Additives and lubricant formulations for improved phosphorus retention properties
a technology of additives and lubricants, applied in the direction of lubricating crankcase compression engines, machines/engines, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of low wear, oxidation and corrosion, and the inability to conveniently match the benefits of phosphorus additives for friction control and wear protection, so as to reduce catalyst poisoning, increase the phosphorus retention of the lubricant composition, and reduce catalyst poisoning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
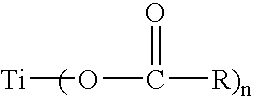
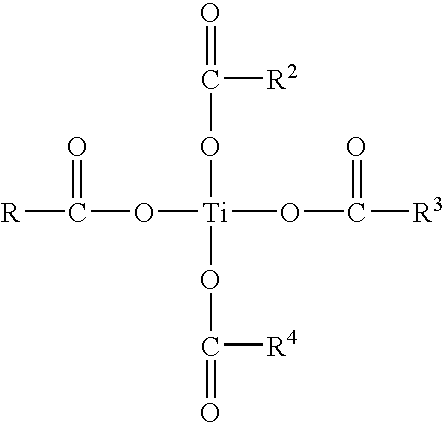
Titanium Neodecanoate
[0071]Neodecanoic acid (600 grams) was placed into a reaction vessel equipped with a condenser, Dean-stark trap, thermometer, thermocouple, and a gas inlet. Nitrogen gas was bubbled into the acid. Titanium isopropoxide (245 grams) was slowly added to the reaction vessel with vigorous stirring. The reactants were heated to 140° C. and stirred for one hour. Overheads and condensate from the reaction were collected in the trap. A subatmospheric pressure was applied to the reaction vessel and the reactants were stirred for an additional two hours until the reaction was complete. Analysis of the product indicated that the product had a kinematic viscosity of 14.3 cSt at 100° C. and a titanium content of 6.4 percent by weight.
[0072]The phosphorus retention (PR) values of comparative fluids and of fluids according to exemplary embodiments of the disclosure were determined using an Afton Catalyst Test (hereinafter “ACT”). The ACT is a fired-engine catalyst-aging test de...
example 2
[0076]A 100,000-mile New York Taxi field test was conducted on a conventional lubricant formulation and a lubricant formulation containing an amount of titanium neodecanoate sufficient to provide 500 ppm titanium metal to the lubricant composition. The results and statistical comparison are shown in Table 3. All vehicles started the test with new engines and had 5000 or 10,000-mile oil change intervals. Four vehicles were operated on a lubricant composition containing 500-ppm Ti; three vehicles were operated on the same lubricant formulation without titanium.
TABLE 3Field Test for Phosphorus Retention (PR)No. ofPhos. Ret.Oil CompositionVehicle IDtests(%)Std. Dev.No titanium12B1988.15.8No titanium14A1986.44.4No titanium 1A2087.74.8500 ppm titanium24A1992.25.4500 ppm titanium57A2091.64.6500 ppm titanium60B1993.34.6500 ppm titanium 7A1991.75.2
[0077]Consistent with Sequence IIIG testing, the vehicles run on lubricants containing the titanium-containing compound averaged higher phosphorus...
example 4
[0078]A design of experiments (DOE) was performed on fully-formulated oils containing various concentrations of titanium from titanium neodecanoate (TND). The formulations and components are shown in Table 4. Another variables included in this DOE was the phosphorus level. In total, fifteen separate blends were evaluated in the Sequence IIIG engine test—a test that operates 100 hours at 150° C. oil temperature. As part of the IIIG test, 20-hour interval oil samples are taken and analyzed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) to determine the changes in elemental concentrations that result from aging. The data were used to calculate Phosphorus Retention percent after 20 hours of aging (PR, %) according to the above formula.
TABLE 4Sequence IIIG Design of Experiment Formulation Data and PhosphorusRetention ResultsPhosphorusZDDPTitaniumRetentionRun No.(wt. %)(ppm)(%)10.5810682.220.585384.630.9310684.140.935378.650.9310683.060.585383.270.585383.580.5810685.290.5810690....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com