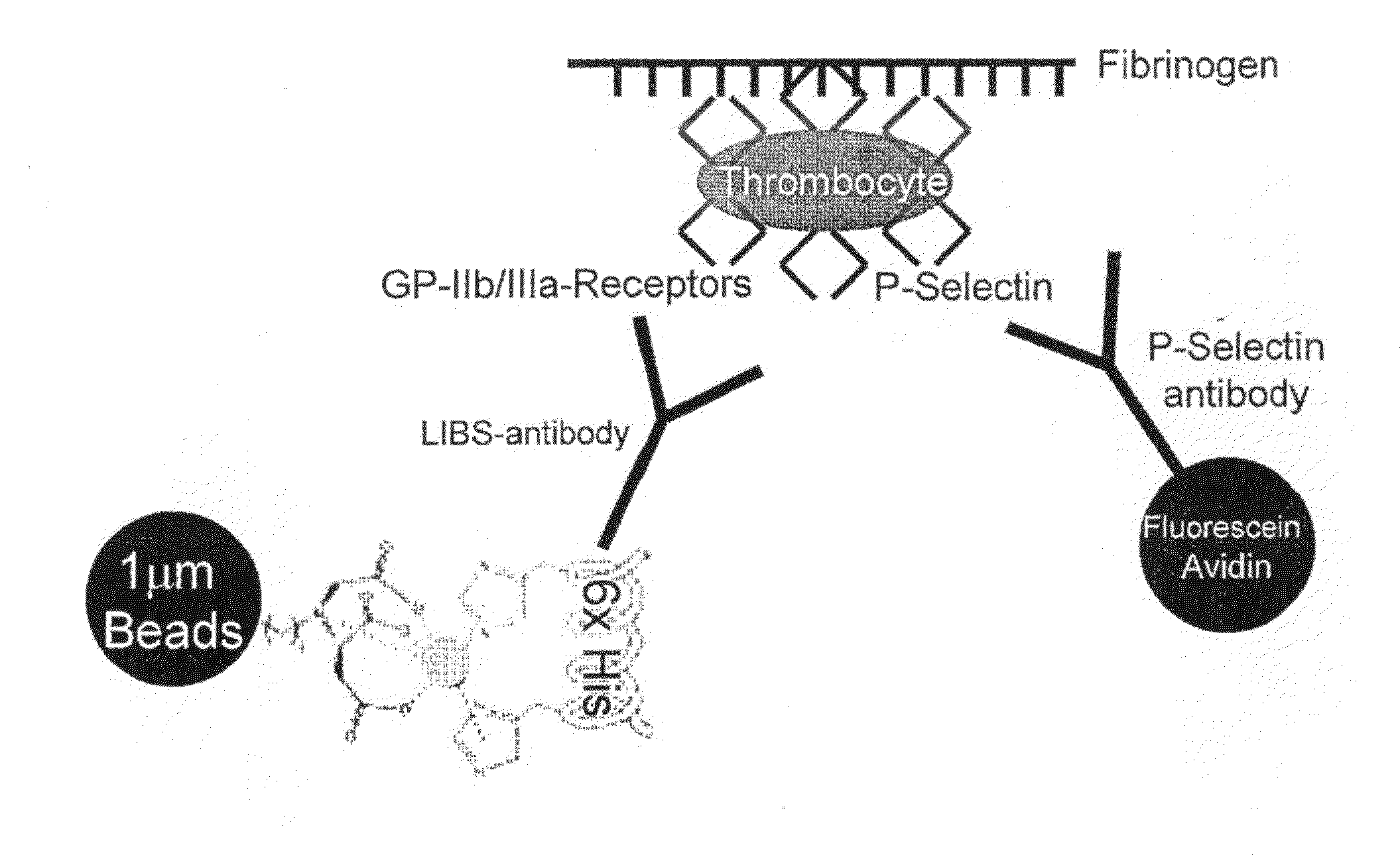
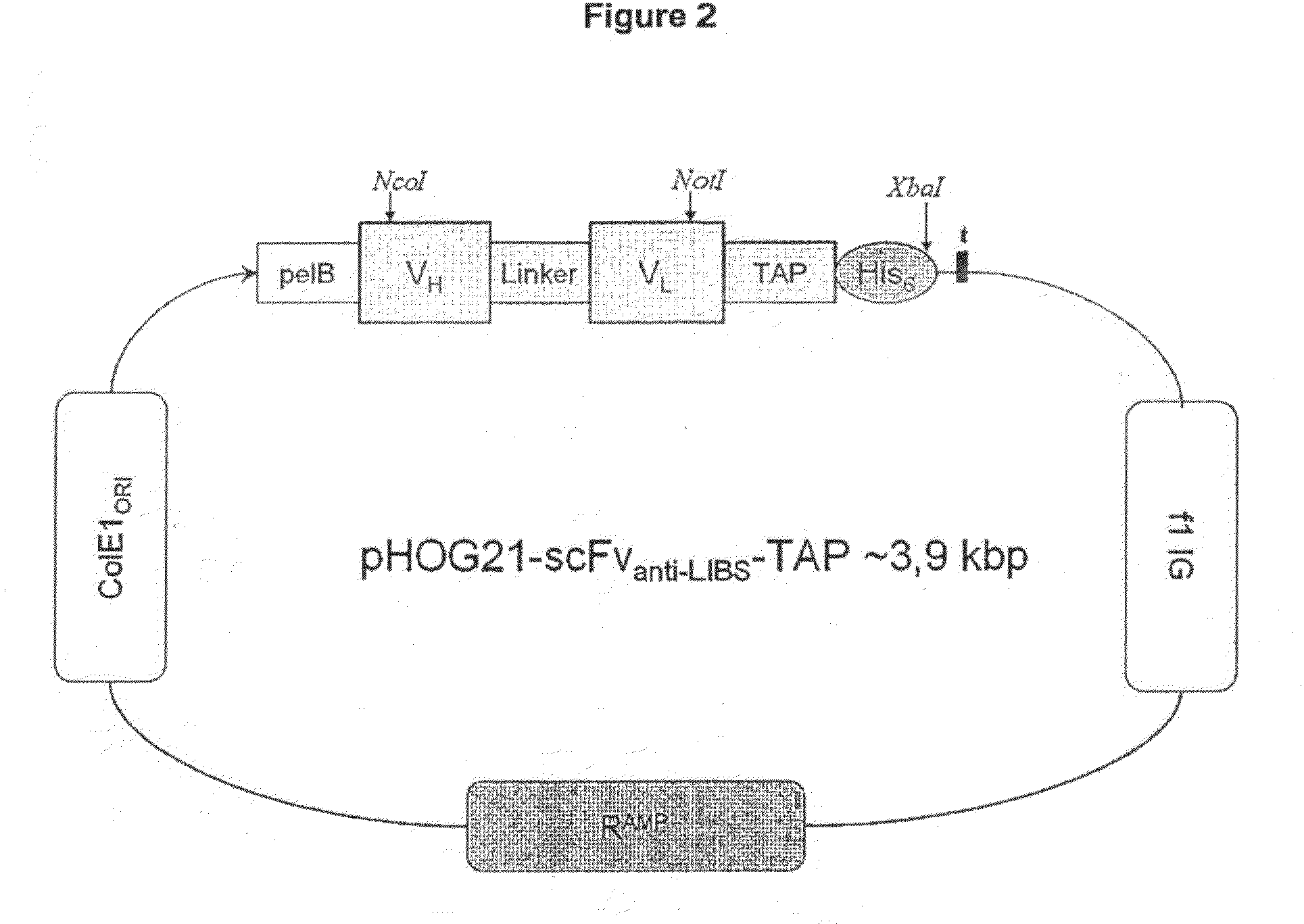
Anticoagulation Agent and Uses Thereof
a technology of anticoagulation agent and anticoagulation agent, which is applied in the field of haemostasis, can solve the problems of reducing the rate of fibrin clot dissolution, affecting the activation of plasminogen, and the inability of the body to control the circulating level, so as to prevent or treat coagulation disorders and achieve higher affinity binding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of the Single-Chain Antibody ScFvAnti-LIBS and the Fusion Construct ScFvAnti-LIBS-Tap
[0110]The generation of the hybridoma cell line expressing a monoclonal antibody against a LIBS epitope on GPIIb / IIIa and its functional characterisation has been described earlier (Schwarz et al. JPET 2004; 308: 1002). Briefly, GPIIb / IIIa purified and eluted with RGD peptides was used as immunogen for hybridoma production. Clones were screened with activated platelets as well as with immobilized GPIIb / IIIa saturated with RGD peptides. One of these clones, monoclonal antibody (mAb) clone 145 demonstrated increased binding to ADP-activated platelets and to platelets pre-incubated with RGD peptides (GRGDSP, BIOMOL Research Laboratories, Plymouth Meeting, Pa.), eptifibatide (Integrilin®, Essex Pharma, Muenchen, Germany), tirofiban (Aggrastat®, MSD, Whitehouse Station, N.J.), and abciximab (ReoPro®, Eli Lilly & Co, Indianapolis, Ind.). The hybridoma was maintained in RPMI, 10% fetal calf seru...
example 2
Expression and Purification of scFv Constructs in E. Coli
[0112]E. coli (TG1) cells were transformed with the pHOG21 plasmids described above and individual colonies from a freshly streaked agar plate were grown in LB media containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin and 100 mM glucose at 37° C. in 500 mL flasks. Cultures were shaken at 200 rpm for approximate 4-6 hours until an OD (600 nm) of ˜0.8 was reached. Bacteria were pelleted by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 min at 4° C. and resuspended with LB media containing 100 μg / ml ampicillin and 0.4 M sucrose. IPTG was added to a final concentration of 0.25 mM for induction of scFv production and incubated at room temperature (22-24° C.) with 200 rpm for 16-20 hours. For purification of soluble protein from whole cell extract, bacteria were harvested by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 min at 4° C. Pelleted bacteria were resuspended in 5 mL 1× BugBuster® (Novagen, Madison, USA) solution / g pellet and incubated for 15 min at room temperature w...
example 3
In Vitro Functional Characterization of the scFv Anti-LIBS-TAP
Blood Preparation
[0113]Human blood was collected by venipuncture with a 21-gauge butterfly needle from healthy volunteers and anticoagulated with citric acid. Platelet-rich plasma was obtained by centrifugation (GS-6R centrifuge, Beckmann Coulter, Gladesville, NSW, Australia) at 100×g in plastic tubes at room temperature for 10 min in a centrifuge.
[0114]Mouse Blood was collected by intracardial puncture with a 27-gauge needle from C57BL / 6 mice and anticoagulated with unfractionated heparin (20 U / mL).
[0115]A volume of 50 μl was resuspended with 1 mL modified Tyrode's buffer (150 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM KCl, 1.2 mM NaHCO3, 2 mM MgCl2, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.1% BSA, 0.1% Glucose) and centrifuged at 1300×g for 5 min. The supernatant was discarded and the pellet was resuspended with 1 mL modified Tyrode's buffer.
[0116]Human citrated whole blood was diluted 1 / 50 in modified Tyrode's buffer, either activated by addition of 20 μM AD...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Paramagnetism | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Superparamagnetism | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com