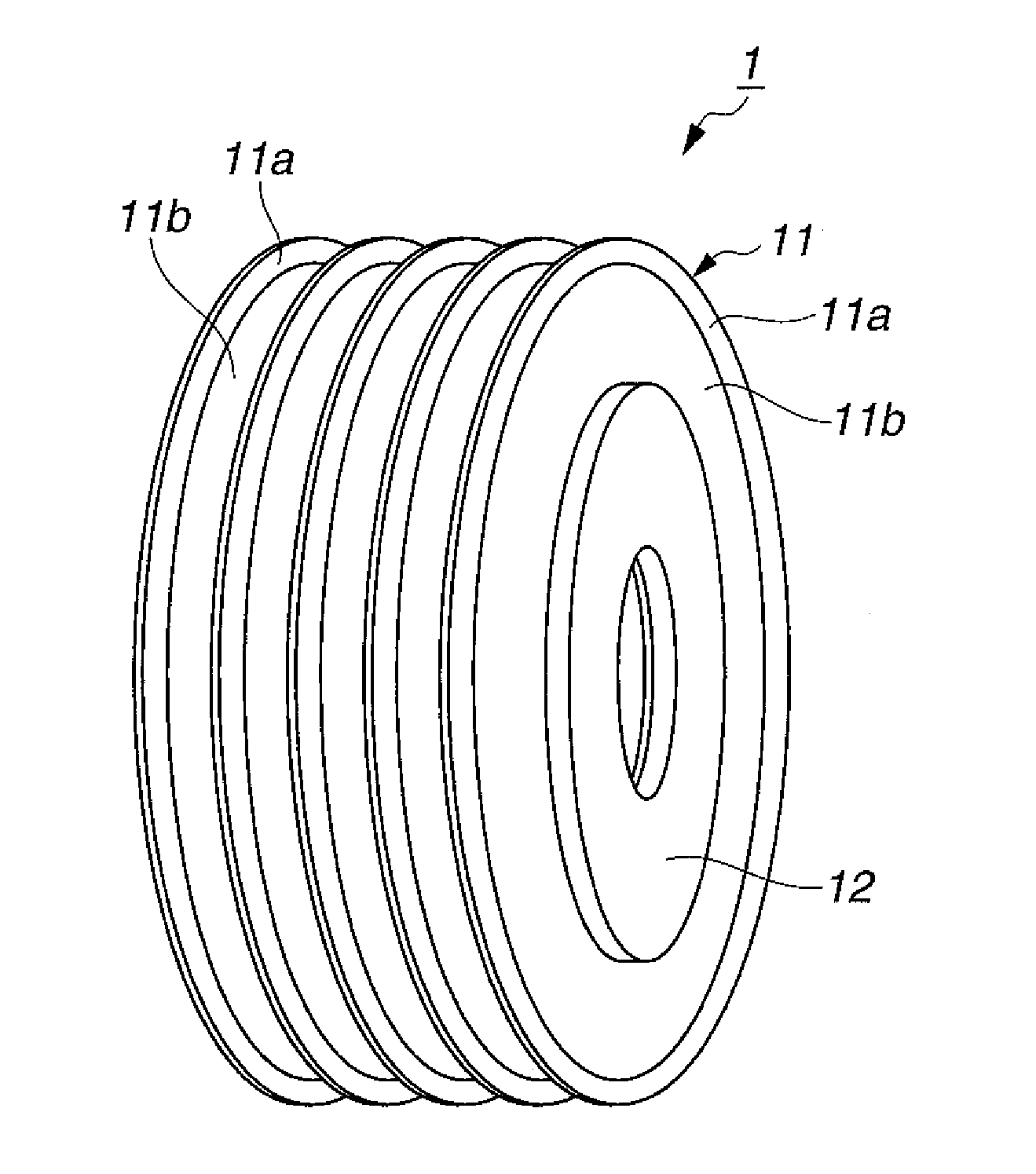
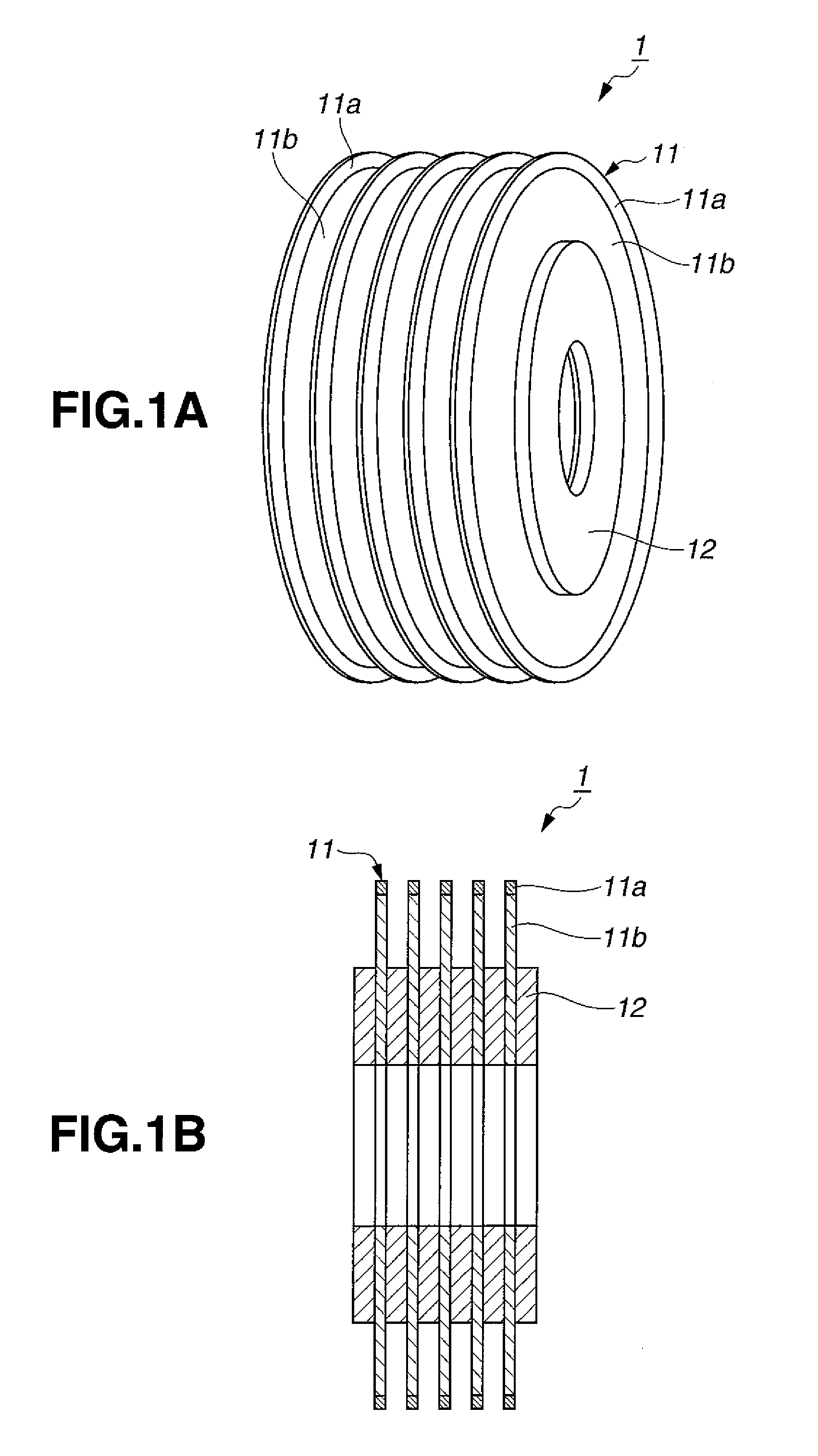
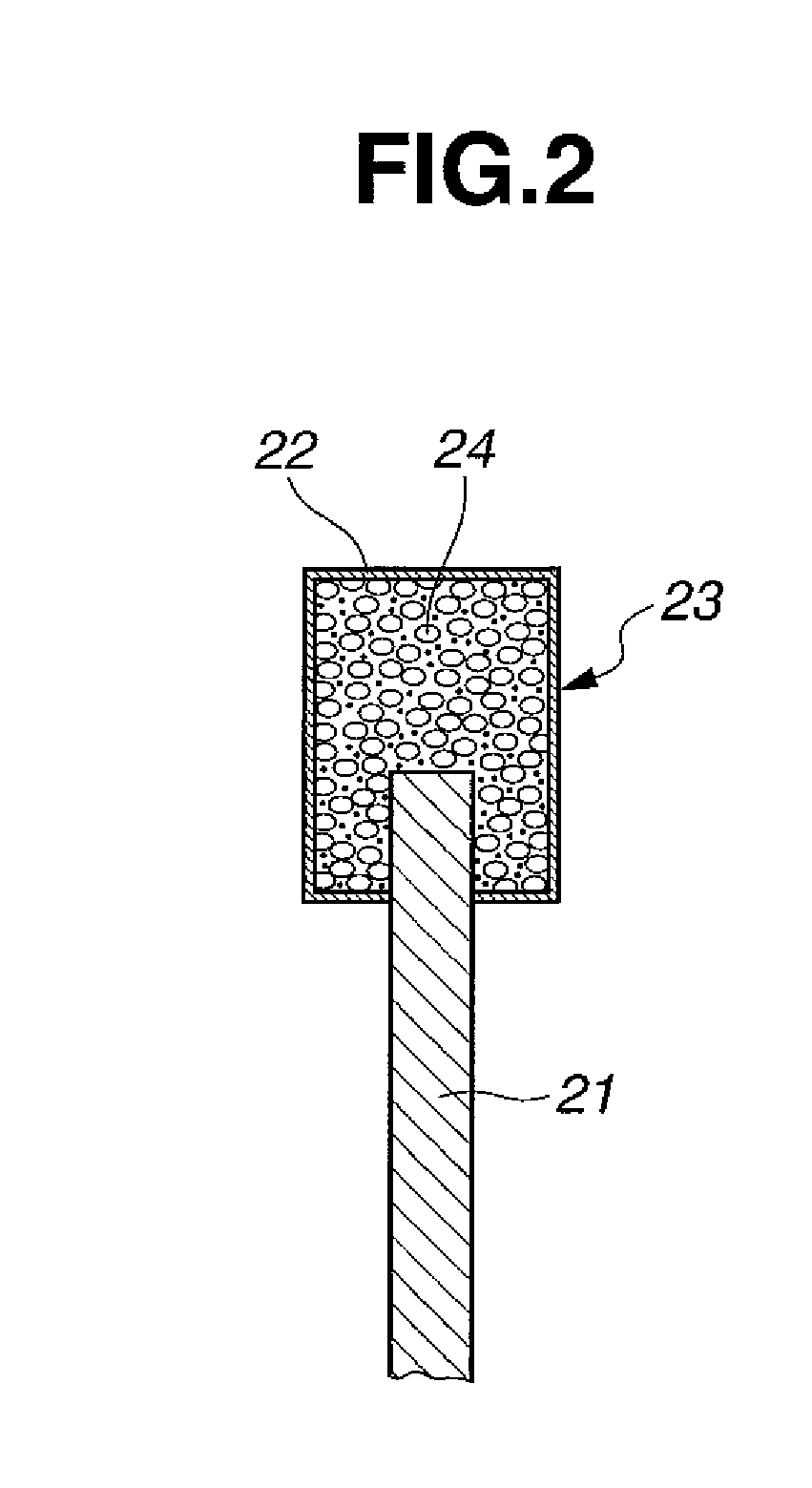
Saw blade and method for multiple sawing of rare earth magnet
a rare earth magnet and sawing blade technology, applied in the direction of gear teeth, manufacturing tools, manufacturing apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of low productivity of sawing technology using id blades, parts cannot be formed, and lowering manufacturing yield, so as to improve sawing accuracy, reduce cutting resistance, and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0036]OD blades were fabricated by providing a doughnut-shaped disk core of cemented carbide (consisting of WC 90 wt % / Co 10 wt %) having an outer diameter 120 mm, inner diameter 40 mm, and thickness 0.3 mm, and heat pressing a composition to an outer peripheral rim of the core to form a resinoid grinding wheel section or cutting part. The composition contained 10 wt % of graphite having a particle size of 5 to 30 μm as the lubricant, 40 wt % of #800 SiC (GC powder) as the matrix, 25 wt % of a phenol formaldehyde resin as the binder, and 25 wt % of synthetic diamond grains having an average particle size of 150 μm. Subsequent finish work completed OD blades (or sawing abrasive blades). The axial extension of the cutting part from the core was 0.05 mm on each side, that is, the cutting part had a width of 0.4 mm (in the thickness direction of the core). The radial extension or length of the cutting part is 2.5 mm, that is, the blade had an outer diameter of 125 mm.
[0037]Using the OD ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com