Extract of vicia faba beans
a technology of vicia faba beans and extract, which is applied in the field of anticonvulsant compounds, can solve the problems of reducing the economic value of plants, reducing and reducing the amount of aqueous extract, so as to reduce the volume of ethanol.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Extraction of Samples For Analysis
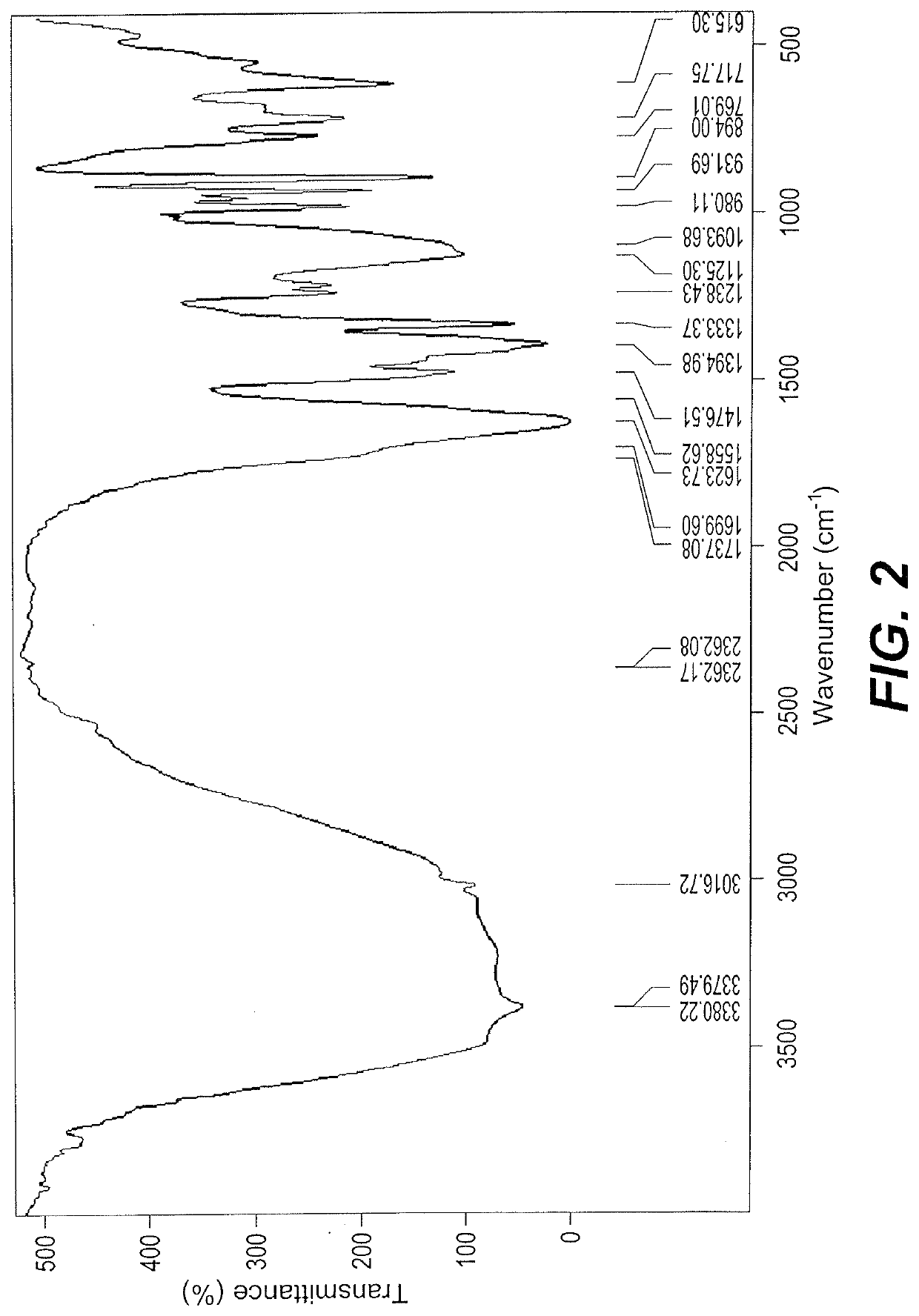
[0025]Nine hundred grams of brown broad beans were soaked in 2.0 L of distilled water overnight, and then boiled in a water bath until the extract was reduced to 600 mL. The extract was homogenized and filtered. The filtrate was then concentrated to a volume of 100 mL, lyophilized, and powdered.
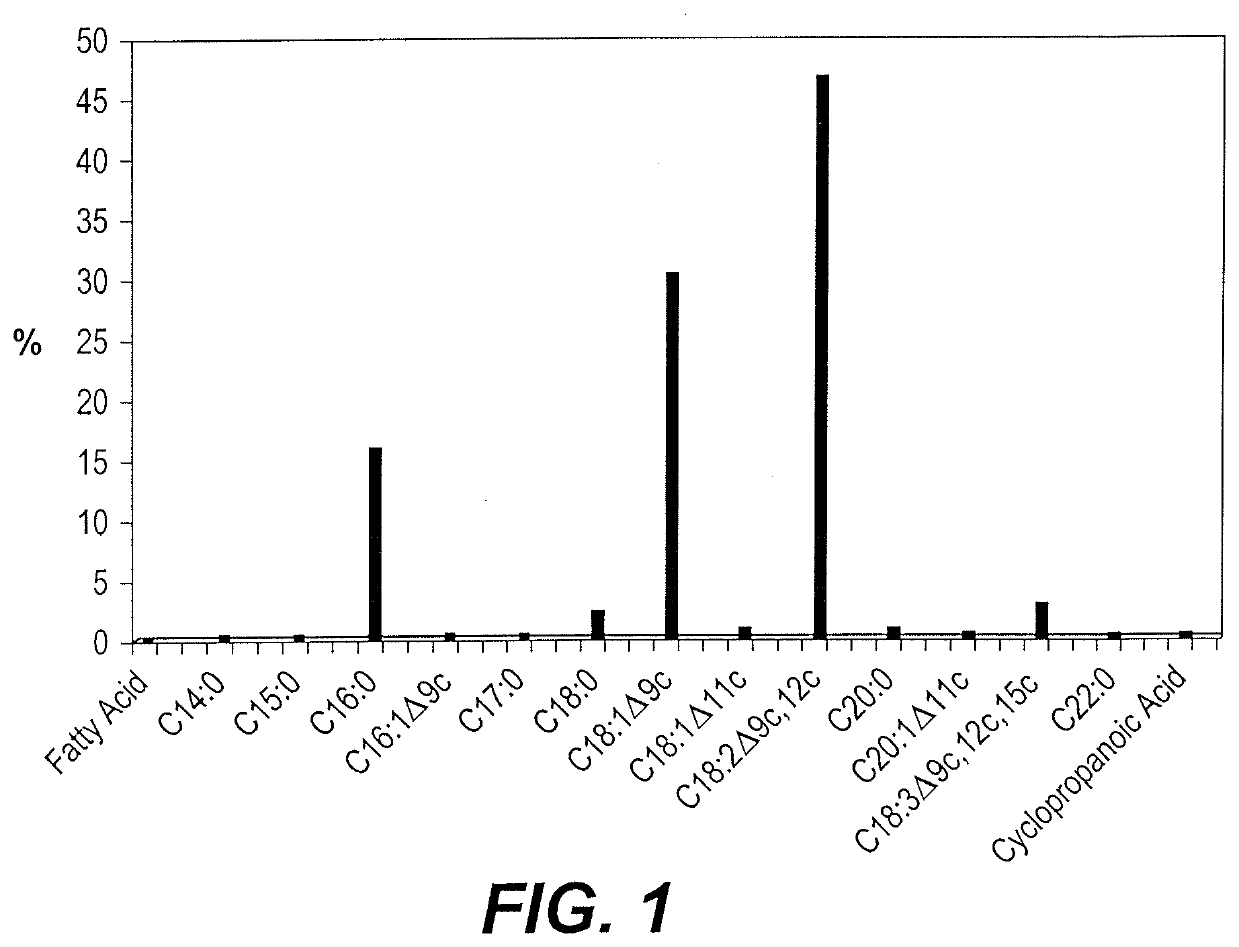
[0026]The lyophilized powder (50 g) was placed into a cellulose paper cone, and extracted with 600 mL hexane using a soxhlet extraction apparatus for 8 hours. The solvent was removed using a rotary vacuum distiller at 50° C., and then the residue was flushed with nitrogen to blanket the oil before storage (AOAC method 920.39). The lipid content was calculated from the weight of the oil (5.65 g), and the results were expressed as the lipid percentage of the original 900 g of beans—1.25%. See FIG. 1 and the analysis of fatty acid composition below.
[0027]The oil-free lyophilized powder was then extracted with ethanol, again using the above-mentioned procedure. T...
example 2
Analysis of Fatty Acid Composition
[0030]The fatty acids (oils) removed by the initial extraction of the lyophilized powder in hexane were analyzed as follows. The fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) composition was determined by converting the oil to fatty acid methyl esters. 200 μl lithium methoxide (2M) was added to a mixture of 40 mg of the oil in 1.0 ml n-hexane, followed by heating in a bath at 50° C. for few seconds. Then, 200 μl HCl (2N) is added. The major fatty acid components found in Vicia faba beans are palmitic acid (15.759%); stearic acid (2.16%) oleic acid (30.21%); linoleic acid (46.41%); and linolenic acid (2.74%). The remaining 2.7% comprises minor amounts of other fatty acids, as shown in the histogram of FIG. 1.
example 3
Thin-Layer Chromatography
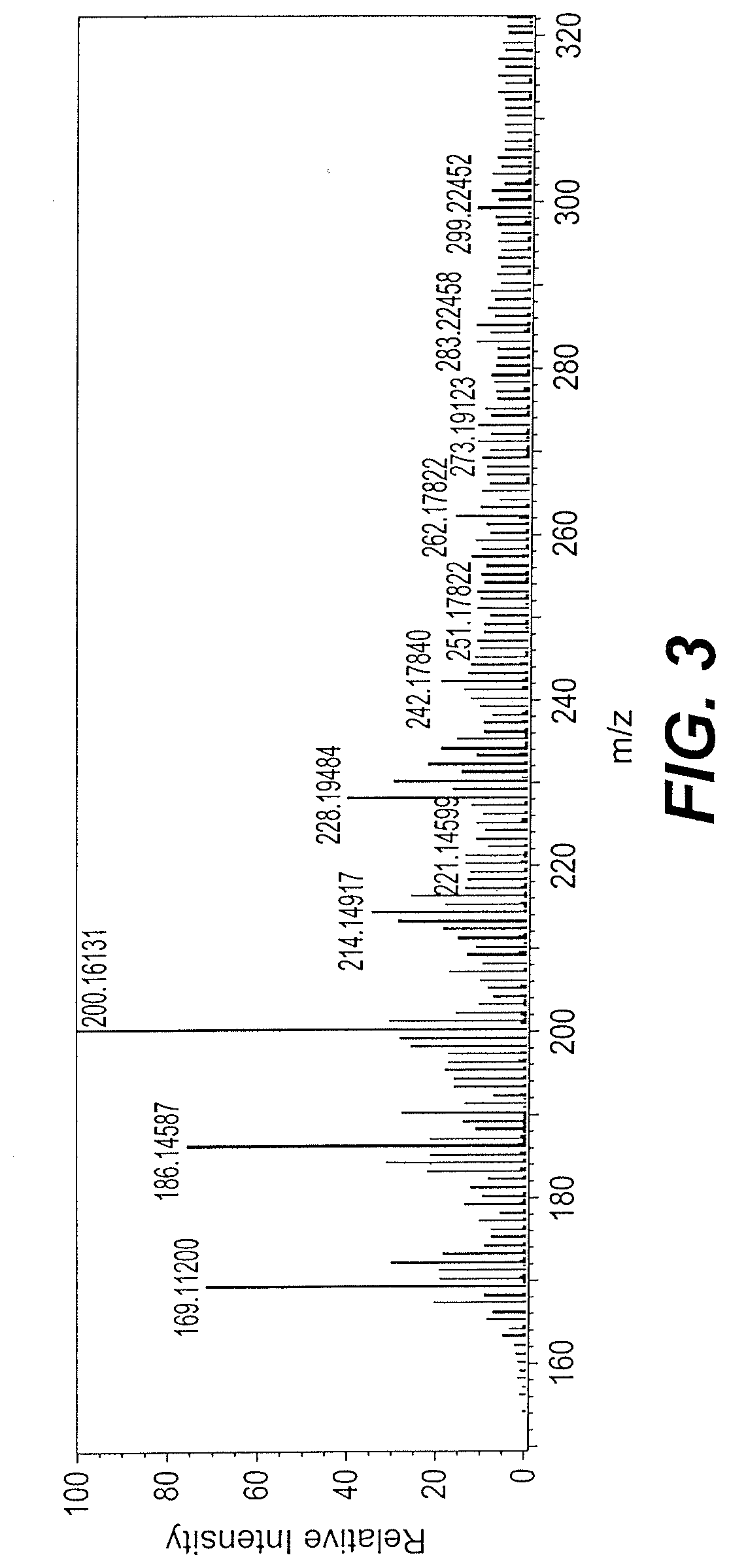
[0031]Thin-layer chromatography consisted of a stationary phase immobilized on a glass, and an organic solvent (55% phosphate buffer and 45% methanol). The constituents of a sample were identified by simultaneously running standards with the unknown. The bottom edge of the plate was placed in a solvent reservoir, and the solvent moved up the plate by capillary action. When the solvent front reached the other edge of the stationary phase, the plate was removed from the solvent reservoir. The separated spots were visualized with ultraviolet light or by placing the plate in iodine vapor. The different components in the mixture move up the plate at different rates due to differences in their partitioning behavior between the mobile liquid phase and the stationary phase. The TLC of the ethanol extract from the oil free lyophilized powder indicated a mixture of six components.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com