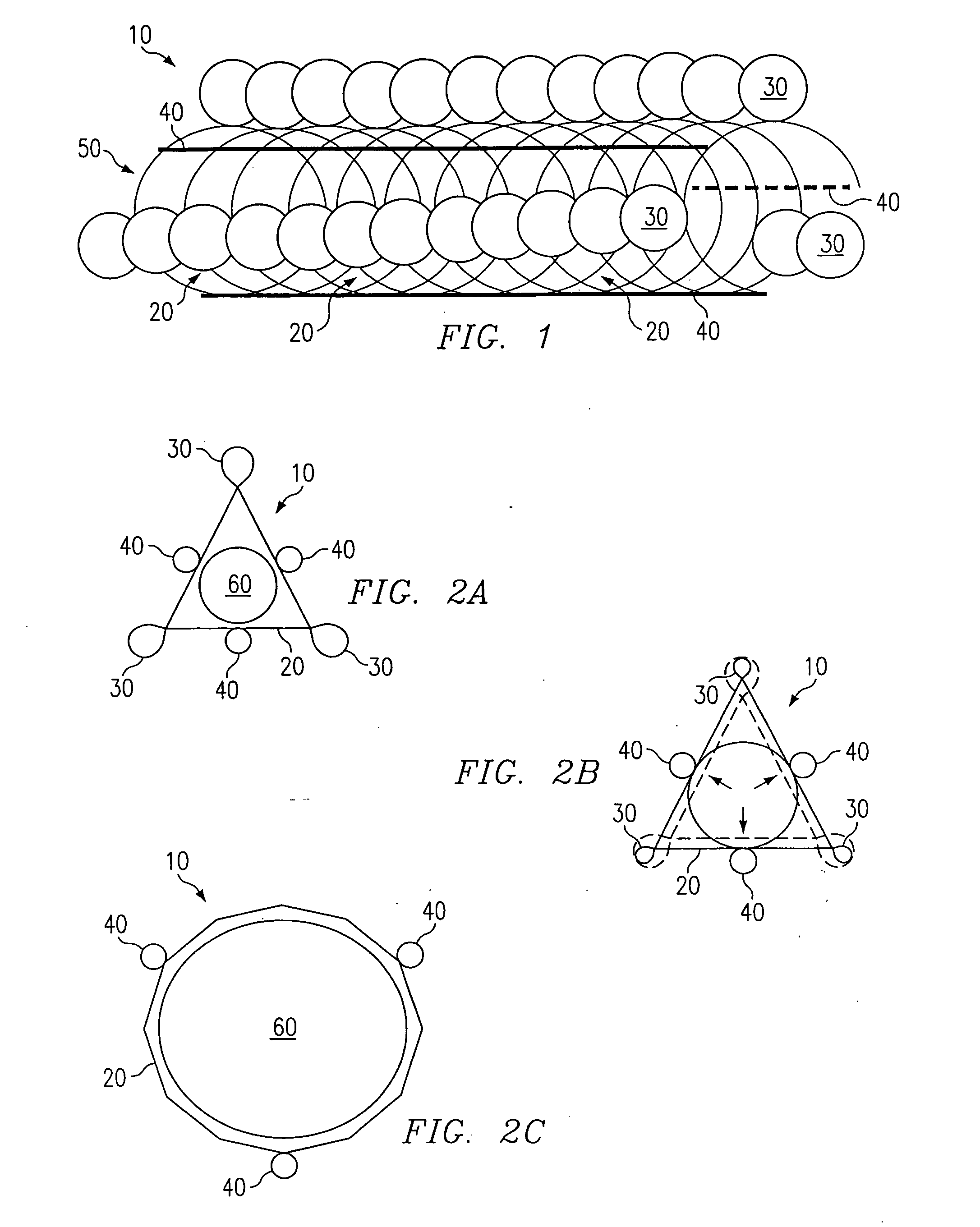
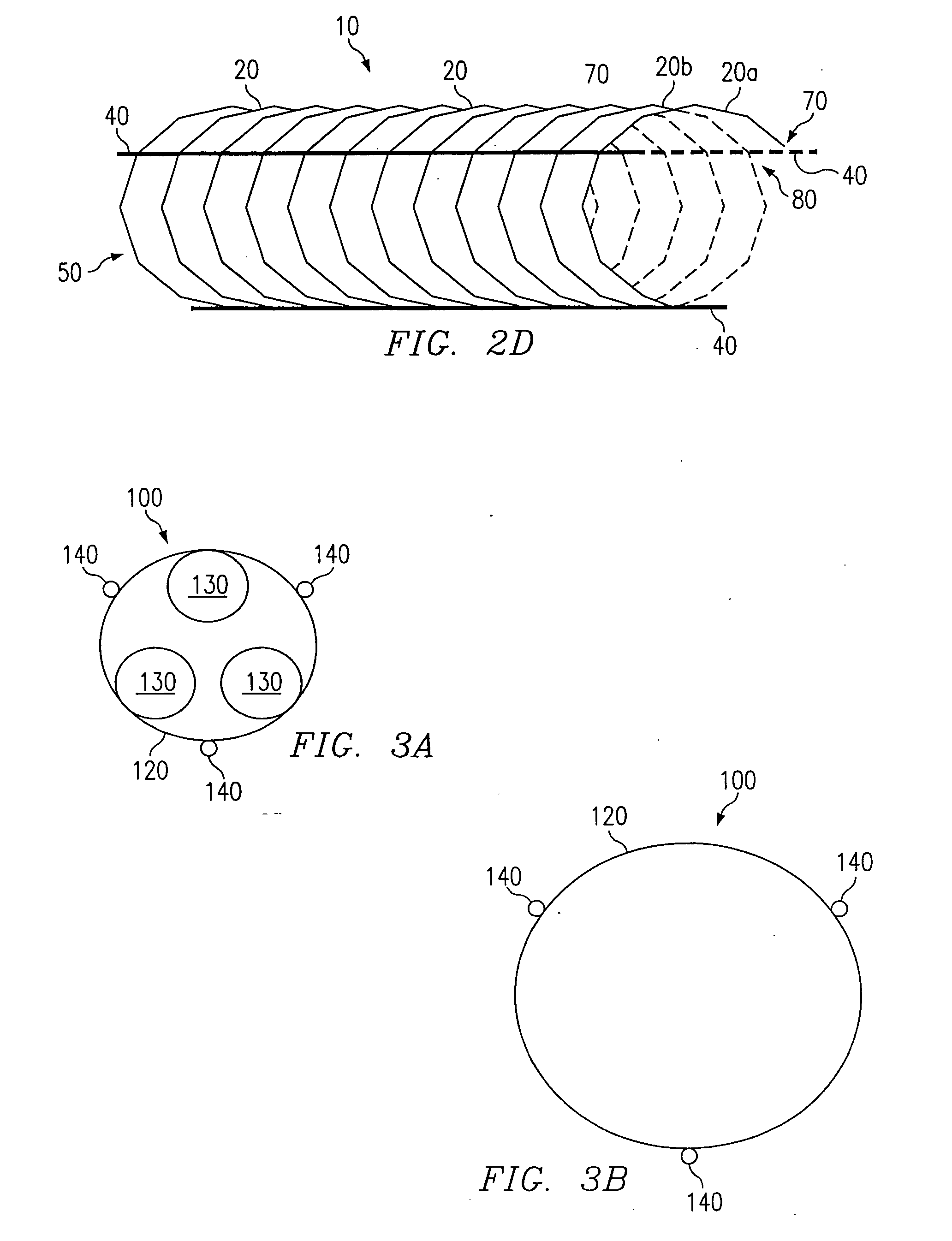
[0014] Referring to FIG. 1, a preferred embodiment of a stent according to the present invention is shown and generally designated by reference numeral 10. The stent 10 comprises a coiled cord 50 of non-metallic material, preferably a polymer fiber or ply of multiple polymer fibers, wherein the polymer preferably comprises Poly-L-Lactic Acid (“PLLA”). The use of PLLA to construct the stent 10 is advantageous because it is biodegradable. It degrades away gradually within the body, the chemical products of the degradation process being primarily carbon dioxide and water, which are harmless to the host patient. Degradation occurs over a period of about six months to three years, mainly depending on the molecular weight of the polymer employed. PLLA is also advantageous because it can be impregnated with drugs or other chemical agents for local treatment of tissue at the stent implant site.
[0015] By way of example, the stent 10 of FIG. 1 is constructed with twelve coil rotations of a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com