Patents
Literature
31 results about "Recovery point objective" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A recovery point objective, or “RPO”, is defined by business continuity planning. It is the maximum tolerable period in which data might be lost from an IT service due to a major incident. The RPO gives systems designers a limit to work to. For instance, if the RPO is set to four hours, then in practice, off-site mirrored backups must be continuously maintained – a daily off-site backup on tape will not suffice. Care must be taken to avoid two common mistakes around the use and definition of RPO. Firstly, BC staff use business impact analysis to determine RPO for each service – RPO is not determined by the existent backup regime. Secondly, when any level of preparation of off-site data is required, rather than at the time the backups are offsited, the period during which data is lost very often starts near the time of the beginning of the work to prepare backups which are eventually offsited.
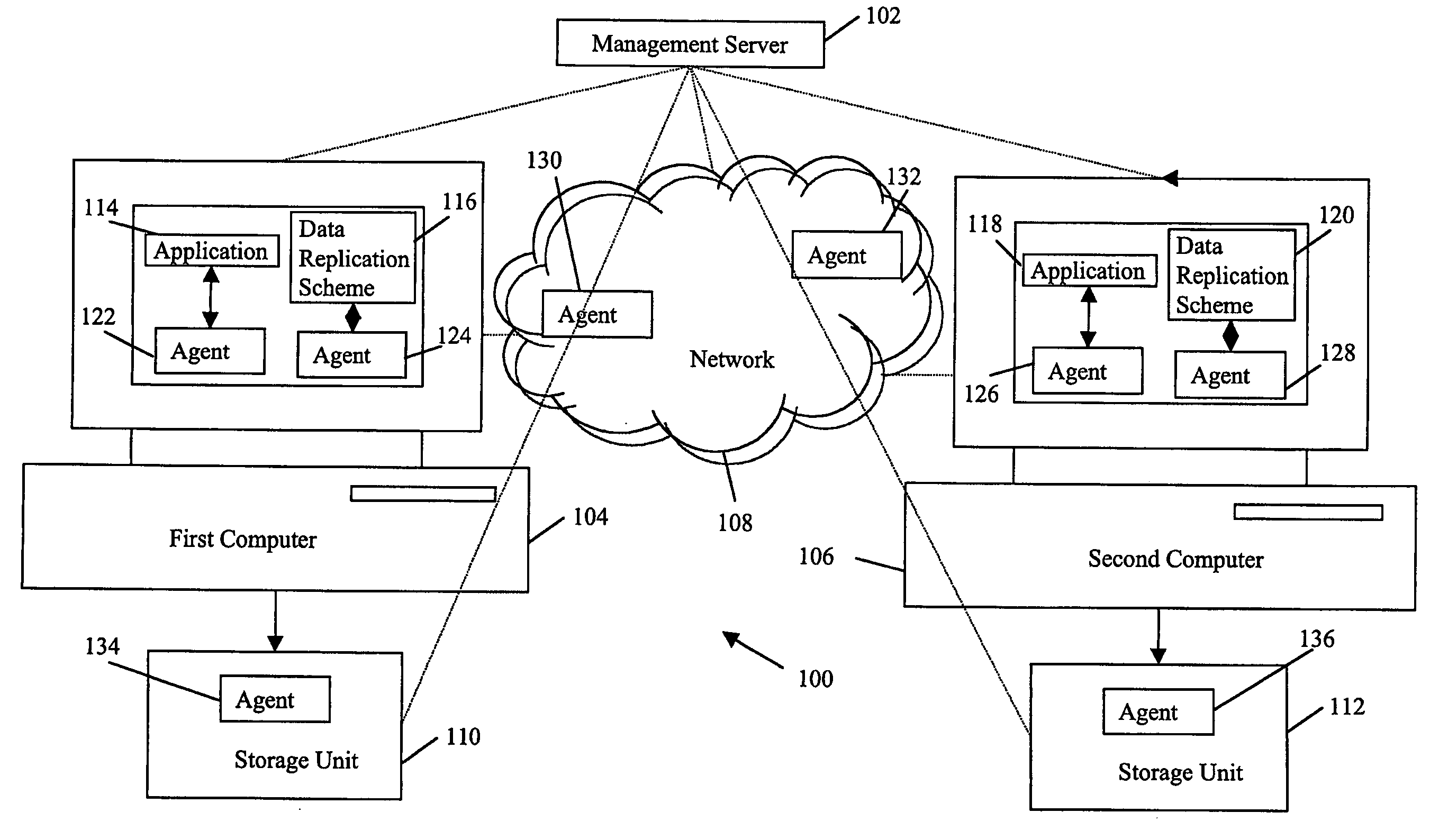
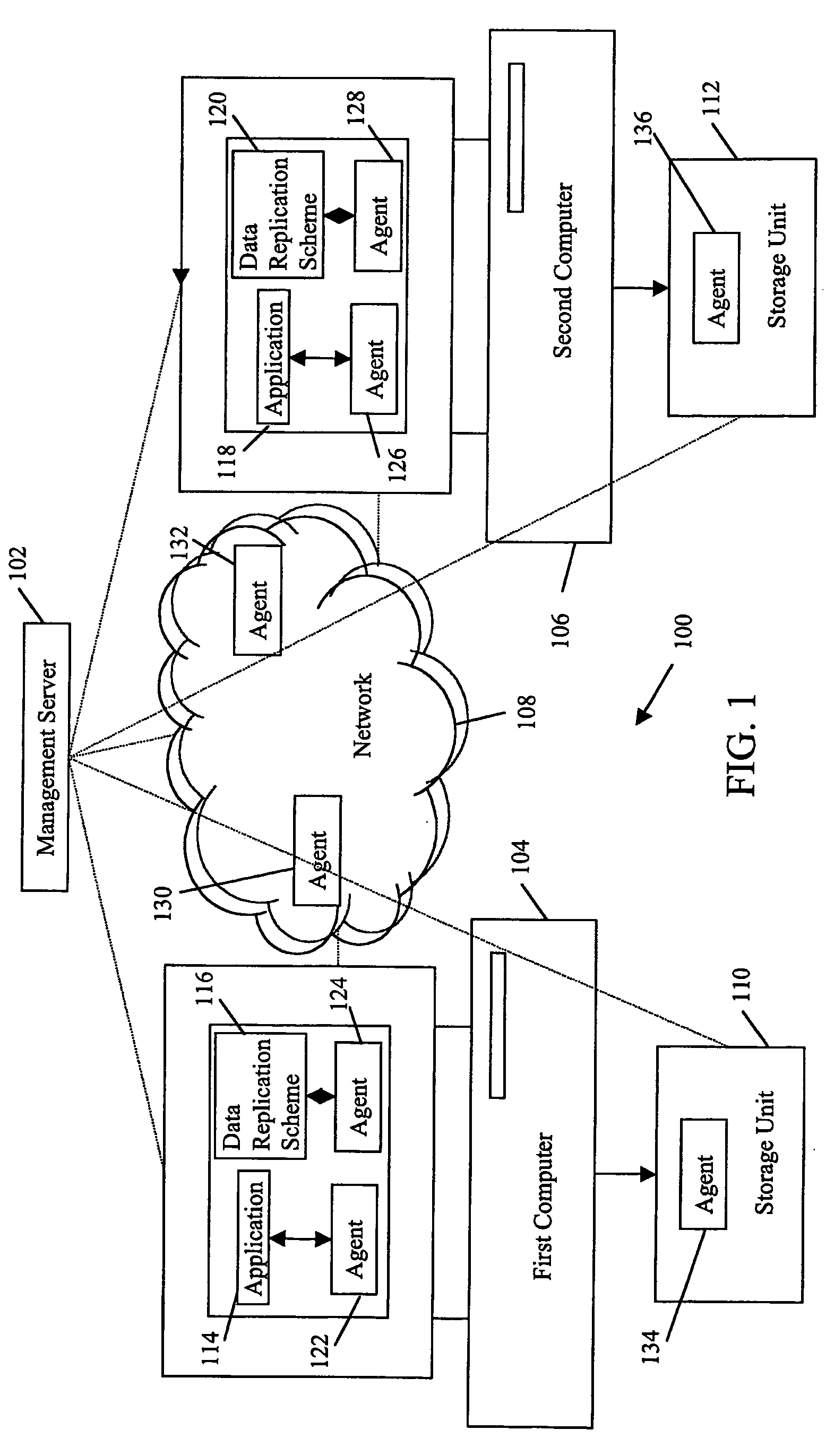
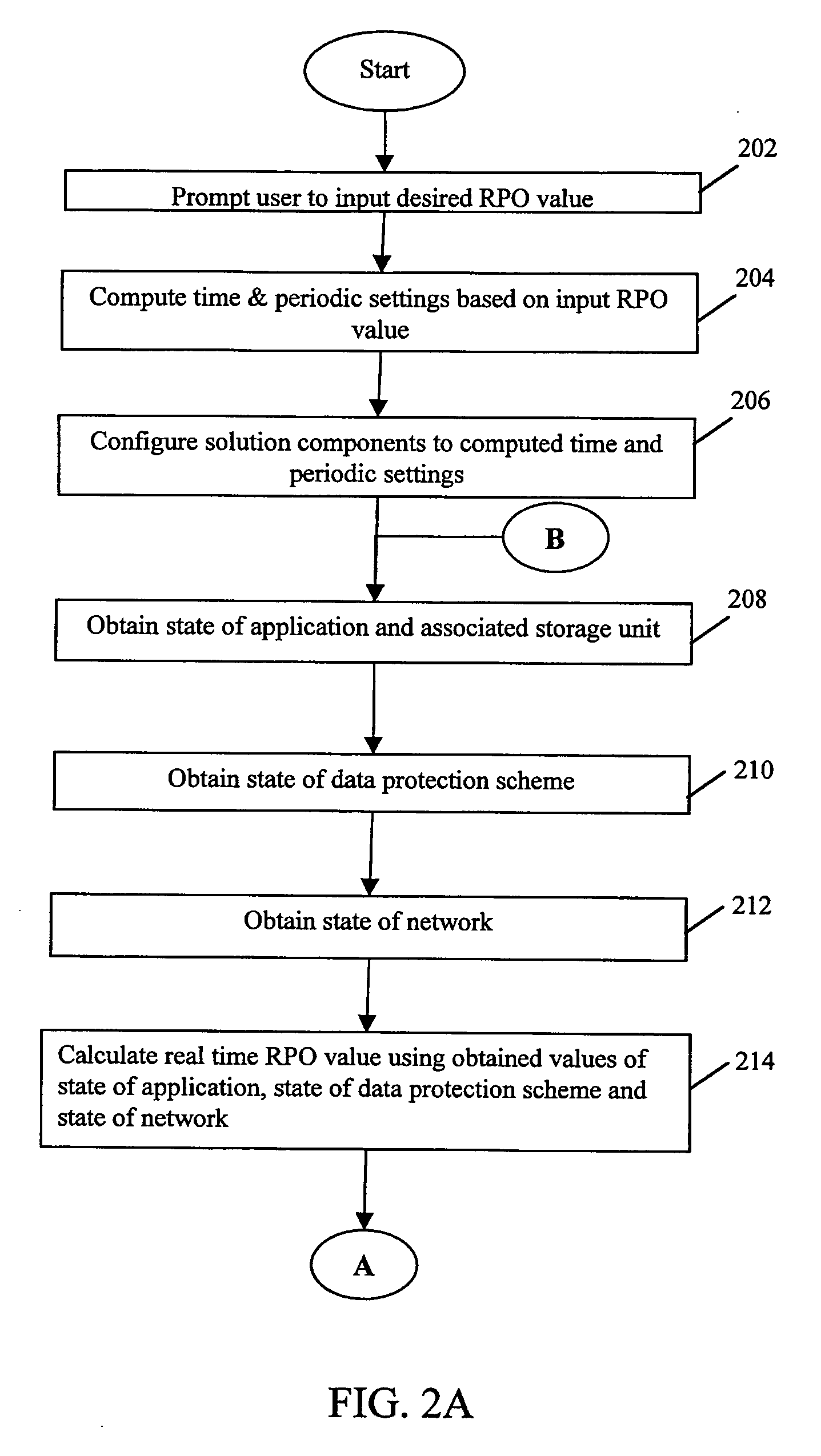
System and method for management of recovery point objectives of business continuity/disaster recovery IT solutions
InactiveUS20060129562A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionIndustrial engineeringRecovery point objective
The present invention provides a system and method for management of Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) of a business continuity or disaster recovery solution. The system comprises a management server logically coupled with at least a first computer, at least a second computer, and a network coupling the first and the second computers. The first and second computers host at least one continuously available application and at least one data protection scheme for replicating the application data; the application data being periodically replicated from the first computer to at least the second computer. The system manages RPO by inputting an RPO value for the solution, calculating a real time RPO value for the solution, and making the real time RPO value equal to the input RPO value.
Owner:IBM GLOBAL SERVICES PTE LTD
Backup of data across network of devices
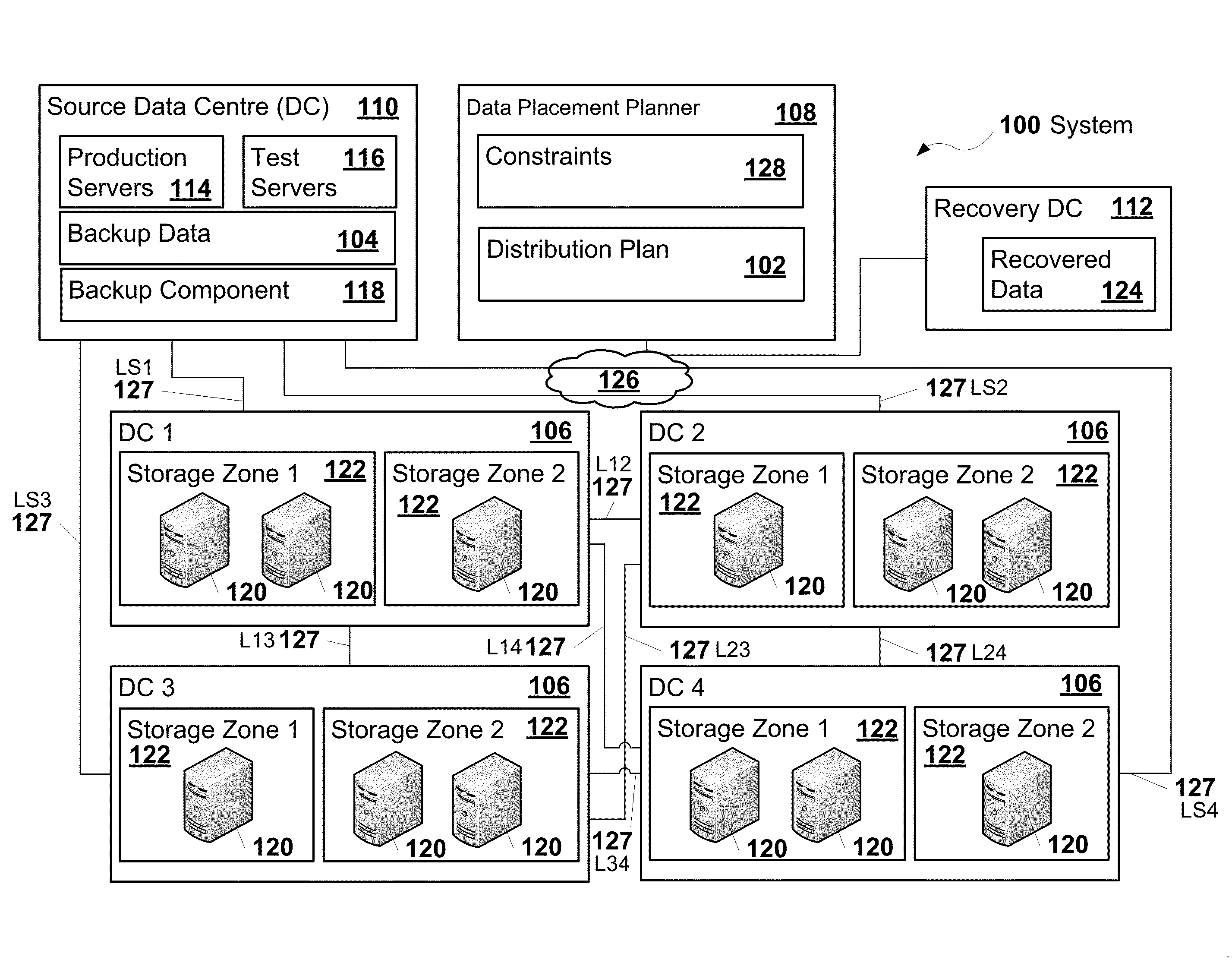
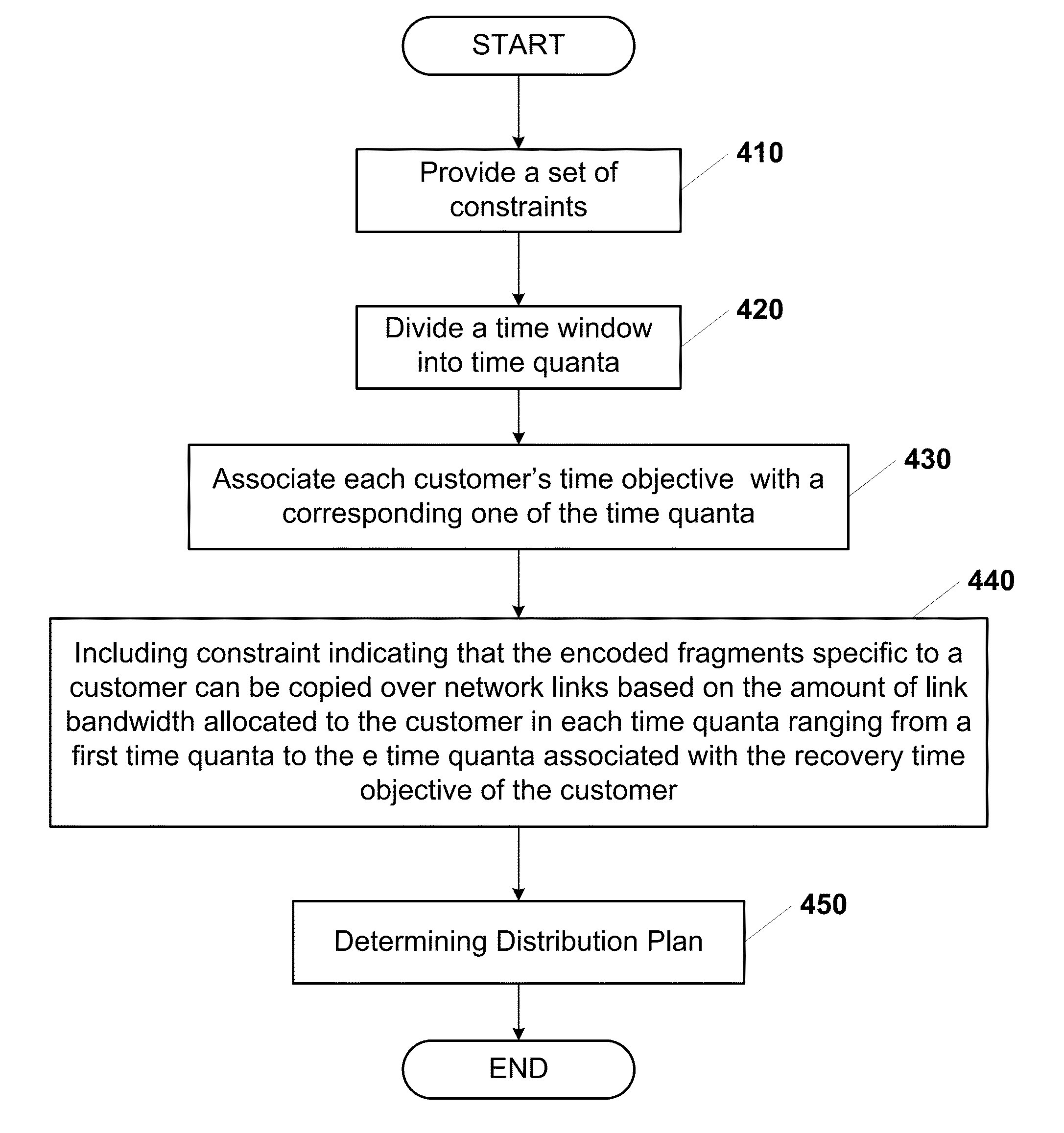
ActiveUS20130054536A1Satisfy constraintsDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionData storingData store
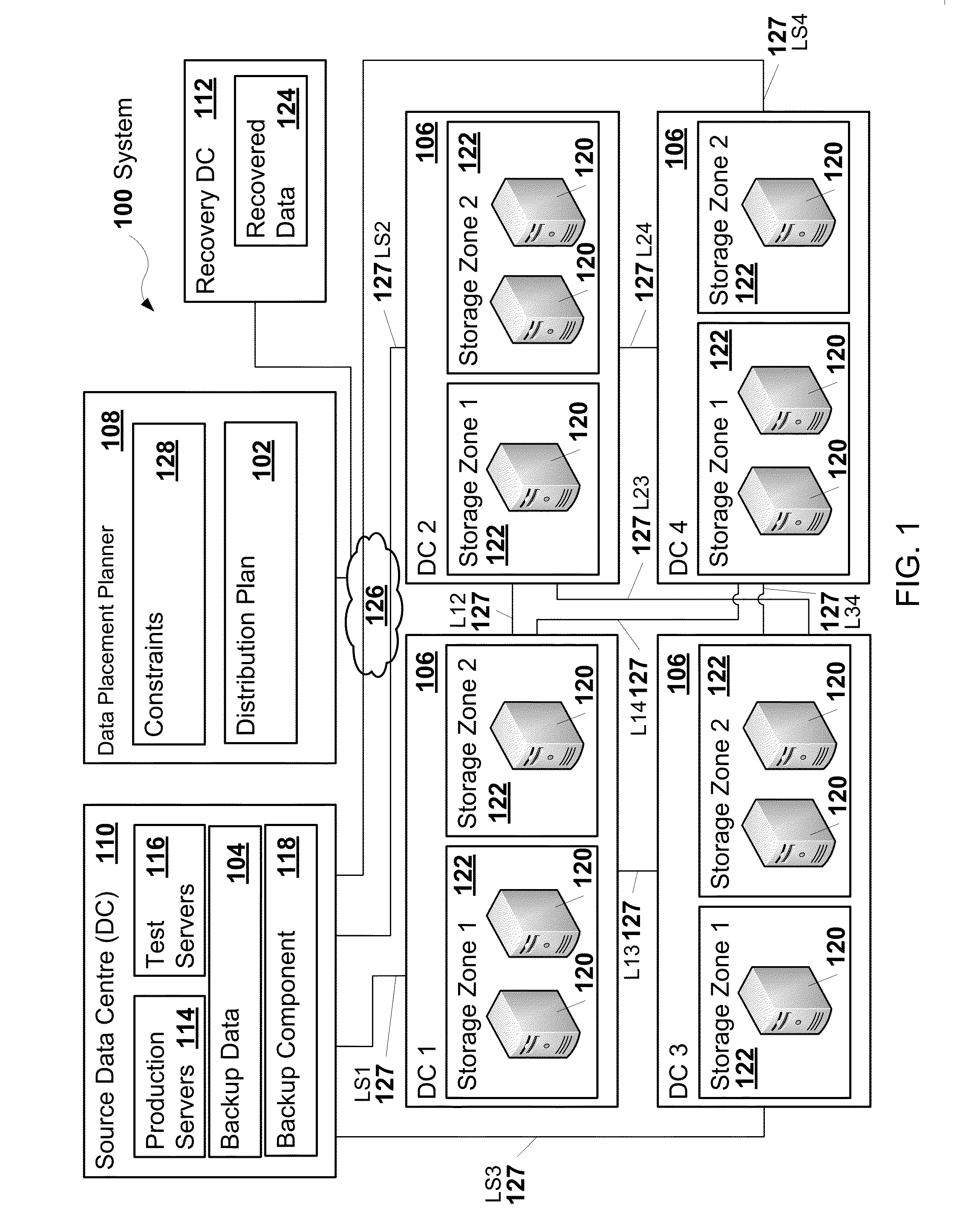
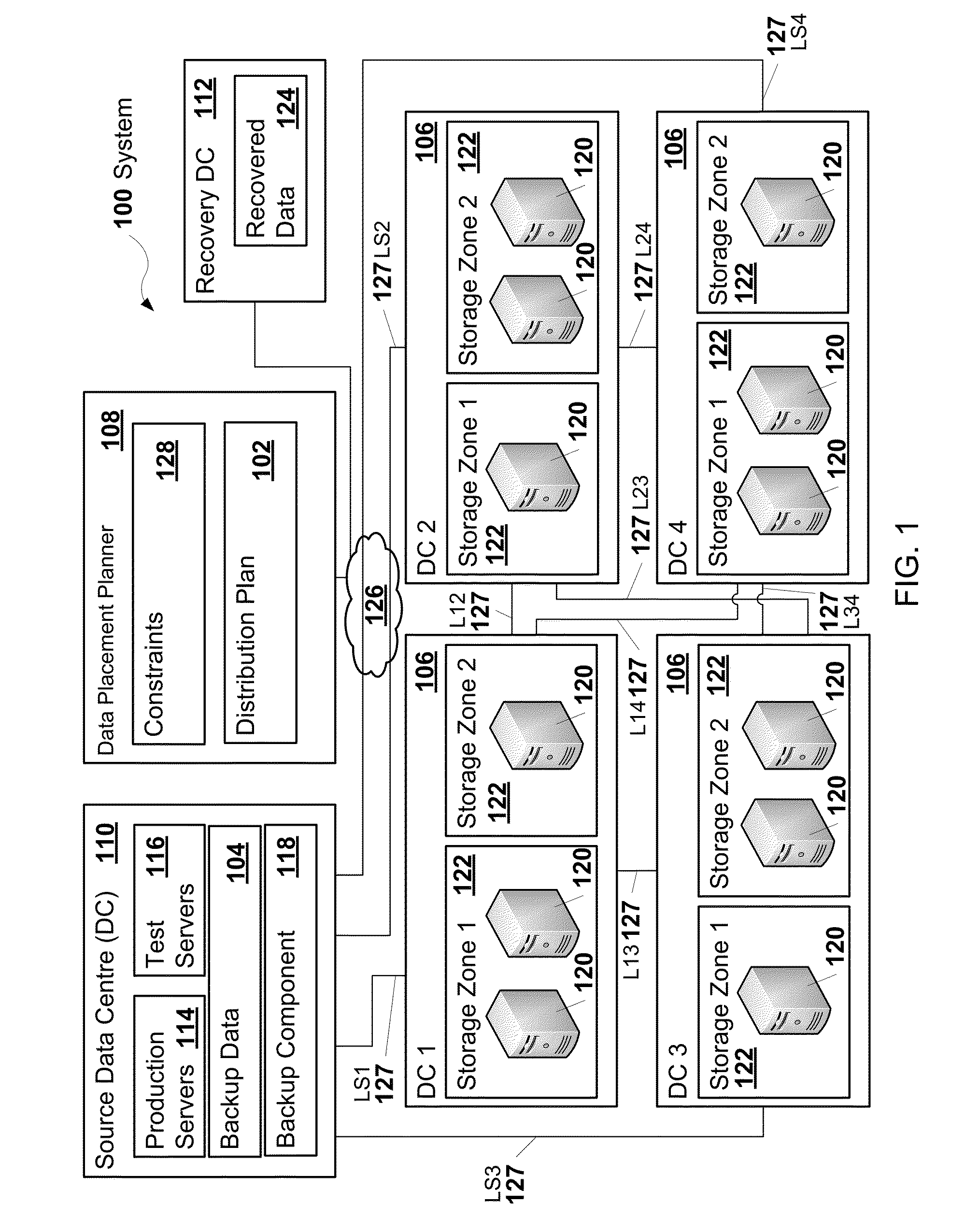
A distribution plan that indicates how to encode and distribute backup data across multiple data centres may be generated. The distribution plan may be generated such that one or more characteristics of the distribution plan, such as costs, are optimized while constraints on the plan, such as protection level, recovery point objective (RPO), and recovery time objective (RTO) are satisfied. The protection level may indicate the number of the data centres that are to remain available such that the backup data is recoverable from encoded fragments of the backup data stored in the data centres that remain available.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Apparatus, system, and method for creating a backup schedule in a san environment based on a recovery plan
InactiveUS20080154979A1Minimal disruptionError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase backupSystem recovery
An apparatus, system, and method for creating a database backup schedule in a SAN environment based on a recovery plan. A user provides a desired recovery point objective (RPO) from a system recovery plan and an identifier of a database for back up. The present invention determines a priority (w) for a recent recovery point and determines a number (N) of volumes for storing backup images and a number (n) of database volumes used by the database. The present invention generates a scheduling formula where RPO is divided by the priority (w) of the most recent recovery point raised to the power of the truncated integer value of the ratio of volumes for storing backup images (N) and the number of volumes in use by the database (n) minus a scheduling interval determinant (i). The scheduling formula is used to determine a backup interval and backup assurance points.
Owner:IBM CORP
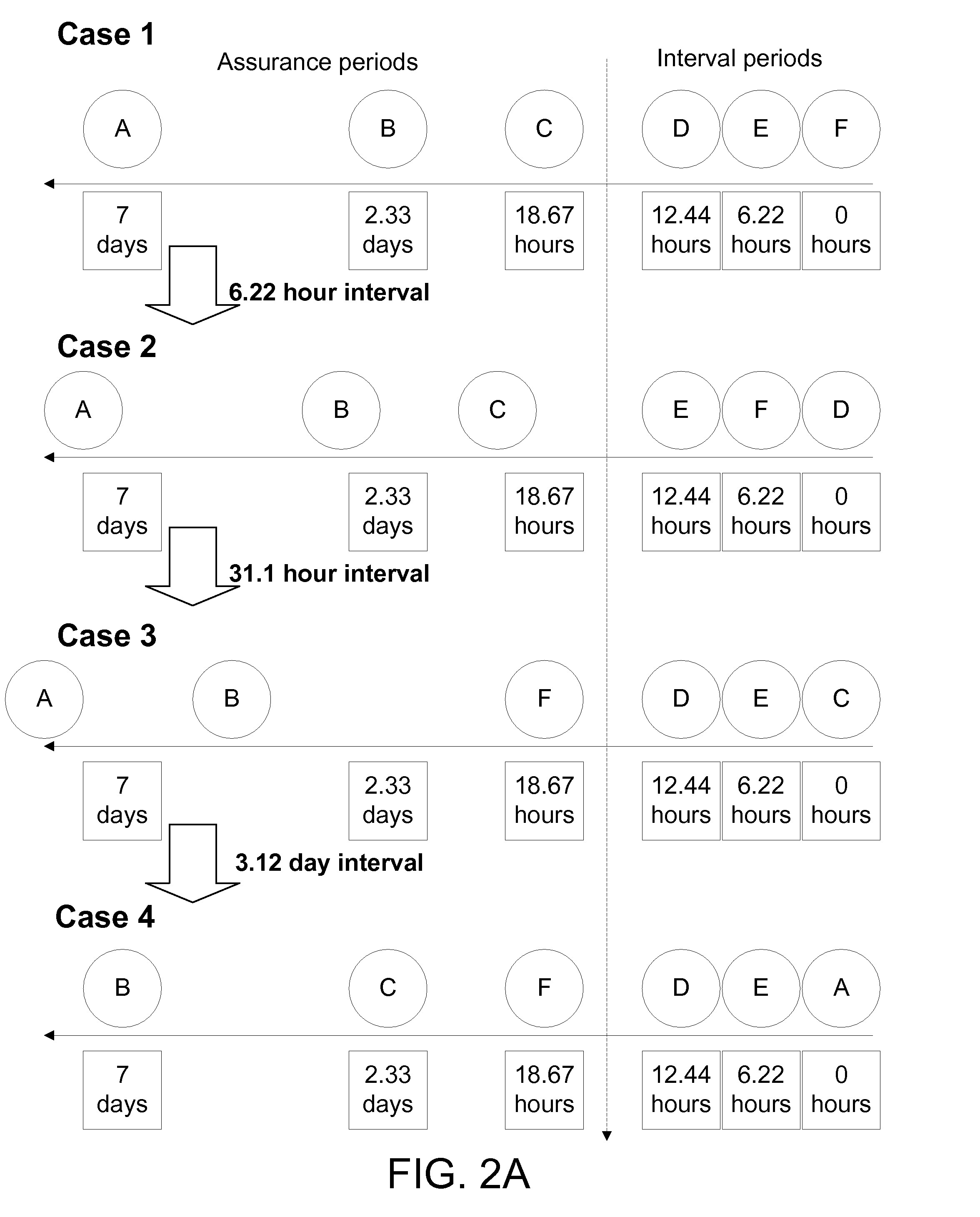
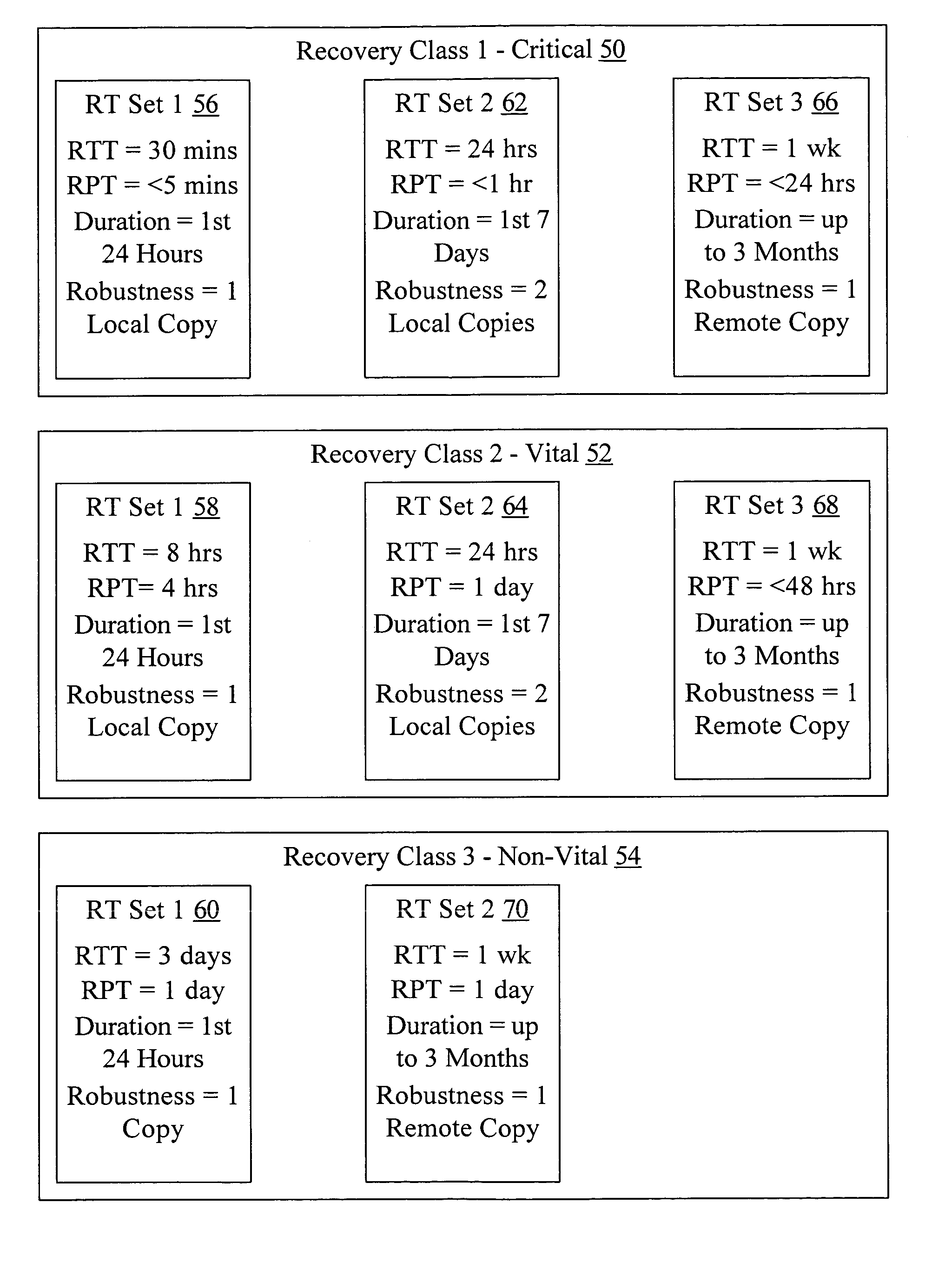
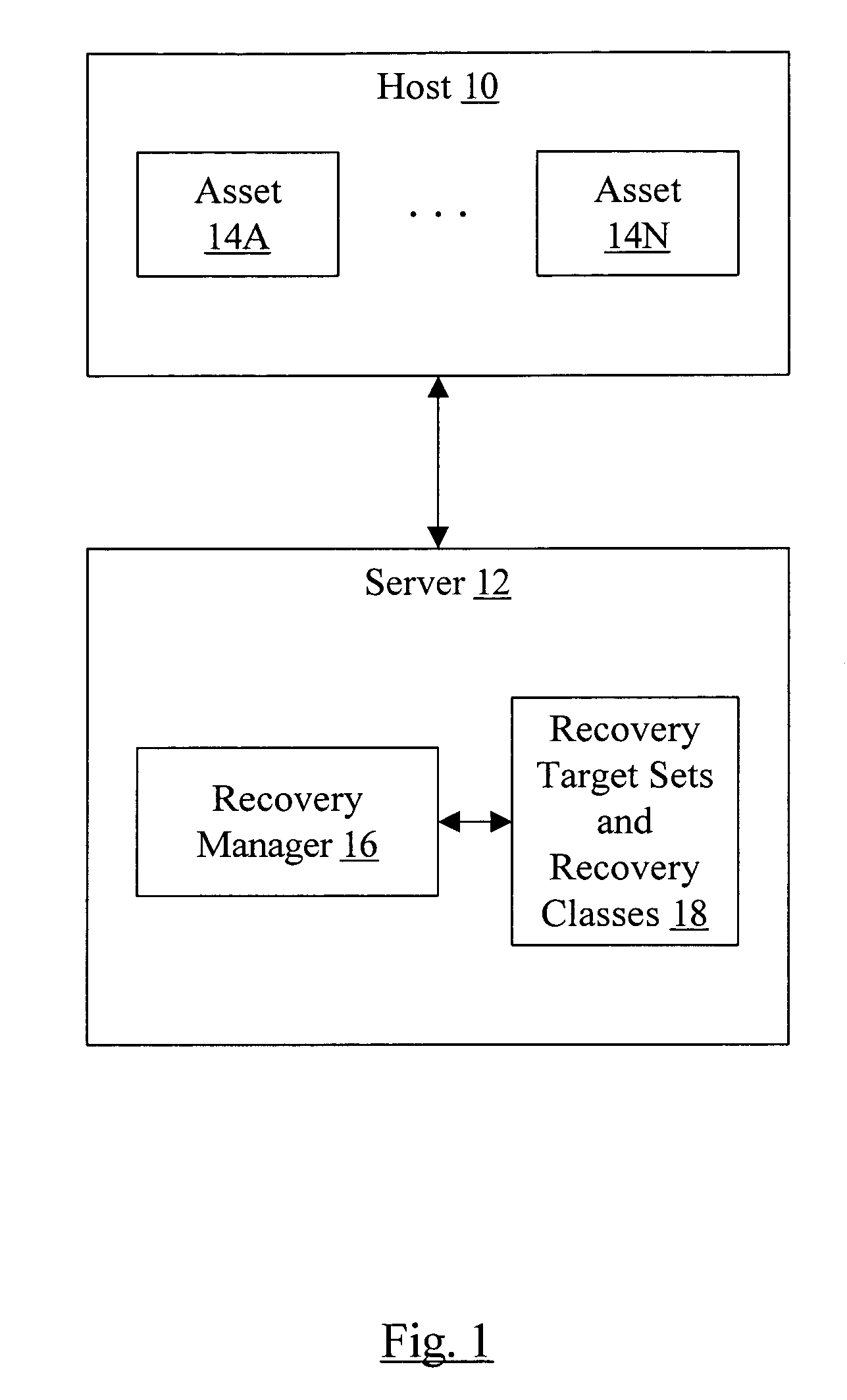
Classification of recovery targets to enable automated protection setup
In one embodiment, a recovery manager may define a plurality of recovery target sets. Each recovery target set comprises a recovery point target, a recovery time target, and at least one other property. The recovery manager also defines a plurality of recovery classes. Each recovery class comprises at least one recovery target set of the plurality of recovery target sets. Each recovery class describes recovery requirements over an asset state life cycle. The recovery manager applies a first recovery class of the plurality of recovery classes to a first asset dependent on an importance of the first asset to an owner of the first asset. In some cases, the first recovery class and / or other recovery classes of the plurality of recovery classes may each be applied to multiple assets. In another embodiment, a recovery manager defines one or more recovery target sets to be applied to one or more assets and saves the one or more recovery target sets. In some embodiments, recovery classes are also saved.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Backup of data across network of devices
ActiveUS8630983B2Digital data processing detailsRedundant operation error correctionData centerData storing
A distribution plan that indicates how to encode and distribute backup data across multiple data centers may be generated. The distribution plan may be generated such that one or more characteristics of the distribution plan, such as costs, are optimized while constraints on the plan, such as protection level, recovery point objective (RPO), and recovery time objective (RTO) are satisfied. The protection level may indicate the number of the data centers that are to remain available such that the backup data is recoverable from encoded fragments of the backup data stored in the data centers that remain available.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
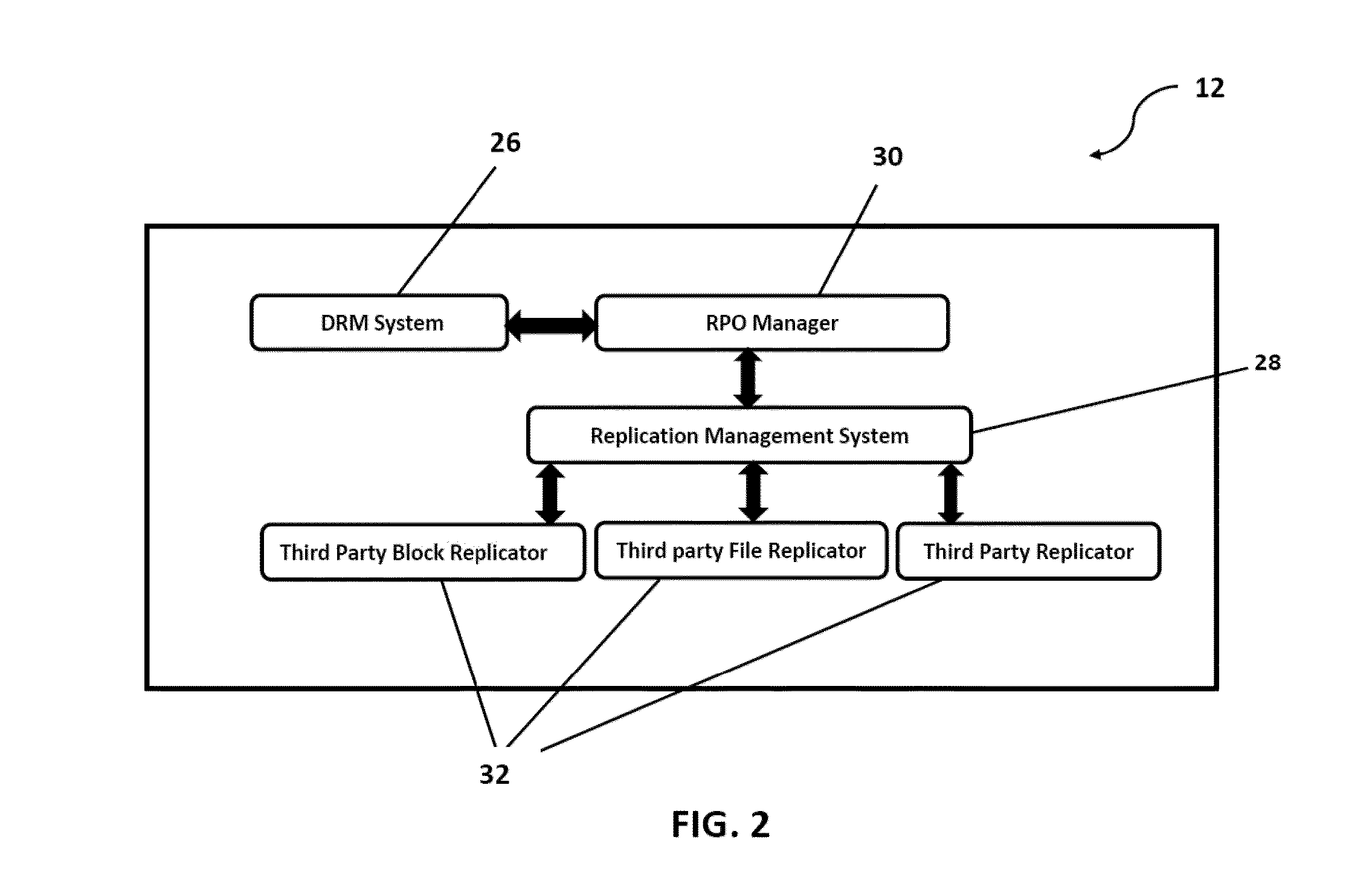
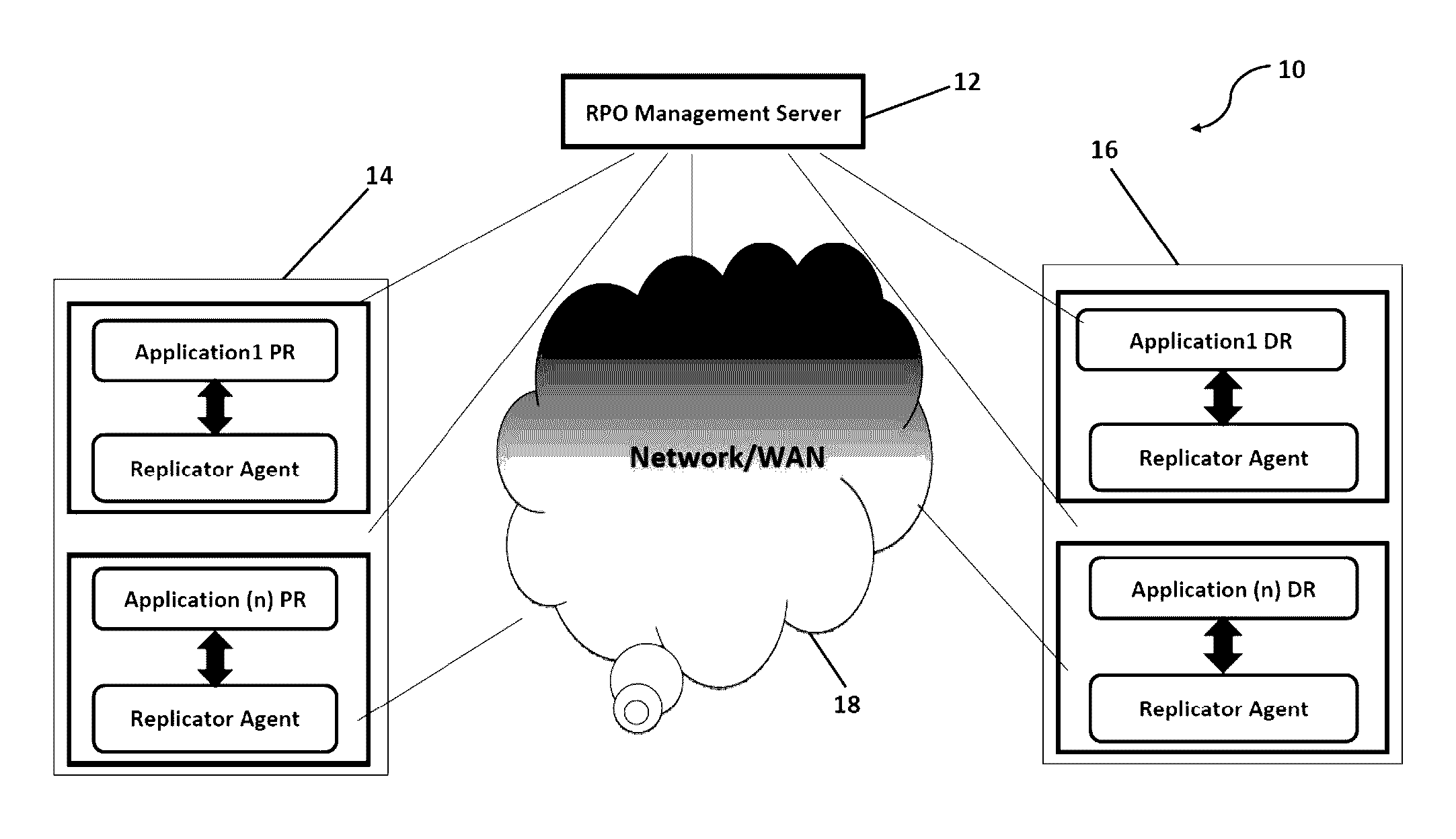
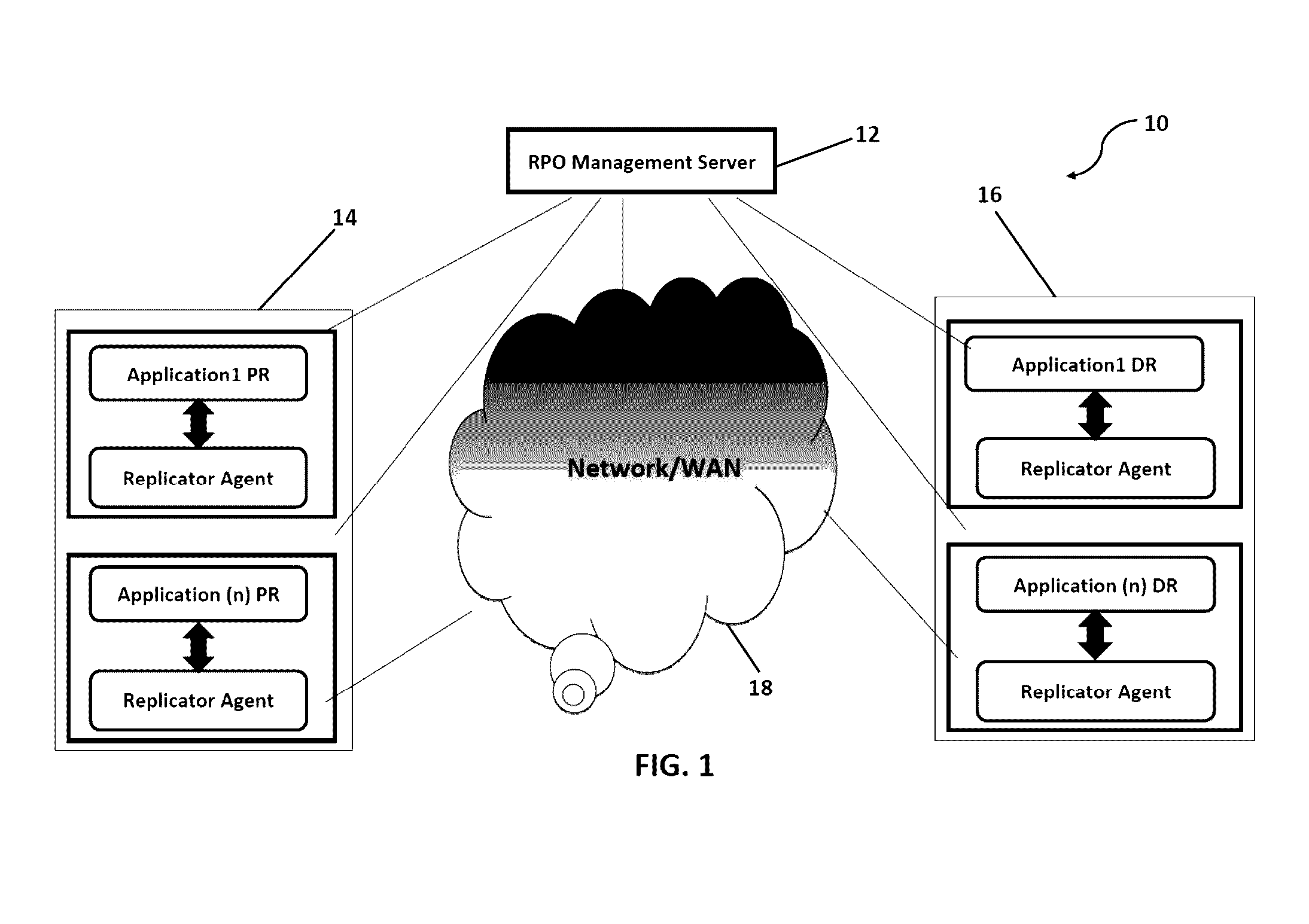
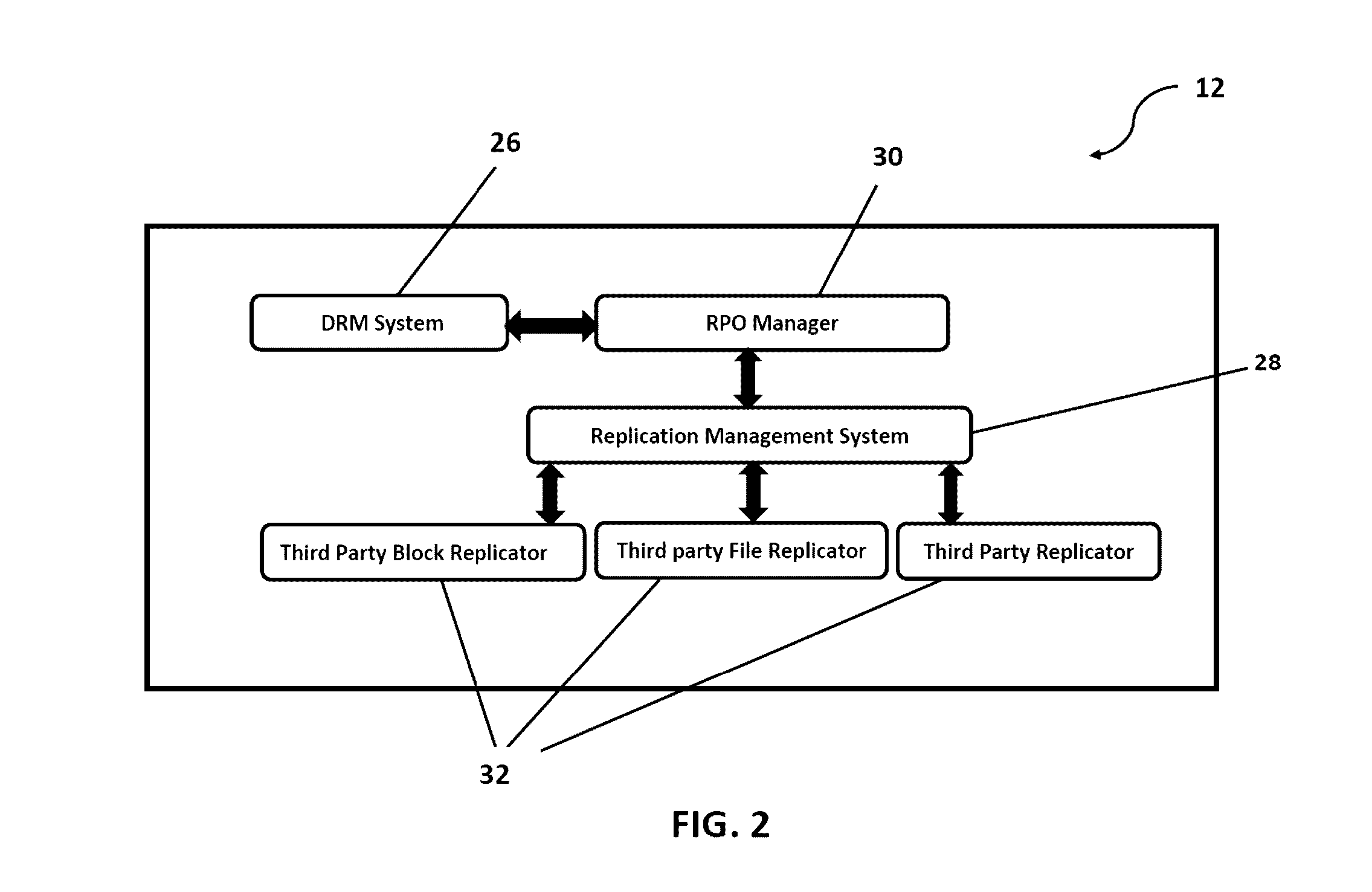
System and method to proactively maintain a consistent recovery point objective (RPO) across data centers
ActiveUS20140297588A1Consistent levelEffective utilization of network bandwidthDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionData centerComputer science
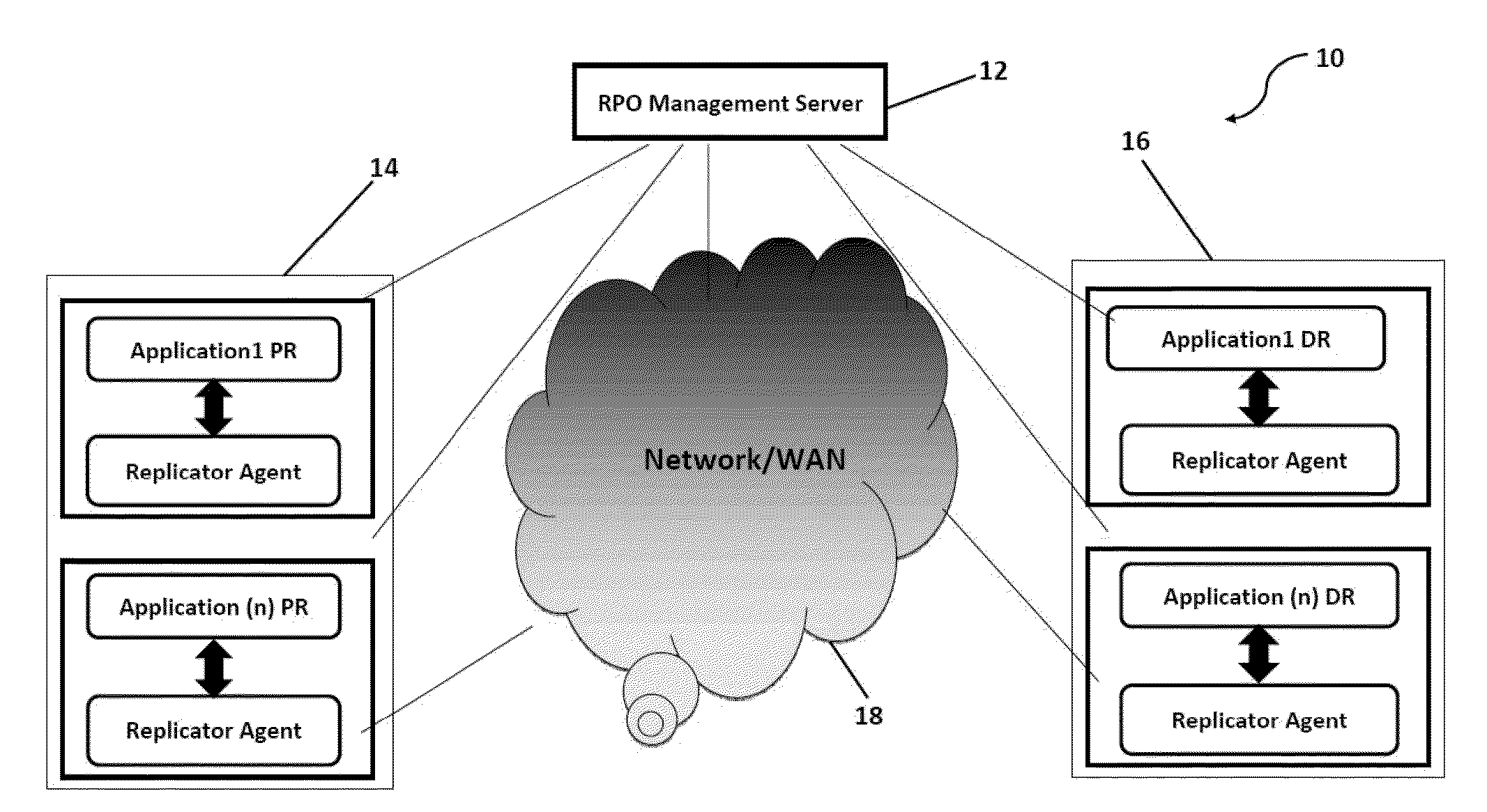
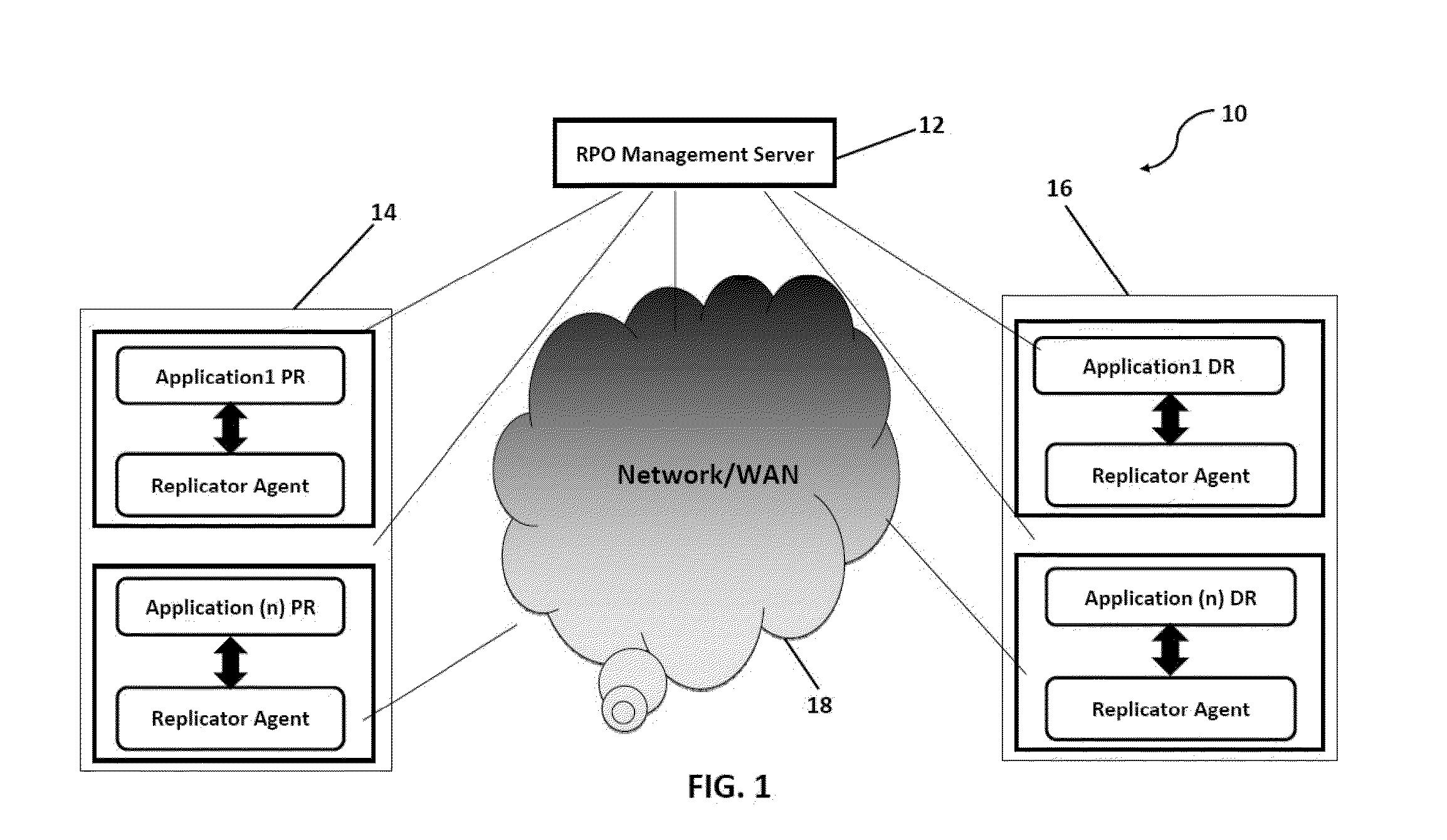
A system and method for proactively monitoring and maintaining a consistent recovery point objective (RPO) across data centers, the system comprising: one or more RPO Management Server(s) logically connected to one or more Production Sites and one or more Disaster Recovery Sites; a Network connecting the said RPO Management Server(s) with the said Production Site and the said Disaster Recovery Site wherein the said RPO Management Server is provided with at least one RPO Manager, at least one Disaster Recovery Management (DRM) System and at least one Replication Management System.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
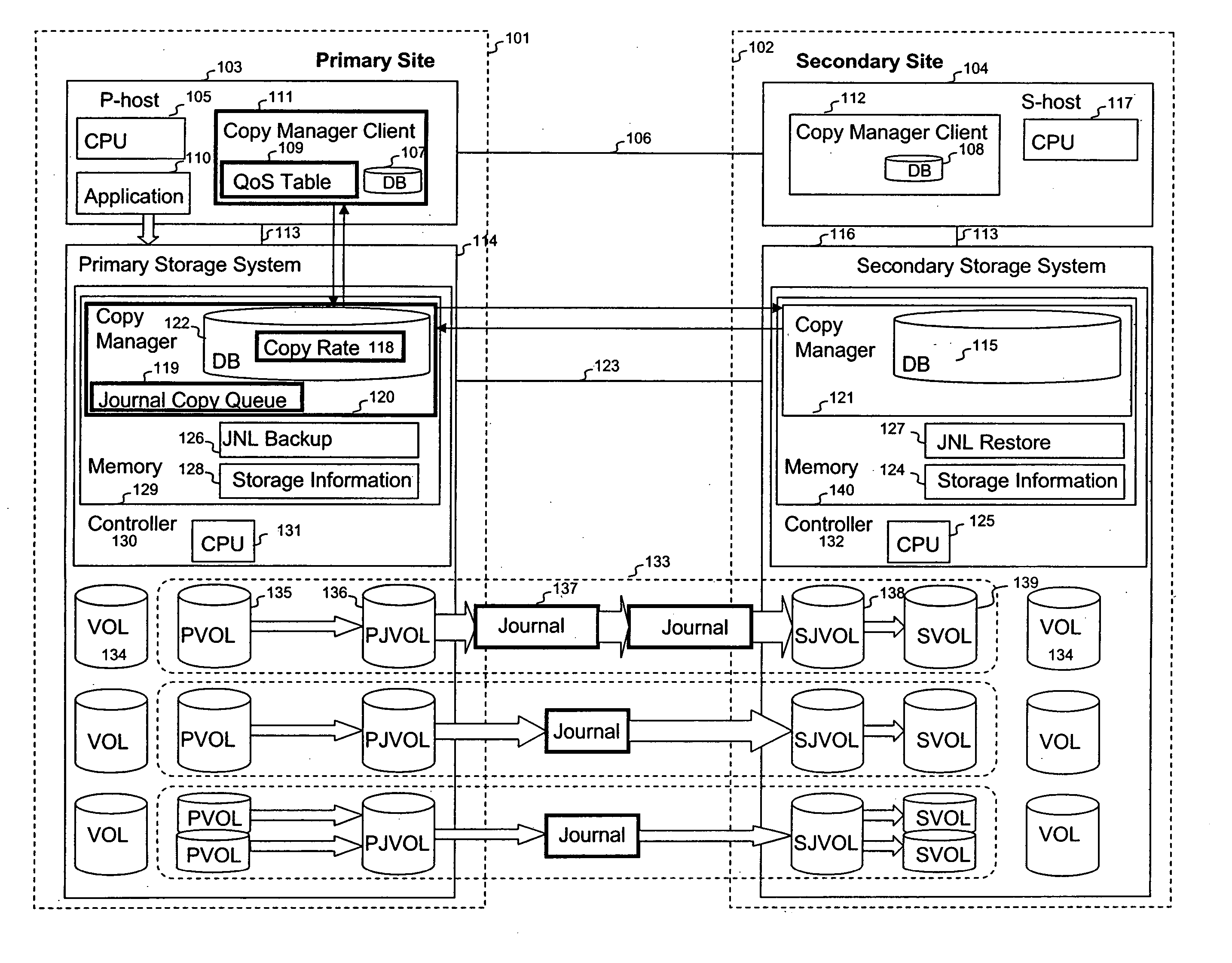
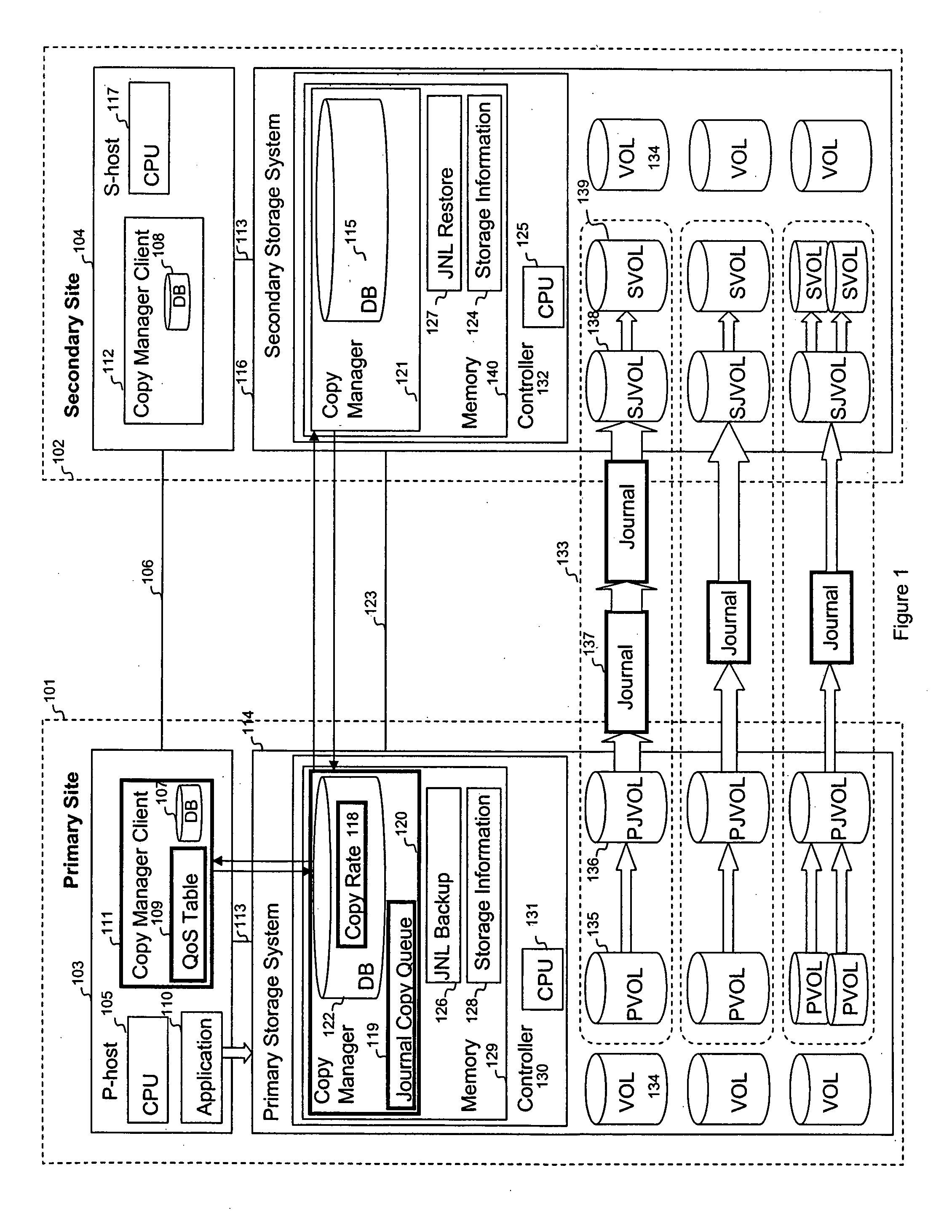
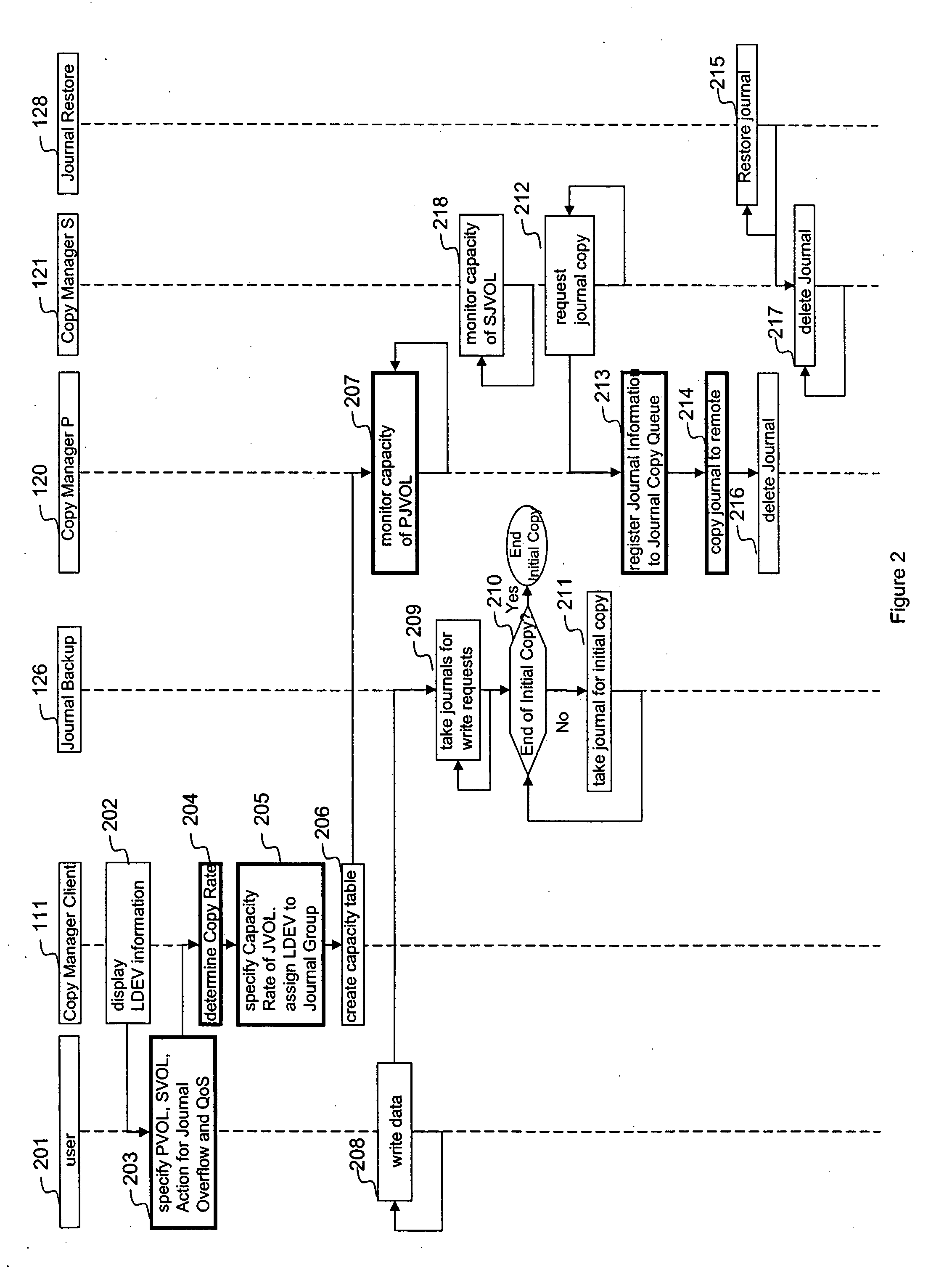
Quality of service for remote copy operations in storage systems
InactiveUS20060095696A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionQuality of servicePrimary sites
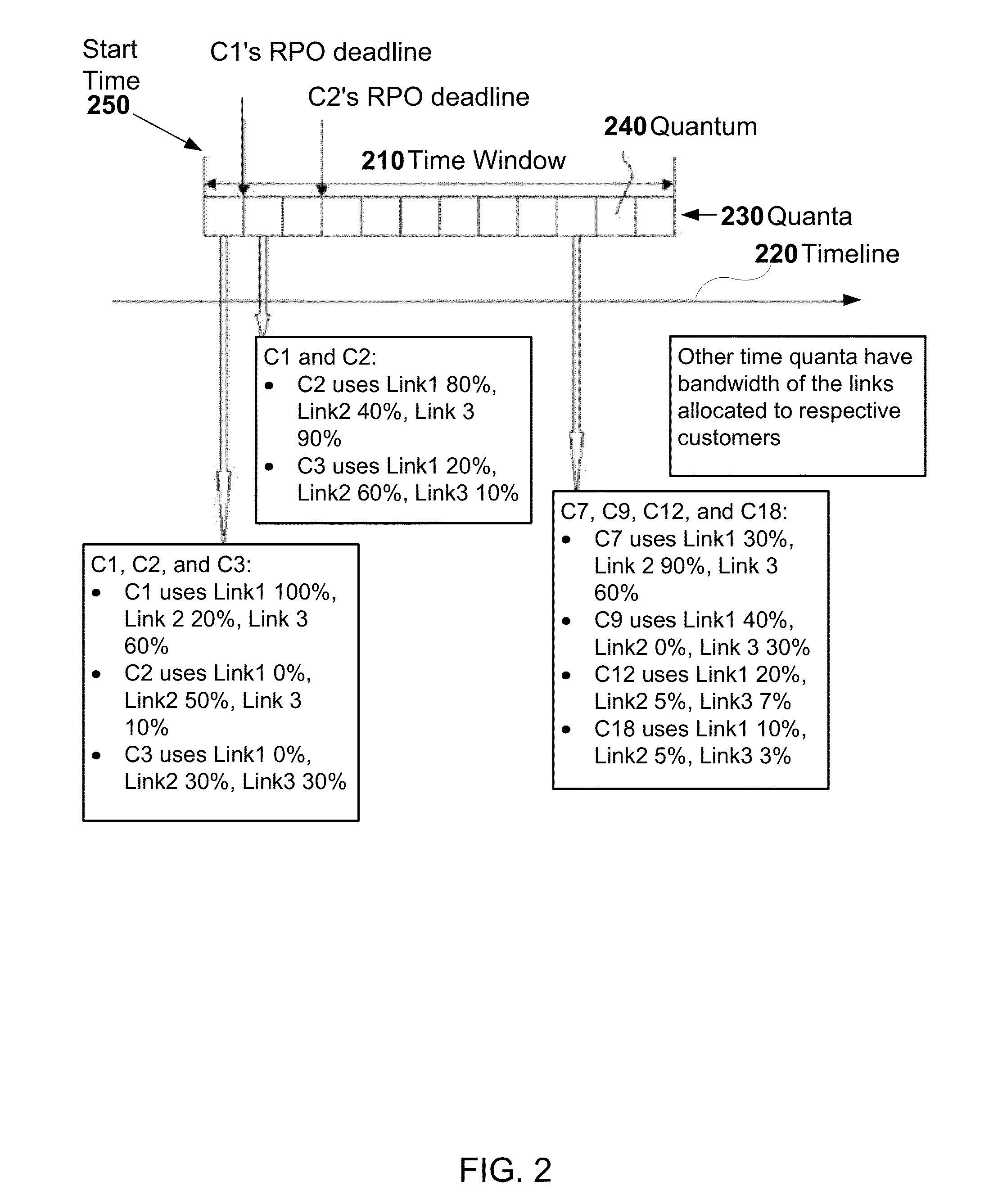
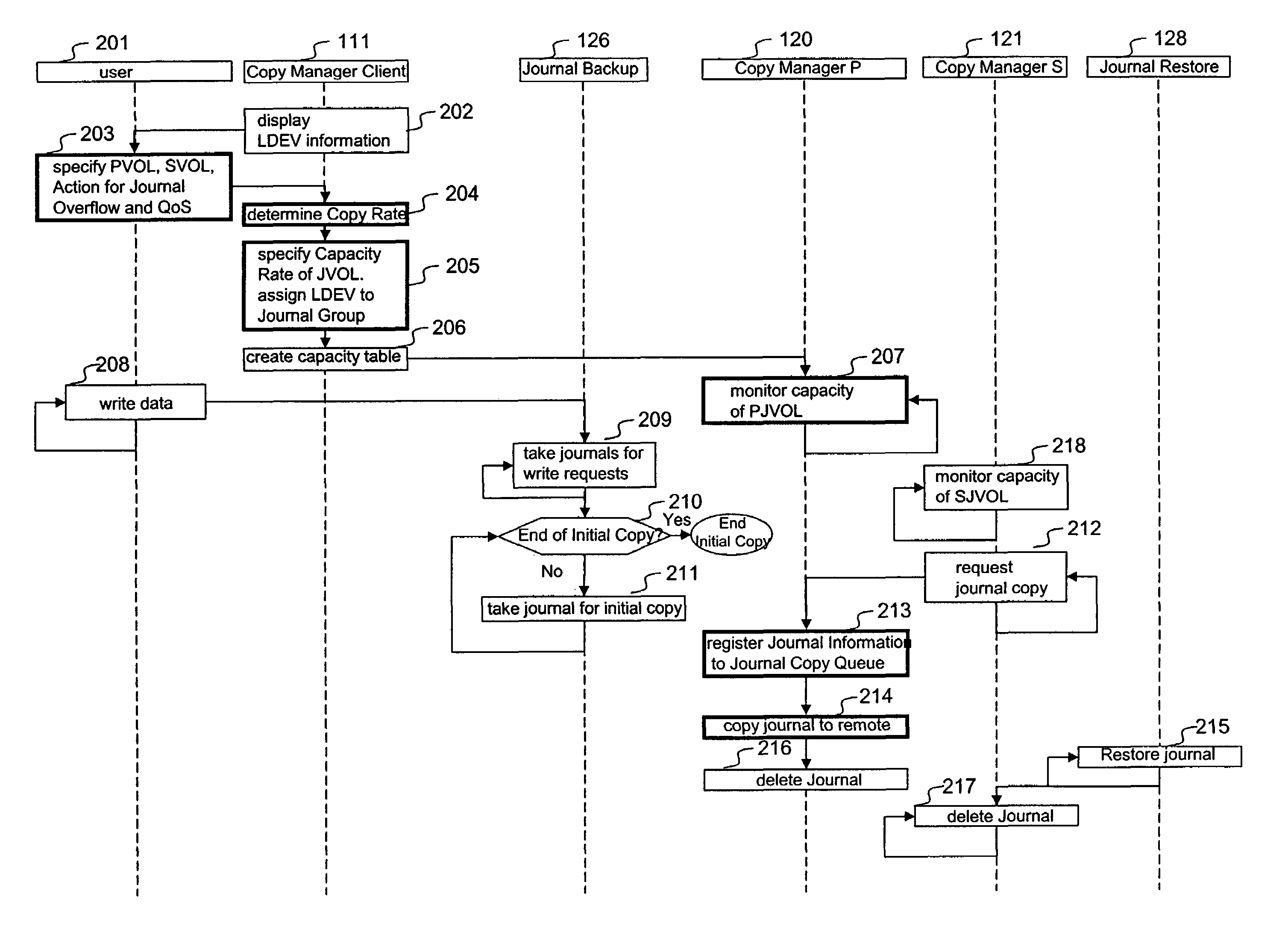
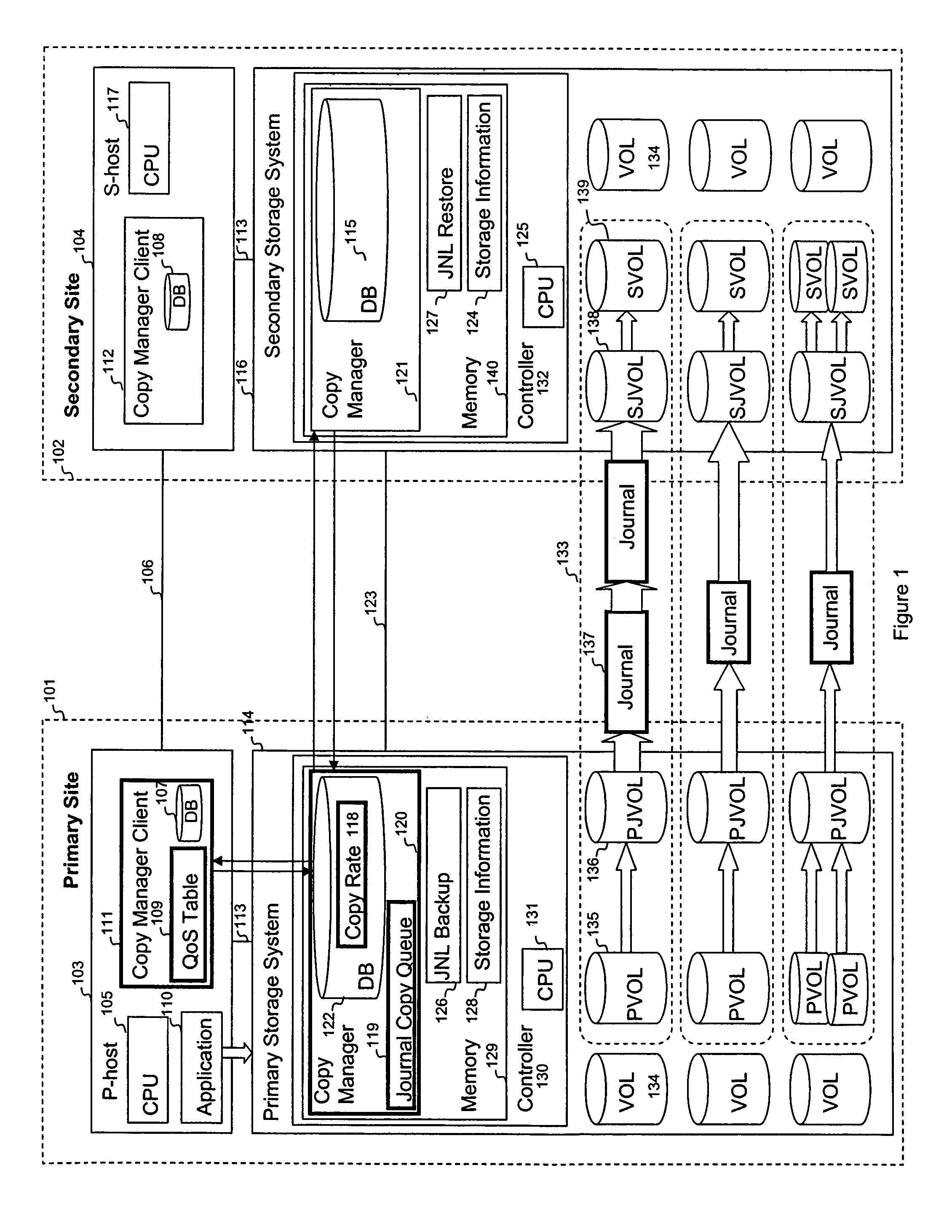
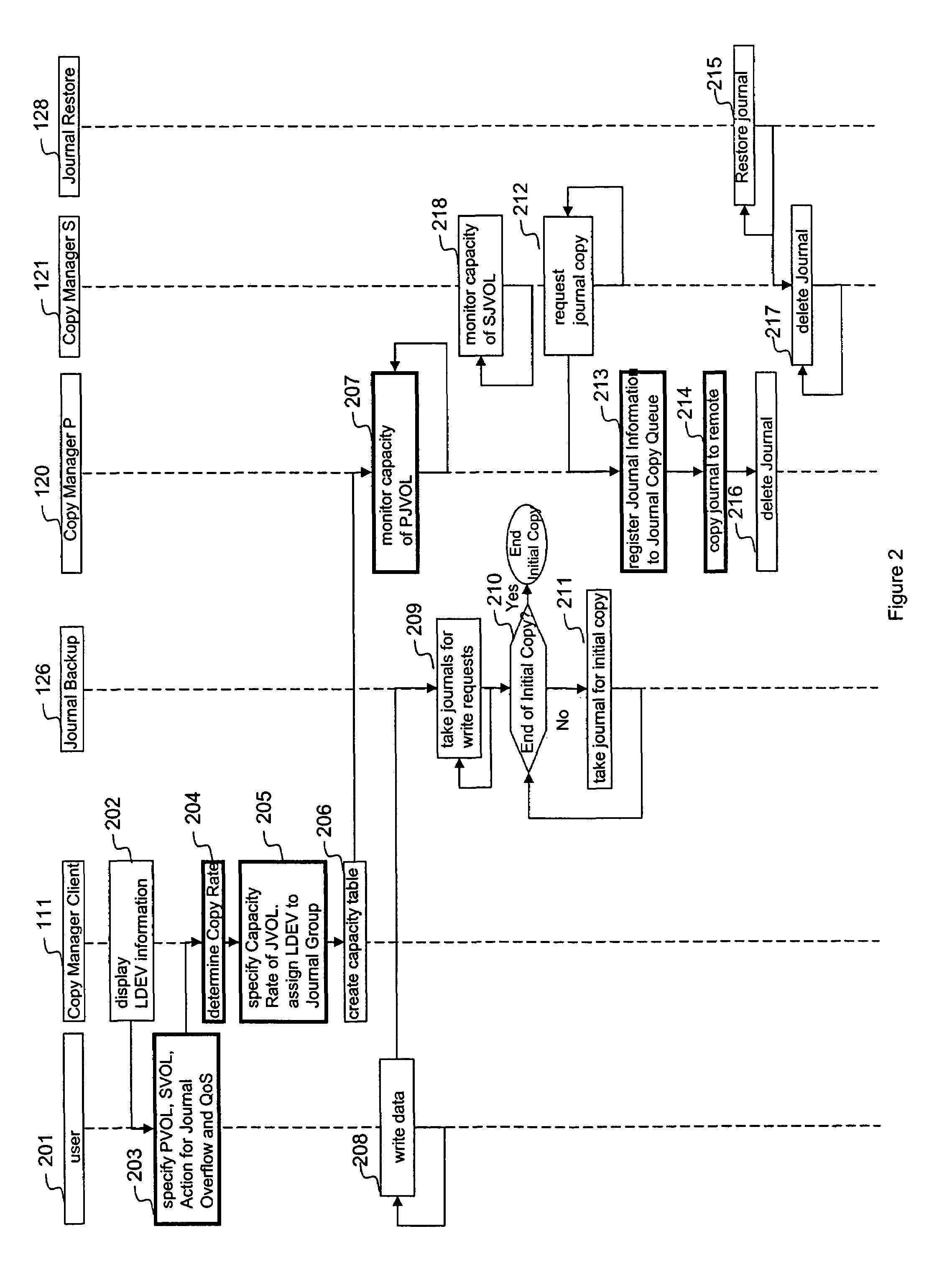
A system is provided for storage of journal data from a primary site to a secondary site with a predefined quality of service. In one implementation, the primary storage system stores information for updating data stored on the primary disk array in the form of a history of updates made to the data. The primary storage system is configured to transfer this journal information to the secondary storage system. The user can specify the quality of service desired using a variety of measures, for example, a recovery point objective or a recovery time objective. In response, a copy manager within one of the storage systems determines the capacity of the various primary and secondary volumes, and determines the copy rate available, typically dependent upon the bandwidth between the primary and secondary systems. The copy manager then copies journal data to the remote site where it is stored.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Logical data backup and rollback using incremental capture in a distributed database
ActiveCN102142024AEfficient reductionEasy insertionDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseDistributed database
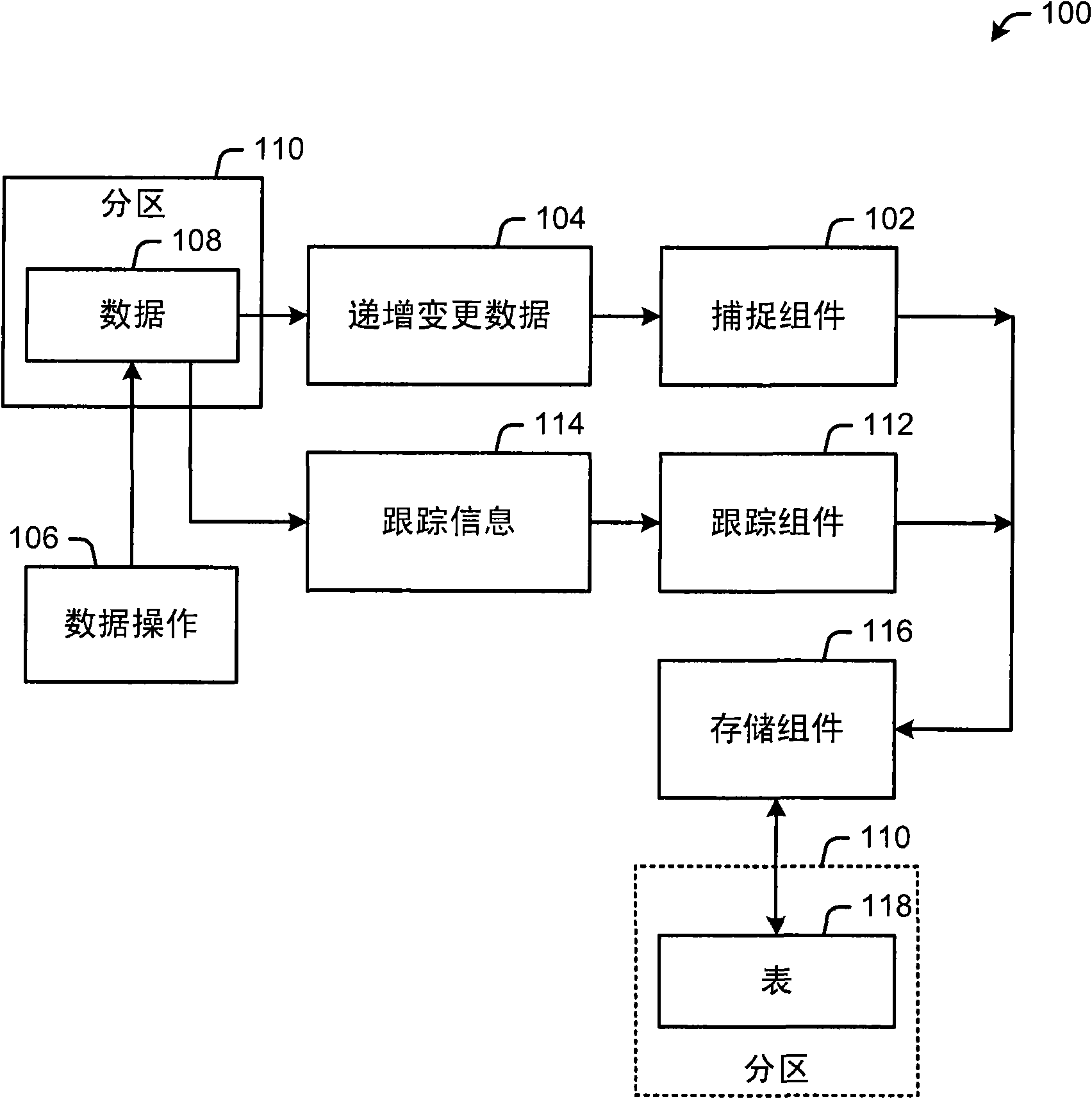
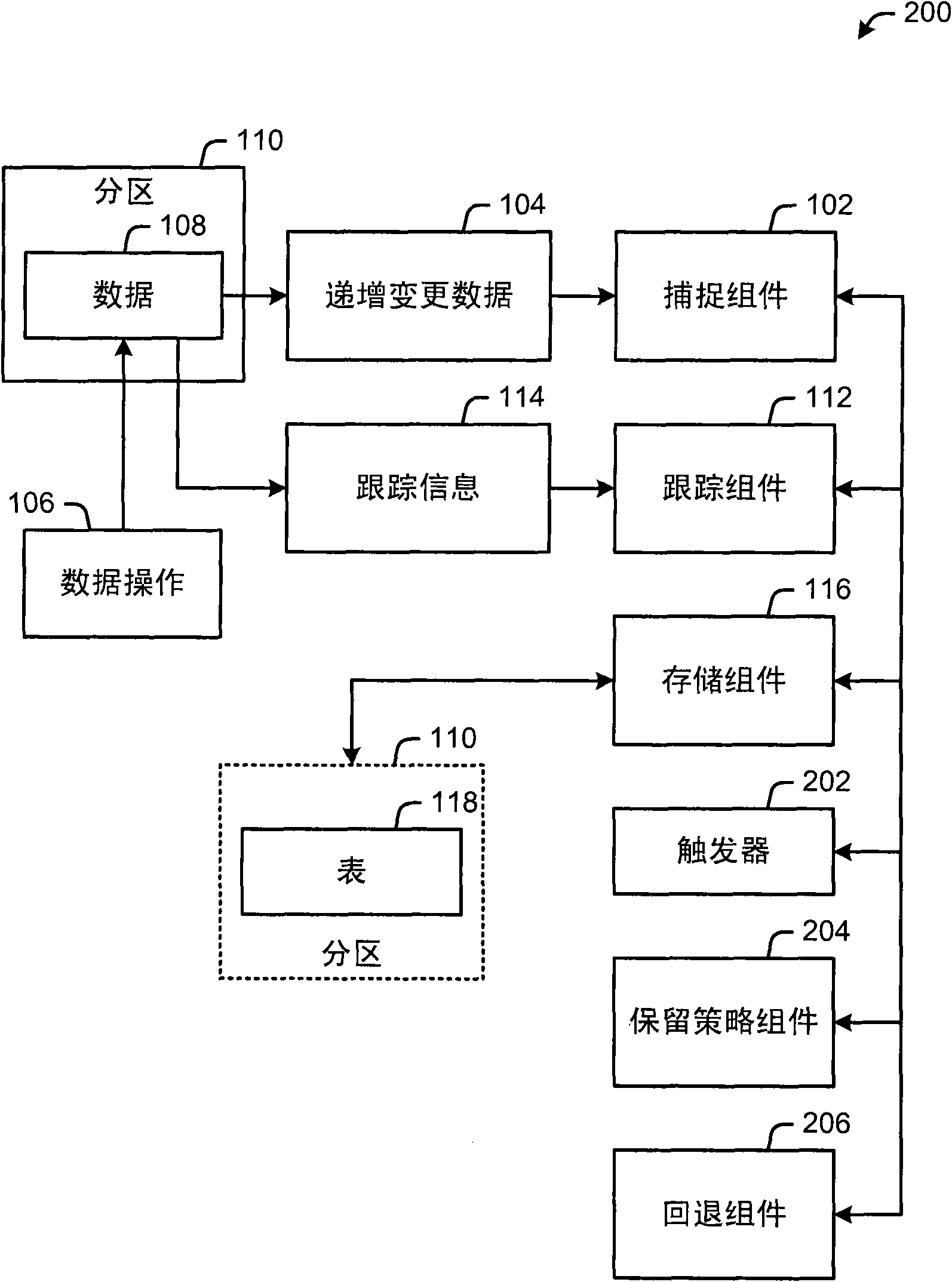
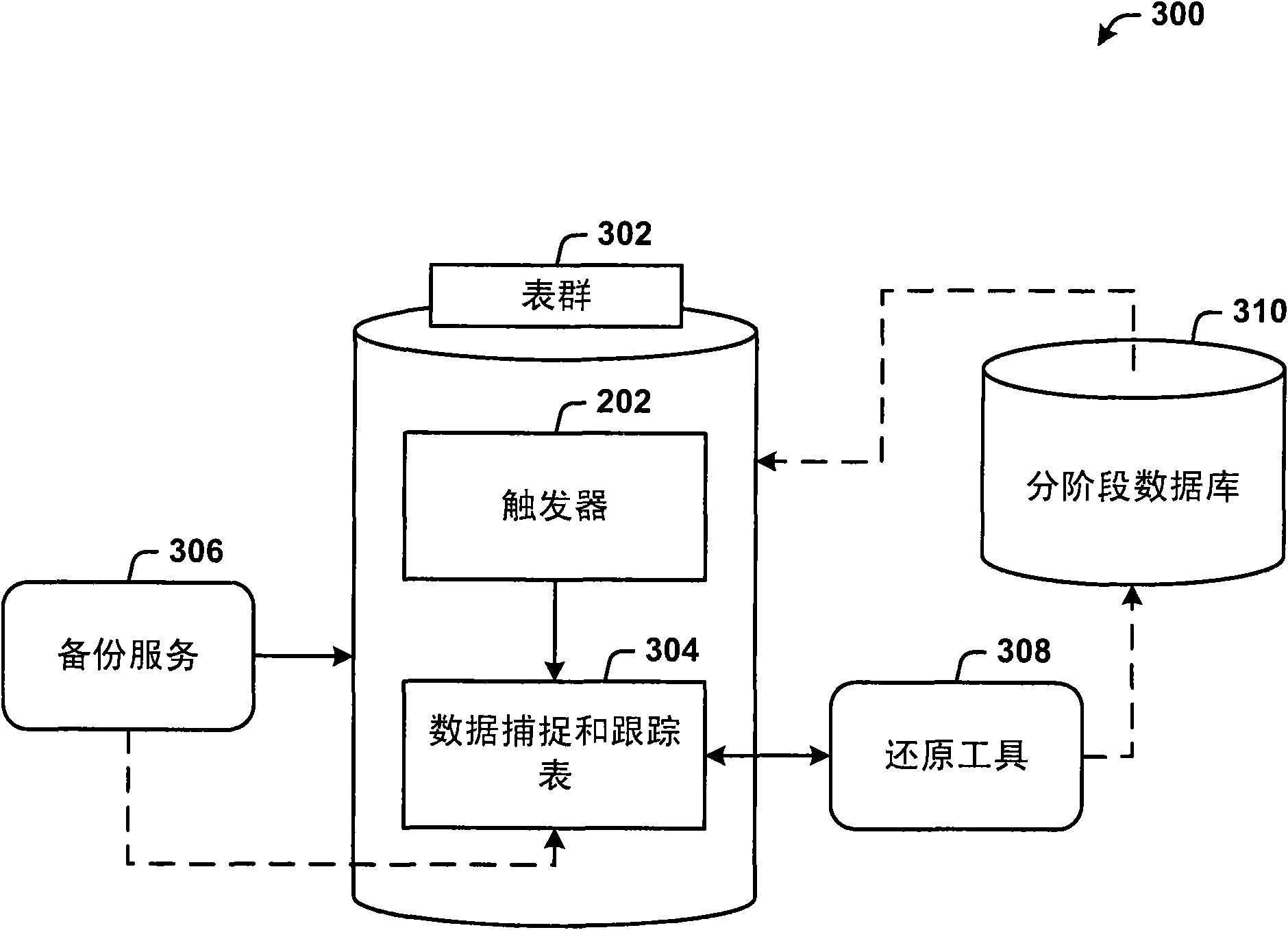
Provided is an architecture that eliminates the need for on-disk full backups of data retaining only changes that have occurred, in a separate table. Thus, the architecture provides for incremental recovery of incremental changes in a relational database (e.g., SQL). The architecture provides improved recovery time and recovery point objectives. By using the incremental capture of changed data (e.g., in an XML format), the capability is provided to capture schema changes, query the incremental change data and efficiently restore user data to an earlier point-in-time state. Changes (e.g., insert, update and delete operations) are tracked (e.g., continuously) by a set of triggers and the incrementally captured changed rows are inserted in a data capture table (a differential change ''delta'' table) in a human-readable format (e.g., XML). Rollback is also provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
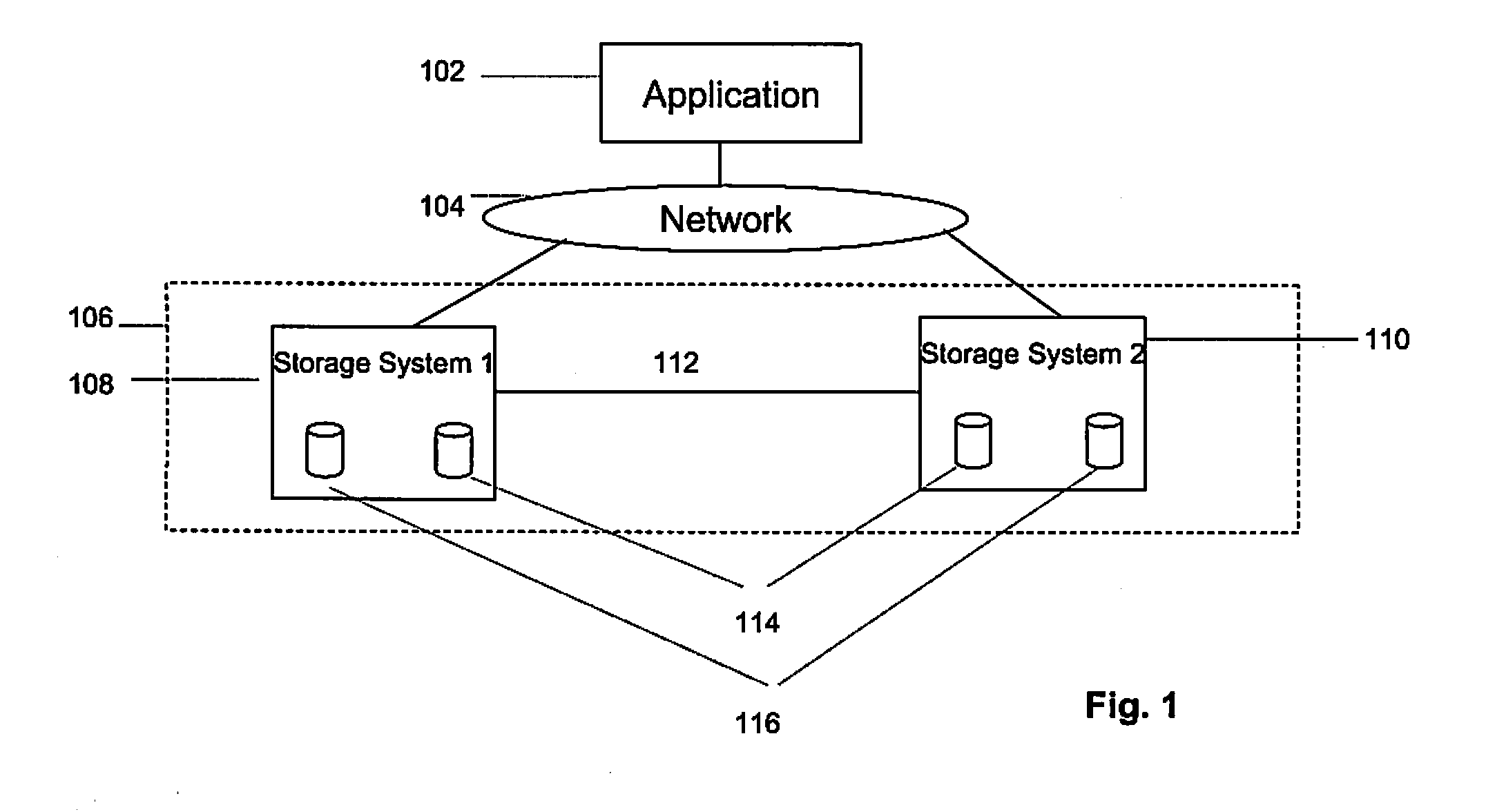
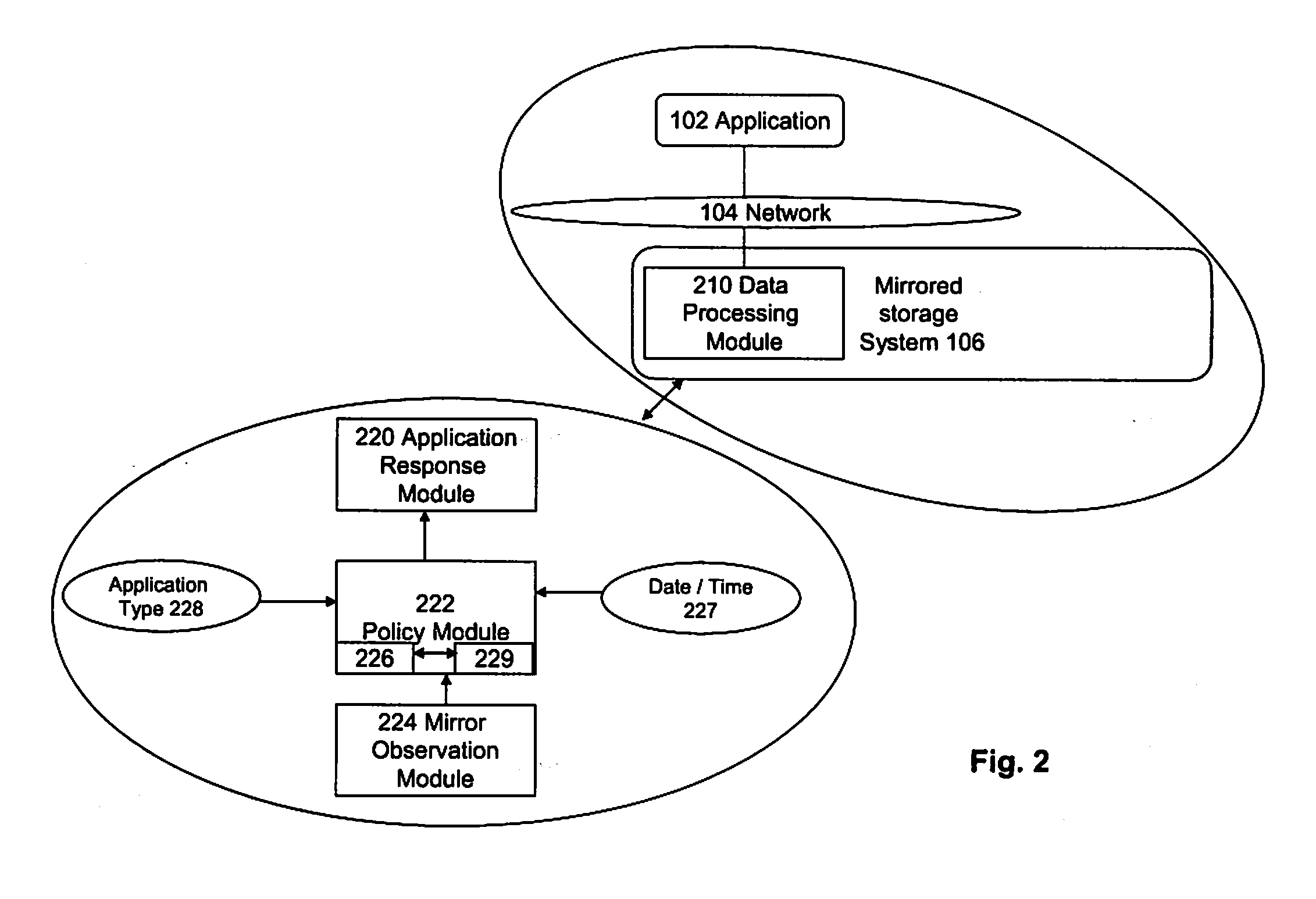
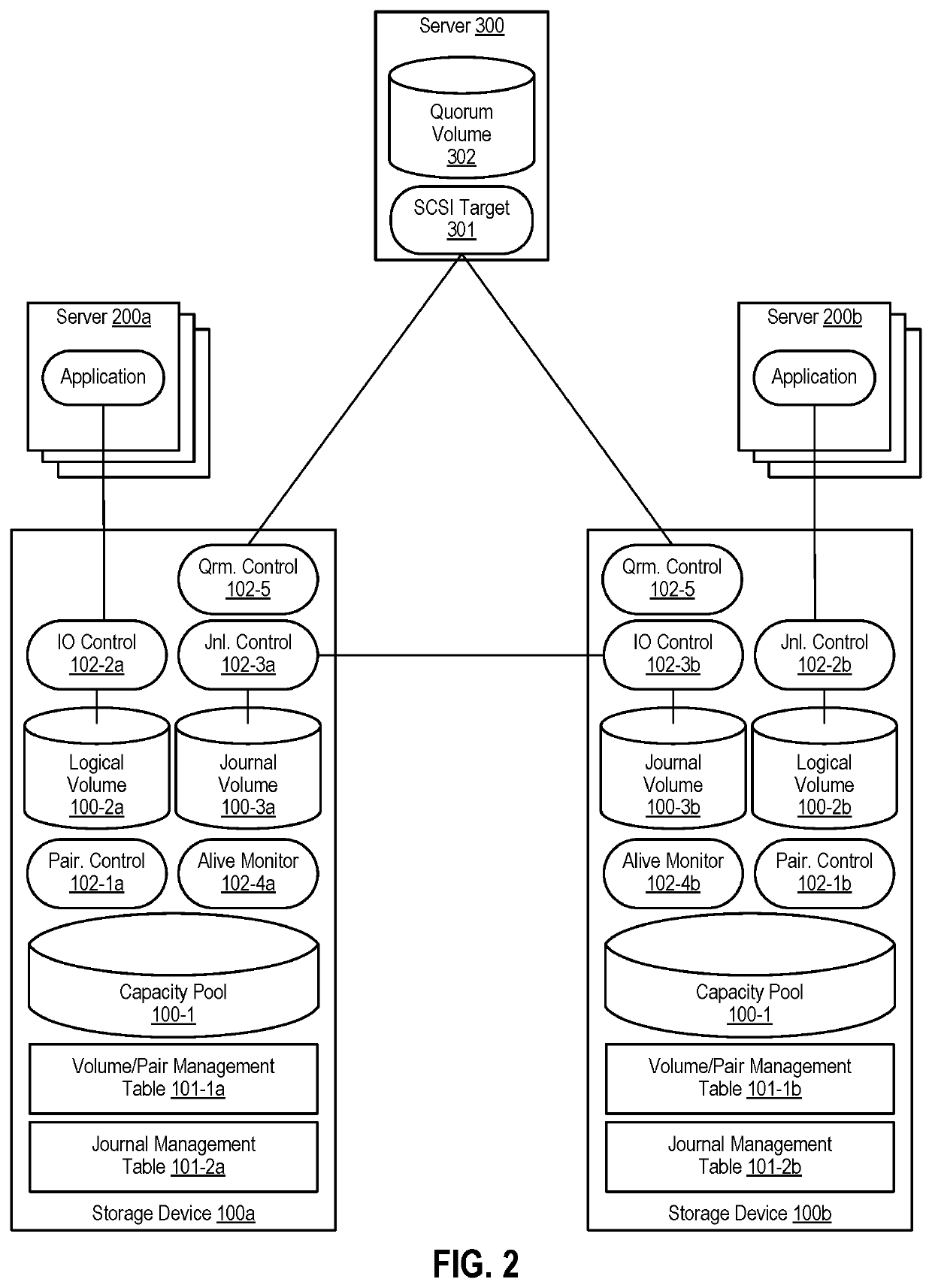
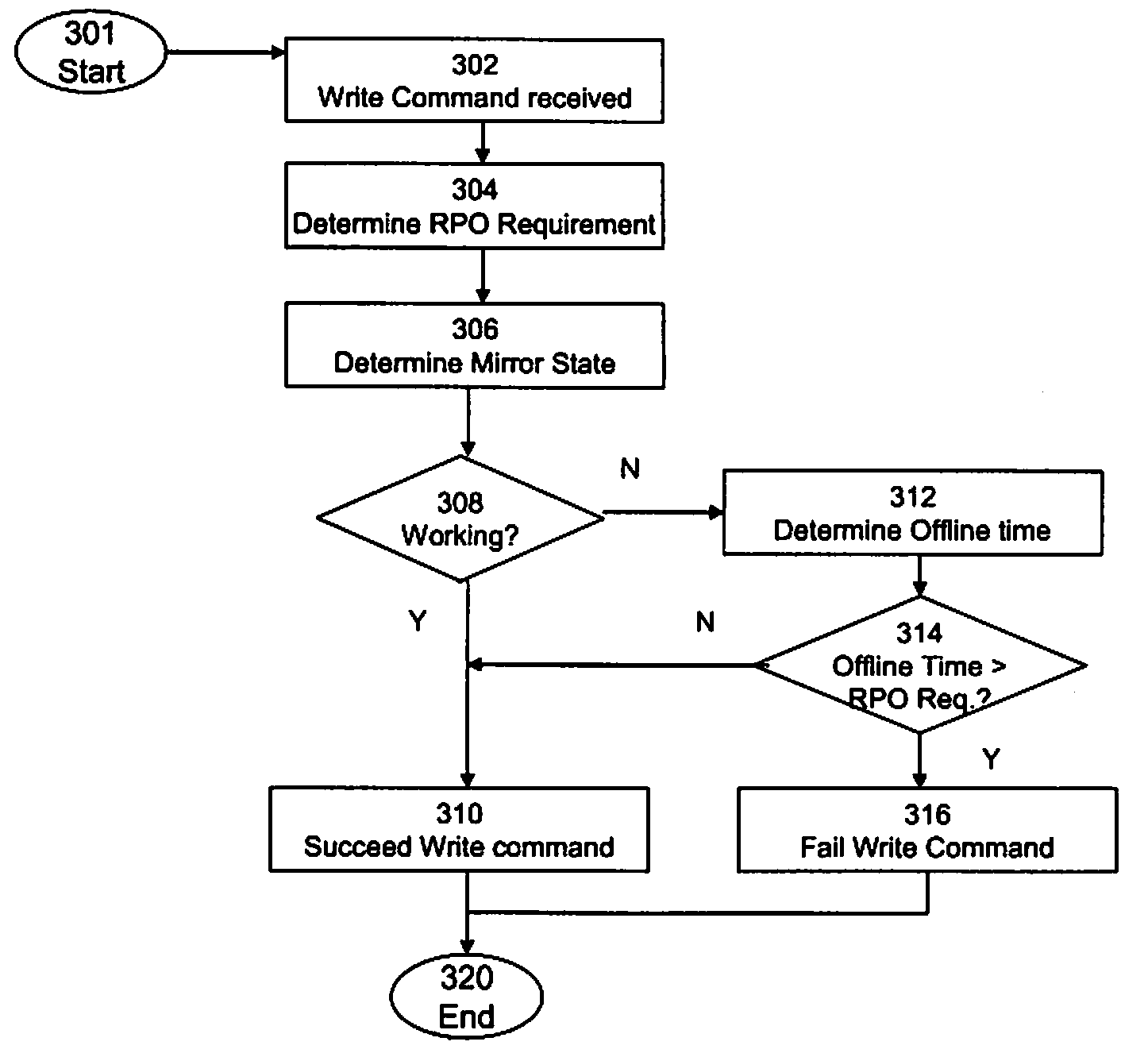
Mirrored Storage System and Methods for Operating a Mirrored Storage System
InactiveUS20080168246A1Detect degradationEfficient managementMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer scienceOperating system
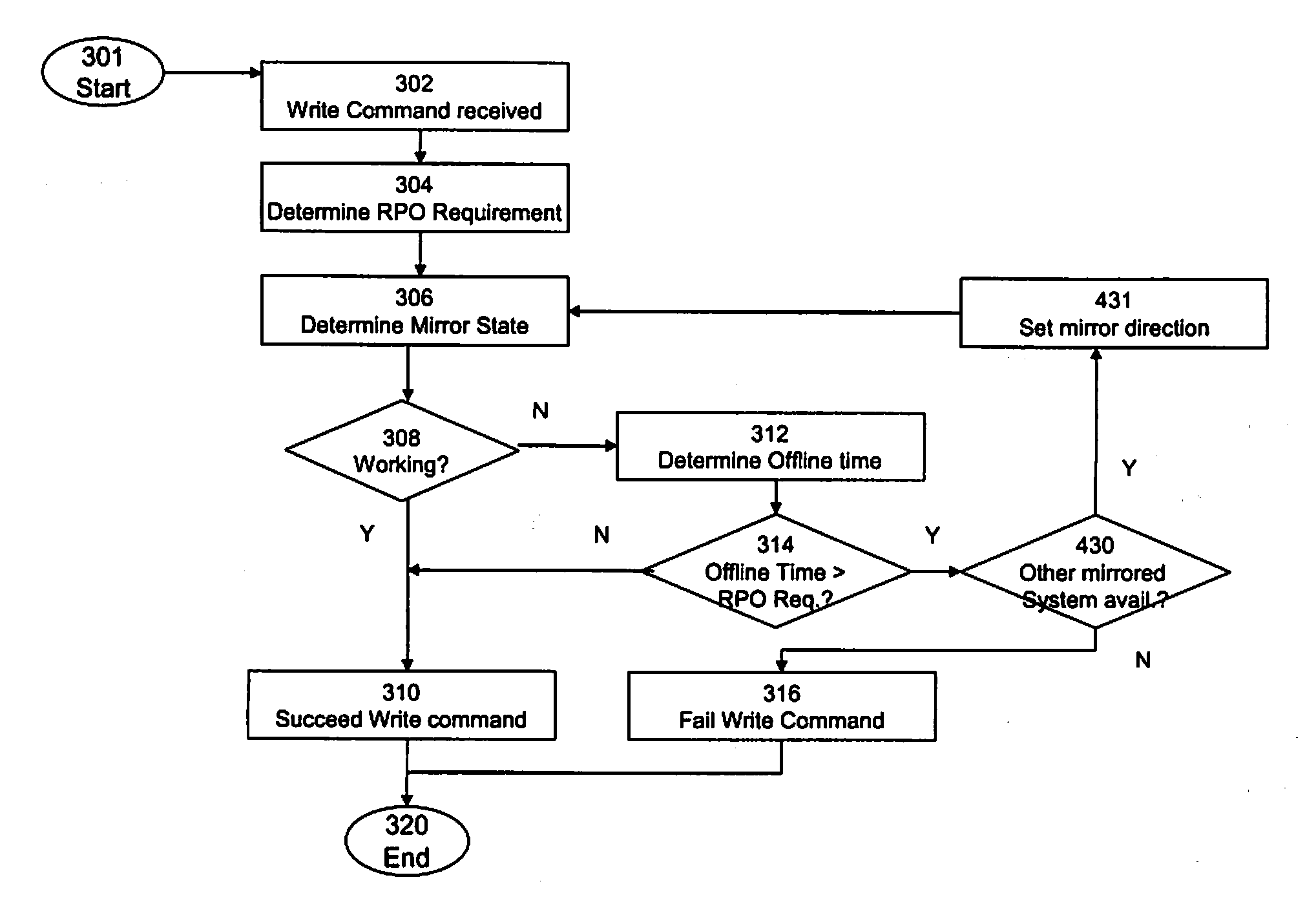
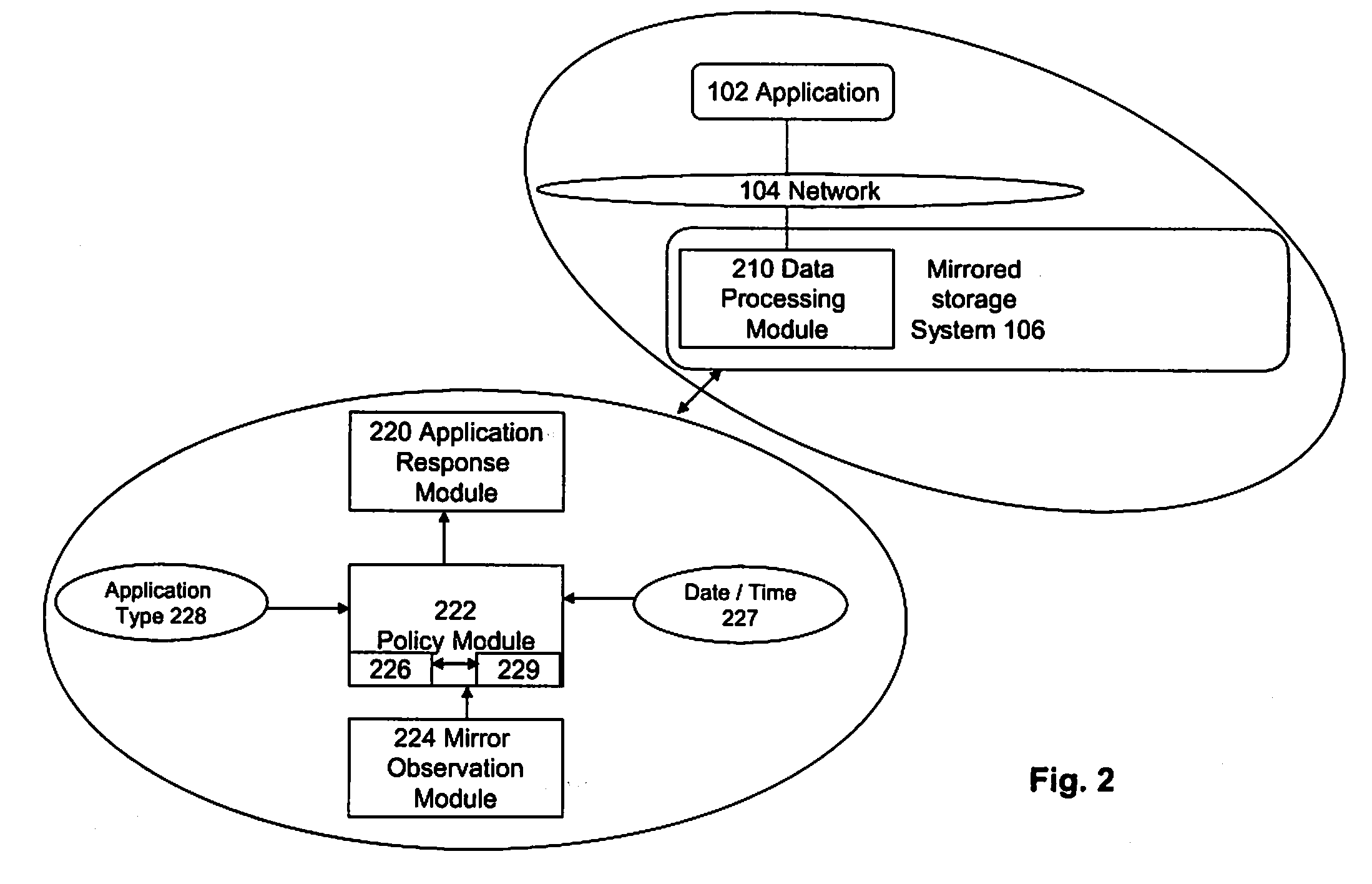
A mirrored storage system for applications is provided, which enables and supports the variation and dynamic adaptation of the Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) based on policies. Furthermore, methods are provided for running such a mirrored storage system. Said mirrored storage system comprises a first storage system and at least one further storage system, wherein said first and said further storage system are connected via at least one mirror link. An application accesses said mirrored storage system via a network. Therewith, the data to be stored as response to a write command of said application can be mirrored according to a configurable time-varying RPO requirement of the application transmitting the corresponding write command.
Owner:IBM CORP
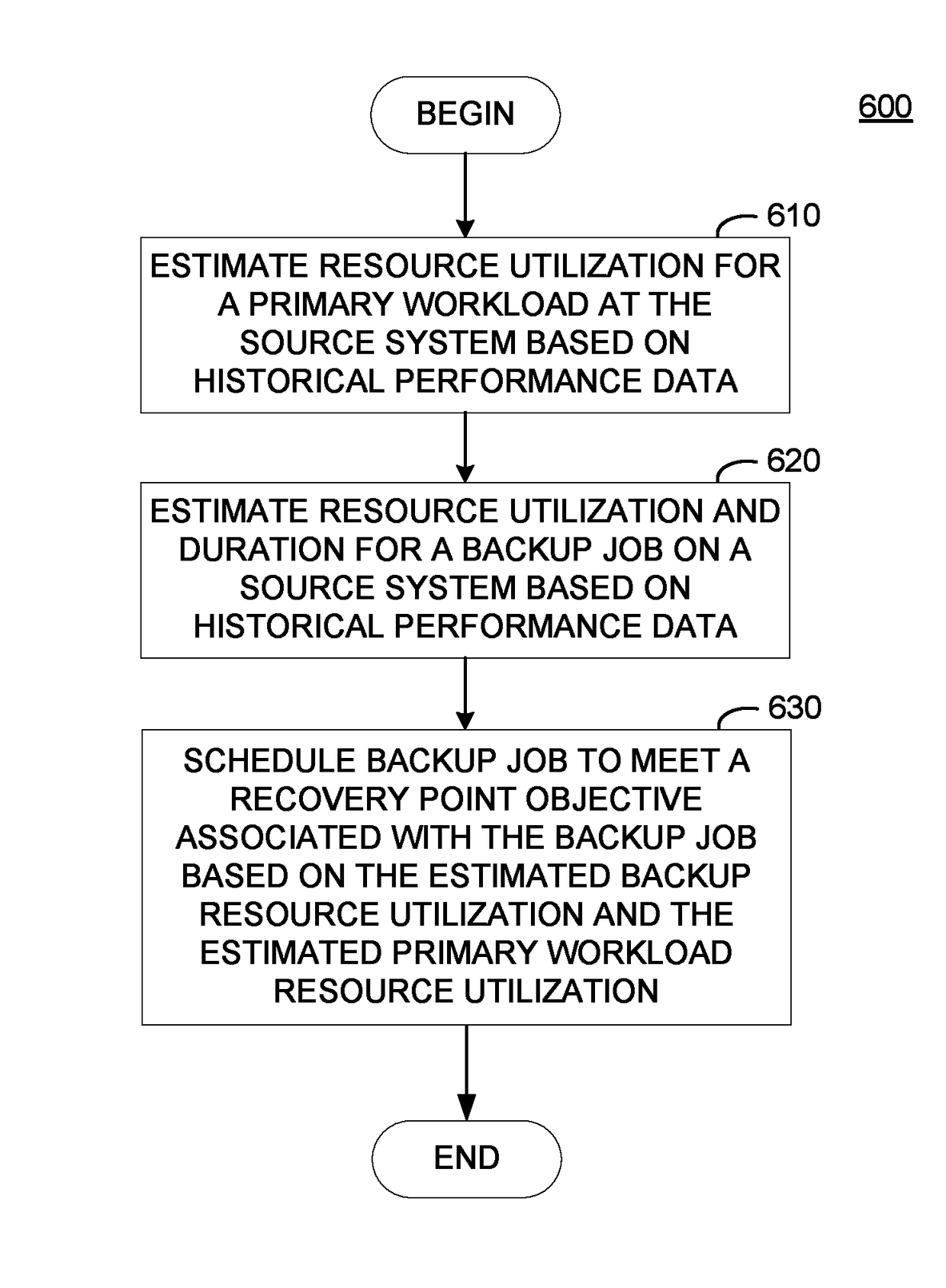
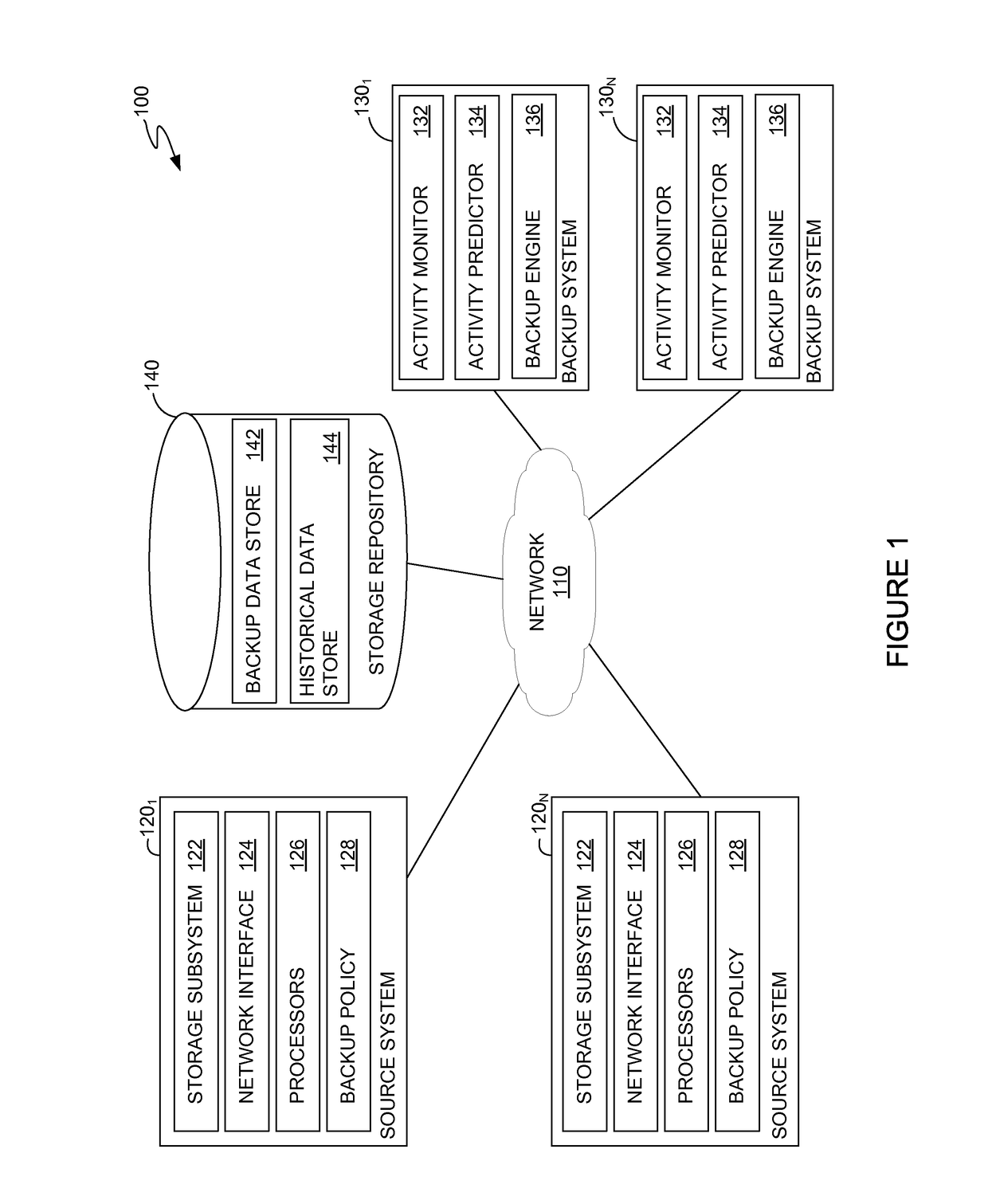
Objective based backup job scheduling
ActiveUS10083094B1Low resource utilizationRedundant operation error correctionResource utilizationSource system
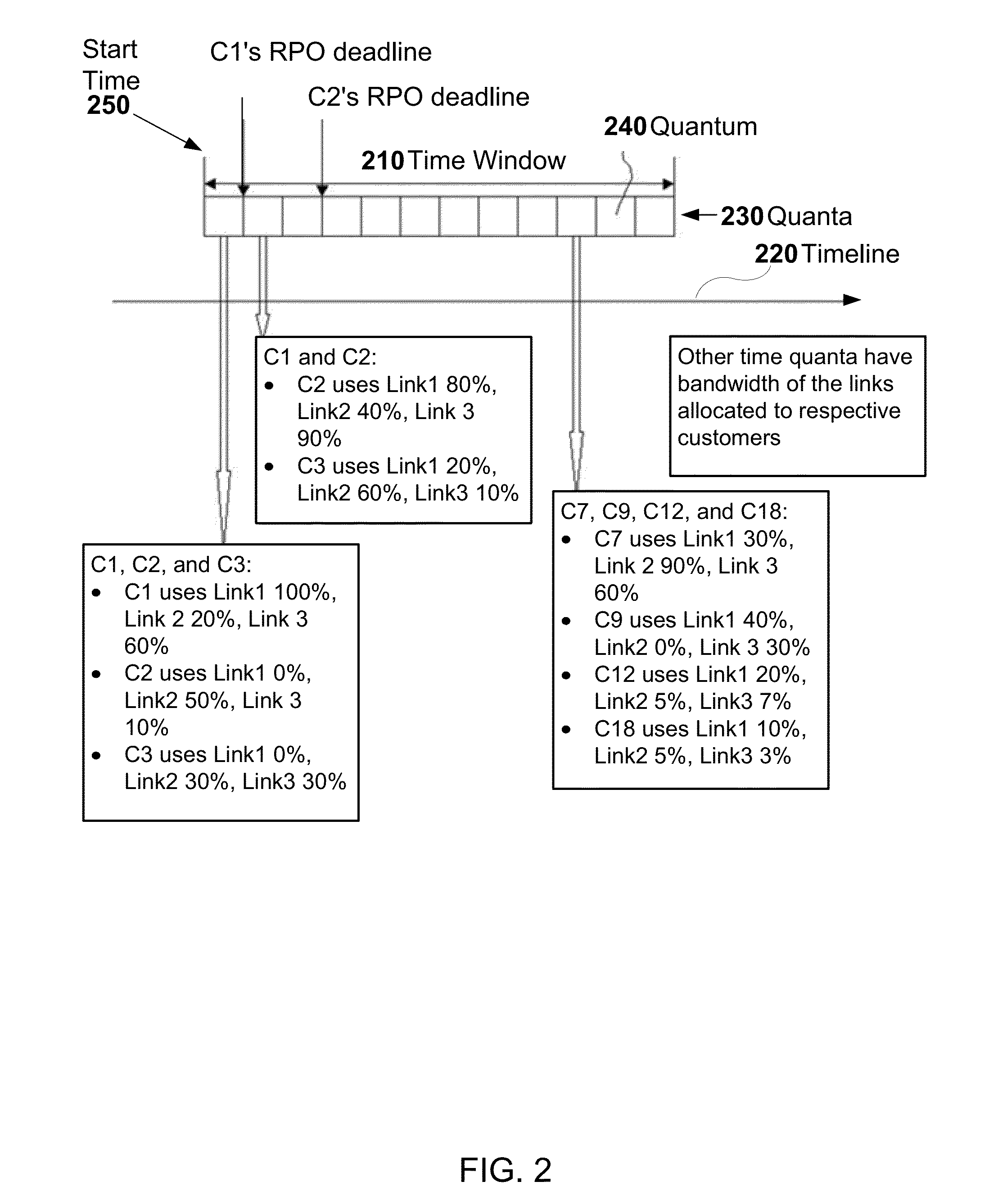
A method and apparatus for scheduling backup tasks on a source system specified by a backup job to meet a recovery point objective (RPO) specified for the backup job is presented. A method generally includes estimating resource utilization at the source system expected during a plurality of time periods based on historical resource utilization by jobs executed on the source system. The backup system estimates a time required to complete the backup tasks during each time period on the source system based on the estimated resource utilization for each time period and historical backup performance data. Upon determining that the estimated time required to complete the backup tasks for one or more of the time periods meets the RPO, the backup system schedules the backup tasks to be executed during a time period of the one or more time periods with the lowest estimated resource utilization.
Owner:COHESITY
Using bandwidth and capacity parameters to control remote copy operations in storage systems
A system is provided for storage of journal data from a primary site to a secondary site with a predefined quality of service. In one implementation, the primary storage system stores information for updating data stored on the primary disk array in the form of a history of updates made to the data. The primary storage system is configured to transfer this journal information to the secondary storage system. The user can specify the quality of service desired using a variety of measures, for example, a recovery point objective or a recovery time objective. In response, a copy manager within one of the storage systems determines the capacity of the various primary and secondary volumes, and determines the copy rate available, typically dependent upon the bandwidth between the primary and secondary systems. The copy manager then copies journal data to the remote site where it is stored.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
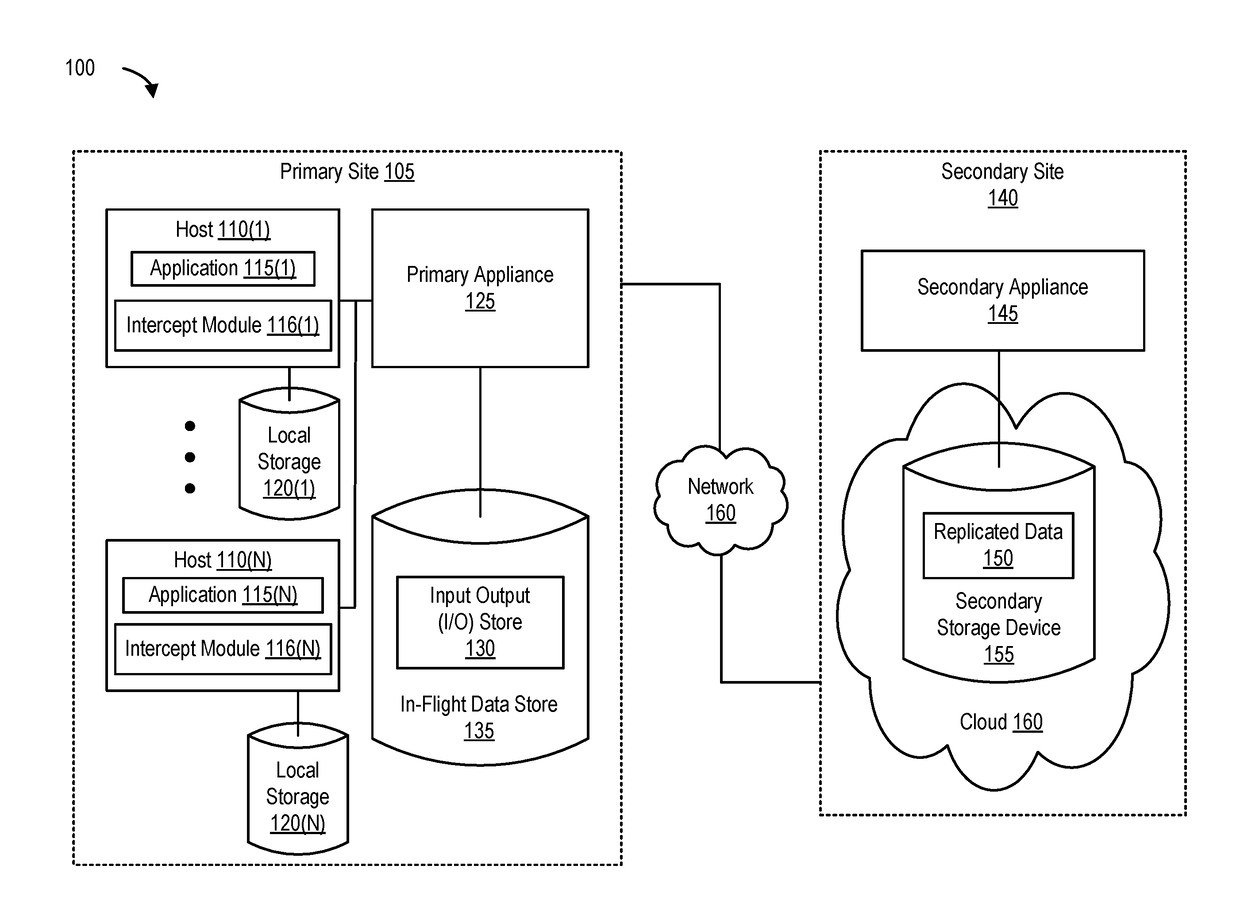
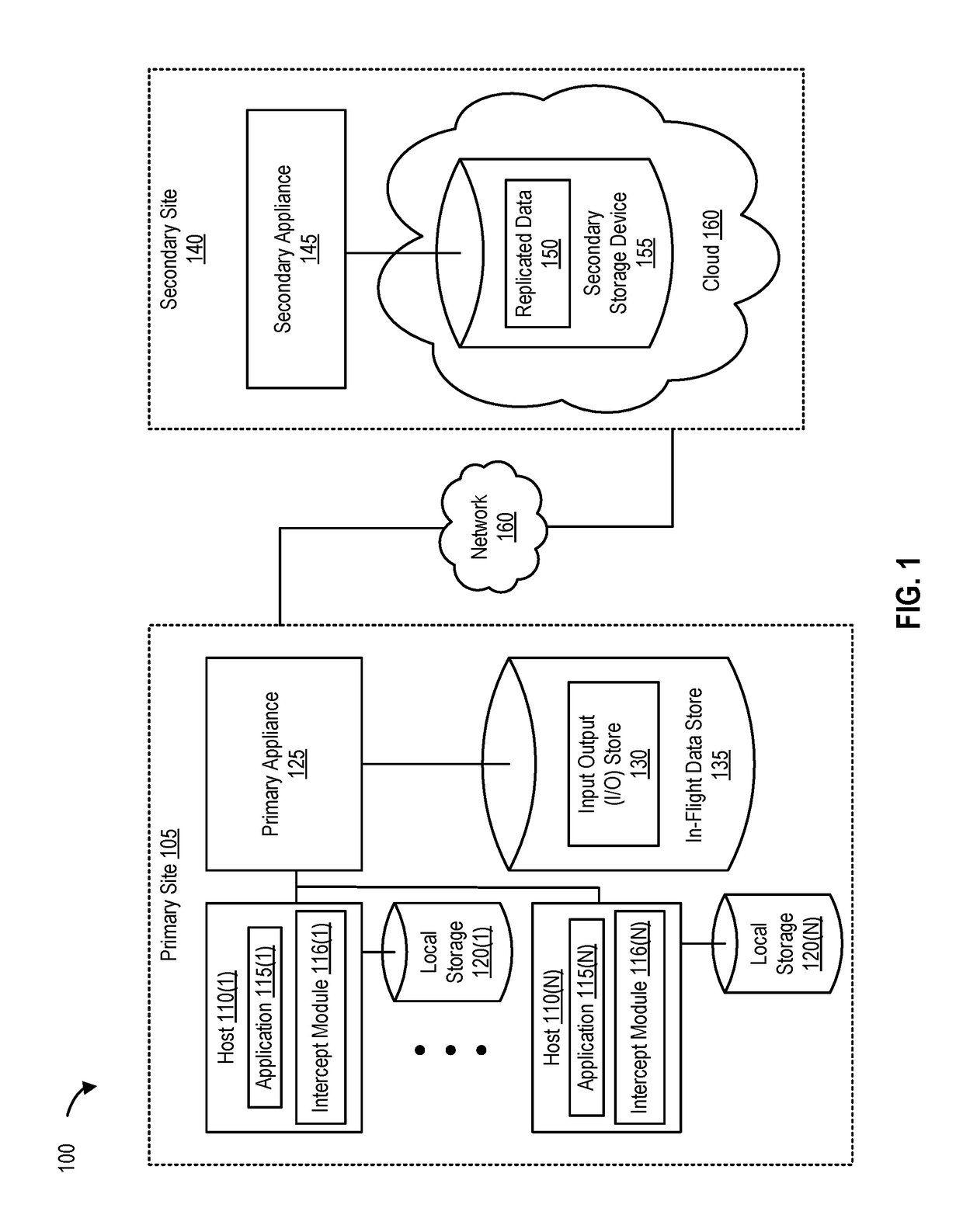
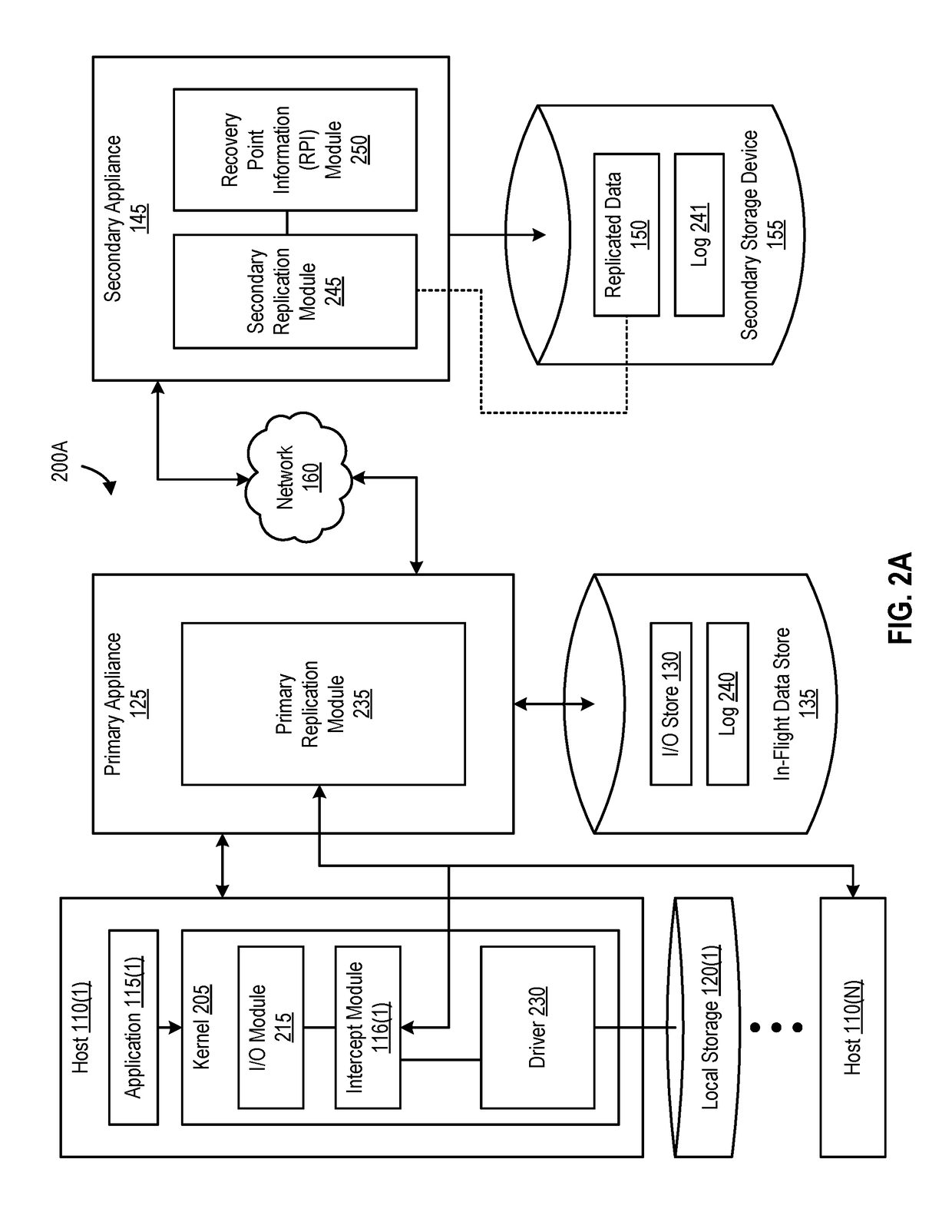
Recovery point objectives in replication envrionments
ActiveUS20170220424A1Increase network bandwidthHigh bandwidthDigital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationData setTimestamp
Disclosed herein are methods, systems, and processes to adjust replication operations in a distributed environment. A set of replicated data is received from a first appliance as a result of a replication operation. The replication operation is initiated by the first appliance and the set of replicated data includes a first timestamp. A write operation is performed to store the set of replicated data and a second timestamp is recorded. Recovery point information is generated based on the first timestamp and the second timestamp. The recovery point information is configured to be utilized in adjusting replication parameters of a subsequent replication operation.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Consistent replication of virtual computing instance data
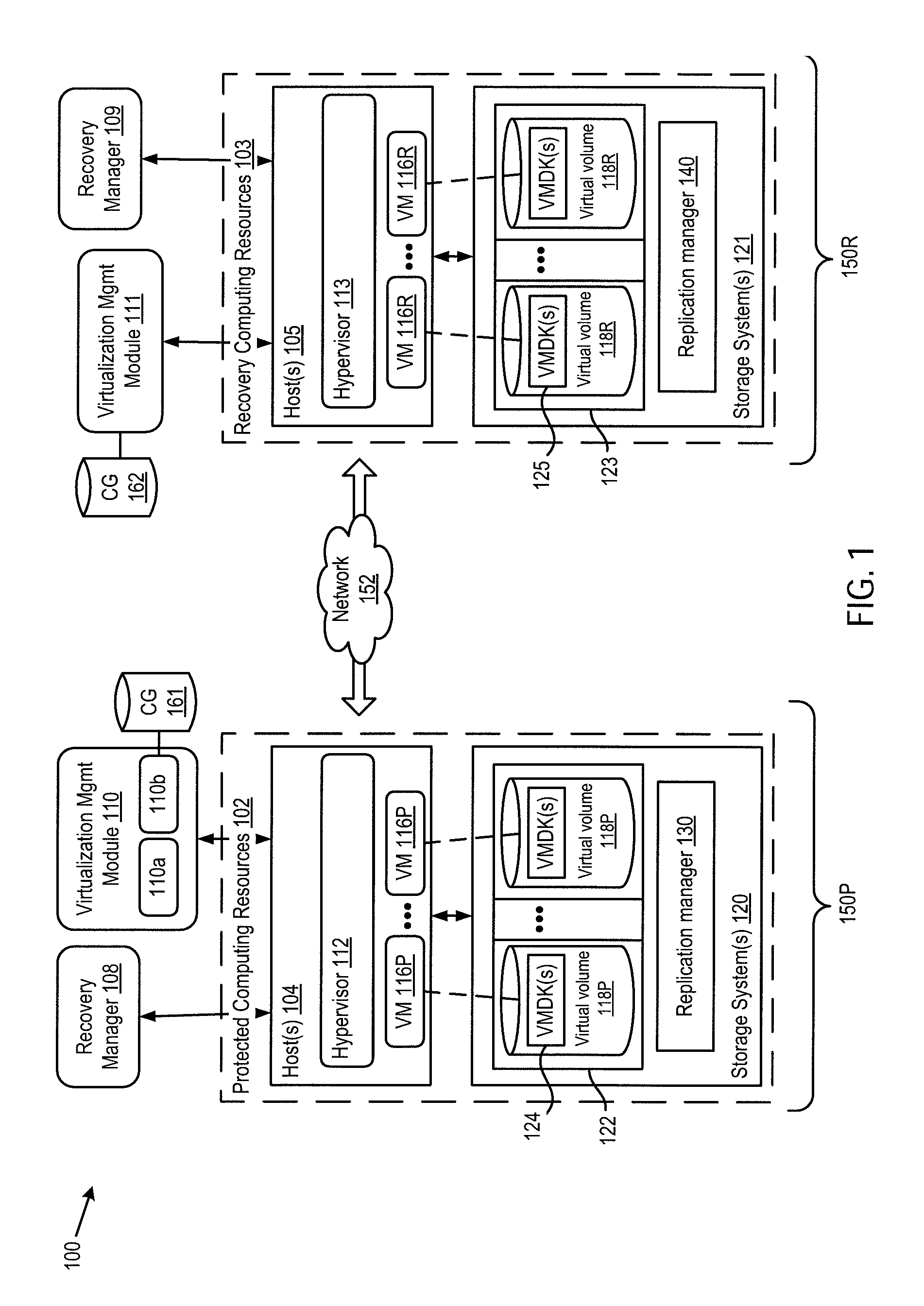
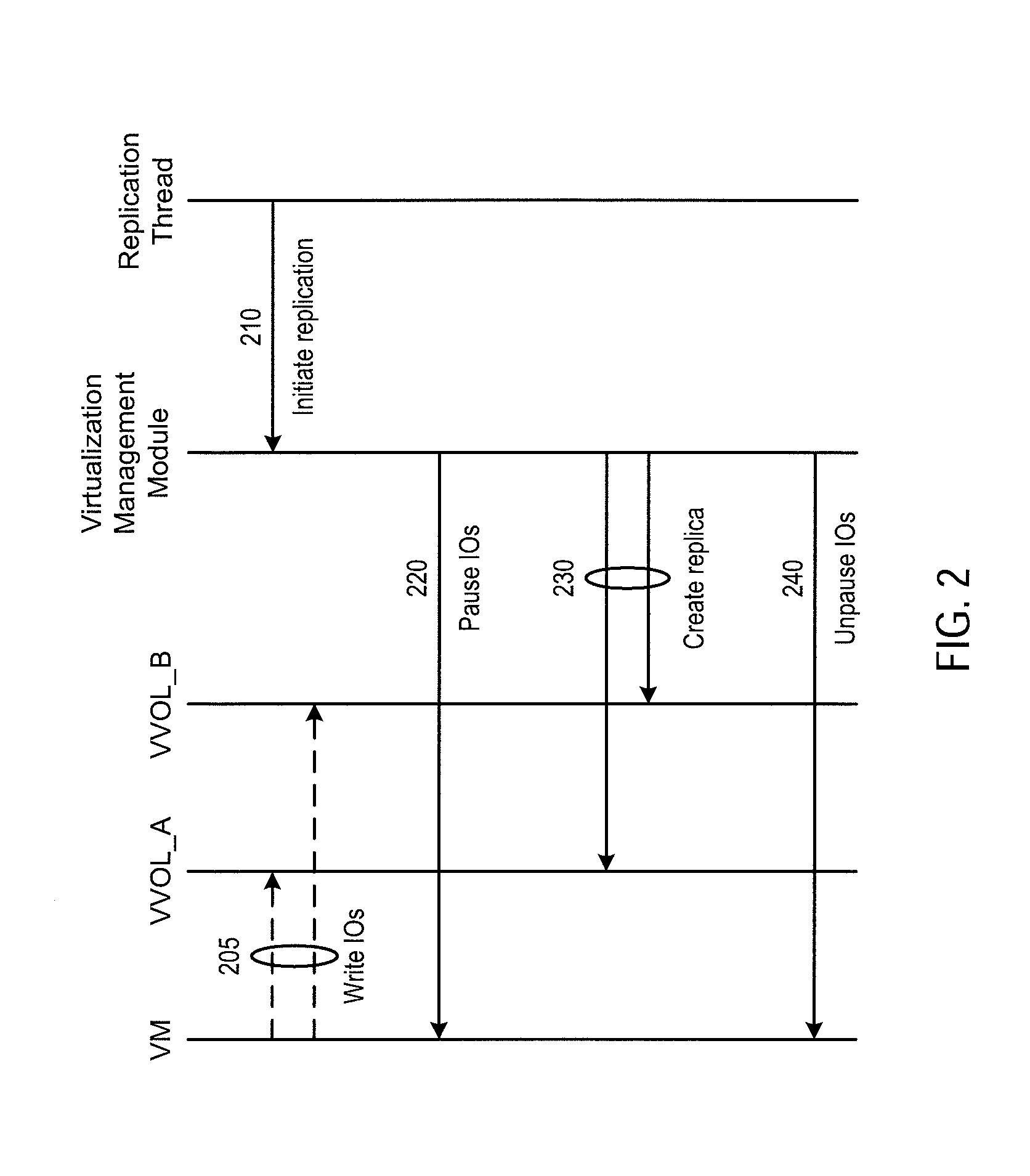
ActiveUS20160179437A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsVirtual computingOperating system
Virtual computing instance data that are stored across multiple storage volumes are replicated in a manner such that the write order is maintained. The frequency of the replication is set so that the recovery point objective defined for the VM data can be satisfied. The replication includes the steps of determining a set of logical storage volumes across which the virtual computing instance issues dependent write IOs, issuing a first command to the virtual computing instance to block new IOs and to block receipt of IO acknowledgements, issuing a command to create replicas of all the logical storage volumes in the set, and then issuing a second command to the virtual computing instance to unblock new IOs and unblock receipt of IO acknowledgements.
Owner:VMWARE INC
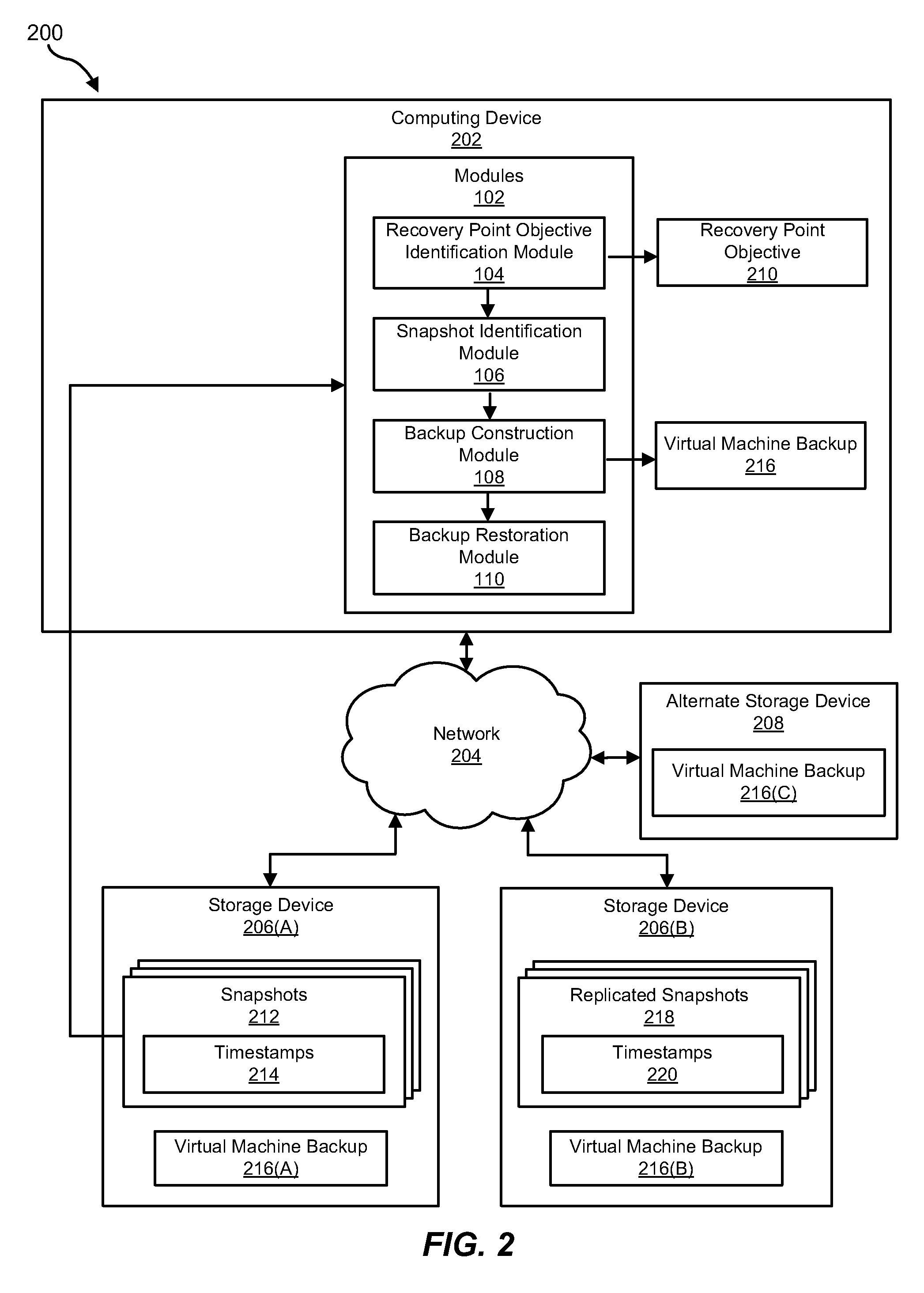
Systems and methods for managing virtual machine backups
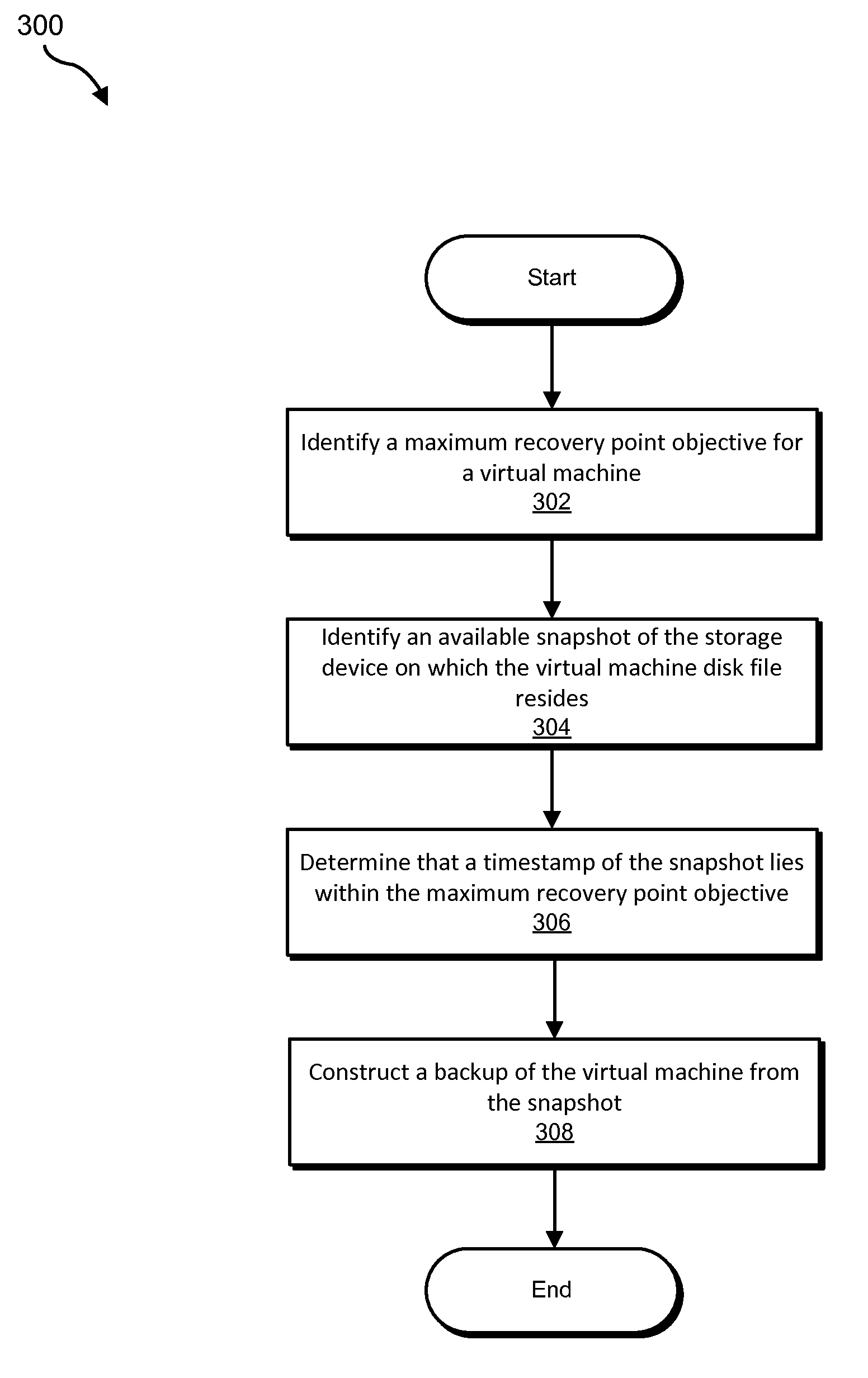
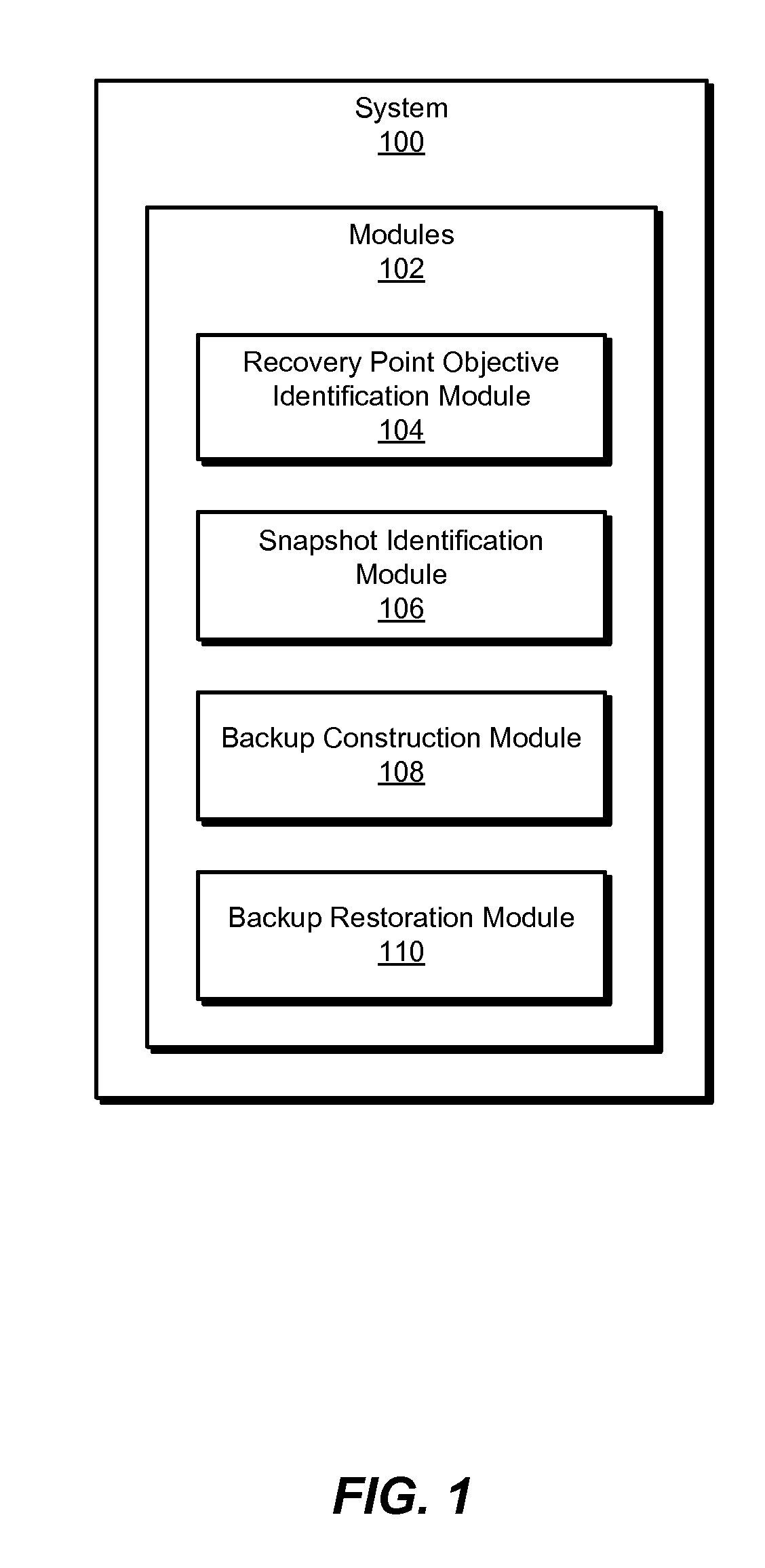
ActiveUS9524215B1Redundant operation error correctionMemory systemsTimestampRecovery point objective
A computer-implemented method for managing virtual machine backups may include (1) identifying a maximum recovery point objective for a virtual machine with a virtual machine disk file on a storage device with snapshot capabilities, (2) identifying an available snapshot of the storage device that contains the virtual machine disk file, (3) determining that the snapshot's timestamp is within the maximum recovery point objective, and (4) constructing a backup of the virtual machine using the snapshot, instead of creating the backup from the virtual machine disk file. Various other methods, systems, and computer-readable media are also disclosed.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
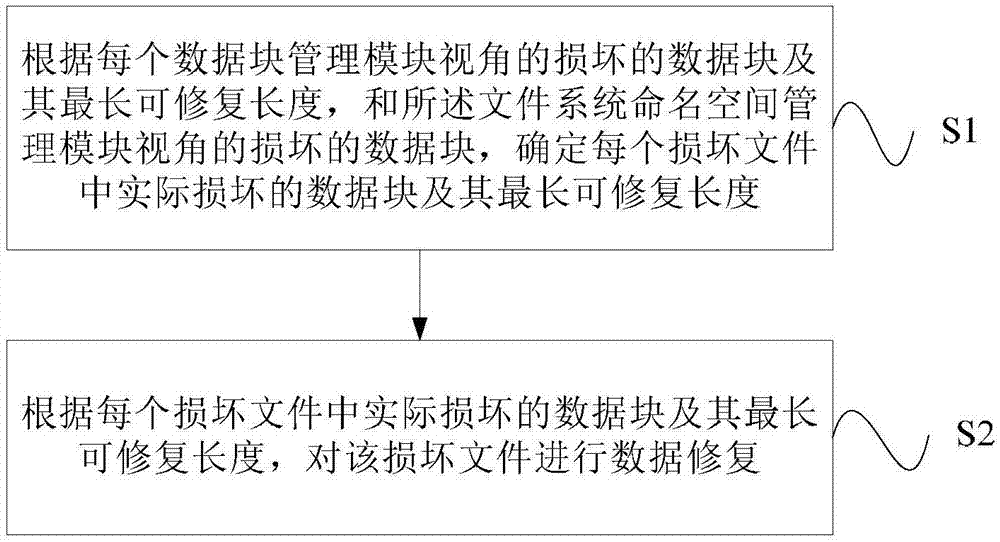
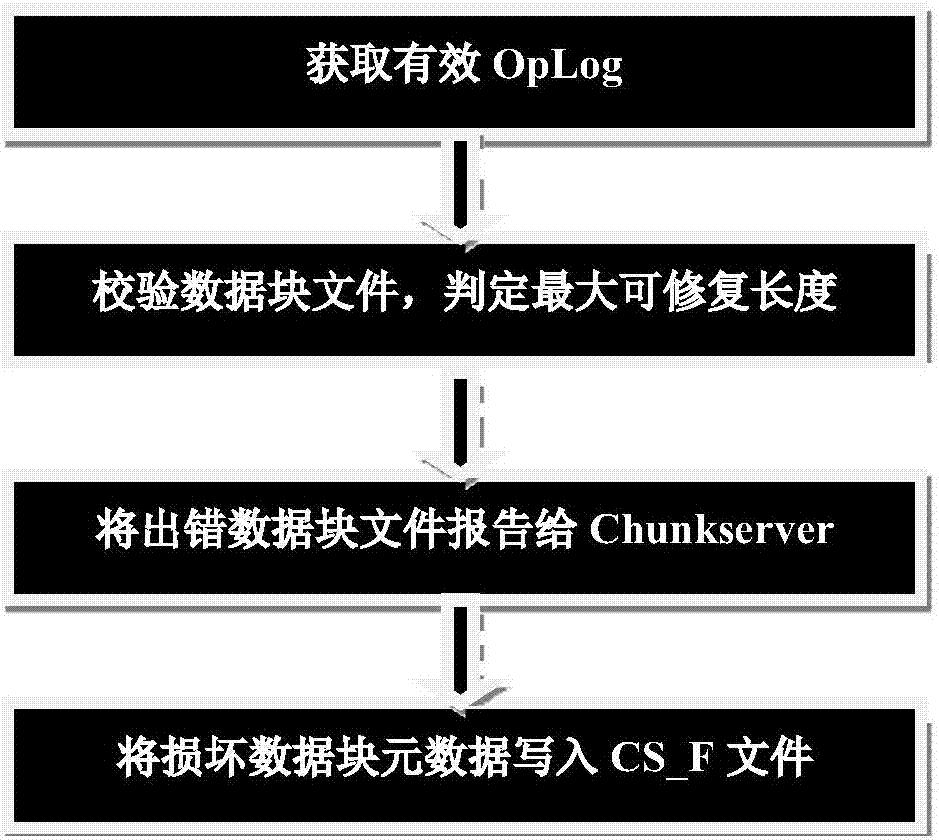
Large-scale distributed file system data recovery method and equipment
ActiveCN107402841AReduce repair timeFast and Efficient Data RepairRedundant operation error correctionSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityFile system
The invention aims to provide a large-scale distributed file system data recovery method and equipment. Actually corrupted data blocks and the largest recoverable length thereof can be determined accurately according to data blocks of the viewing angle of each data block management module and the largest recoverable length thereof and corrupted data blocks of the viewing angle of a file system namespace management module, further the actually corrupted data blocks and the largest recoverable length thereof in each corrupted file are determined accurately, and quick and effective data recovery of the corrupted files is realized according to the actually corrupted data blocks and the largest recoverable length thereof in each corrupted file during the process of data recovery for distributed file system cluster power failure reboot caused by power supply failure, RPO (recovery point objective) can be increased effectively while RTO (recovery time objective) can be shortened effectively, data recovery capability is improved, and time for data recovery is reduced.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
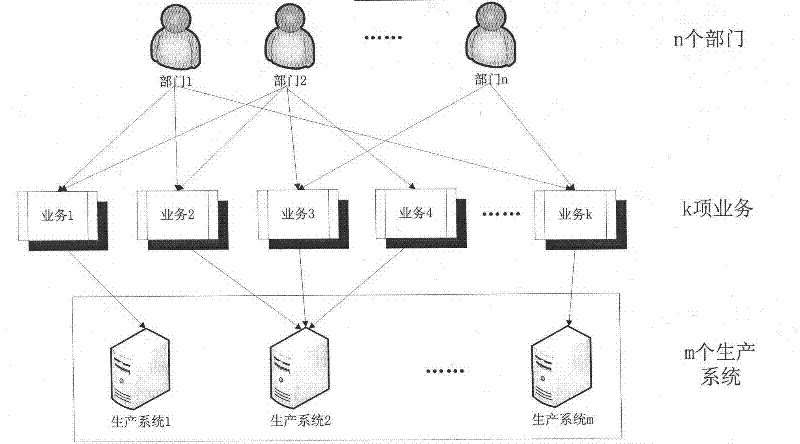
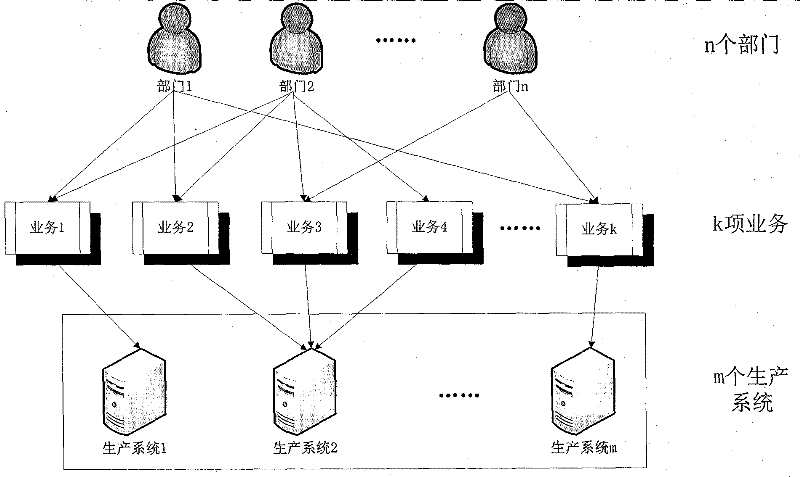
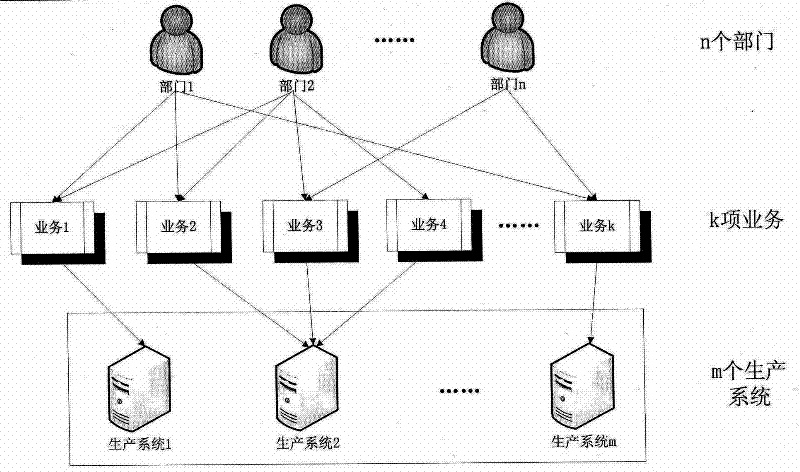
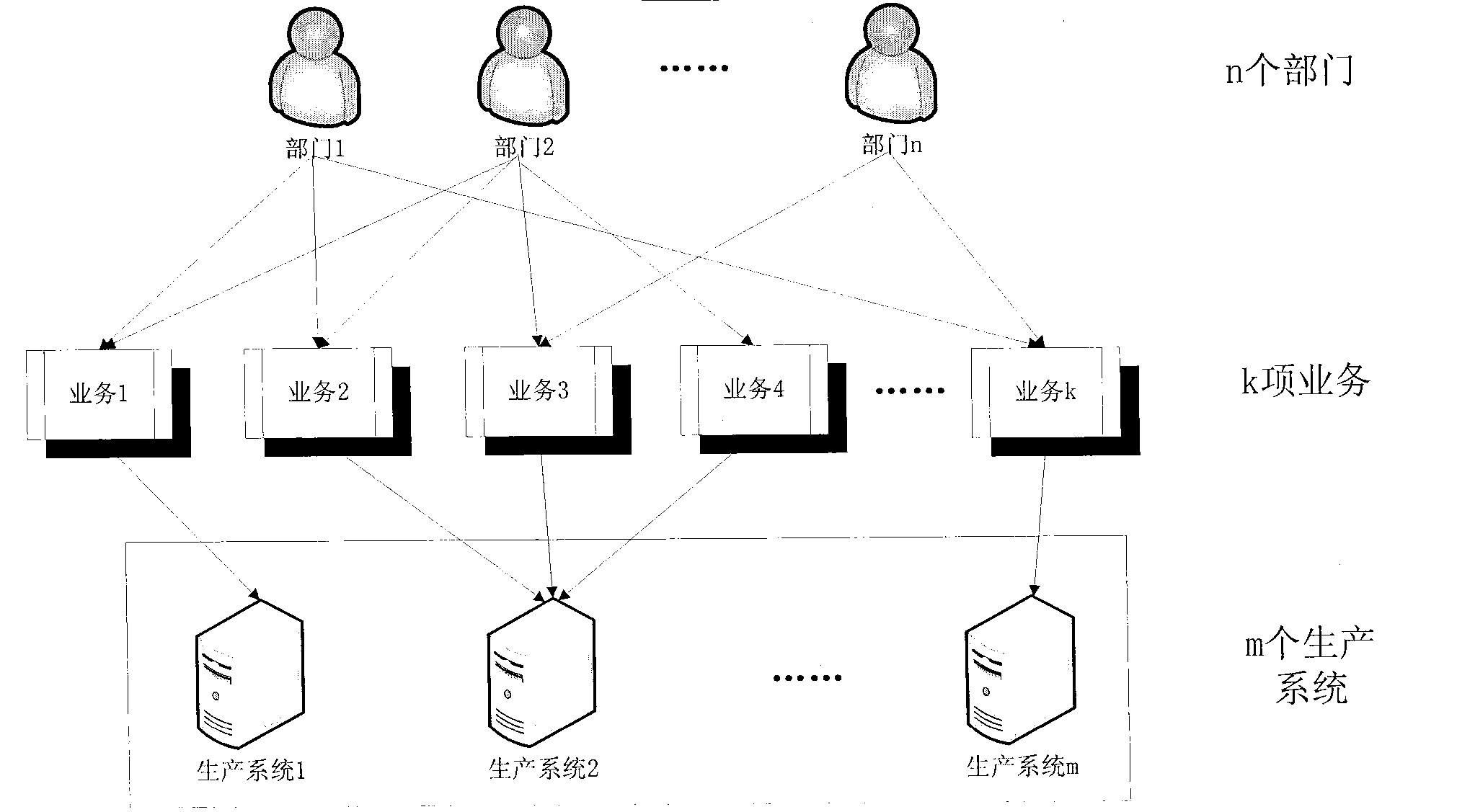
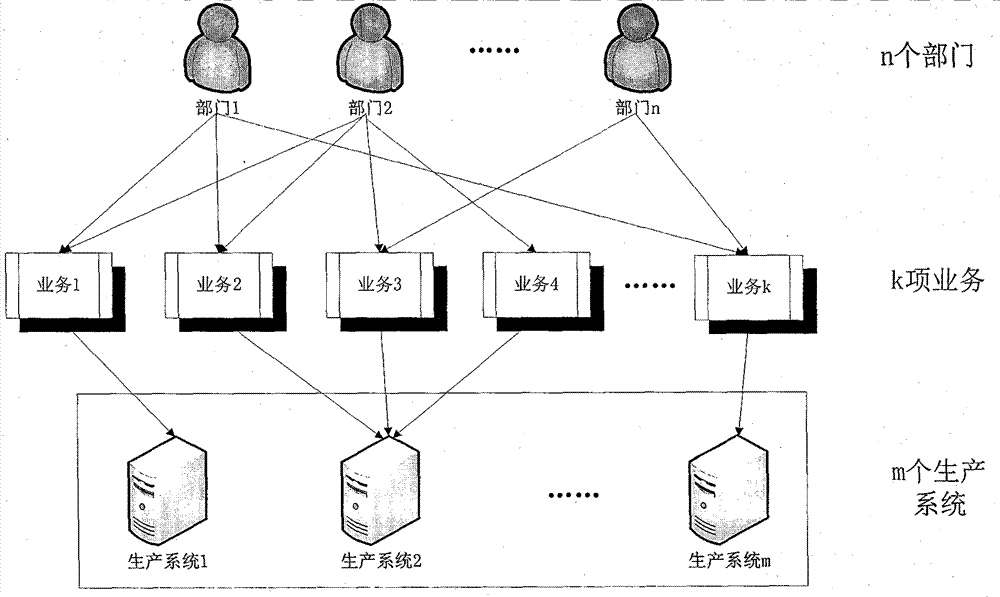
Method for calculating disaster recovery point objective of information system
The invention provides a method for calculating a disaster recovery point objective of an information system. The key of the method is an information system consisting of m production systems, wherein k items of services K1, K2,..., Kk run on the information system, and each item of service only can run on one production system. Through analyzing the importance of each production system, the importance of each service, the existing data volume and the data volume (per second) generated by each department in the information system, and based on the generated data volume (per second) relevant to each service, according to the percentage of the existing data volume in a service used by a department to the total data volume of the department, new generated data (per second) of each service and new generated data (per second) of the production system relevant to each service are estimated; and then, through synthesizing the importance of each production system in the information system, the generated data volume of a production system is divided by the newly increased weighted data volume of the production system so as to obtain a value of the disaster RPO (recovery point objective) ofthe whole information system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-RPO data protection
ActiveUS9442748B2Great flexibility and cost-effectivenessOvercomes drawbackSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationRedundant operation error correctionComputer scienceData recovery
Owner:ZERTO
System and method to proactively maintain a consistent recovery point objective (RPO) across data centers
ActiveUS9489268B2Reduce the RPO violations/deviations significantlyEfficient comprehensive utilizationDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringData centerComputer science
A system and method for proactively monitoring and maintaining a consistent recovery point objective (RPO) across data centers, the system comprising: one or more RPO Management Server(s) logically connected to one or more Production Sites and one or more Disaster Recovery Sites; a Network connecting the said RPO Management Server(s) with the said Production Site and the said Disaster Recovery Site wherein the said RPO Management Server is provided with at least one RPO Manager, at least one Disaster Recovery Management (DRM) System and at least one Replication Management System.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Automated failover for asynchronous remote copy
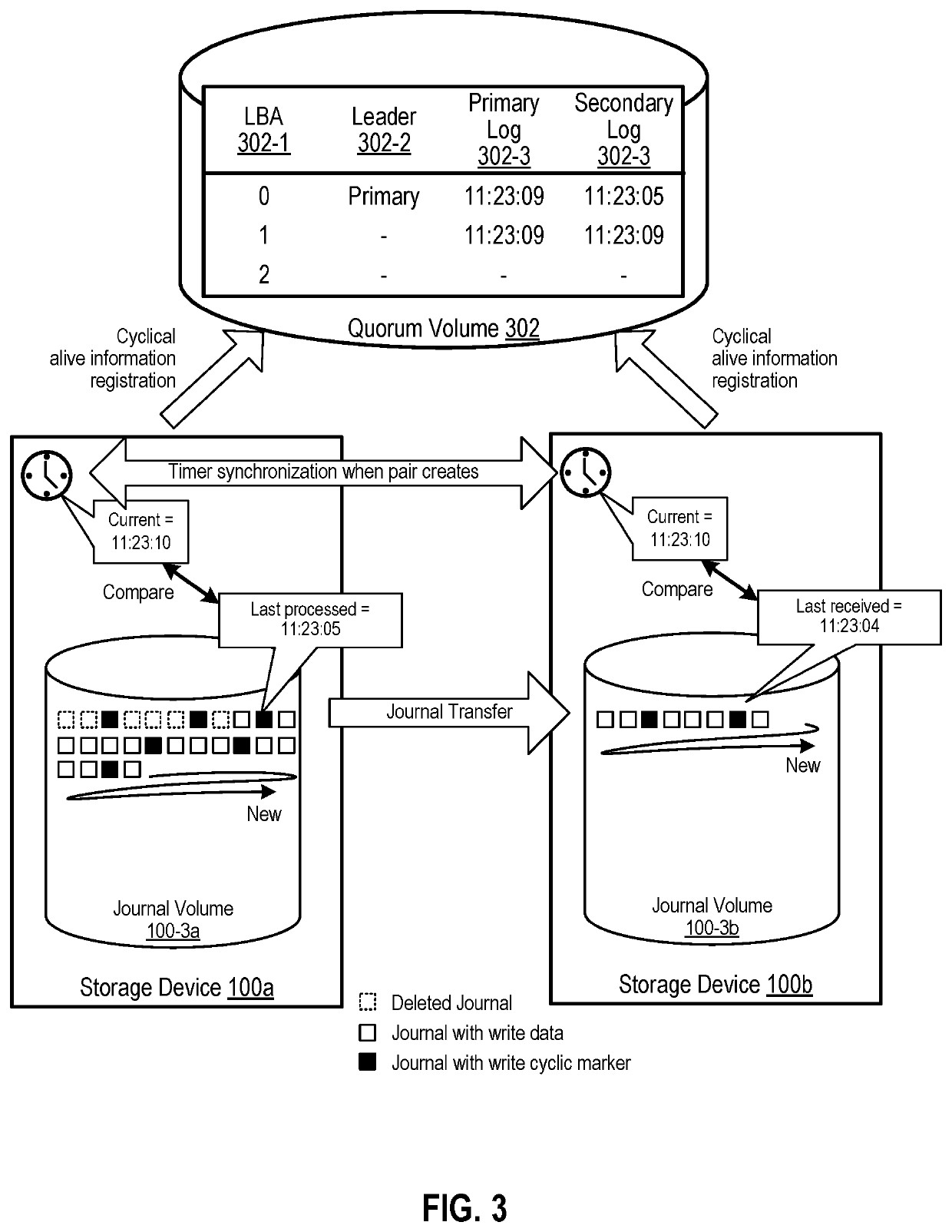
ActiveUS20210382799A1Communication delay is longRedundant operation error correctionFile system functionsFailoverEmbedded system
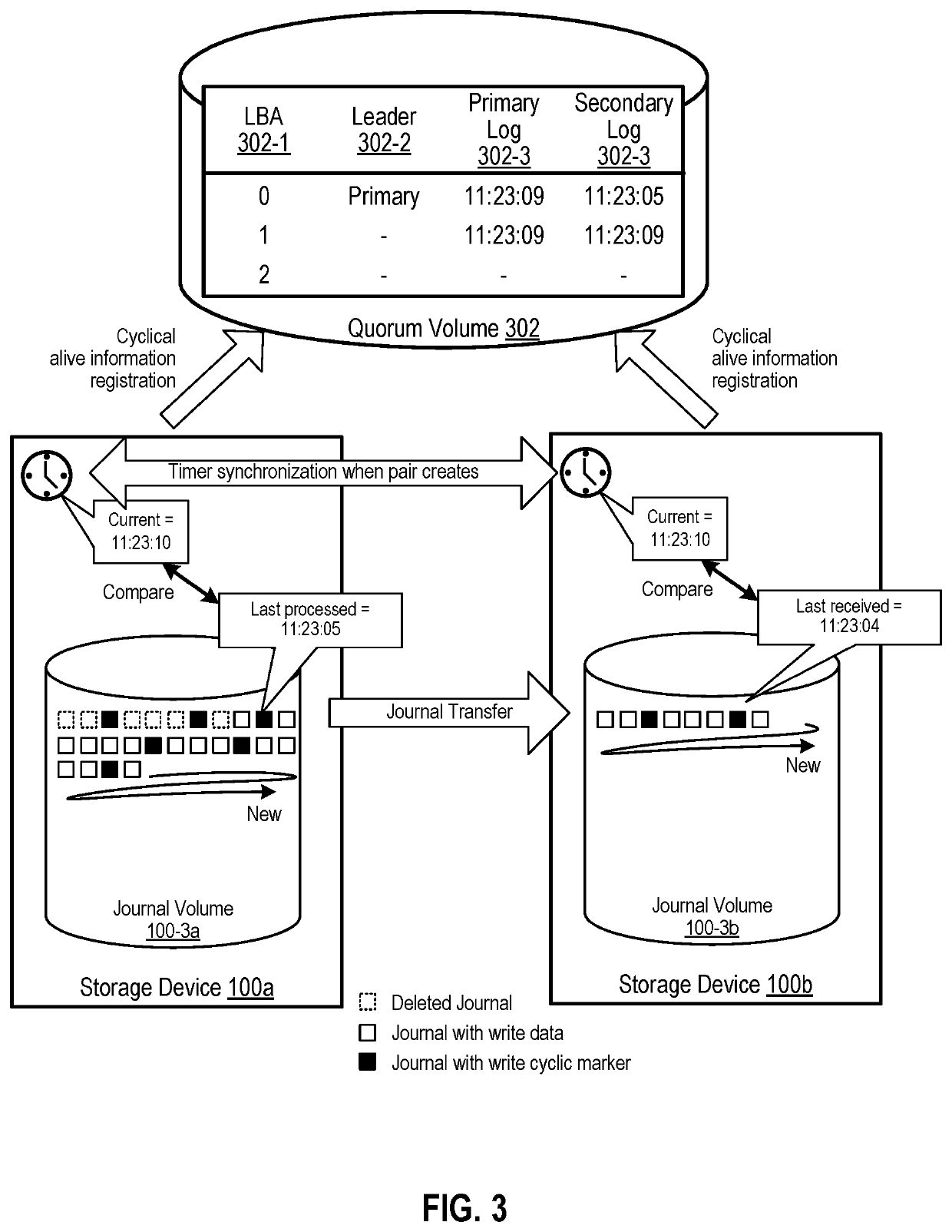
Example implementations described herein are directed to automated failover and assuring RTO (Recovery Time Objective) assurance, and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) on asynchronous remote copy feature of storage. By using markers that are cyclically stored to the journal volume, the storage device can thereby determine an accurate communication loss period.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Mirrored storage system and methods for operating a mirrored storage system
InactiveUS8055866B2Efficient managementDetect degradationMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsOperating systemRecovery point objective
A mirrored storage system for applications is provided, which enables and supports the variation and dynamic adaptation of the Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) based on policies. Furthermore, methods are provided for running such a mirrored storage system. Said mirrored storage system comprises a first storage system and at least one further storage system, wherein said first and said further storage system are connected via at least one mirror link. An application accesses said mirrored storage system via a network. Therewith, the data to be stored as response to a write command of said application can be mirrored according to a configurable time-varying RPO requirement of the application transmitting the corresponding write command.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
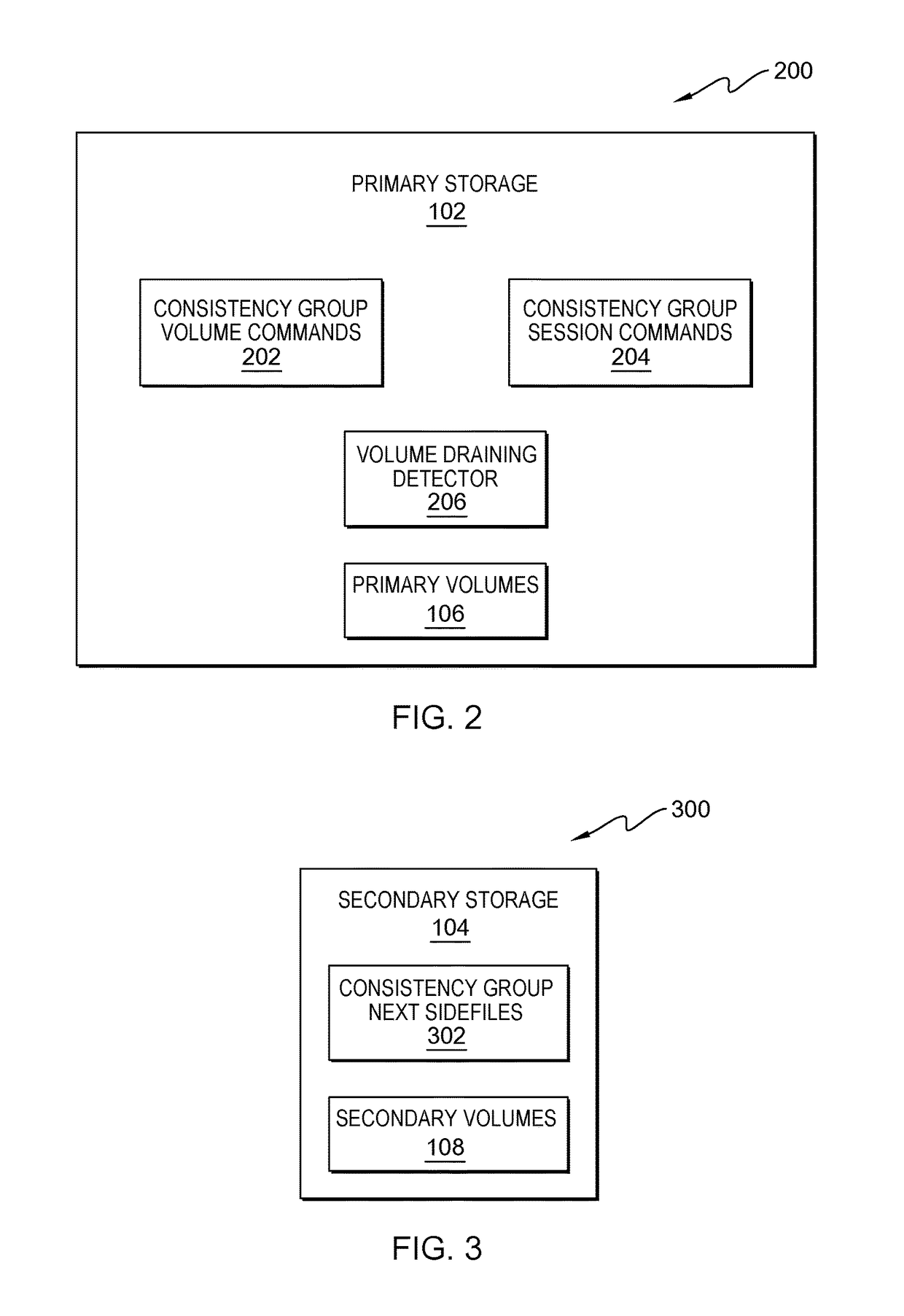
Recovery point objective via dynamic usage of bind segments in a global mirror environment
InactiveUS20170161190A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersData storingMirror image
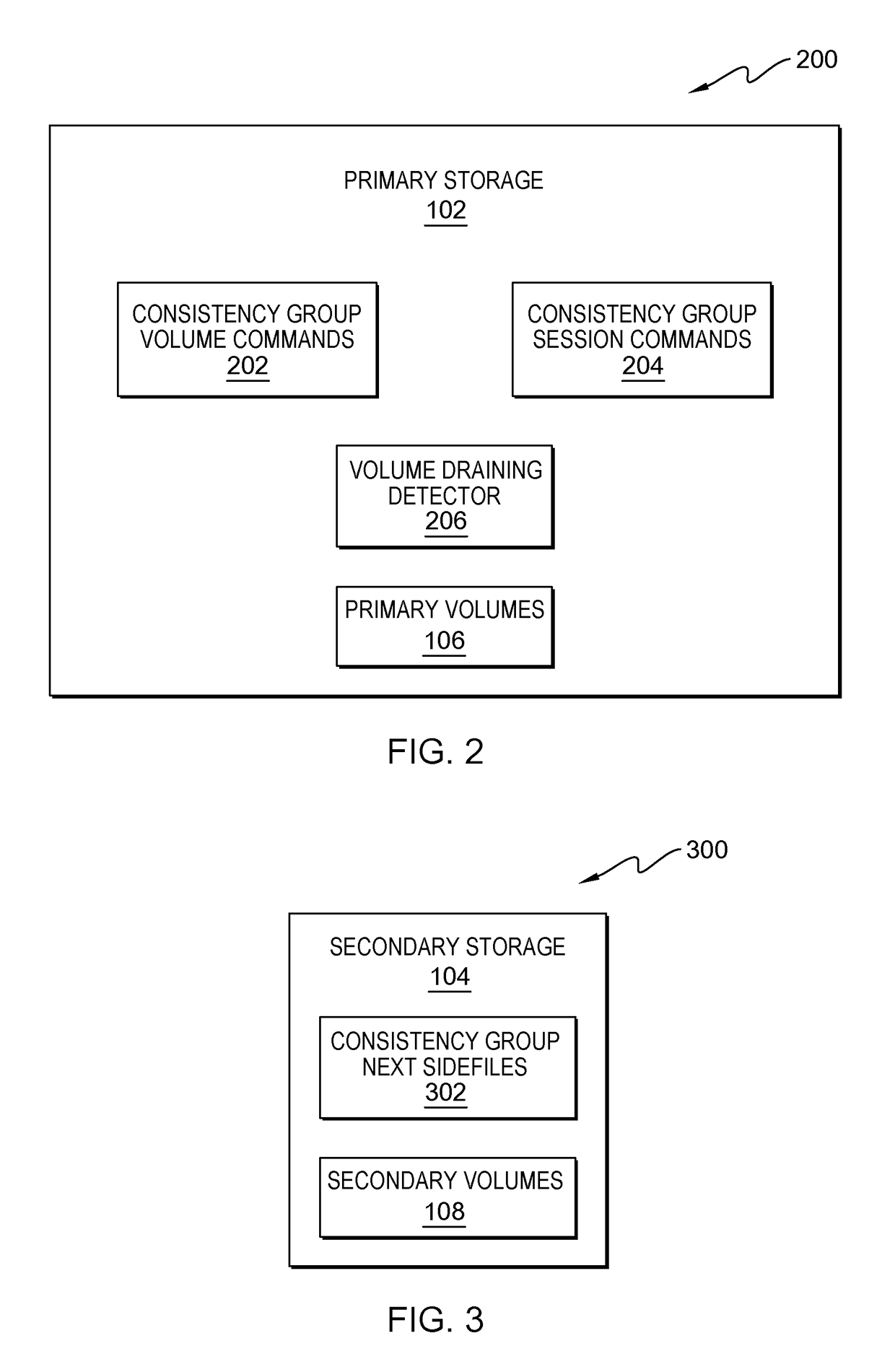
Embodiments for an approach to resource optimization during consistency group formation associated with a global mirror environment is provided. The approach detects when a primary volume associated with the consistency group has completed transmitting its out-of-sync (OOS) data towards its associated secondary volume. A command is sent to create a next consistency group sidefile so further writes can be sent to the sidefile rather than queueing at the primary volume. The approach repeats this process for each primary volume associated with the global mirror environment until all primary volumes are complete. Commands are sent to disable writes to the associated sidefiles and to merge the data stored in the sidefiles into normal cache as the next consistency group becomes the current consistency group.
Owner:IBM CORP
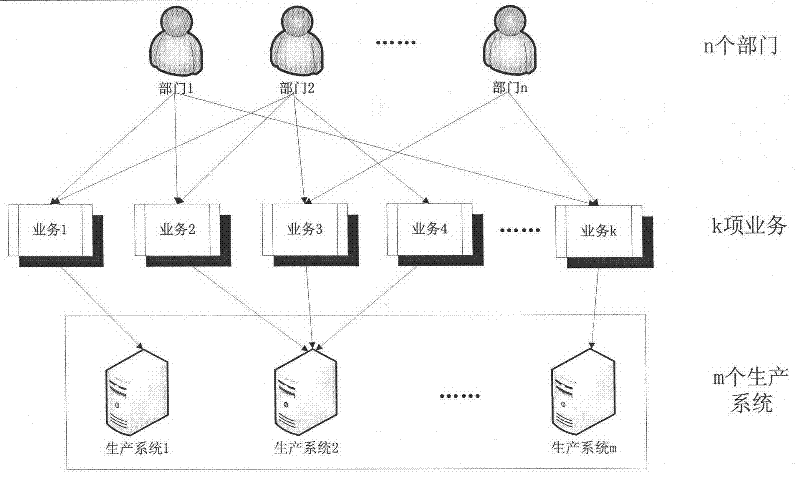
Information system disaster recovery time objective calculation method
The invention provides an information system disaster recovery time objective calculation method. The key of the method is that k services (K1, K2...Kk) altogether operate on an information system comprising m production systems and that each service only can operate on one production system. By analyzing the importance of each production system in the information system, the importance of each service, the profit produced per second by each department and post-disaster tolerable loss, and on the basis of the post-disaster tolerable loss related to a service, the profit newly produced per second by each service, the profit newly produced per second by the production system related to the service and post-disaster tolerable loss are estimated according to the percentage of the post-disaster tolerable loss of the service used by a department accounting for the total post-disaster tolerable loss of the department, and according to the importance of each production system in the information system and the CPU (Central Processing Unit) load condition, the ratios of the tolerable losses to the produced profits of the production systems are weighted and averaged in order to work out the RTO (recovery time objective) value of the disaster recovery point objective of the whole information system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
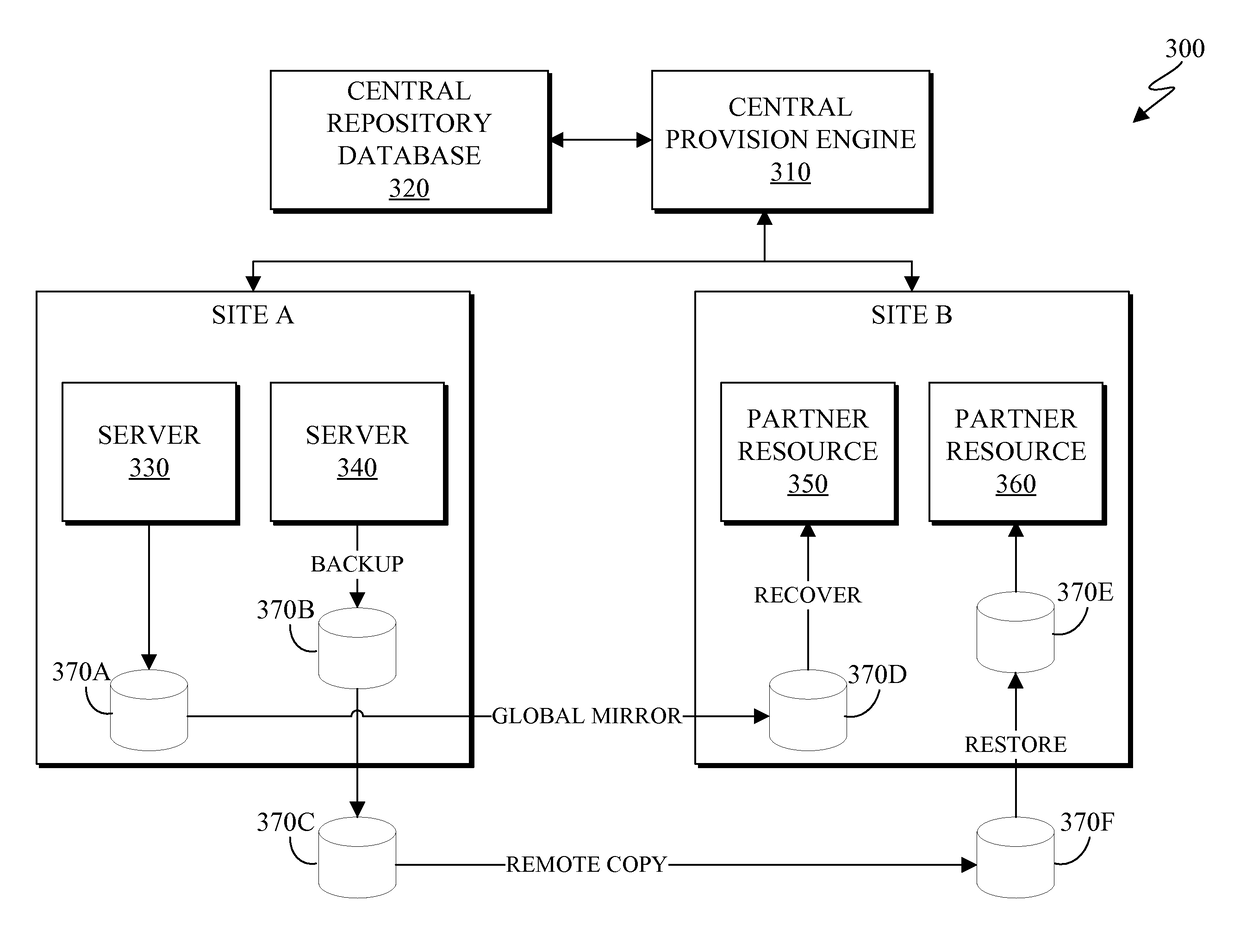
Allocating and managing cloud computing resources for disaster recovery
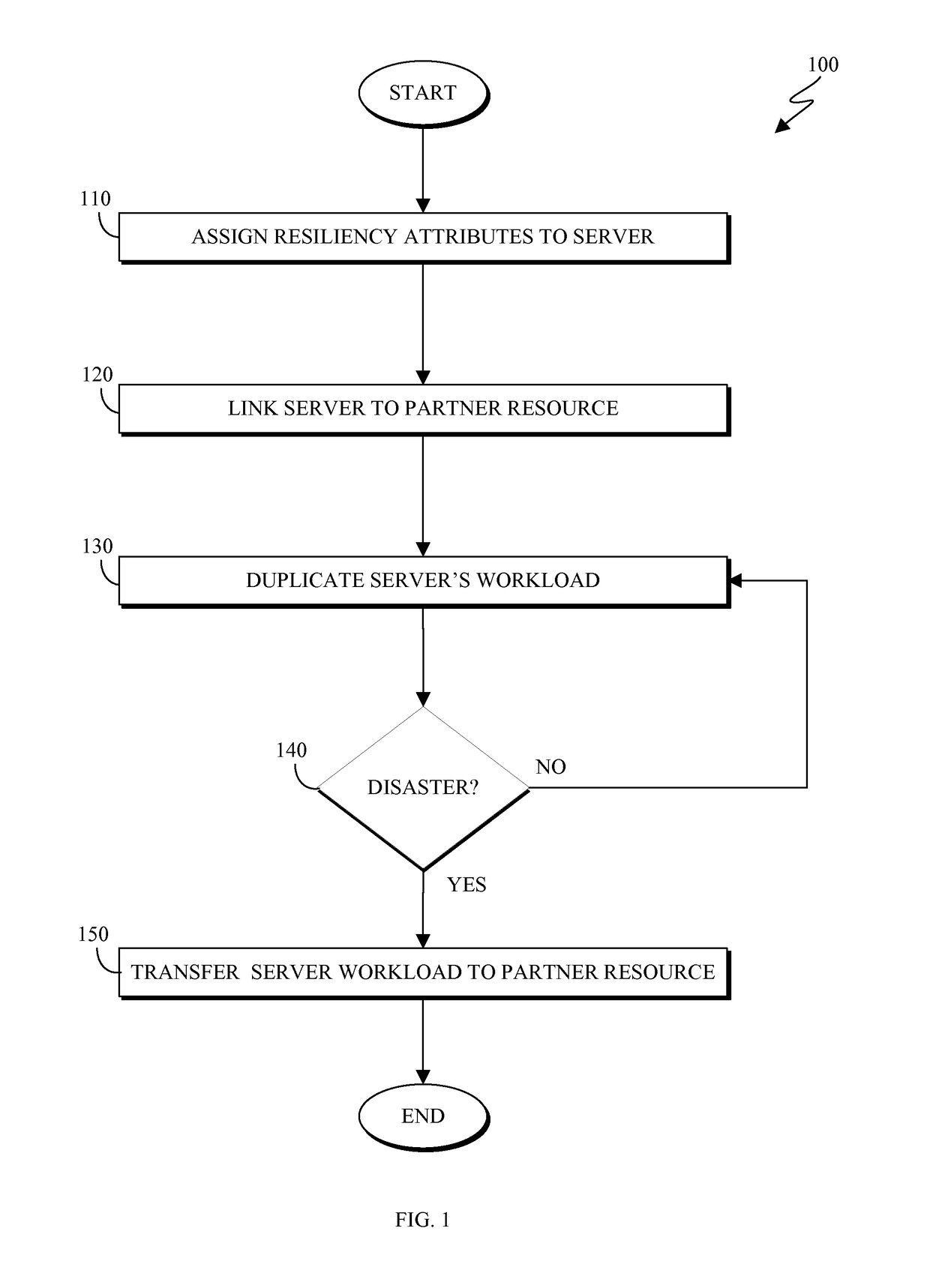
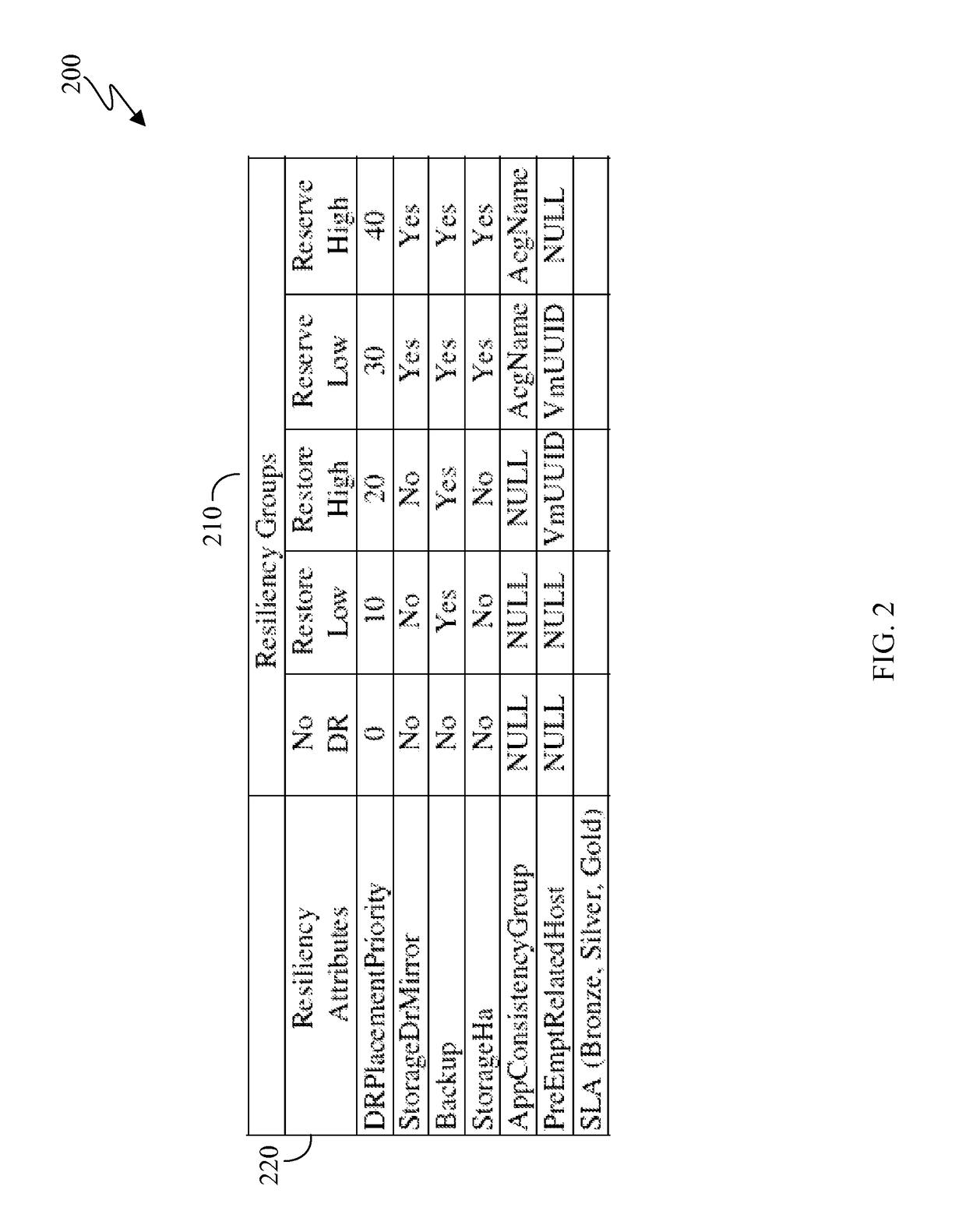
A method, executed by a computer, for allocating resources includes assigning resiliency attributes to a server having a workload, linking each server to a partner resource, duplicating the workload of each server in an offsite location accessible to the partner resource, detecting a disaster event, and transferring the workload of the server automatically to the partner resource. In some embodiments, the partner resource is a plurality of pool servers. The partner resource may be calculated by performing a capacity analysis. The partner resource may not a specifically assigned resource until a disaster occurs. In some embodiments, the workload is duplicated such that the recovery point objective of the workload is minimized. A computer program product and computer system corresponding to the methods are also disclosed herein.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Automated failover for asynchronous remote copy
ActiveUS11307944B2Communication delay is longRedundant operation error correctionFile system functionsFailoverEmbedded system
Example implementations described herein are directed to automated failover and assuring RTO (Recovery Time Objective) assurance, and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) on asynchronous remote copy feature of storage. By using markers that are cyclically stored to the journal volume, the storage device can thereby determine an accurate communication loss period.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Disaster recovery method and device for double available areas, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113987066ADatabase distribution/replicationRelational databasesDatabaseRecovery point objective
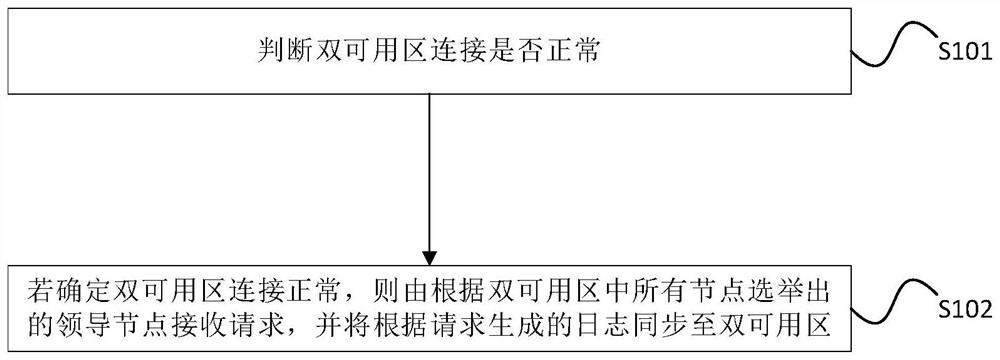
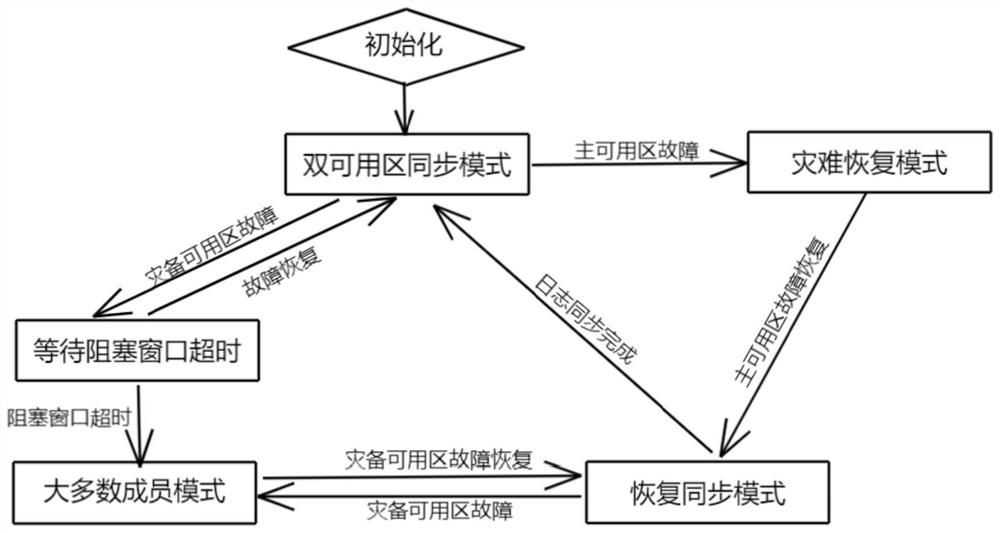
The embodiment of the invention provides a disaster recovery method and device for double available areas, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and relates to the technical field of databases. The method comprises the steps that if it is determined that connection of the dual-available area is normal, a leader node elected according to all nodes in the dual-available area receives a request, and logs generated according to the request are synchronized to the dual-available area. Compared with the prior art, the disaster recovery capability with the recovery point target being 0 can be provided.
Owner:PINGCAP XINGCHEN (BEIJING) TECH CO LTD
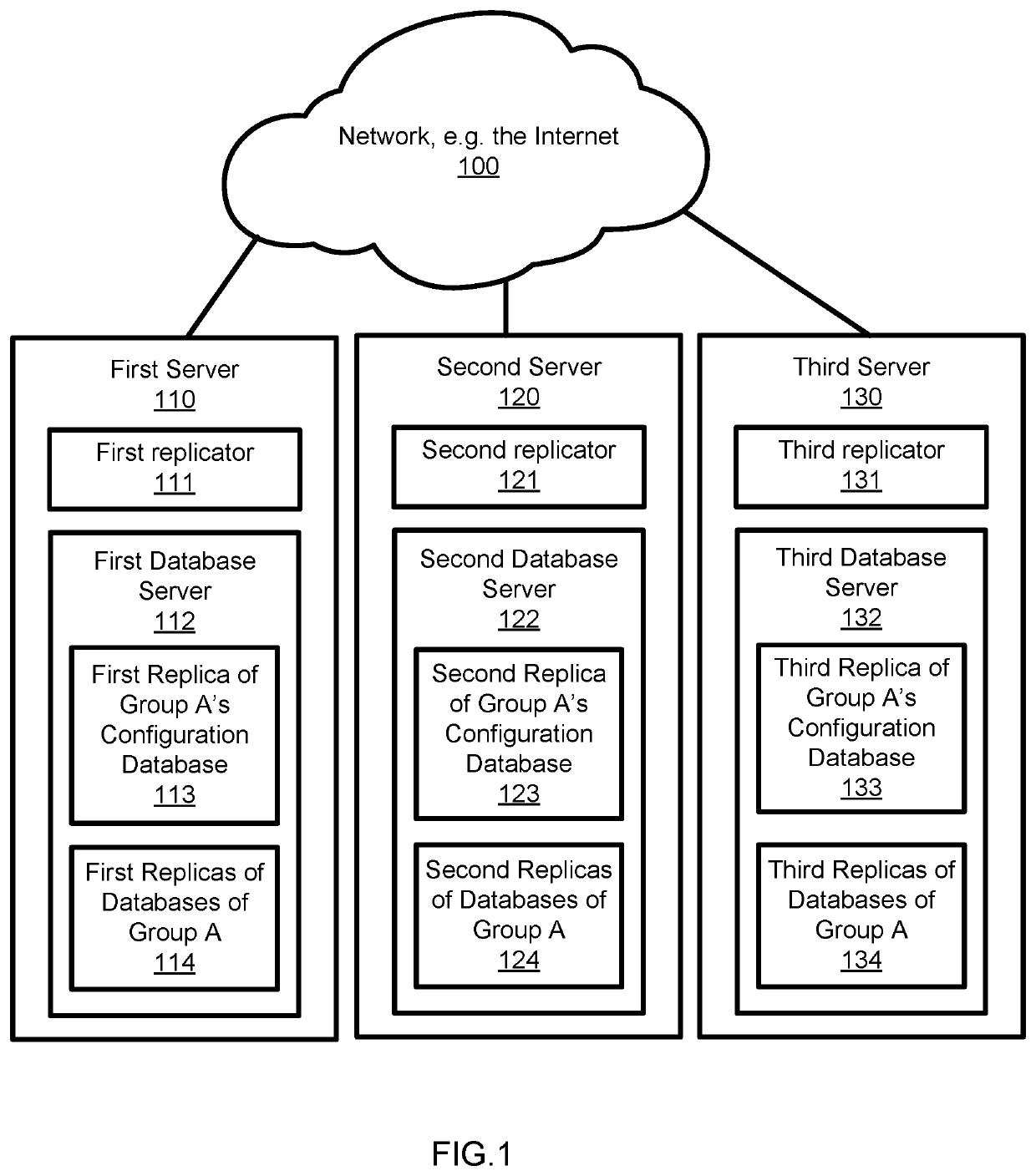
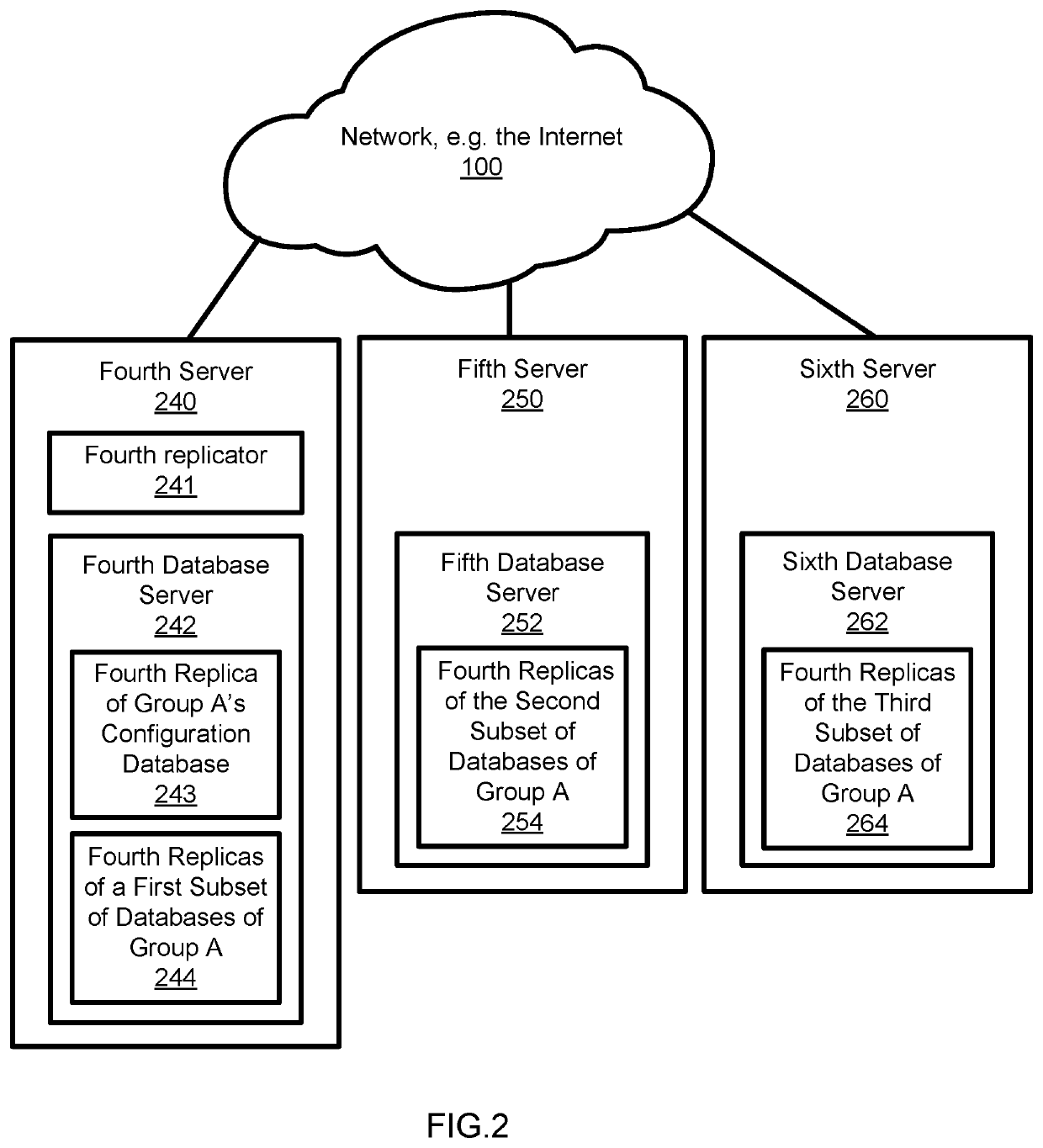
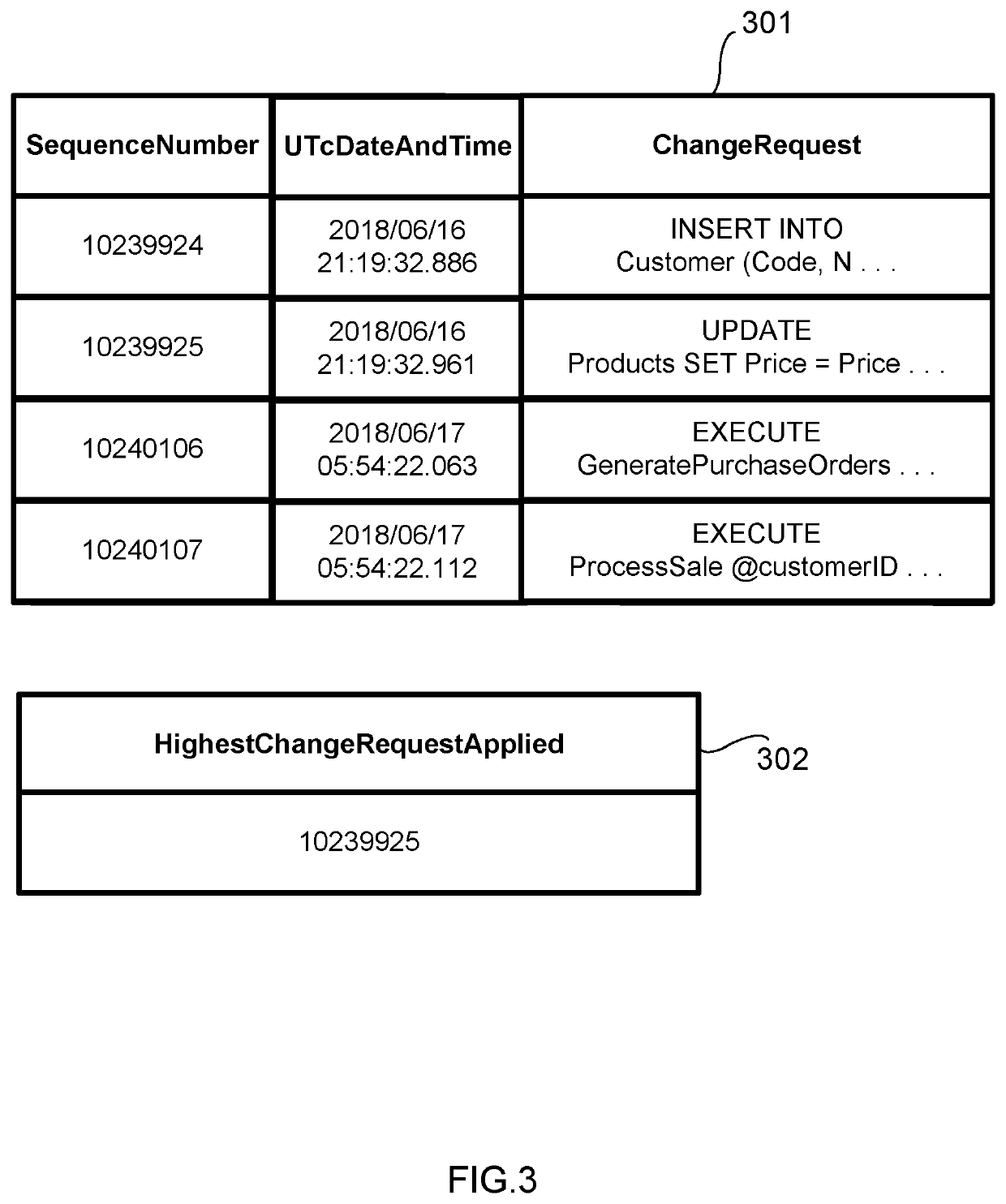
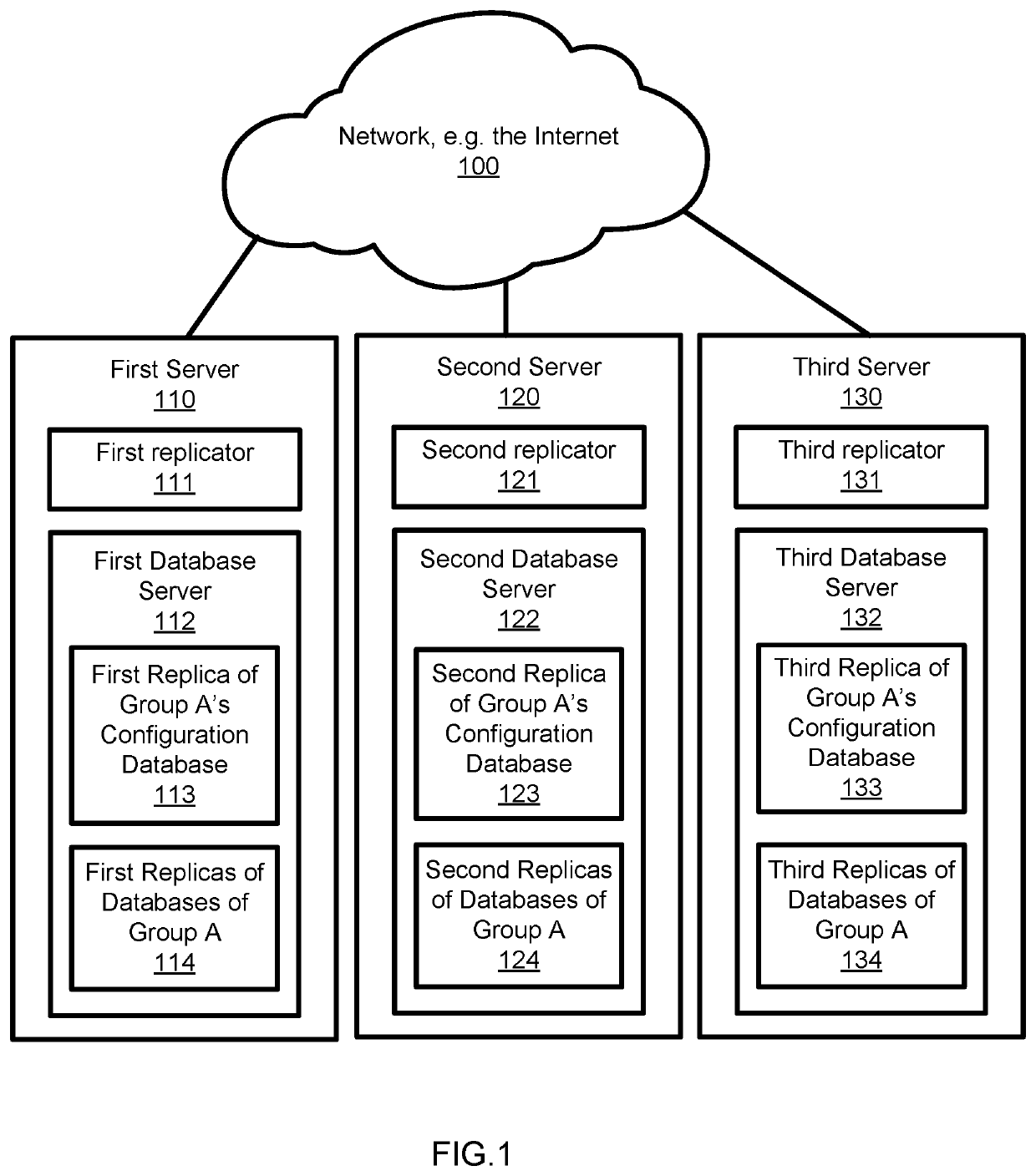
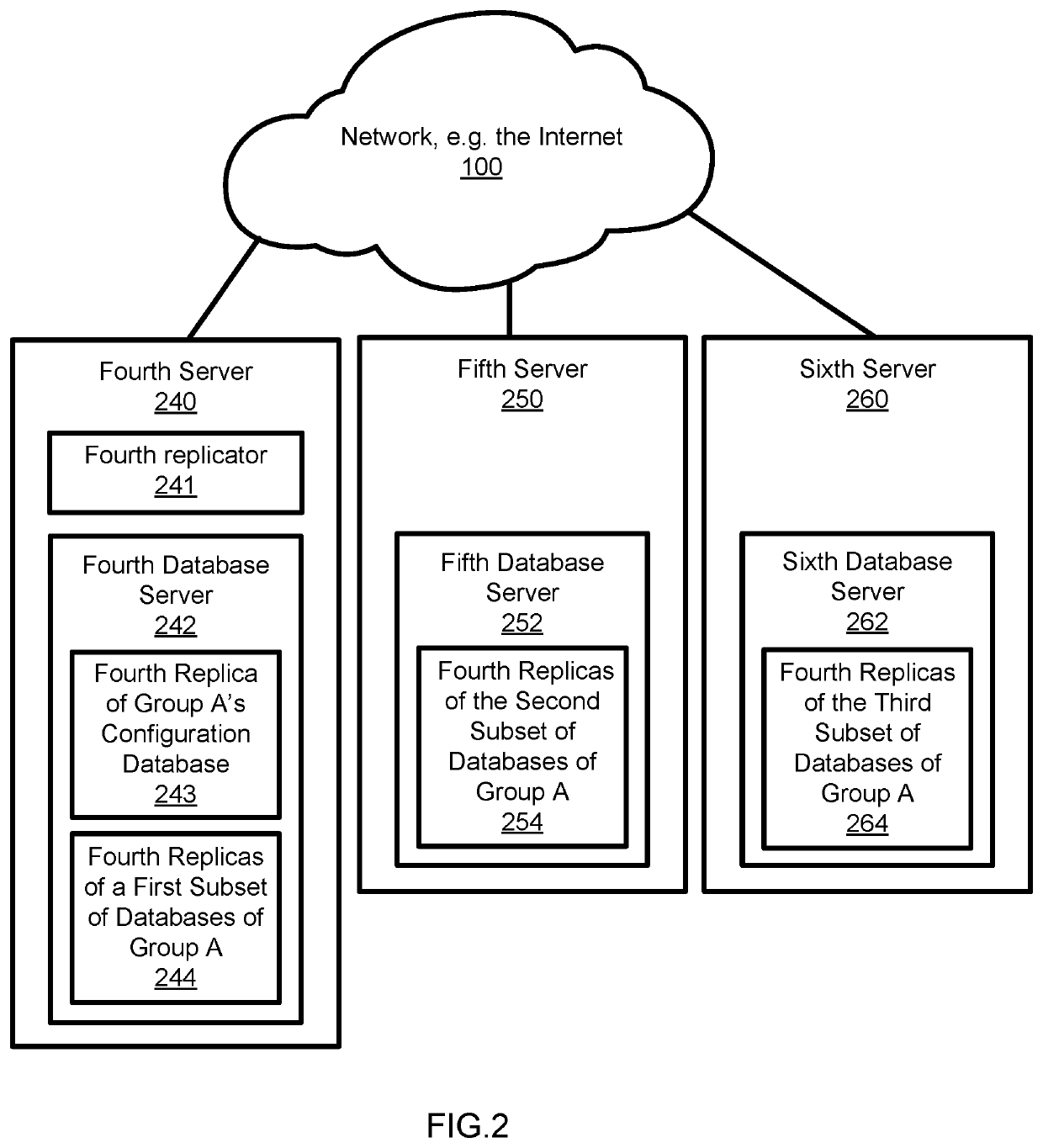
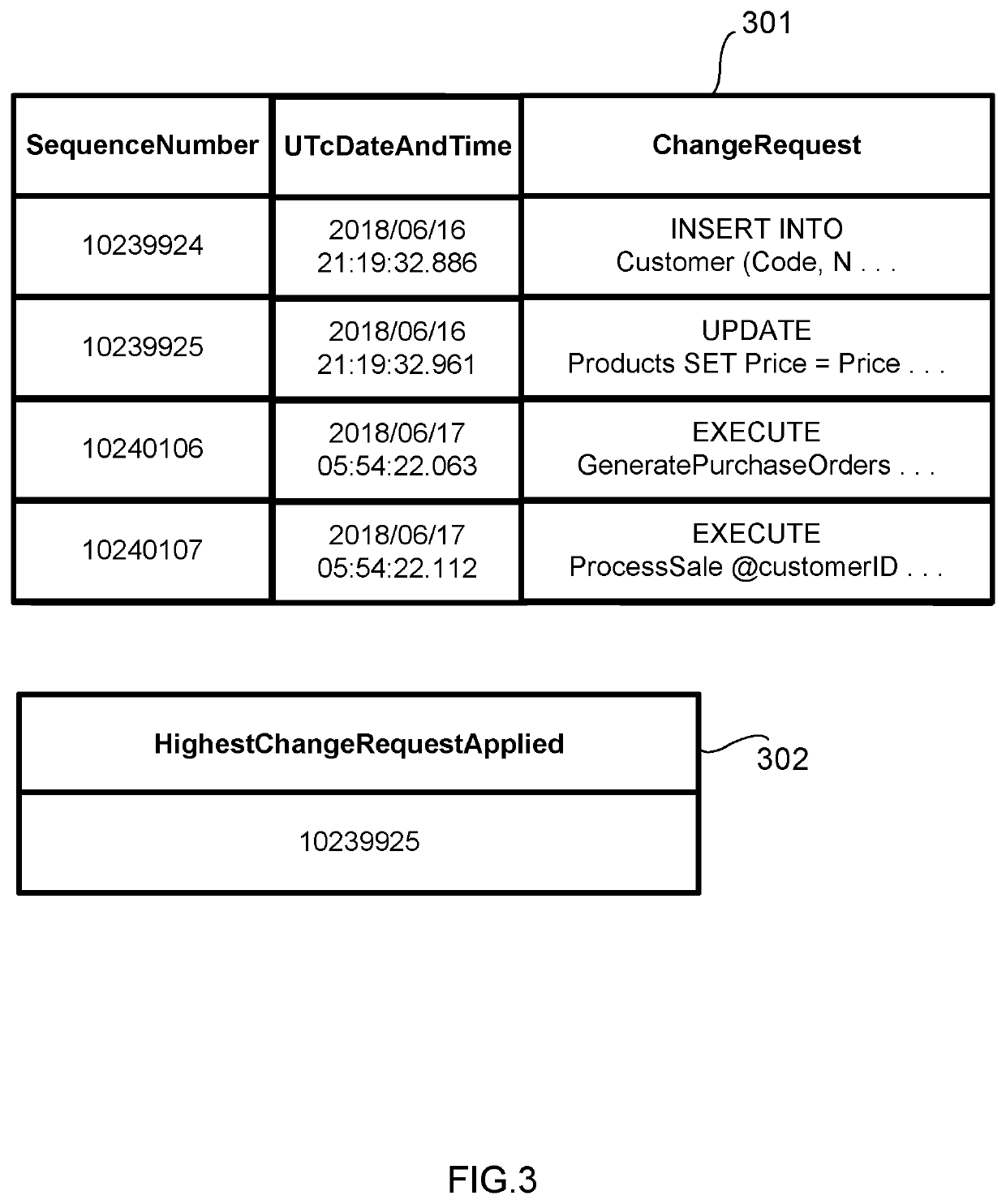
Data replication system
ActiveUS20200042535A1Reduce riskFaster and more resilientDatabase updatingError detection/correctionData setDowntime
An improved data replication system with goals of Recovery Point Objective of zero, meaning a zero potential for loss of data, and a Recovery Time Objective in the seconds, meaning very short downtime after a failure. The system includes duplicates of a data set preferably on multiple drives in multiple computers. Change requests are stored within duplicates, and when a change request has been stored in enough duplicates, it may be applied to any duplicate after all prior change requests have been applied to that duplicate. The system applies changes to duplicates of a data set in the same order. The system further includes a replicator operable to implement accessing and changing steps to meet the goals.
Owner:JOEL MARTIN LOUIS
Data replication system
ActiveUS11100133B2Reduce riskWide applicationDatabase updatingError detection/correctionData setSystem recovery
An improved data replication system with goals of Recovery Point Objective of zero, meaning a zero potential for loss of data, and a Recovery Time Objective in the seconds, meaning very short downtime after a failure. The system includes duplicates of a data set preferably on multiple drives in multiple computers. Change requests are stored within duplicates, and when a change request has been stored in enough duplicates, it may be applied to any duplicate after all prior change requests have been applied to that duplicate. The system applies changes to duplicates of a data set in the same order. The system further includes a replicator operable to implement accessing and changing steps to meet the goals.
Owner:JOEL MARTIN LOUIS
Recovery point objective via dynamic usage of bind segments in a global mirror environment
InactiveUS10033810B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersData storingData store
Embodiments for an approach to resource optimization during consistency group formation associated with a global mirror environment is provided. The approach detects when a primary volume associated with the consistency group has completed transmitting its out-of-sync (OOS) data towards its associated secondary volume. A command is sent to create a next consistency group sidefile so further writes can be sent to the sidefile rather than queueing at the primary volume. The approach repeats this process for each primary volume associated with the global mirror environment until all primary volumes are complete. Commands are sent to disable writes to the associated sidefiles and to merge the data stored in the sidefiles into normal cache as the next consistency group becomes the current consistency group.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for calculating disaster recovery point objective of information system
The invention provides a method for calculating a disaster recovery point objective of an information system. The key of the method is an information system consisting of m production systems, wherein k items of services K1, K2,..., Kk run on the information system, and each item of service only can run on one production system. Through analyzing the importance of each production system, the importance of each service, the existing data volume and the data volume (per second) generated by each department in the information system, and based on the generated data volume (per second) relevant to each service, according to the percentage of the existing data volume in a service used by a department to the total data volume of the department, new generated data (per second) of each service and new generated data (per second) of the production system relevant to each service are estimated; and then, through synthesizing the importance of each production system in the information system, the generated data volume of a production system is divided by the newly increased weighted data volume of the production system so as to obtain a value of the disaster RPO (recovery point objective) of the whole information system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Information system disaster recovery time objective calculation method
The invention provides an information system disaster recovery time objective calculation method. The key of the method is that k services (K1, K2...Kk) altogether operate on an information system comprising m production systems and that each service only can operate on one production system. By analyzing the importance of each production system in the information system, the importance of each service, the profit produced per second by each department and post-disaster tolerable loss, and on the basis of the post-disaster tolerable loss related to a service, the profit newly produced per second by each service, the profit newly produced per second by the production system related to the service and post-disaster tolerable loss are estimated according to the percentage of the post-disaster tolerable loss of the service used by a department accounting for the total post-disaster tolerable loss of the department, and according to the importance of each production system in the information system and the CPU (Central Processing Unit) load condition, the ratios of the tolerable losses to the produced profits of the production systems are weighted and averaged in order to work out the RTO (recovery time objective) value of the disaster recovery point objective of the whole information system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com