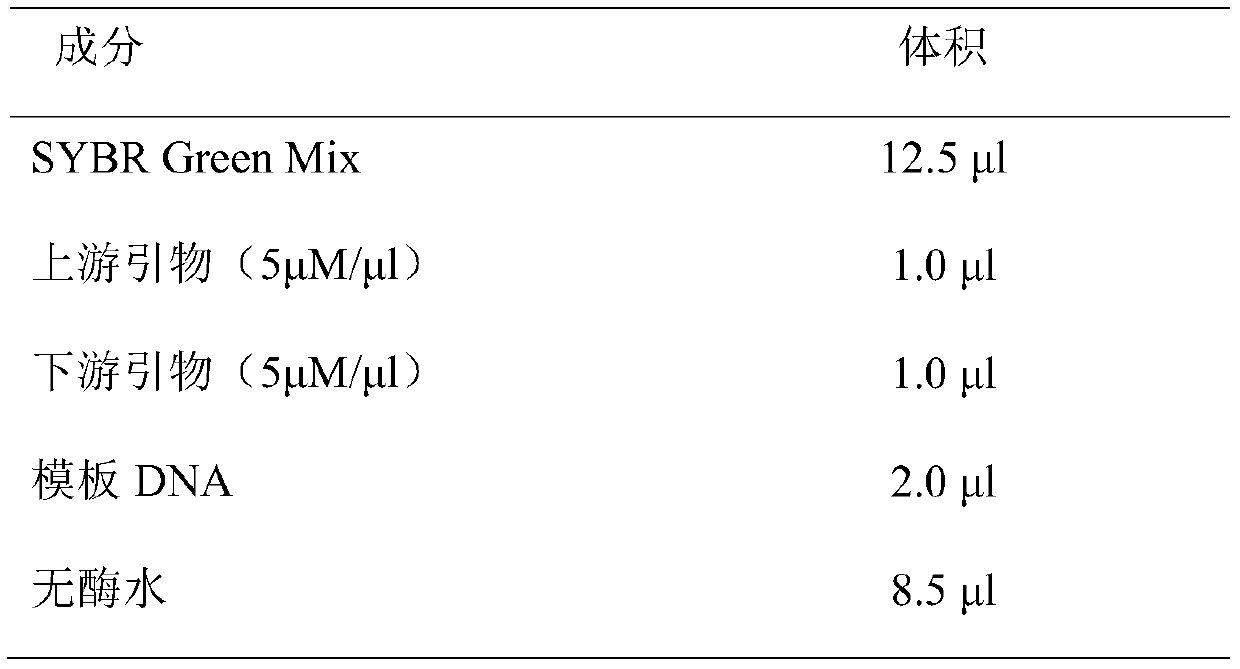
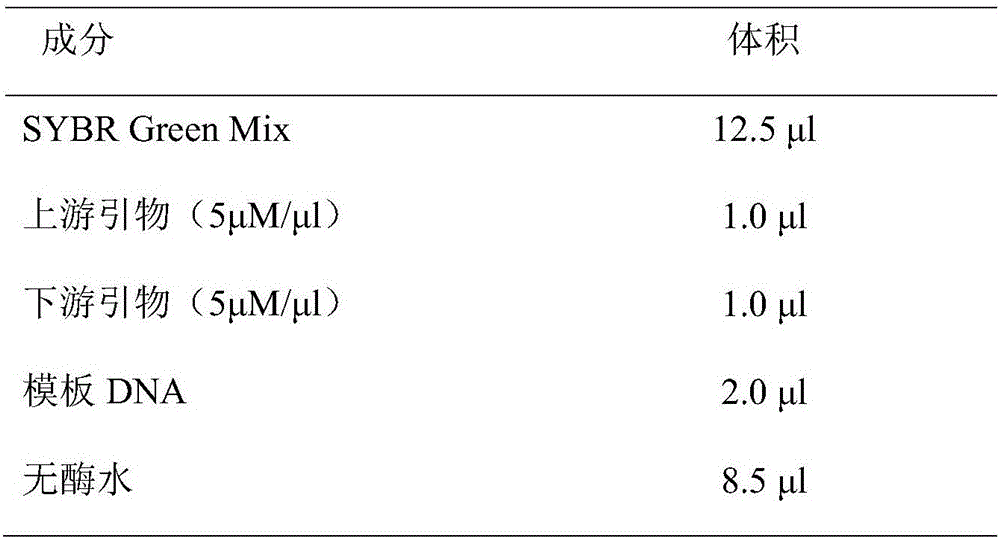Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49results about How to "Provide survival rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Breeding method of bactrocera cucurbitae
The invention discloses a breeding method of bactrocera cucurbitae, which comprises the steps of egg collection, pupa collection, pupa eclosion and imago breeding. According to the method, a natural-growth environmental condition and a living habit of the Bactrocera cucurbitae are researched and analyzed, so that a successful method for artificially breeding the Bactrocera cucurbitae is obtained by creative exploration, and the Bactrocera cucurbitae with basically-consistent growth and development conditions can be obtained in batches; on the basis of the method, the bactrocera cucurbitae meeting a using requirement of scientific experiment research can be provided for scientific experiments all the year around without limitation of natural conditions and seasons; and the breeding method can increase a survival rate of artificial breeding of the Bactrocera cucurbitae, and improve the breeding efficiency.
Owner:DONGGUAN SHENGTANG CHEM +1
Molecular marker for diagnosing and treating multiple myeloma
ActiveCN106222259AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiagnosis methodsCancer research
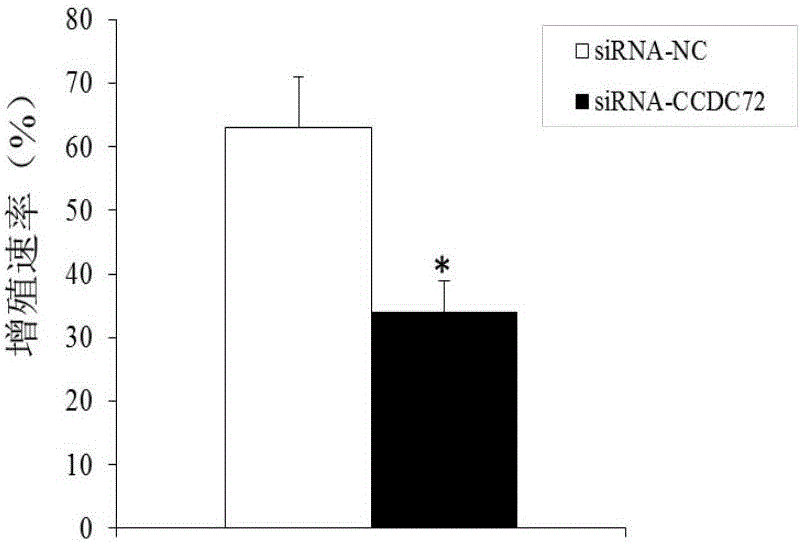
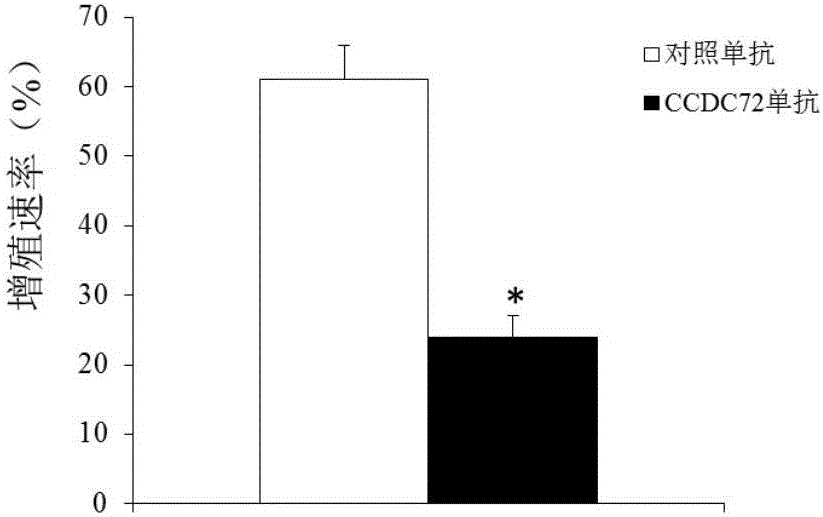
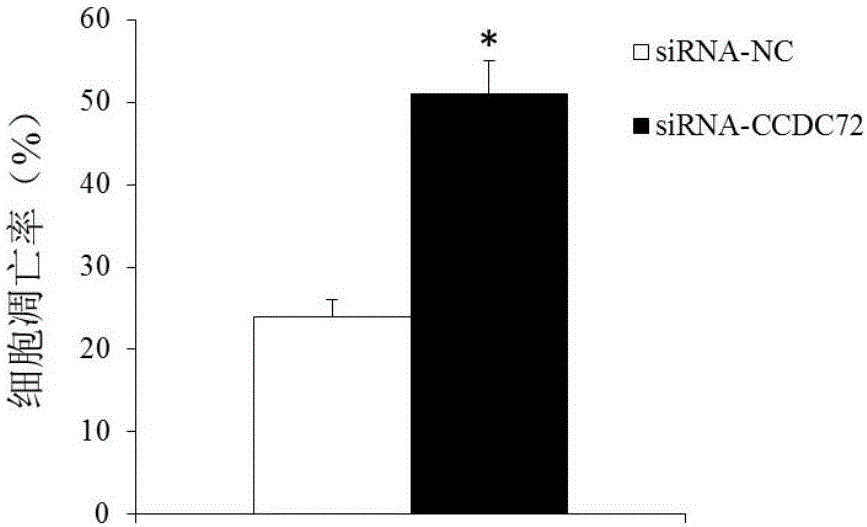
The invention discloses a molecular marker with a CCDC72 gene for diagnosing the multiple myeloma. An experiment shows that compared with a normal myeloid tissue, the CCDC72 gene has a large expression quantity in a multiple myeloma tissue. The invention further discloses application of the CCDC72 gene in preparation of a medicine for treating the multiple myeloma. The research achievement provides a novel clinical multiple myeloma diagnosis method, and also provides a novel medicine target for treating the multiple myeloma.
Owner:GUAN BOJIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
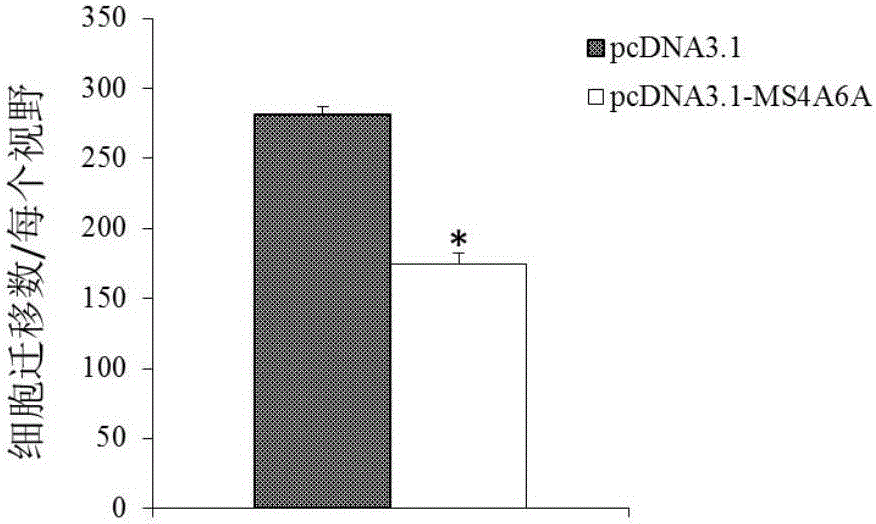
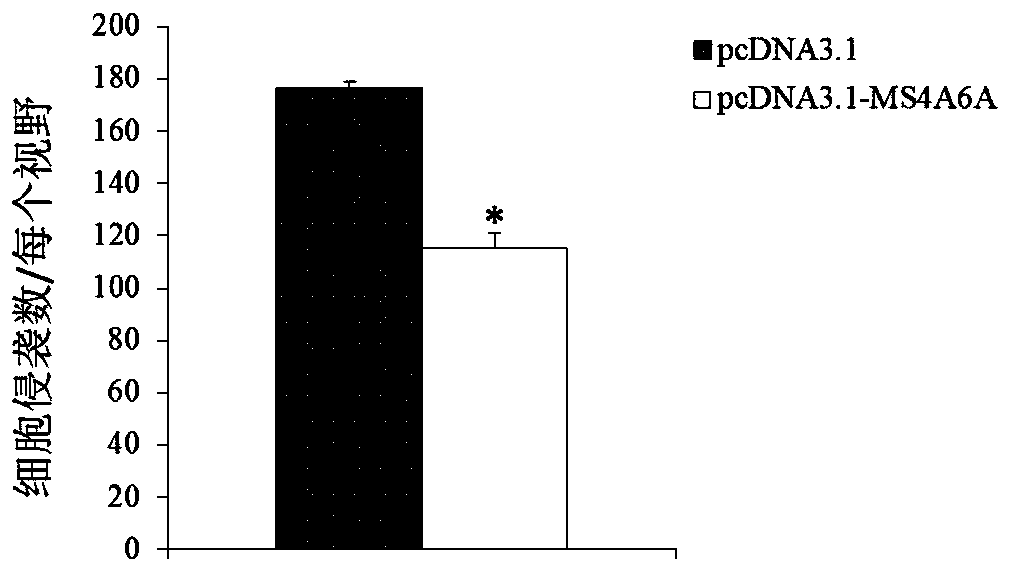
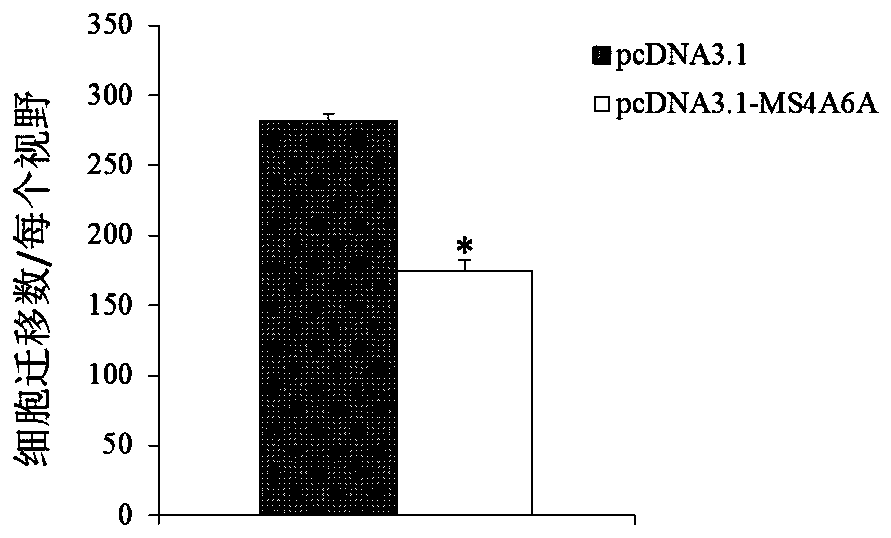
Application of MS4A6A serving as multiple myeloma diagnosis and treatment marker
ActiveCN105969901AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMolecular levelDrug target
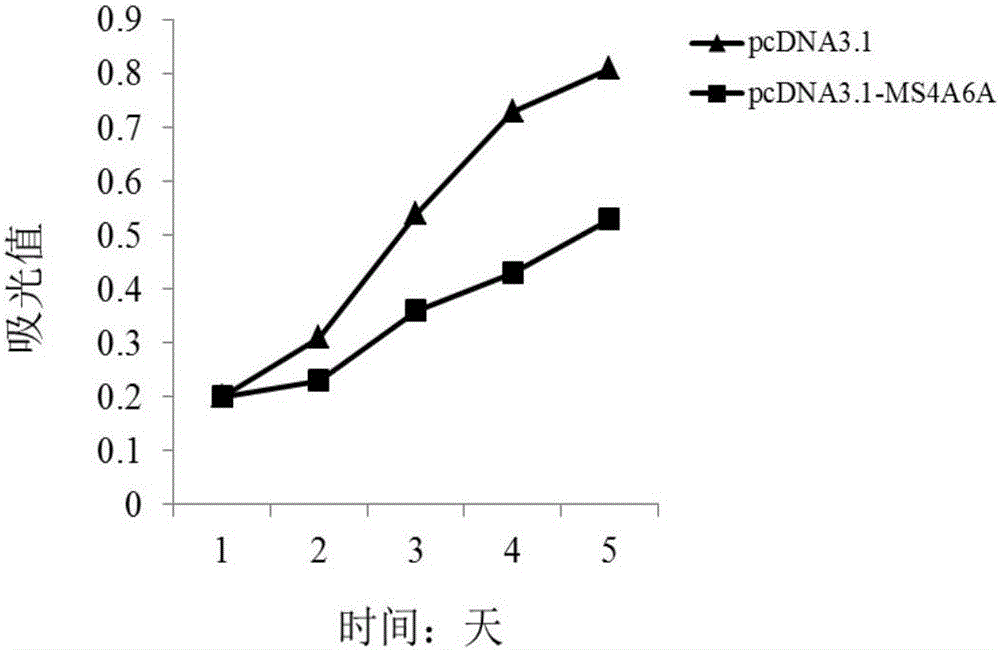
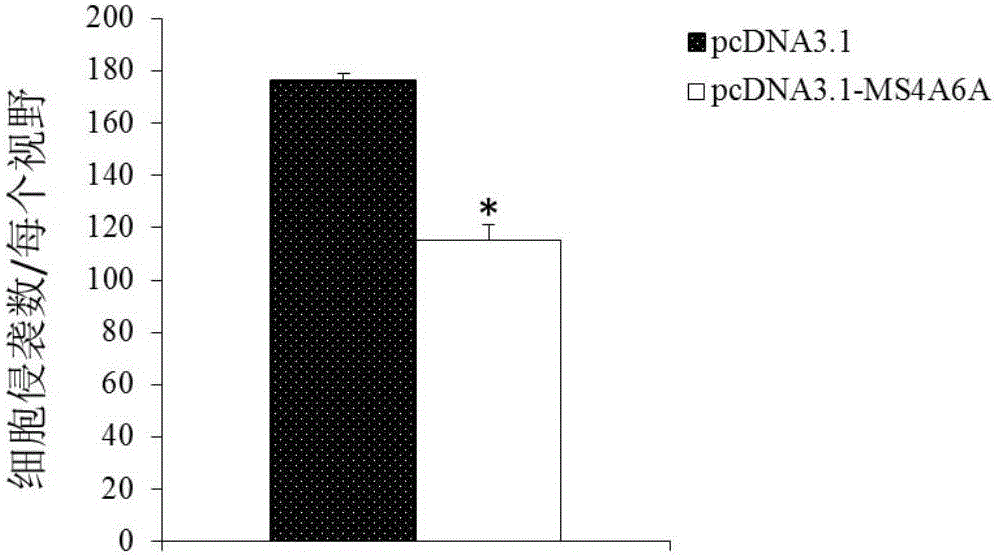
The invention discloses a genetic marker, namely, MS4A6A. The MS4A6A can be used for judging whether a subject has a risk of suffering from multiple myeloma or not or judging whether the subject suffers from the multiple myeloma. In additions, the MS4A6A can also be used for preparing drugs for treating the multiple myeloma. According to the MS4A6A, a novel diagnostic method is provided for diagnosing the multiple myeloma at the molecular level clinically, and meanwhile a novel drug target is provided for a gene therapy of the multiple myeloma.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
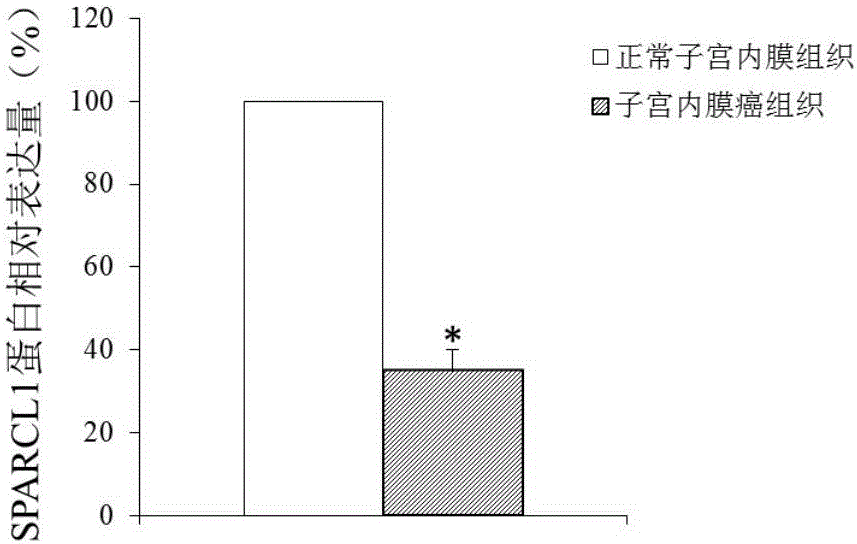
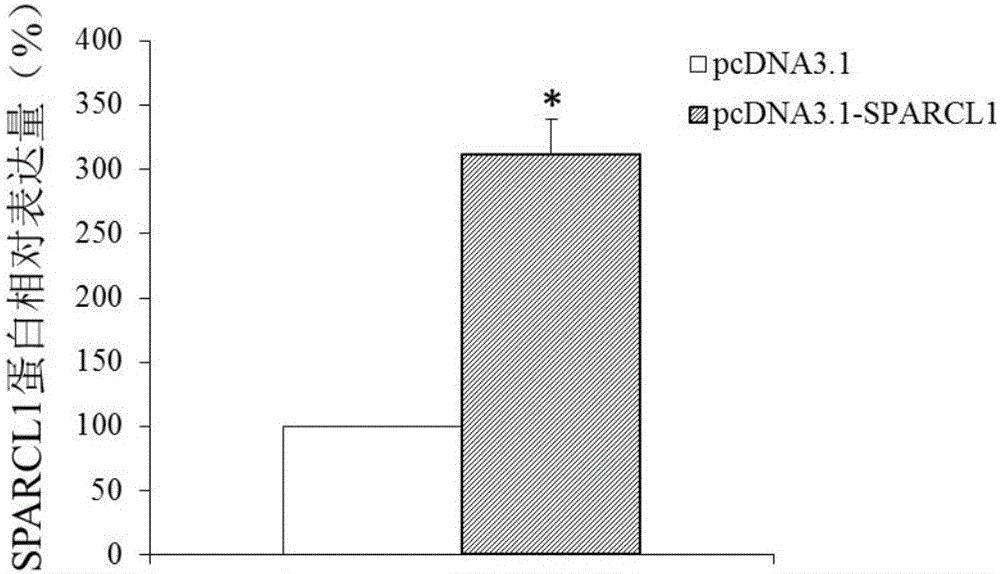
Endometrial cancer biological marker
ActiveCN105907879AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsSPARCL1Biomarker (petroleum)
The invention discloses application of SPARCL1 to a diagnosis and treatment marker of endometrial cancer. The SPARCL1 can be used for developing a product for diagnosing the endometrial cancer and developing a medicine for treating the endometrial cancer. A research result of the invention provides a theoretical foundation for formulating personalized treatment programs by clinical doctors and provides a new medicine target spot for developing endometrial cancer medicines.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
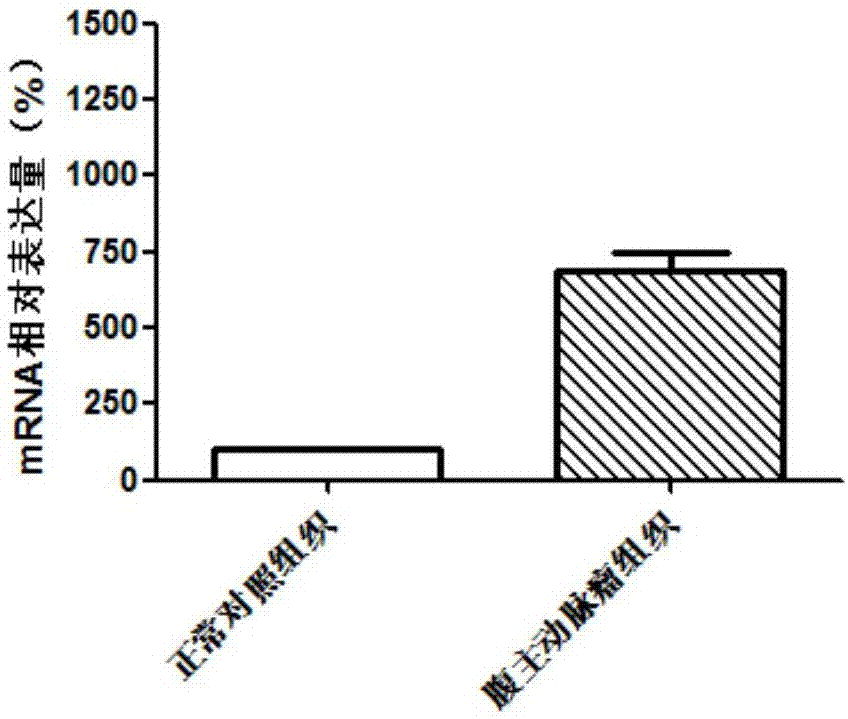
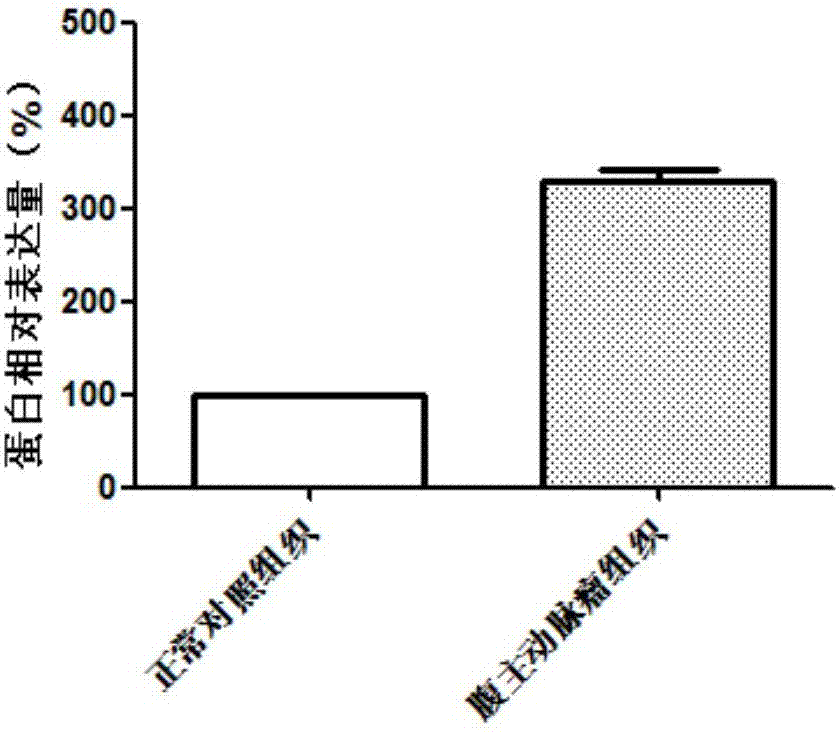
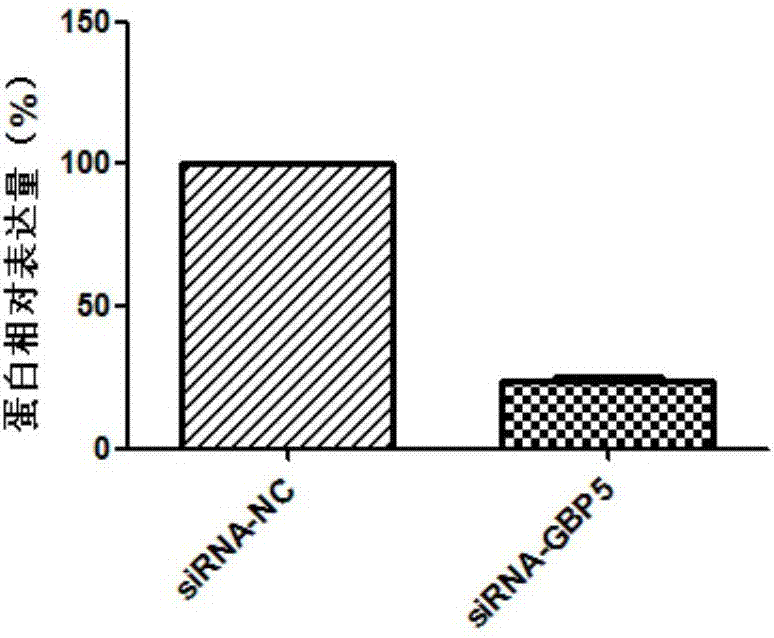
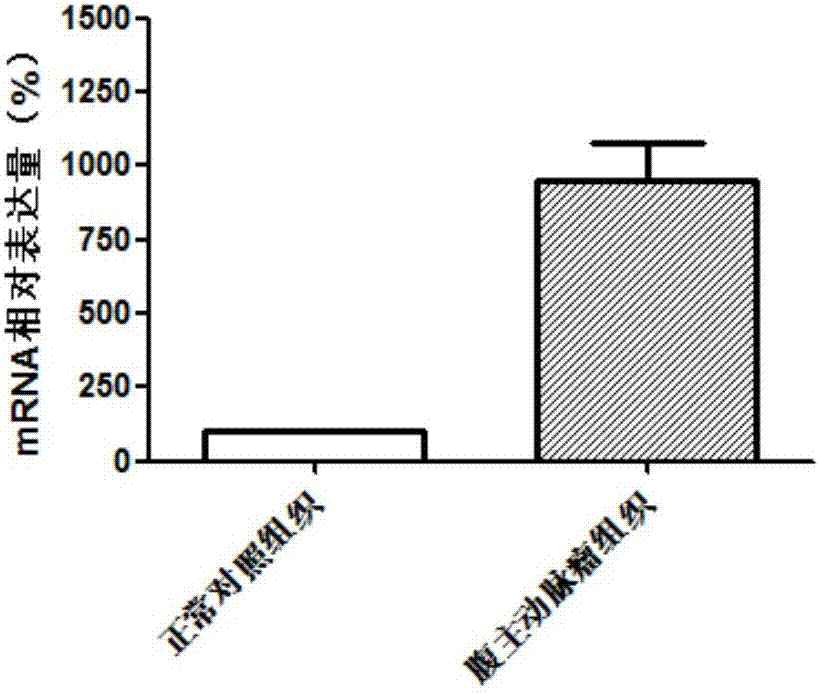
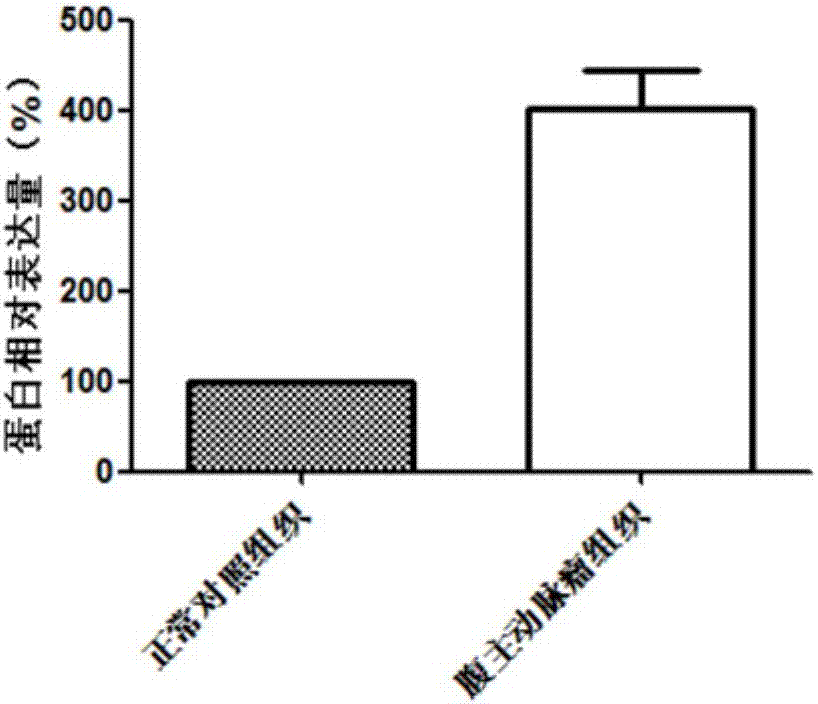
Diagnostic marker for abdominal aortic aneurysm
InactiveCN107012256AProvide survival rateOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementApoptosisDrug target
The invention discloses application of a GBP5 gene and an expression product thereof as molecular markers for diagnosis of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Whether a subject suffers from the abdominal aortic aneurysm or has the risk of suffering from the abdominal aortic aneurysm is determined by detecting the contents of the GBP5 gene and the expression product thereof in the abdominal aortic aneurysm tissue of the subject. The results of research on the apoptosis of smooth muscle cells cultured in vitro show that cell apoptosis can be inhibited via interference in the expression of the GBP5 gene. Such research results prove that the GBP5 gene and the expression product thereof are potential drug targets for treatment of the abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
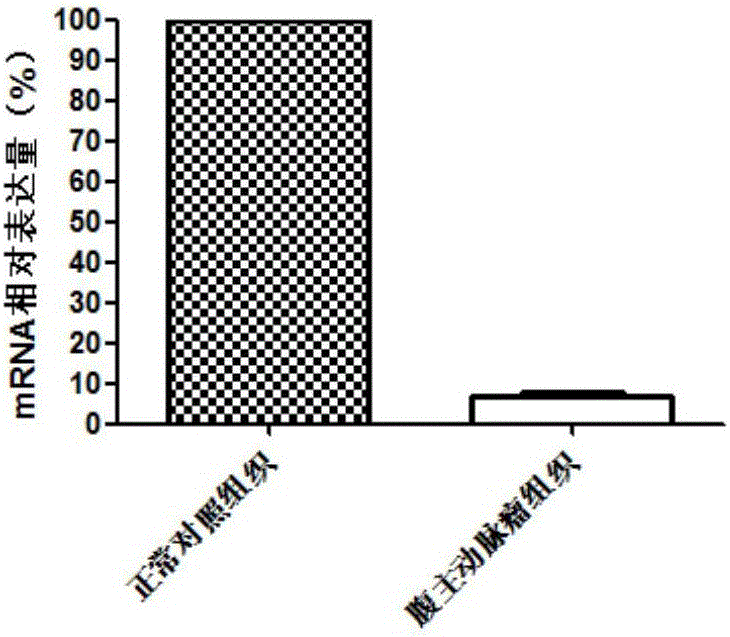
Diagnosis and treatment related gene for abdominal aortic aneurysm
InactiveCN107177673AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsSmooth muscleApoptosis
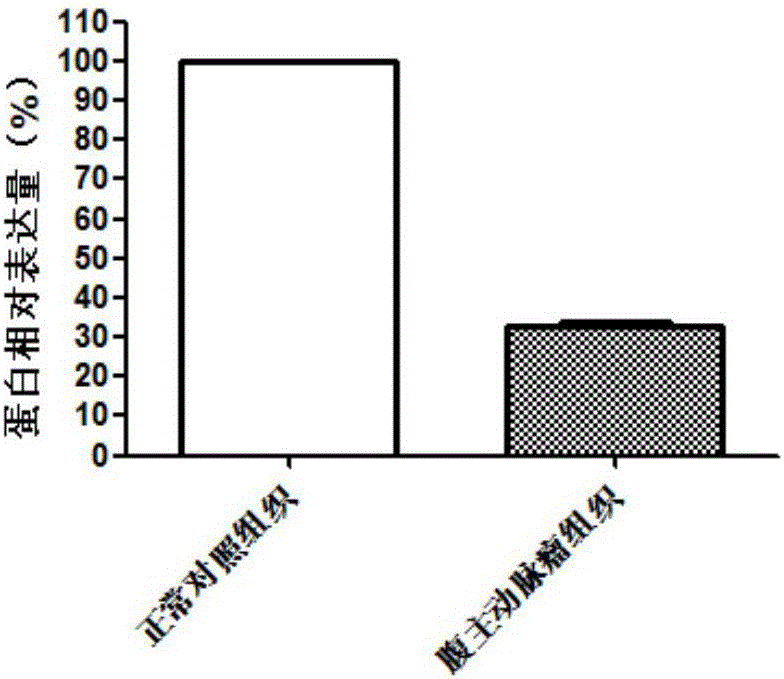
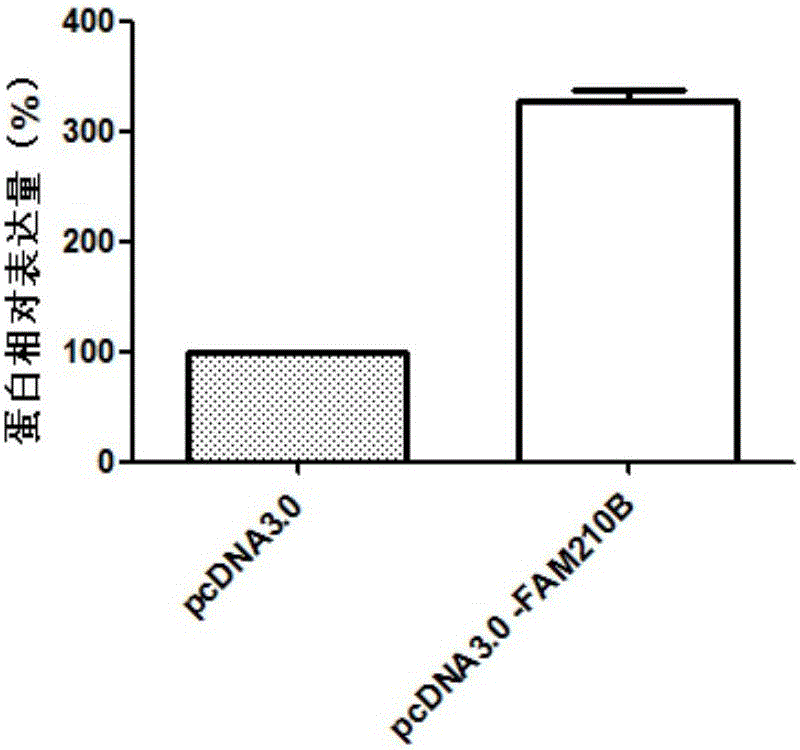
The invention discloses application of FAM210B in the preparation of diagnostic tools for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Experiments prove that FAM210B has expression differences in normal control tissues and abdominal aortic aneurysm tissues; therefore, it is reckoned that FAM210B is a molecular marker for diagnosing abdominal aortic aneurysm. Experiments via in-vitro cultured cells prove that by accelerating the expression of FAM210B, it is possible to inhibit the apoptosis of human aortic smooth muscle cells; therefore, it is reckoned that FAM210B is a drug target for treating abdominal aortic aneurysm. As a new molecular marker for diagnosing and treating abdominal aortic aneurysm, the molecular marker has a promising clinical application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
DSTN gene and expression product thereof as diagnosis and treatment target of endometrial cancer
InactiveCN105886659AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTreatment targetsPoor correlation
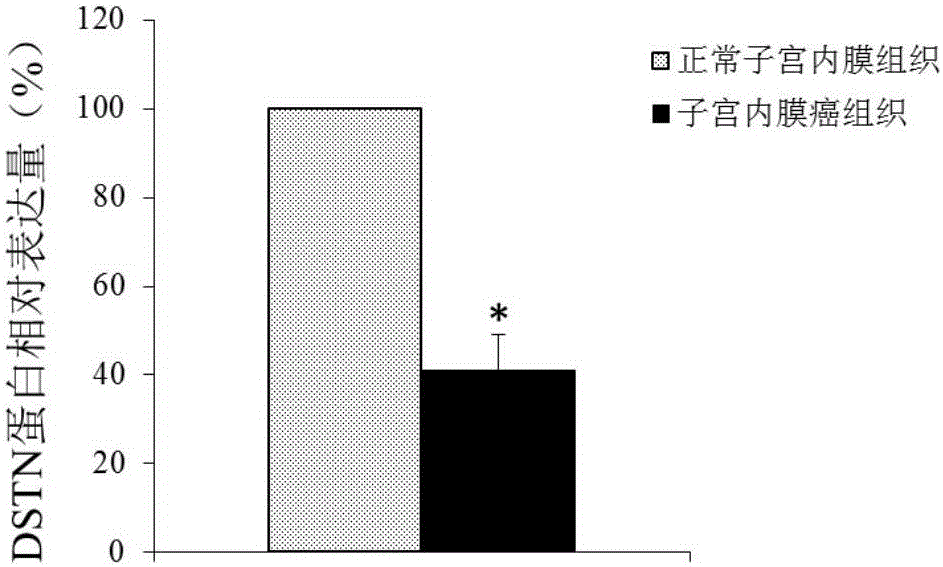
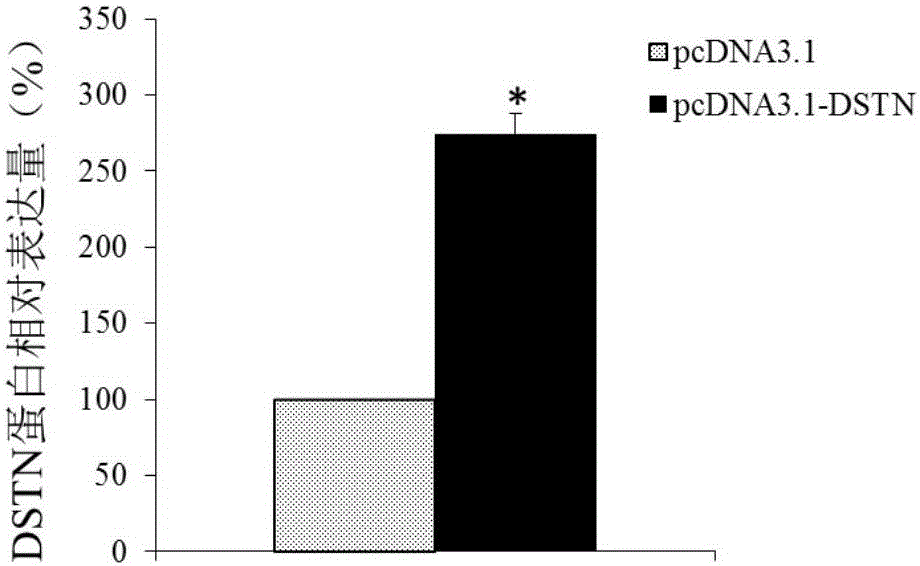
The invention discloses a DSTN gene which can be used as a molecular marker of endometrial cancer diagnosis. A gene chip and a QPCR experiment are utilized to find that the DSTN gene and a coding protein thereof have remarkable difference in expression in a normal endometrial tissue and an endometrial cancer tissue, namely that the expression condition of the DSTN gene in the endometrial tissue can be detected to judge whether a subject suffers from endometrial cancer or has the risk of suffering from endometrial cancer or not. According to the correlation of the two, the invention develops a kit for diagnosing the endometrial cancer, and the kit is used for diagnosing the endometrial cancer by detecting the expression of the DSTN gene. The diagnosis kit can be used for early-stage diagnosis of diseases, and has a wide application prospect clinically. Besides, the invention further discloses the DSTN gene which can be used as a molecular target for treating the endometrial cancer, so that a foundation is provided for developing an endometrial cancer treatment drug.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Molecular marker for diagnosing and treating endometrial cancer
ActiveCN106011260AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEndometrial cancerClinical diagnosis
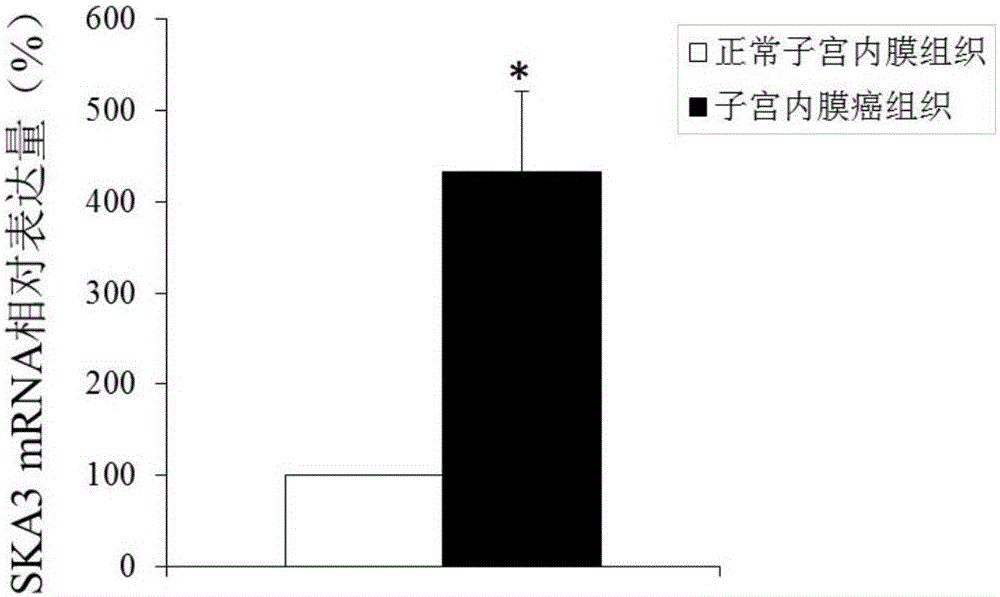
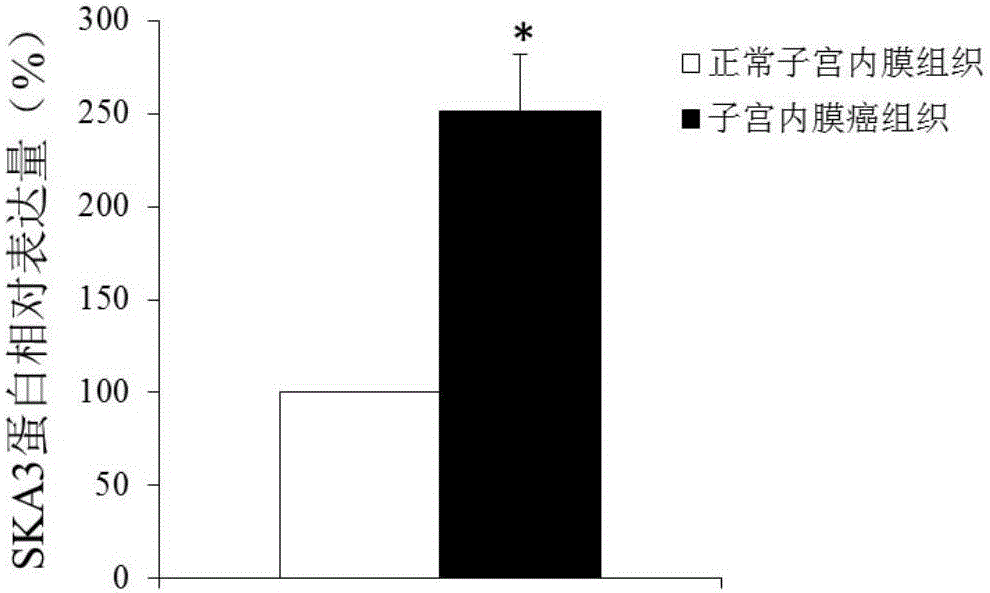
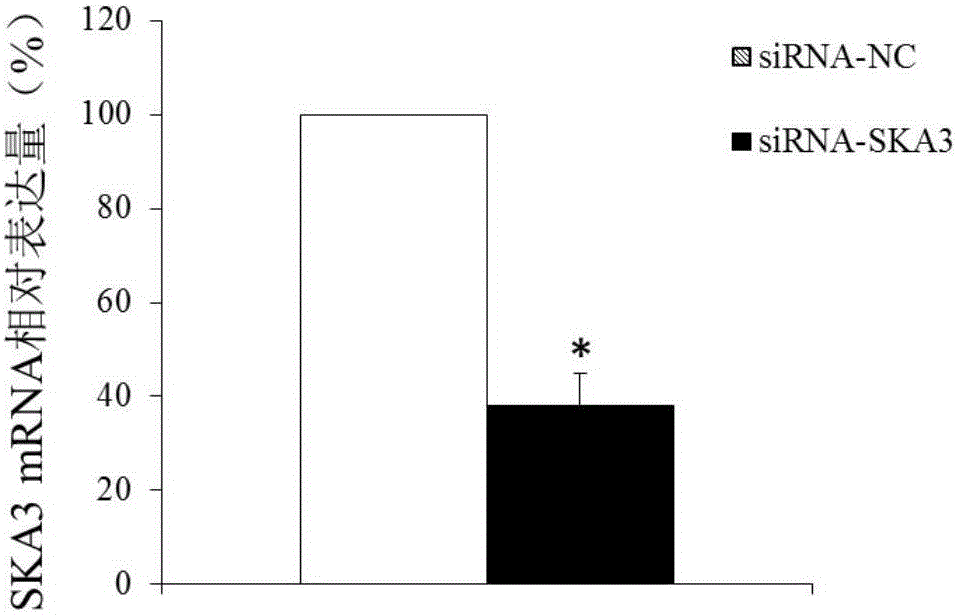
The invention discloses that the SKA3 gene can be used as a molecular marker for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. Experiments prove that the expression quantity of the SKA3 gene in the endometrial cancer tissue is high in comparison with normal endometrial tissue. The invention also discloses that the SKA3 gene also can be used for preparing a medicine for treating endometrial cancer. The research result of the invention provides a new method for clinical diagnosis of endometrial cancer as well as a new target for the medicine for treating endometrial cancer.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Multiple myeloma diagnosis and treatment marker and application thereof
ActiveCN106011288AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCancer researchMolecular marker
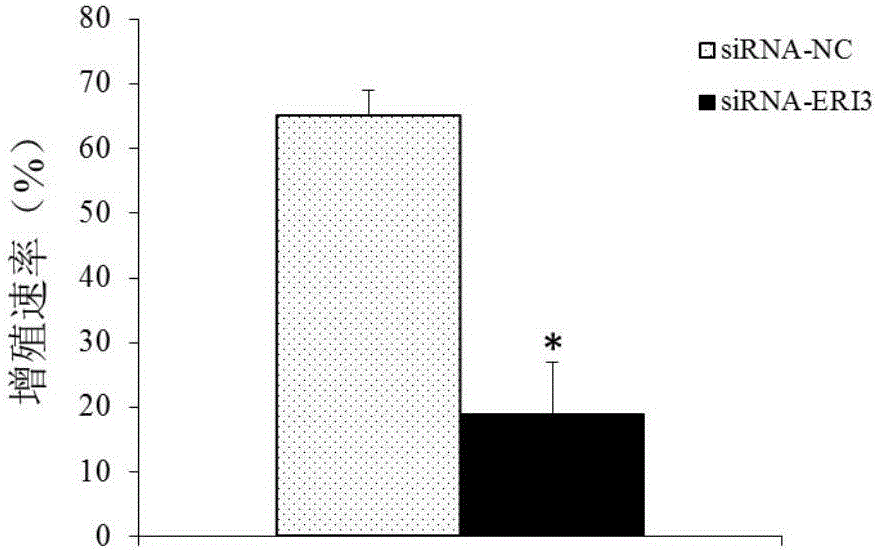
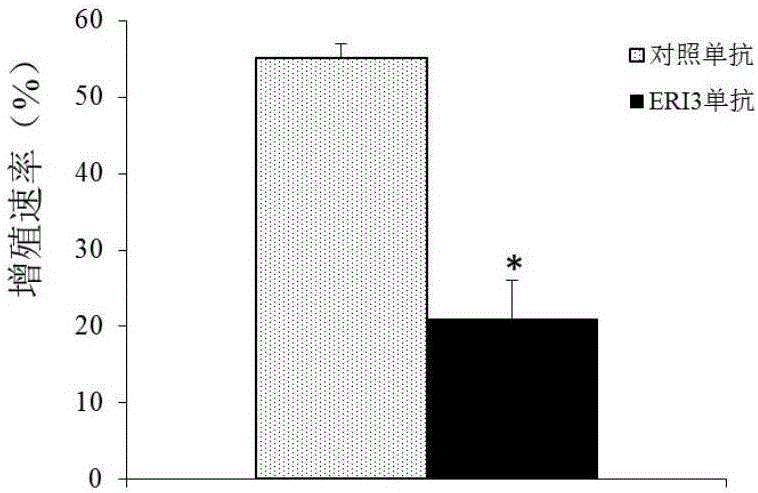
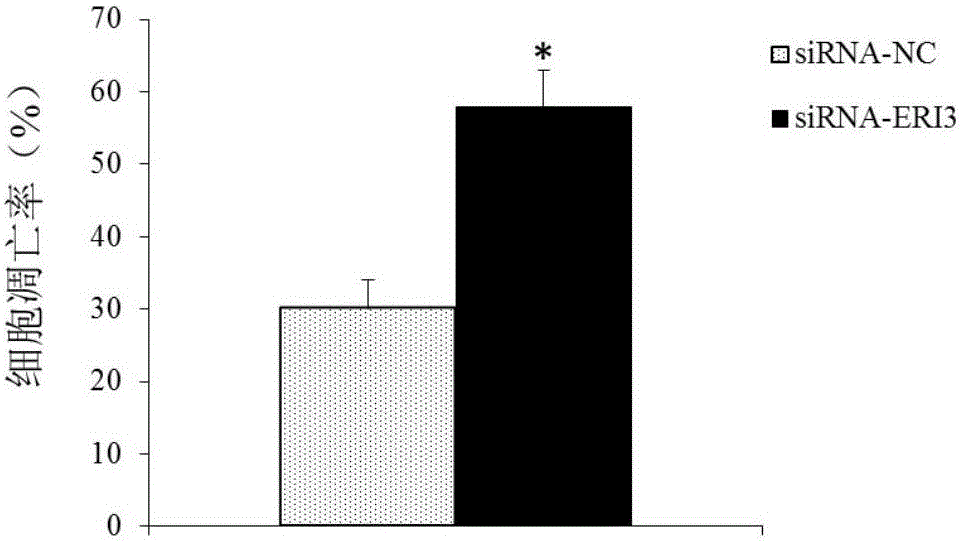
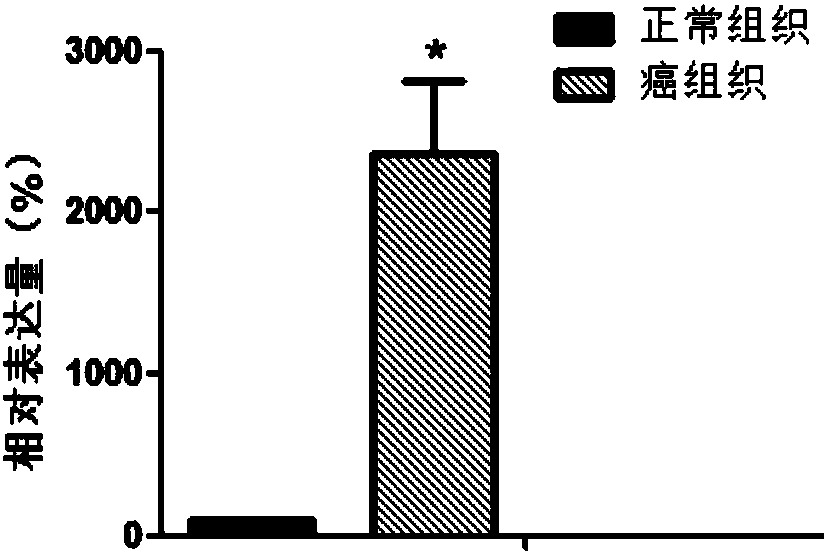
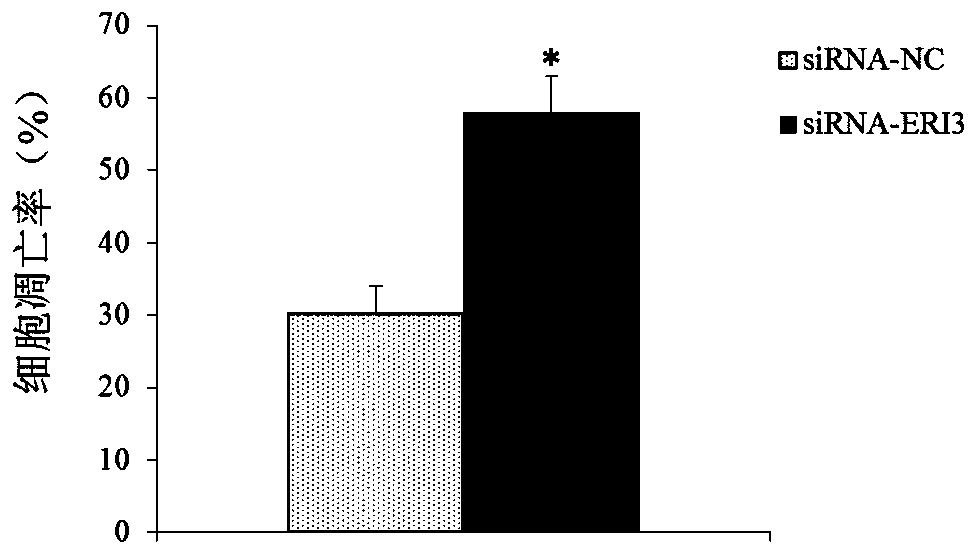
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and discloses an ERI3 gene and new use of a code thereof. Studies prove that the ERI3 gene and encoded protein thereof not only can be taken as a molecular marker for diagnosing the multiple myeloma, but also can be used as a molecular target for treating the multiple myeloma. Based on the study results, the invention provides a new diagnosis method and treatment means for clinically.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
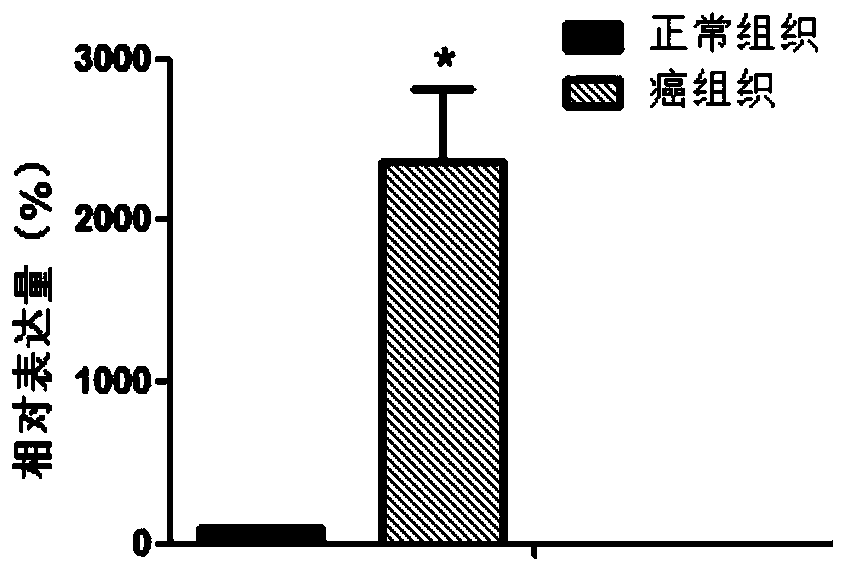
Diagnostic marker-C16orf74 gene of renal clear cell carcinoma
ActiveCN108531607AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisRenal clear cell carcinomaBiomarker (petroleum)
The invention discloses a C16orf74 gene which can be taken as a biomarker for the renal clear cell carcinoma. The experiment proves that compared with normal nephridial tissues, the C16orf74 gene expression in renal clear cell carcinoma tissues is significantly improved. According to the research result, the C16orf74 gene can be applied to research and development of a kit used for diagnosing therenal clear cell carcinoma and also can be used for researching and developing medicines capable of inhibiting the C16orf74 gene expression, thereby achieving clinical prevention and treatment for therenal clear cell carcinoma.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Multiple myeloma biomarker
ActiveCN105969904AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingIndividualized treatmentDrug target
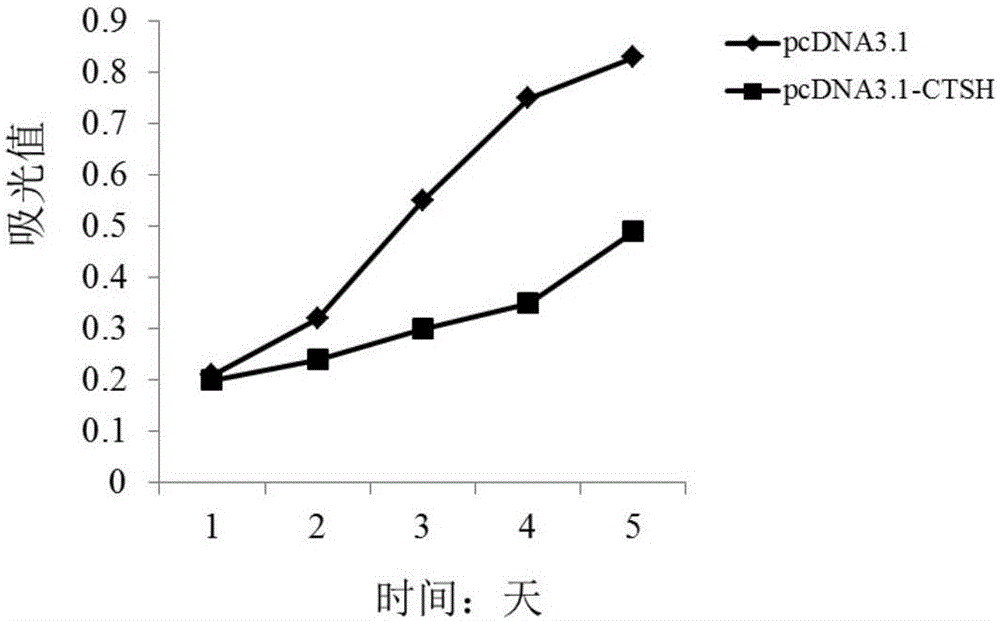
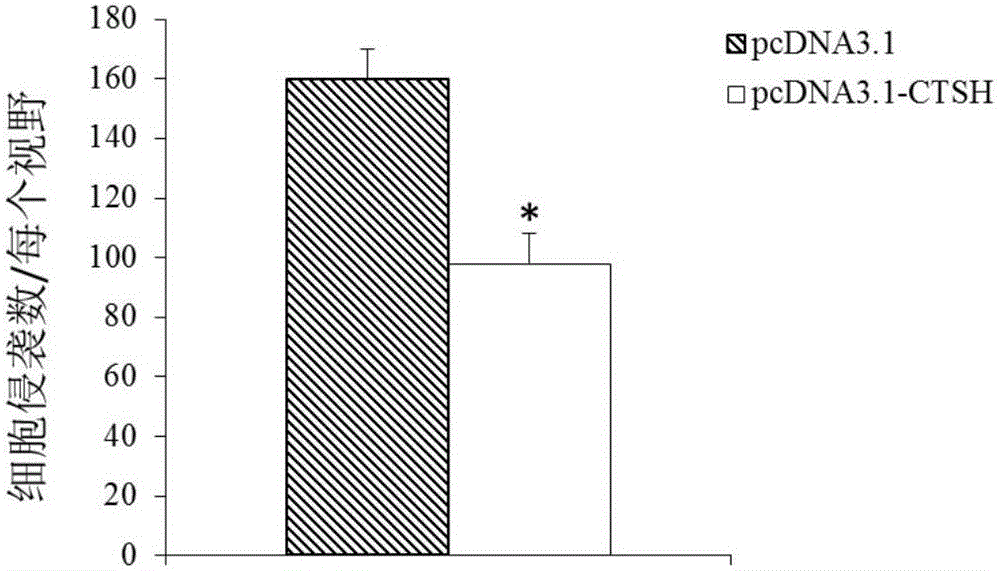
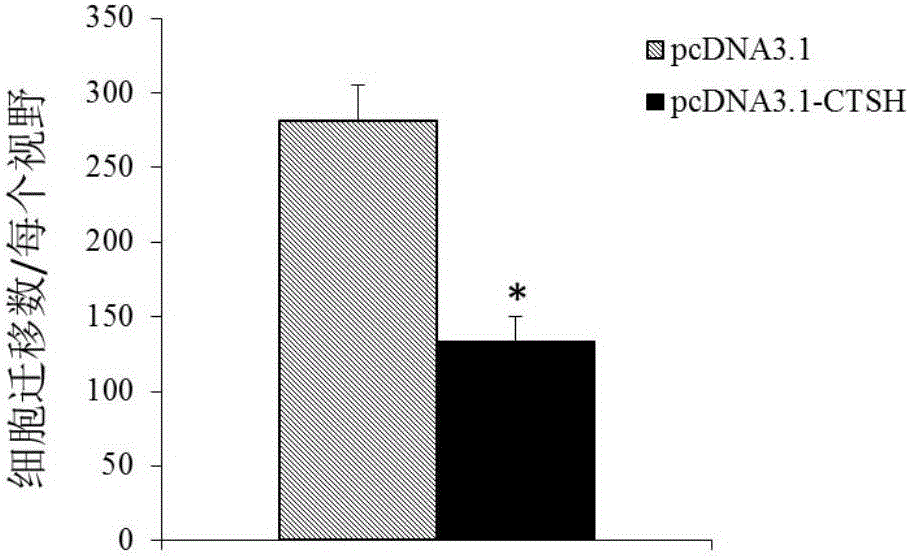
The invention discloses application of CTSH serving as a diagnosis and treatment marker of multiple myeloma. Accordingly, the CTSH can be used for developing products for diagnosing the multiple myeloma and drugs for treating the multiple myeloma. According to research results, a theoretical basis is provided for clinicians to establish individualized treatment plans, and a novel drug target can be provided for development of multiple myeloma drugs.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
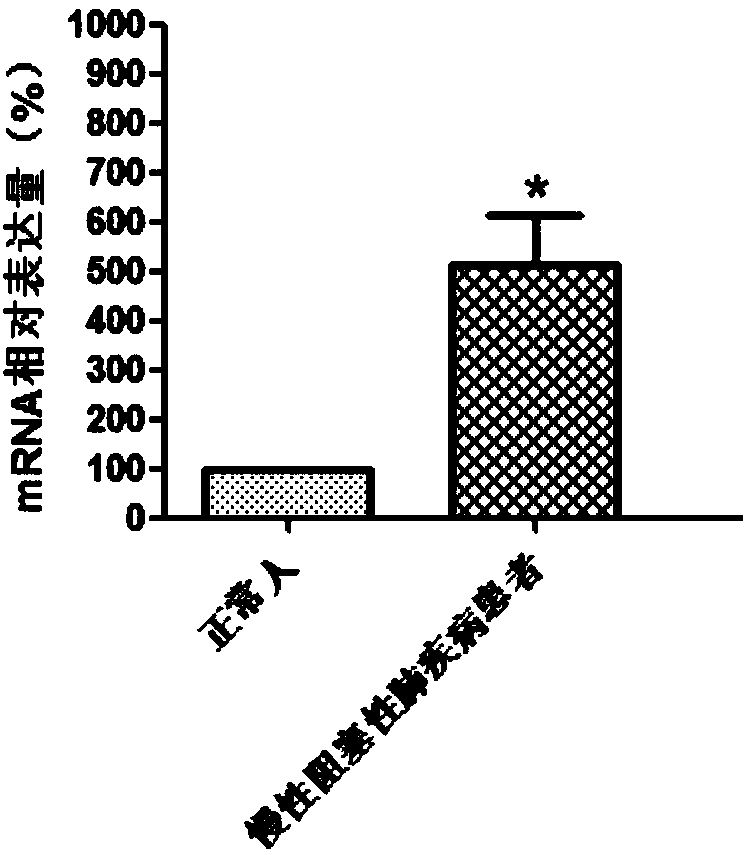
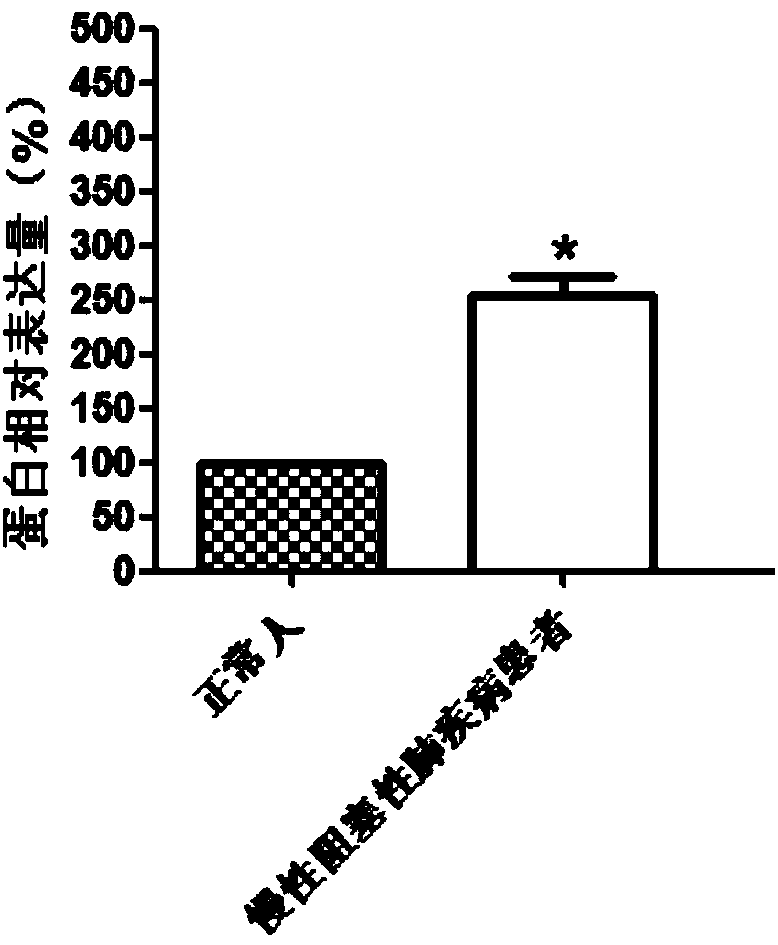
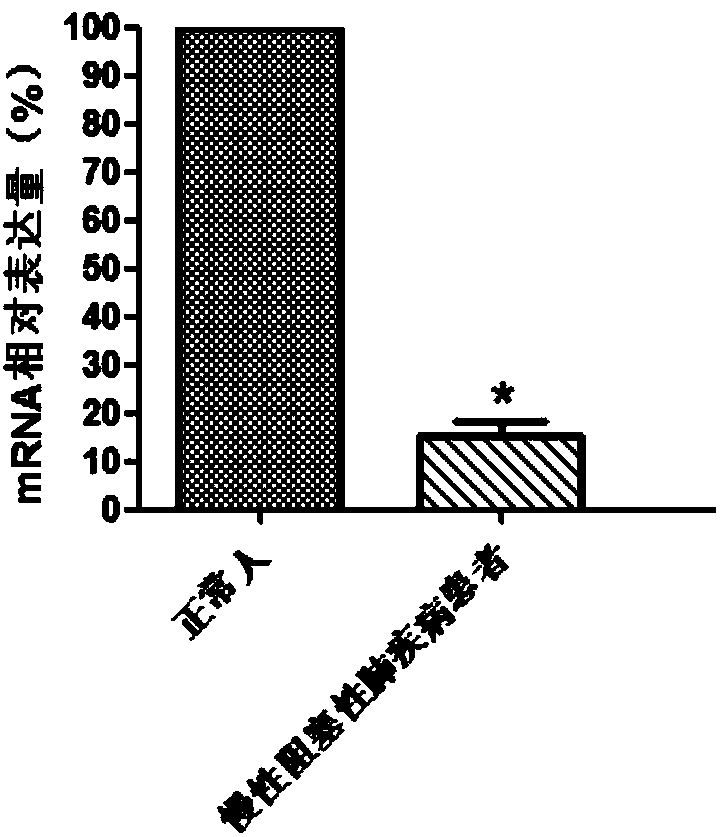
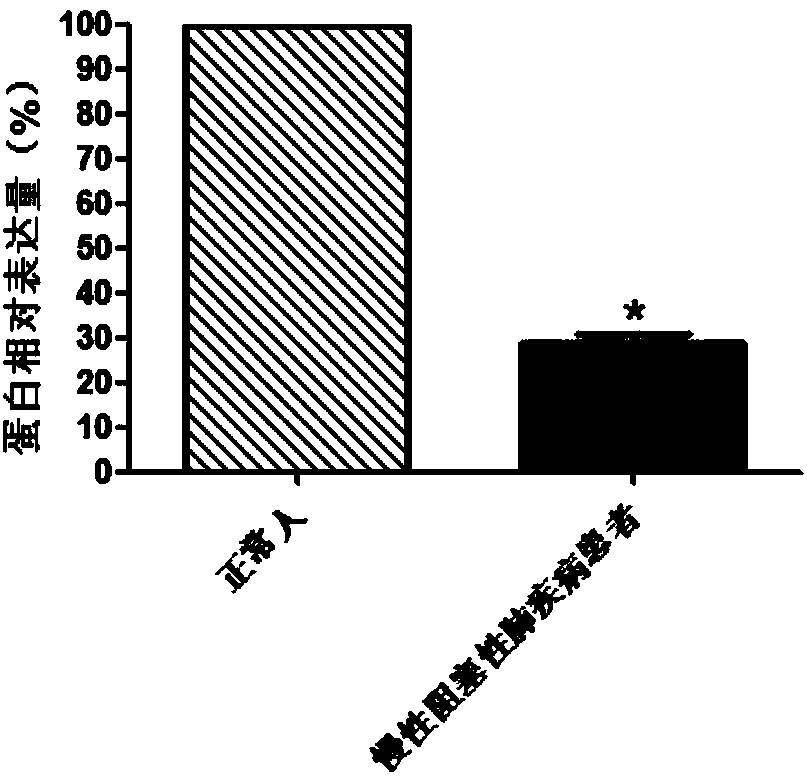
Molecular marker for diagnosing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveCN108303547AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisChronic obstructionPhysical therapy
The invention discloses a molecular marker for diagnosing a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The gene marker is a GMFG gene. Through detecting levels of the GMFG gene and GMFG proteins in bloodof a testee, whether the testee suffers from the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can be judged or whether the testee is at risk of the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can be judged. According to the GMFG gene and the GMFG proteins, a product for diagnosing the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through detecting the GMFG gene or the content of the GMFG proteins can be developed; thediagnostic product can be popularized and used in clinic.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
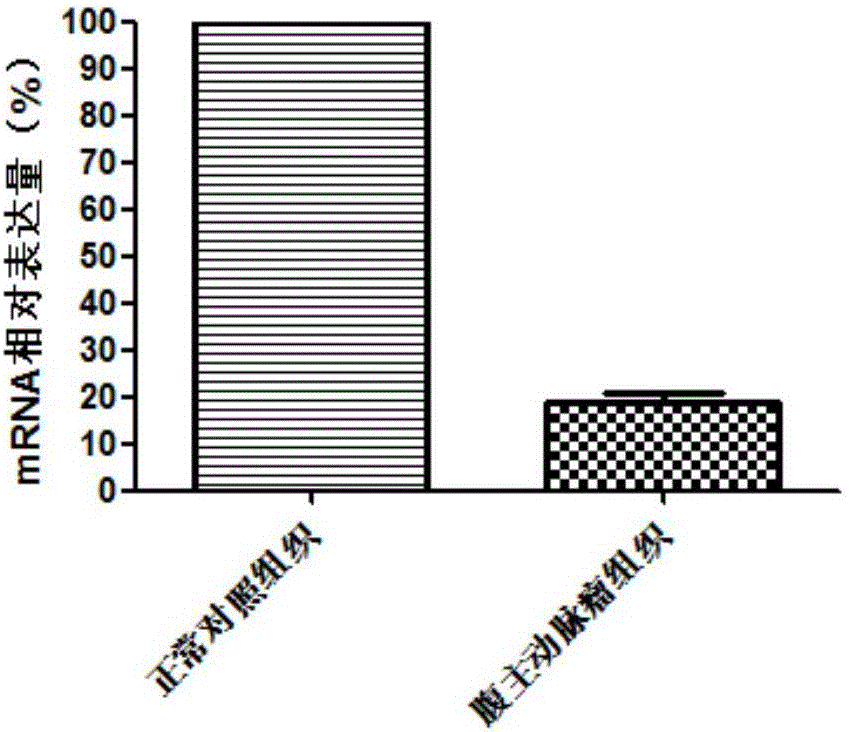
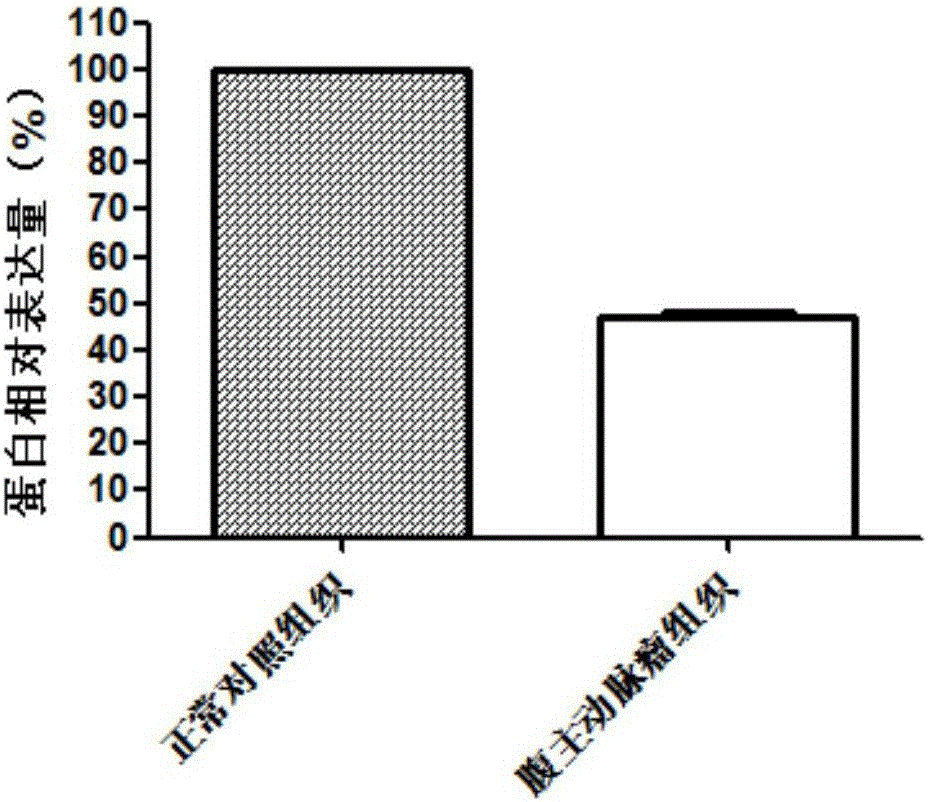
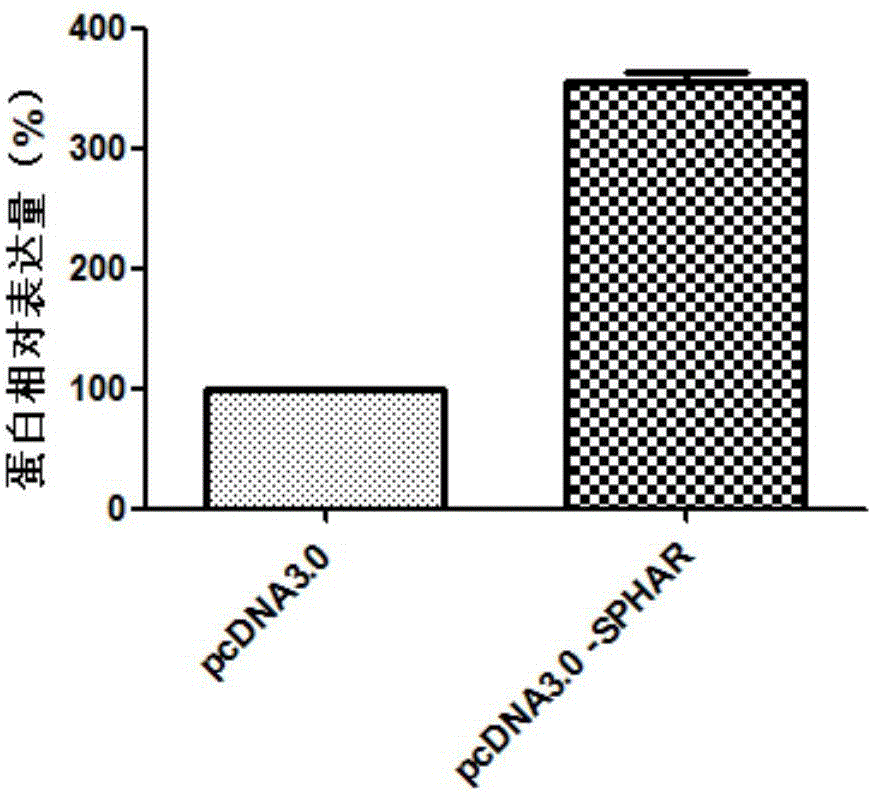
Application of SPHAR (S-phase response) as diagnosis and treatment target for abdominal aortic aneurysm
ActiveCN107177674AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingS phaseTreatment targets
The invention discloses application of SPHAR (S-phase response) as diagnosis and treatment marker for abdominal aortic aneurysm. SPHAR may be applied to the development of products for diagnosing abdominal aortic aneurysm and drugs for treating abdominal aortic aneurysm. From research findings herein, theoretical basis can be provided for clinicians to make personalized treatment schemes, and novel drug targets can be provided for the development of abdominal aortic aneurysm drugs.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
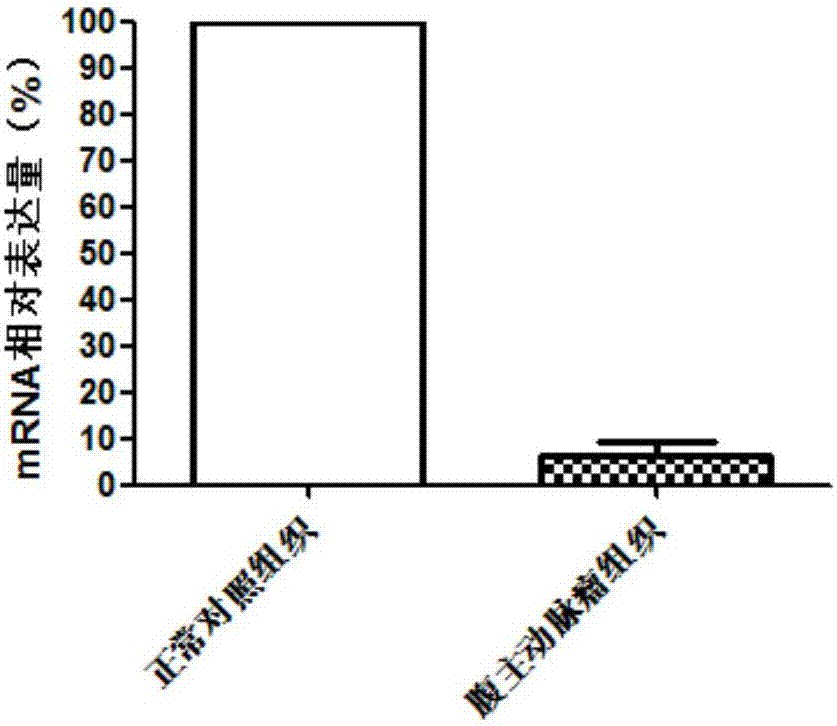
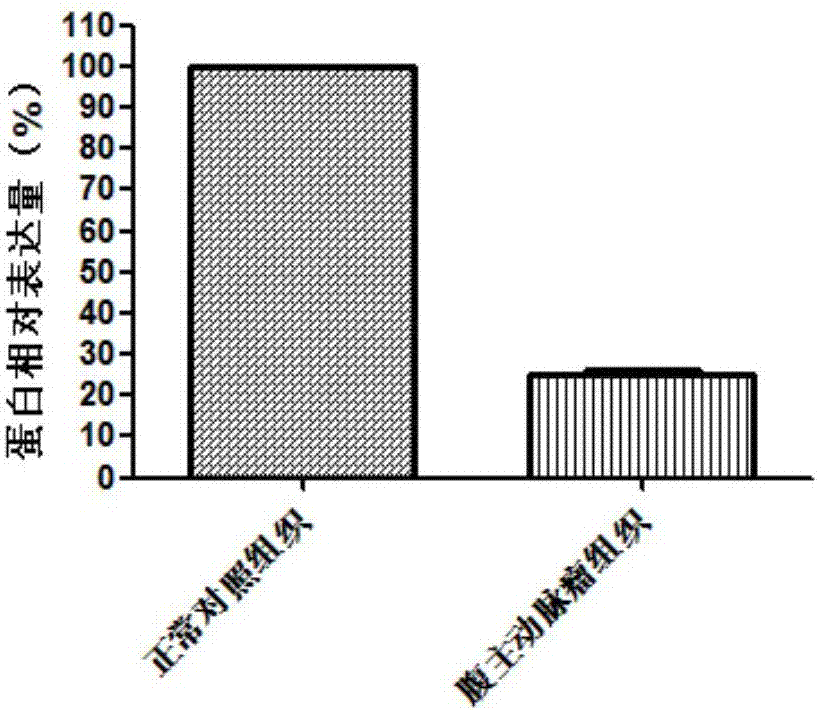
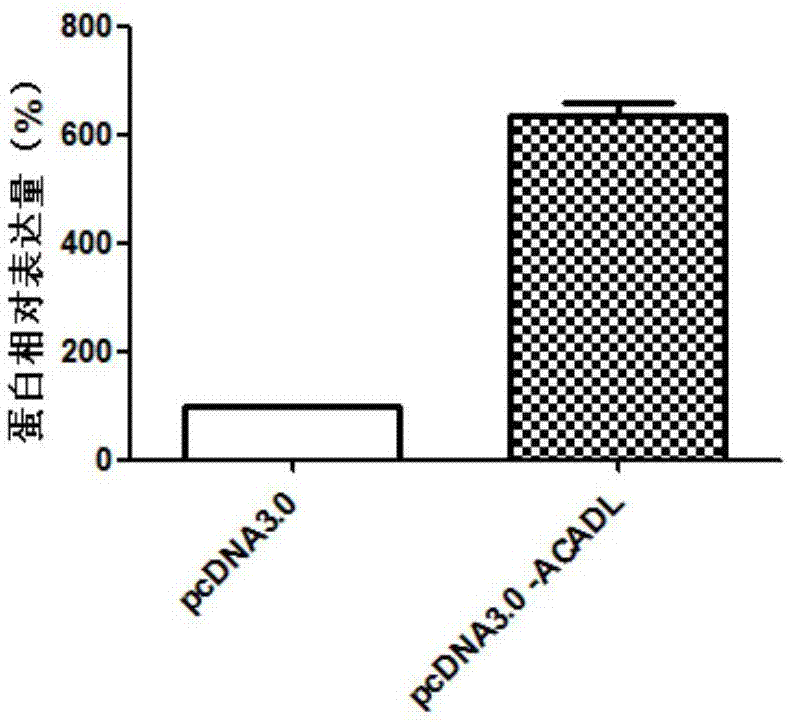
ACADL gene and application of expression product of ACADL gene to preparation of abdominal aortic aneurysm diagnosis and treatment product
ActiveCN107022635AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNormal tissuePoor correlation
The invention discloses an ACADL gene and application of an expression product of the ACADL gene to preparation of an abdominal aortic aneurysm diagnosis and treatment product. As proved by gene chip and QPCR (Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) experiments, compared with normal tissues, ACADL gene expression in abdominal aortic aneurysm tissues is different. A product for diagnosing abdominal aortic aneurysm is provided according to the relevance, and can be used for assisting in diagnosing the abdominal aortic aneurysm by detecting the level of the ACADL gene or the expression product of the ACADL gene in tissues. Moreover, the invention further provides an ACADL gene and an expression product of the ACADL gene, which can be taken as a target for developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm treating medicament in order to assist a clinician in making a personal treatment scheme.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
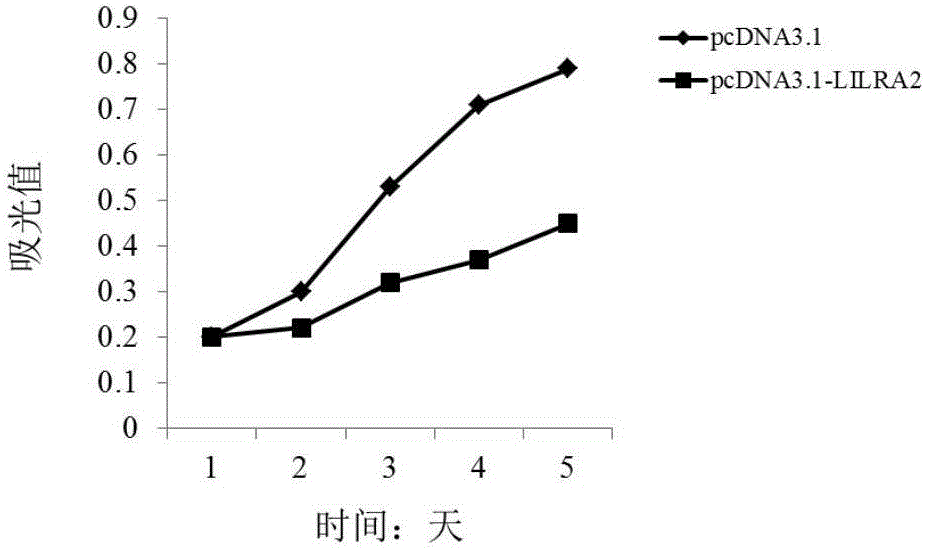
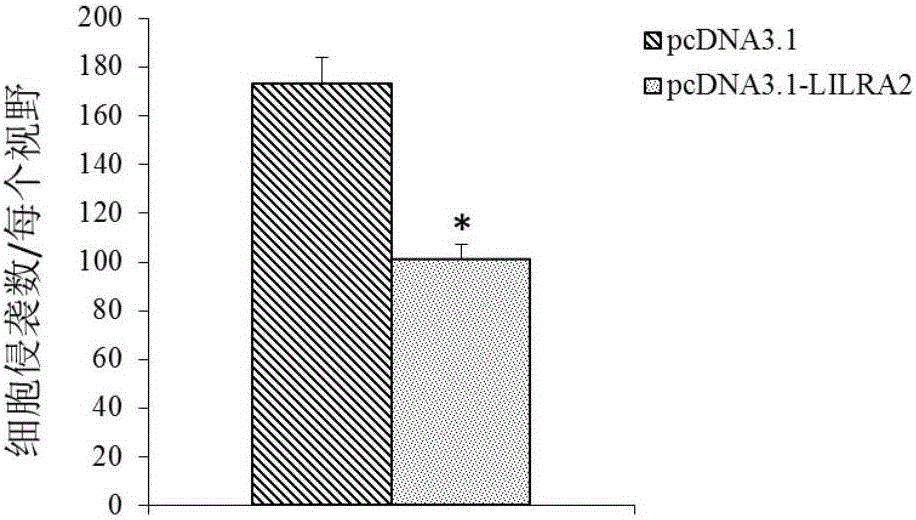
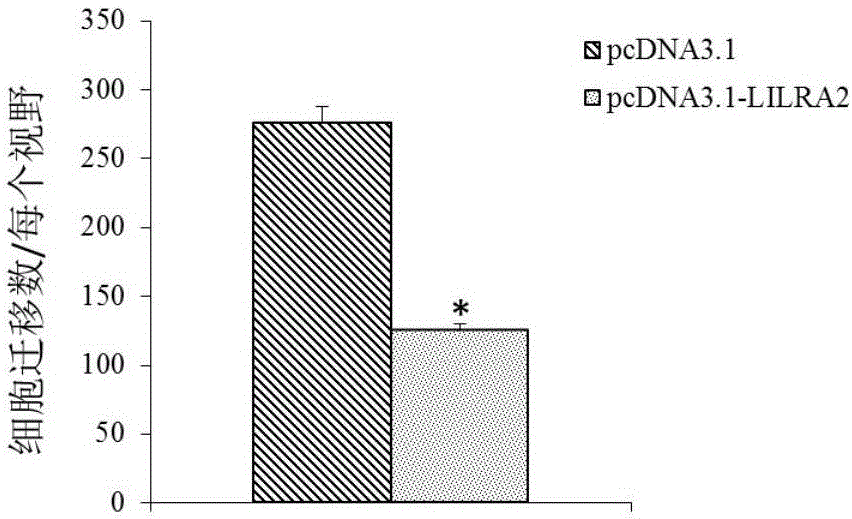
Application of LILRA2 gene and expression product thereof as diagnosis and treatment target of multiple myeloma
ActiveCN106011289AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseTreatment targets
The invention discloses application of an LILRA2 gene as a molecular marker for diagnosing multiple myeloma. Through adoption of a gene chip, a QPCR experiment shows that an LILRA2 gene expression product has significant difference between expression in normal myeloid tissue and expression in multiple myeloma tissue, namely the detection of expression condition of the LILRA2 gene in the myeloid tissue can be used for determining whether a tested person suffers from multiple myeloma or has the risk of suffering from multiple myeloma. A kit for diagnosing multiple myeloma is developed according to the relevance between the LILRA2 gene and the multiple myeloma; the kit can be applied to early diagnosis of diseases and has an extensive application prospect in clinic. In addition, the invention also discloses application of the LILRA2 gene as a molecular target for treating multiple myeloma and provides the basis for development work of medicines for treating multiple myeloma.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
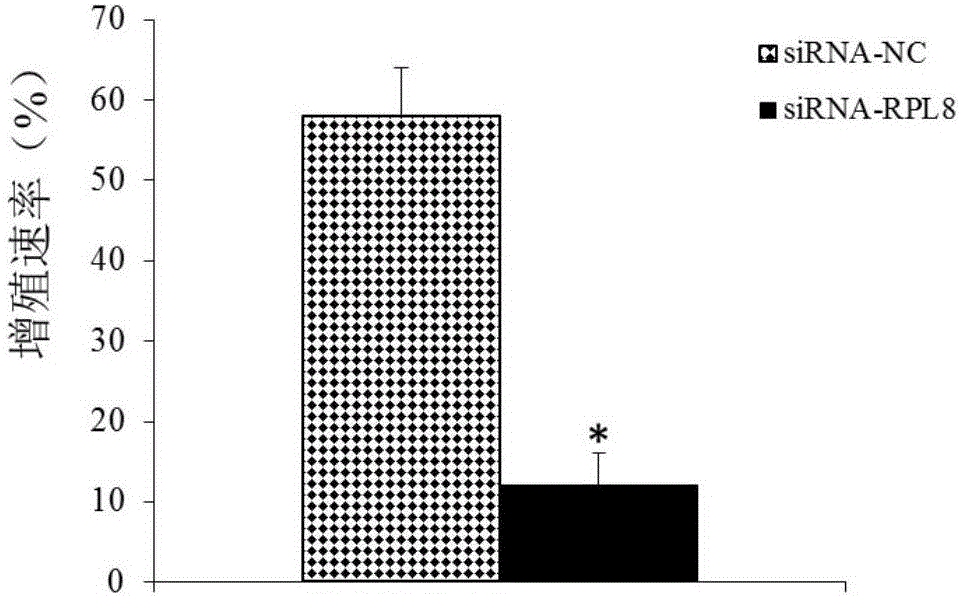
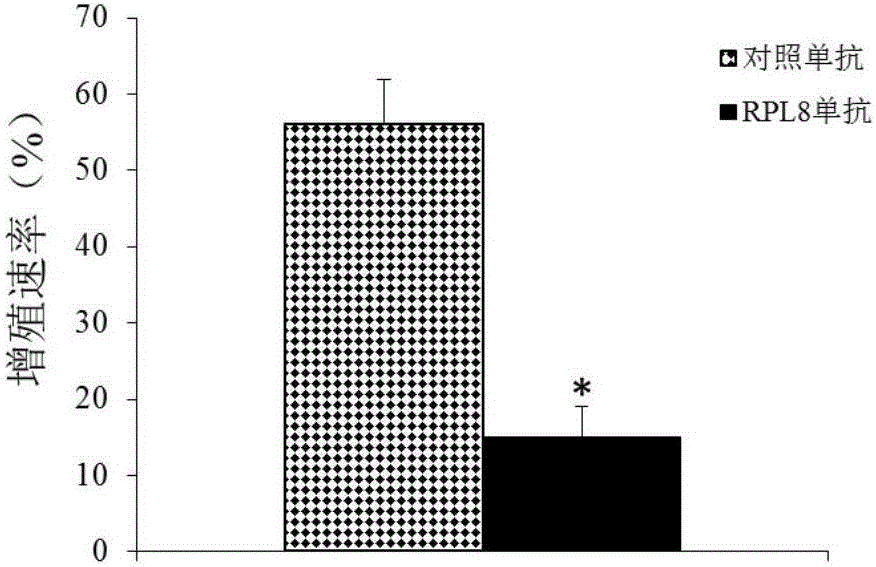
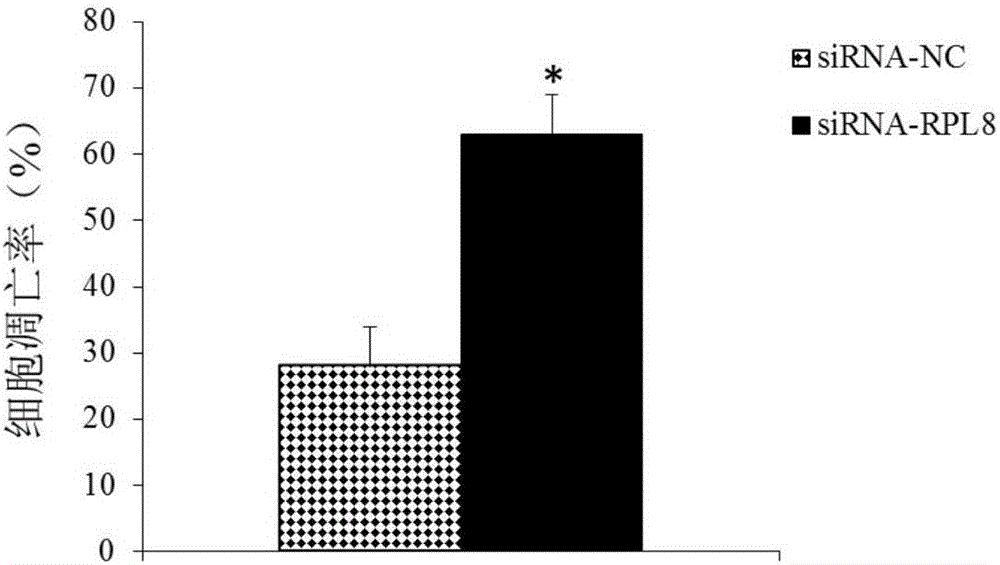
Application of RPL8 to preparation of tool for diagnosing or treating multiple myeloma
InactiveCN106011290AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDrugMultiple myeloma
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines and discloses application of an RPL8 gene as a diagnosis and treatment marker of multiple myeloma. Experiment proves that the RPL8 gene has significant difference between expression in normal myeloid tissue and expression in multiple myeloma tissue; accordingly, the RPL8 can be used for developing a product for diagnosing multiple myeloma. The invention also discloses application of the RPL8 gene as a treatment target of multiple myeloma. The research achievement provides the theoretical basis for clinicians to make personalized treatment plans, and can provide a novel medicine target for development of medicines for treating multiple myeloma.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
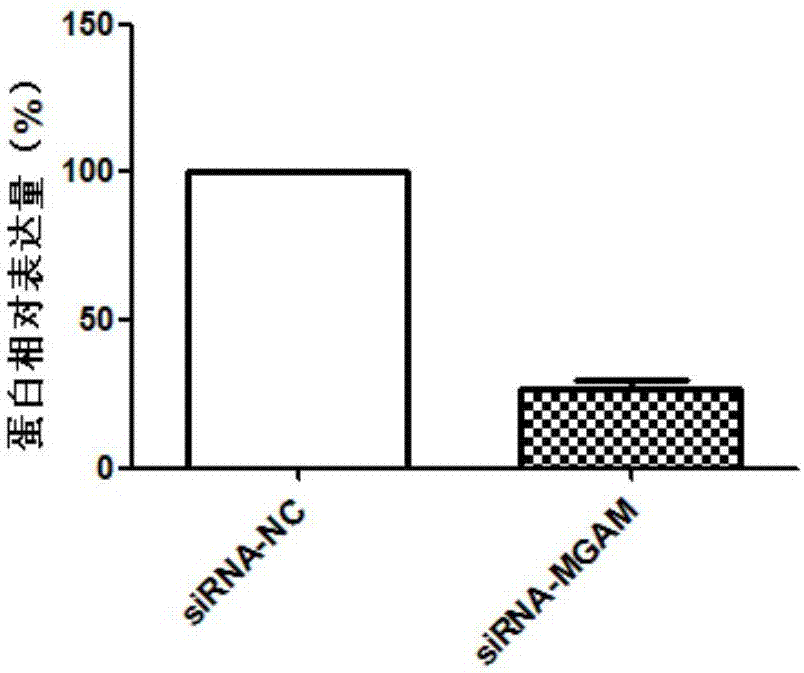
Biomarker for diagnosis and treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms
InactiveCN107012257AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSmooth muscleApoptosis
The invention discloses application of a MGAM gene as a biomarker for diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Experimental results in the invention prove that the expression of the MGAM gene in the tissue of abdominal aortic aneurysms substantially increases compared with the expression of the MGAM gene in normal control tissue; and interference experiment results prove that the MGAM gene can influence the apoptosis of human aortic smooth muscle cells. According to the research results of the invention, a drug capable of inhibiting the expression of the MGAM gene can be developed so as to prevent and treat the abdominal aortic aneurysms clinically.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
High-yield cultivation method of pterocephalus hookeri (C. B. Clarke) hoeck on eastern edge of Qinghai-Tibet plateau
InactiveCN102690149AImprove germination rateGreatly improves the survival rateFertilizer mixturesGreenhousePotassium
The invention belongs to the technical field of cultivation of Tibetan medicines and specifically discloses a high-yield cultivation method of pterocephalus hookeri (C. B. Clarke) hoeck on the eastern edge of Qinghai-Tibet plateau. The high-yield cultivation method comprises the step of processing seeds through hot water and a constant temperature box, the step of raising seedlings in a greenhouse, the step of land preparation and fertilization through palygorskite powder, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers and farmyard manure, the step of transplanting germchits and the step of field management. According to the high-yield cultivation method disclosed by the invention, the emergence rate and survival rate of the seedlings are high, the yield and the quality are also high, and the high-yield cultivation method can be popularized to the regions on the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau.
Owner:杨敬军 +3
Diagnosis and treatment product for multiple myeloma biomarker
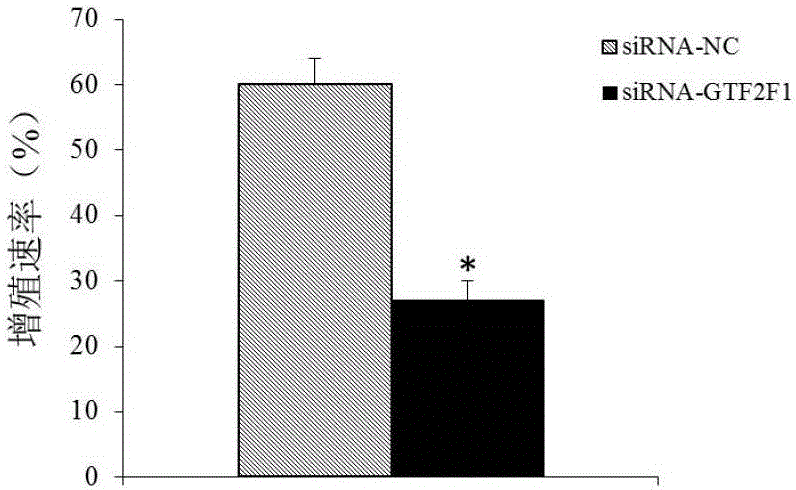
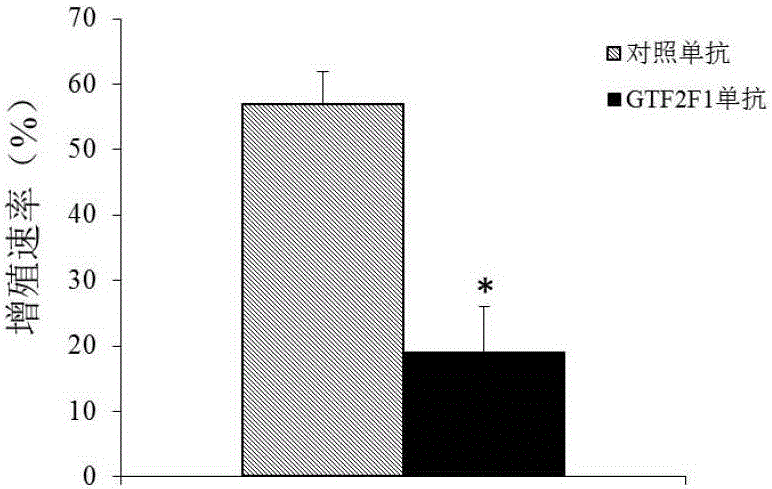
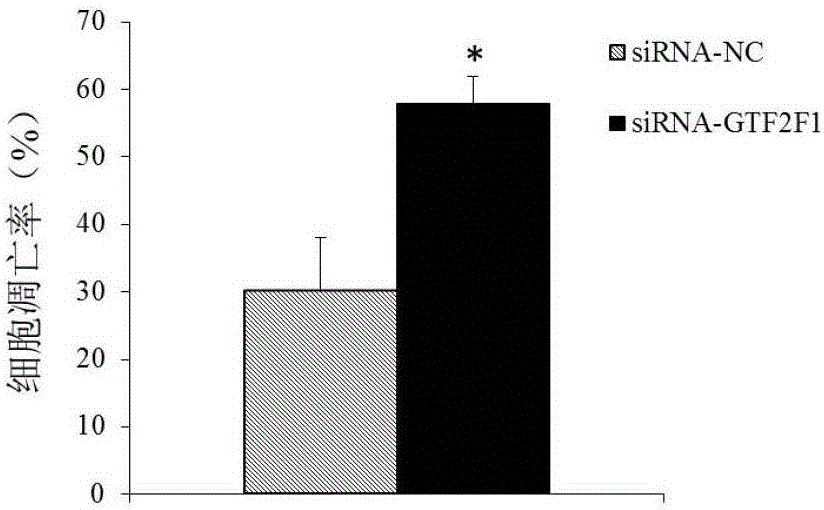
ActiveCN106191283AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMultiple myelomaGTF2F1 Gene
The invention discloses a GTF2F1 gene and an expression product thereof. The GTF2F1 gene and the expression product can be used as a molecular marker for multiple myeloma diagnosis and treatment. Whether a subject has multiple myeloma or has the risk of suffering the multiple myeloma or not can be determined by detecting the content of GTF2F1 gene and expression product thereof in myeloid tissues of the subject. Studies on proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of an in-vitro cultured multiple myeloma cell discover that, by inhibiting expression of the GTF2F1 gene, cell proliferation can be inhibited, cell apoptosis can be promoted, and cell migration can be inhibited. Studying results indicate that the GTF2F1 gene and the expression product thereof are a potential medicine target for multiple myeloma treatment.
Owner:GUAN BOJIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
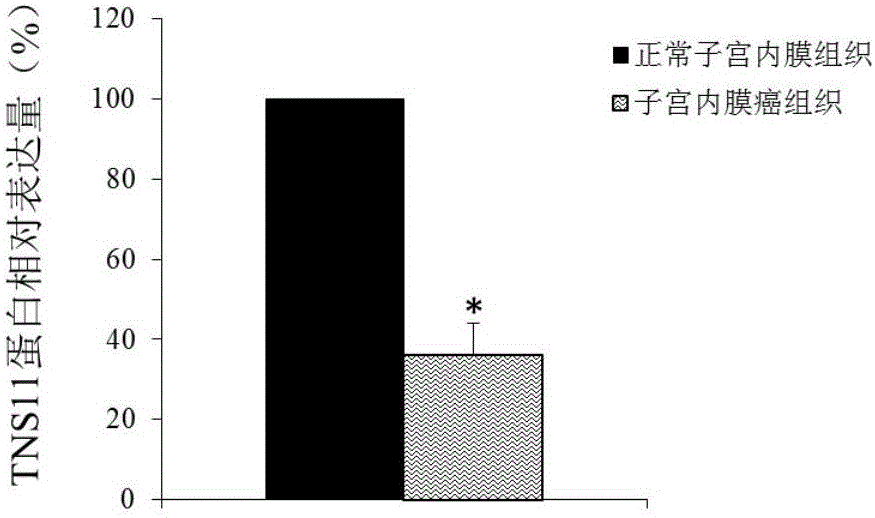
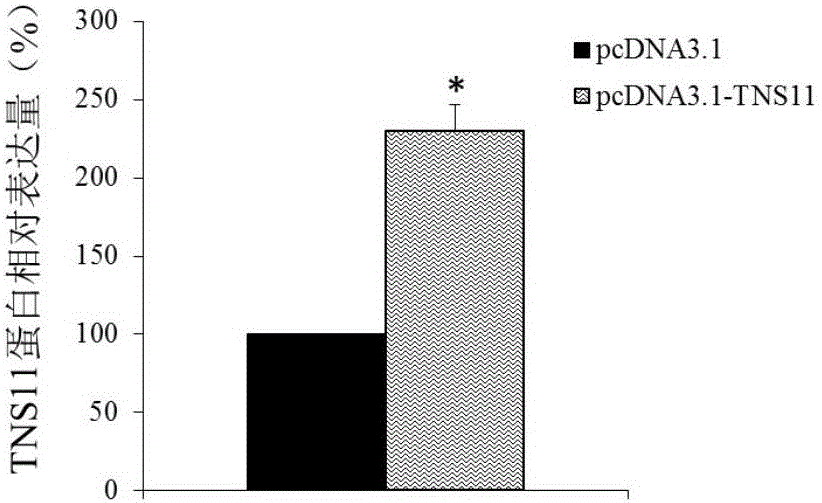
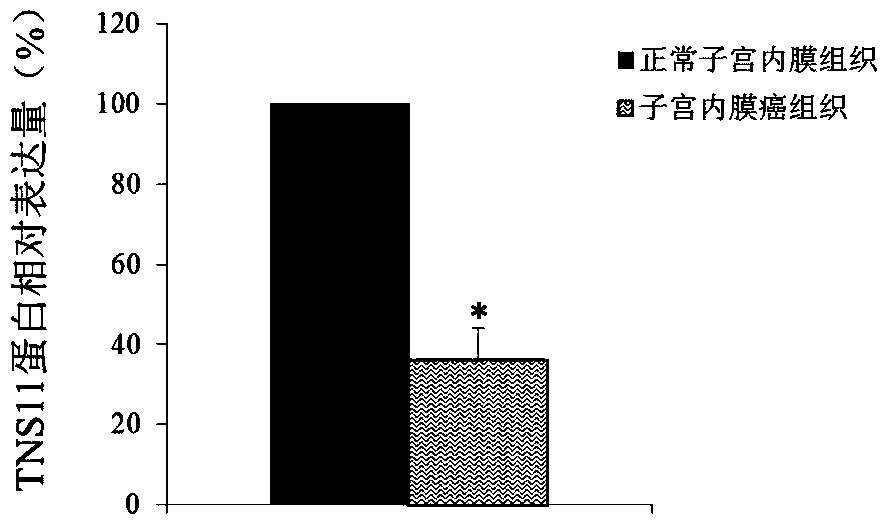
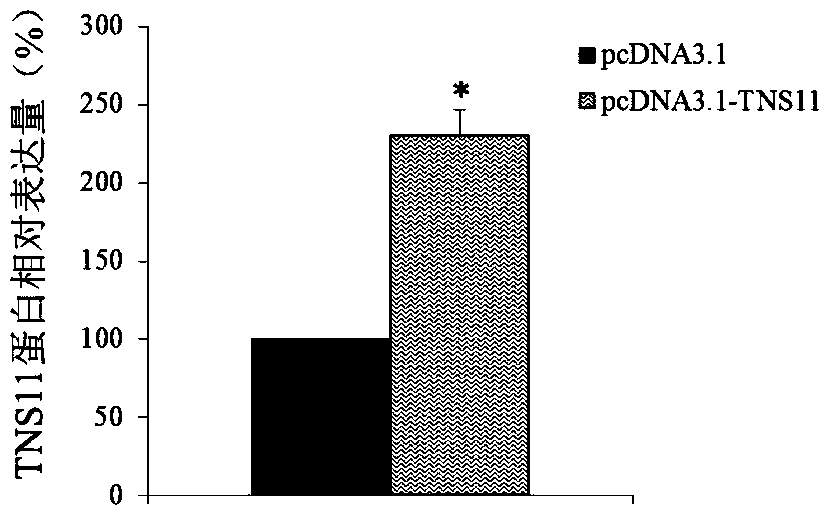
Application of TNS11 in preparing product for diagnosing and treating endometrial cancer
ActiveCN106119357AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGynecologyTreatment targets
The invention discloses a diagnosis and treatment target, namely TNS11 gene, for endometrial cancer. By detecting the contents of the TNS11 gene and expression products thereof, in the uterus tissue of a tested object, it can judge whether the tested object is affected by the endometrial cancer or not or it can diagnose whether the risk of the endometrial cancer exists in the tested object or not. In addition, by conducting researches on the proliferation and migration indexes of endometrial cancer cells which are cultured in vitro, it proves that the TNS11 gene can serve as a drug target for treating the endometrial cancer.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
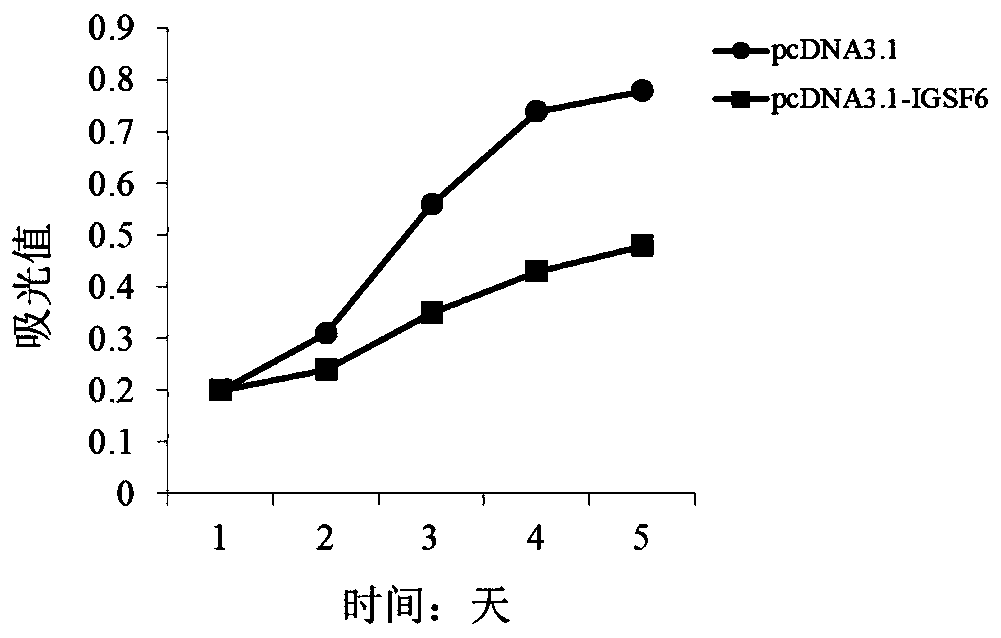
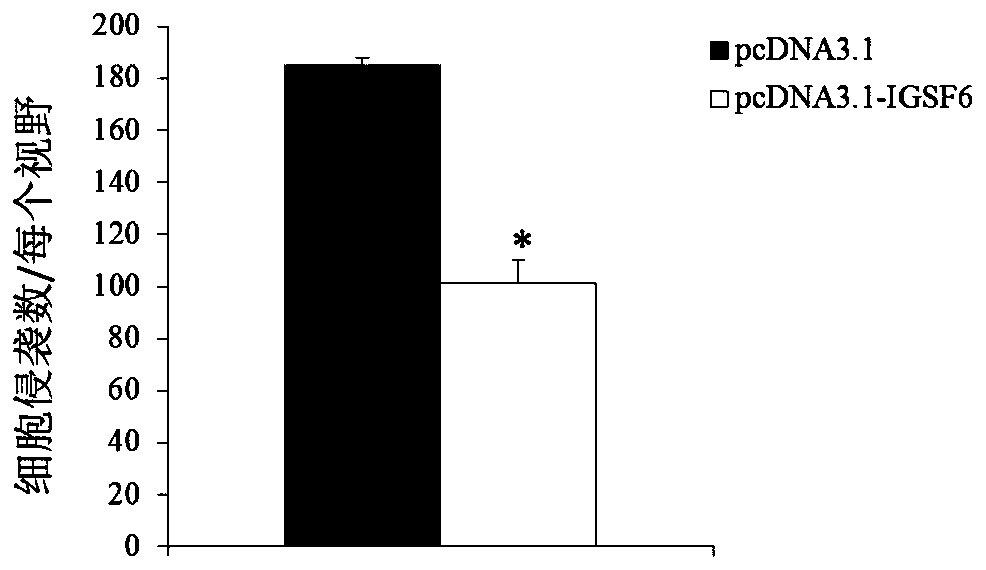
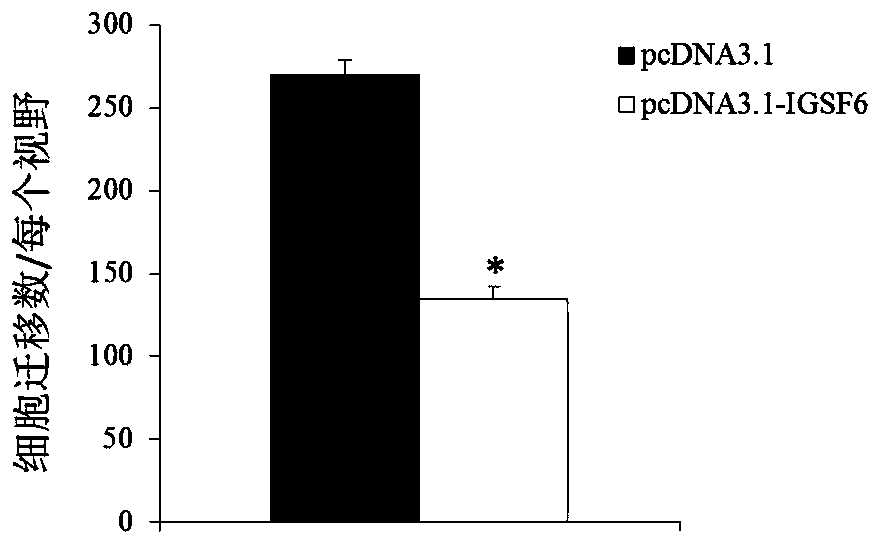
Application of igsf6 in preparation of products for diagnosis and treatment of multiple myeloma
ActiveCN106222257BProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTreatment targetsCultured cell
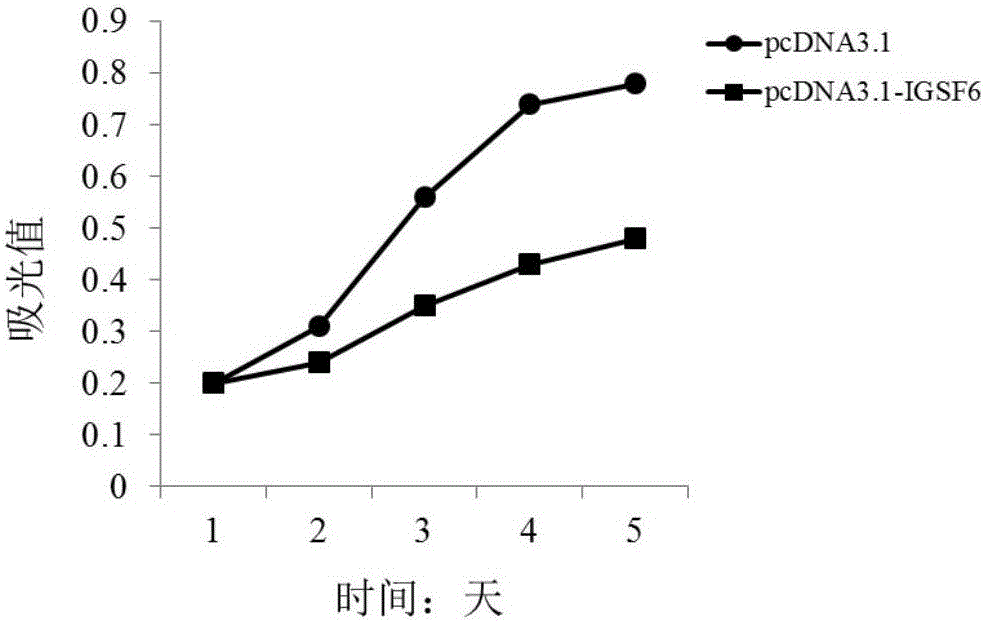
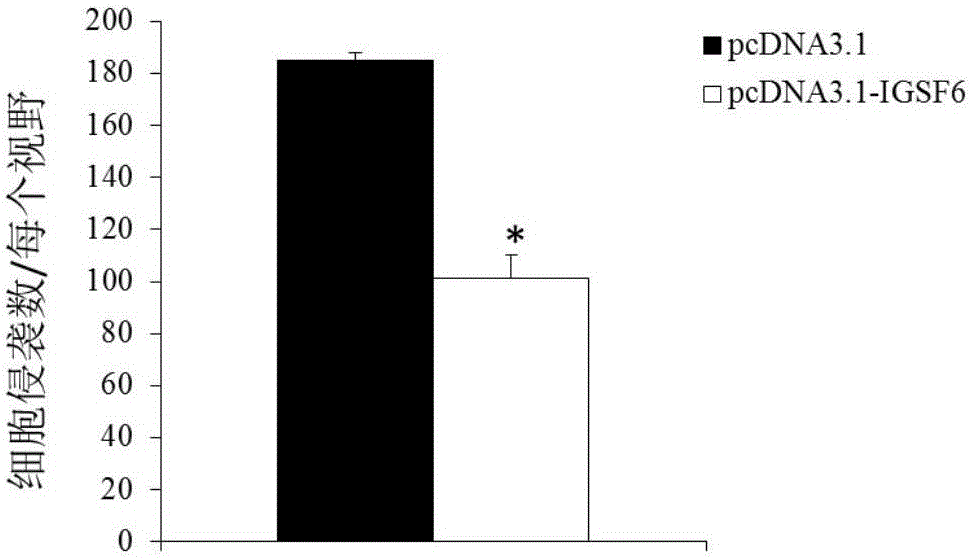
The invention discloses a diagnosis and treatment target-IGSF6 gene for the multiple myeloma. By detecting the content of the IGSF6 gene and expression products of the IGSF6 gene in myeloid tissue of a testee, whether the testee suffers from the multiple myeloma or not can be judged or whether the testee bears a risk of suffering from the multiple myeloma or not can be diagnosed. In addition, by studying the proliferation, migration and invasion indexes of in-vitro cultured cells of the multiple myeloma, it is proved that the IGSF6 gene serves as a medicine target for treating the multiple myeloma.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
SHISA4 serving as biomarker for early diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveCN108034718AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiagnosis earlyMedicine
The invention discloses an SHISA4 gene serving as a diagnosis tool for a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. High-throughput sequencing and QPCR (Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) researchesfind out that the content of the SHISA4 gene in blood of a patient with the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is remarkably reduced when being compared with the content in a normal person; a western blot experiment proves that the content of SHISA4 protein in the blood of the patient with the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is remarkably reduced when being compared with the content in the normal person. Therefore, the SHISA4 gene and the SHISA4 protein can be used as biomarkers for diagnosing the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A method for characterizing the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by utilizing the content of the gene or the protein in the blood has the following advantages that tissue sampling detection is avoided and pains of subjects are alleviated; meanwhile, the characterizing method can be used for screening healthy people and the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is effectively prevented.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Diagnostic marker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma-c16orf74 gene
ActiveCN108531607BProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisRenal clear cell carcinomaBiomarker (petroleum)
The invention discloses a C16orf74 gene which can be taken as a biomarker for the renal clear cell carcinoma. The experiment proves that compared with normal nephridial tissues, the C16orf74 gene expression in renal clear cell carcinoma tissues is significantly improved. According to the research result, the C16orf74 gene can be applied to research and development of a kit used for diagnosing therenal clear cell carcinoma and also can be used for researching and developing medicines capable of inhibiting the C16orf74 gene expression, thereby achieving clinical prevention and treatment for therenal clear cell carcinoma.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
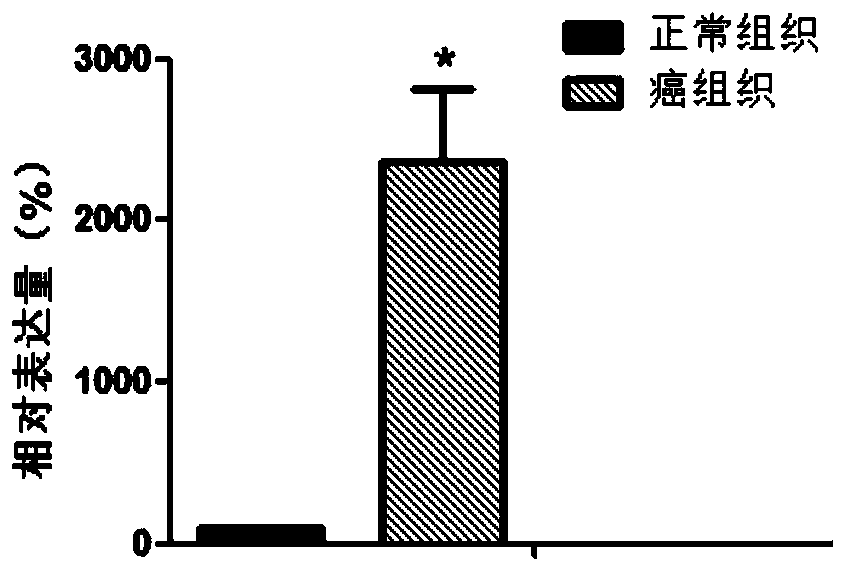
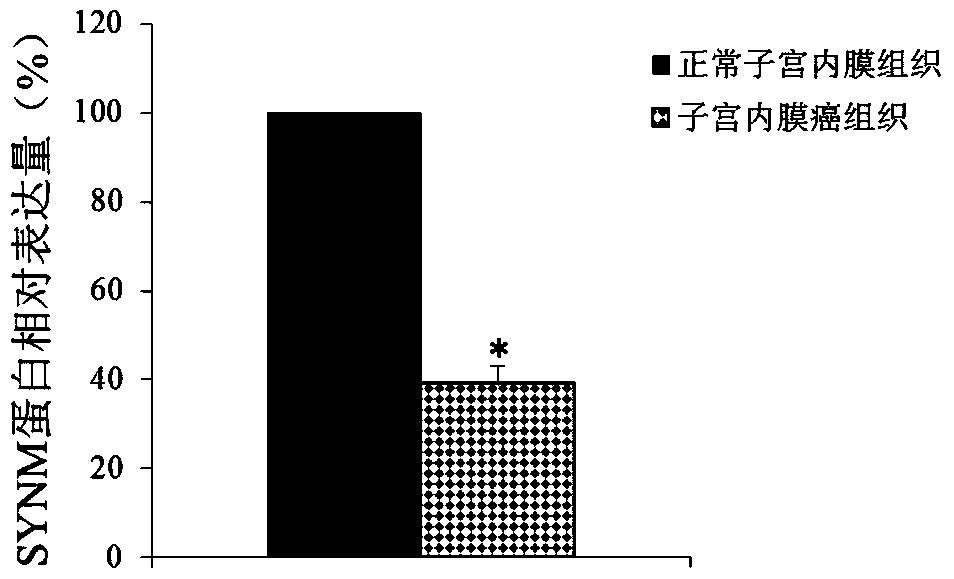
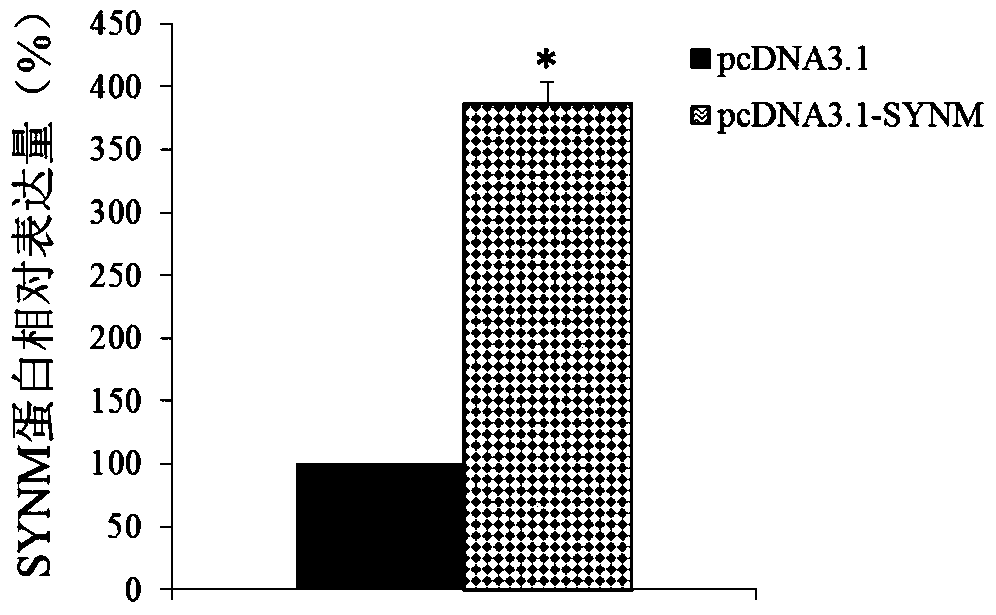
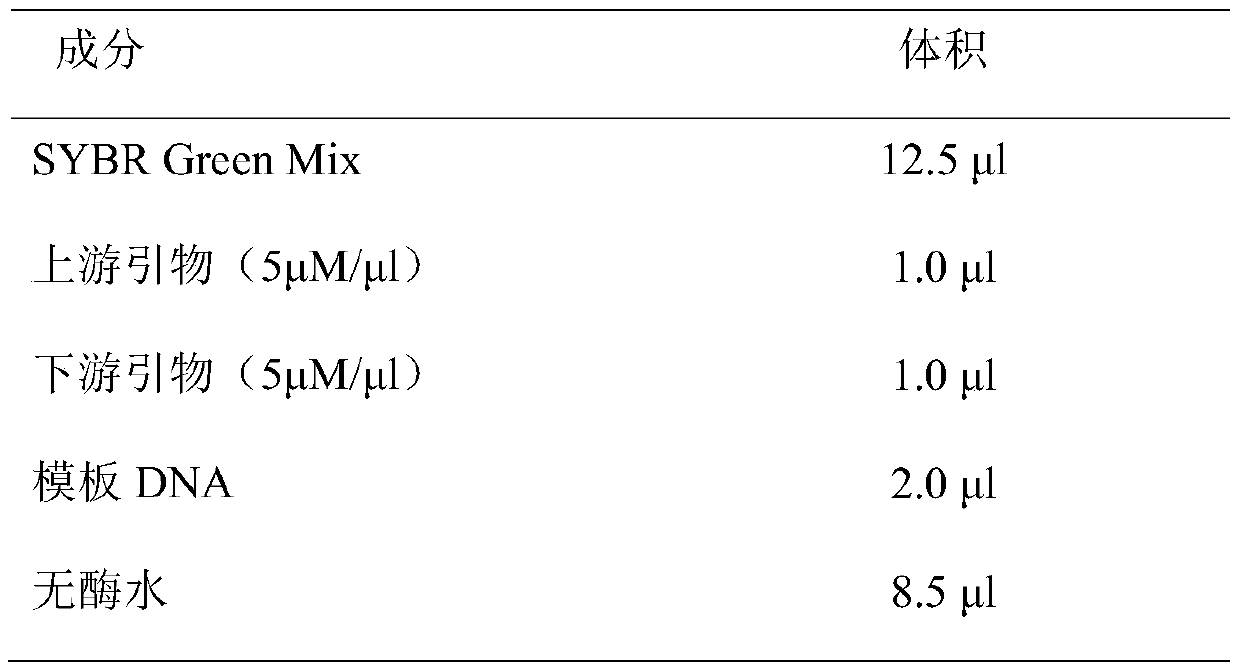
Application of synm in preparation of tools for diagnosing or treating endometrial cancer
ActiveCN106048031BProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGynecologyEndometrial cancer
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines and discloses application of SYNM in preparation of tool for diagnosing or treating endometrial cancer. Experiments prove that the expressions of an SYNM gene in a normal endometrial tissue and an endometrial cancer tissue are significantly different, so that the SYNM can be used for developing products for diagnosing the endometrial cancer. The invention further discloses the SYNM gene which can be taken as a treatment target of the endometrial cancer. According to the research results of the invention, theoretical basis can be provided for clinicians to formulate individual-based treatment scheme, and a new drug target can be provided for the development of medicines for the endometrial cancer.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Application of IGSF6 to preparing multiple myeloma diagnosis and treatment products
ActiveCN106222257AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTreatment targetsCultured cell
The invention discloses a diagnosis and treatment target-IGSF6 gene for the multiple myeloma. By detecting the content of the IGSF6 gene and expression products of the IGSF6 gene in myeloid tissue of a testee, whether the testee suffers from the multiple myeloma or not can be judged or whether the testee bears a risk of suffering from the multiple myeloma or not can be diagnosed. In addition, by studying the proliferation, migration and invasion indexes of in-vitro cultured cells of the multiple myeloma, it is proved that the IGSF6 gene serves as a medicine target for treating the multiple myeloma.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Diagnostic application of MYOM2
ActiveCN106435011AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTest objectGene
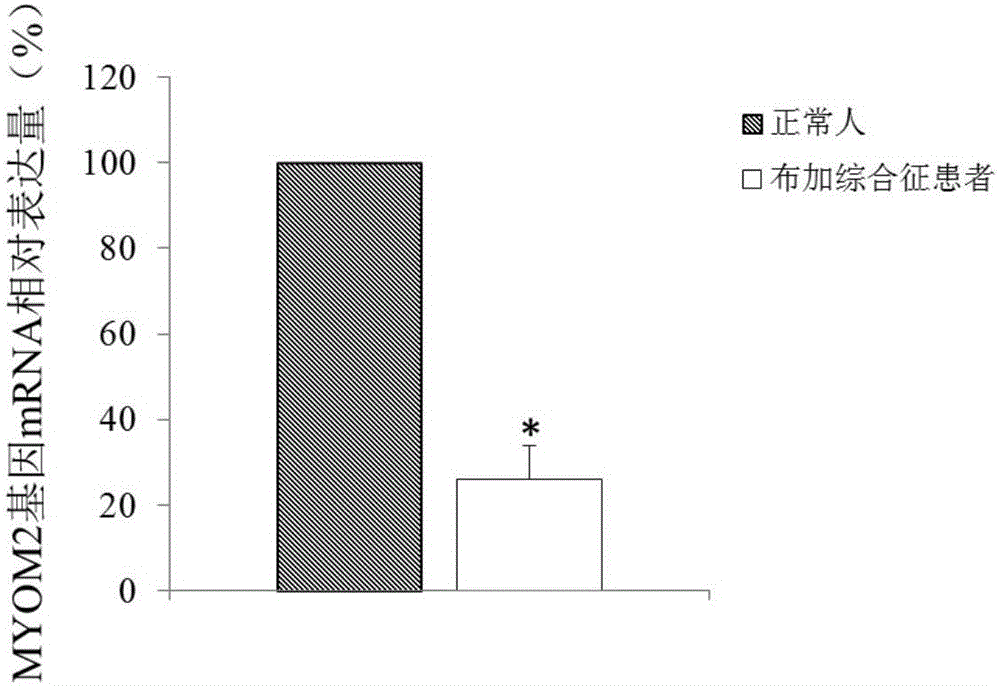
The invention discloses application of MYOM2 to the preparation of a diagnostic tool for the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Through detection, in the blood of a patient suffered from the Budd-Chiari syndrome, the expression of an MYOM2 gene is obviously lowered; the Budd-Chiari syndrome can be diagnosed through detecting the expression of the MYOM2 gene. According to a diagnostic method provided by the invention, the blood of a testee is used as a to-be-tested object; the pain of biopsy carried out on the testee is avoided; therefore, the diagnostic application of the MYOM2 can be suitable for being clinically widely applied.
Owner:北京微未来科技有限公司
Use of ms4a6a as a marker for diagnosis and treatment of multiple myeloma
ActiveCN105969901BProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMolecular levelDrug target
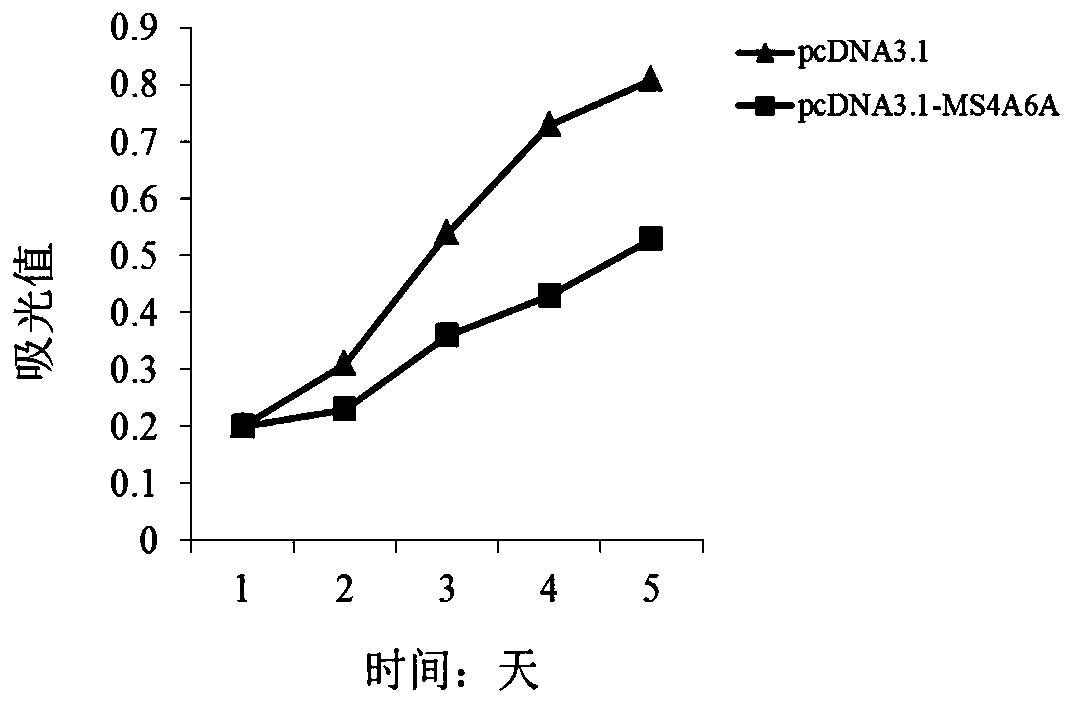
The invention discloses a genetic marker, namely, MS4A6A. The MS4A6A can be used for judging whether a subject has a risk of suffering from multiple myeloma or not or judging whether the subject suffers from the multiple myeloma. In additions, the MS4A6A can also be used for preparing drugs for treating the multiple myeloma. According to the MS4A6A, a novel diagnostic method is provided for diagnosing the multiple myeloma at the molecular level clinically, and meanwhile a novel drug target is provided for a gene therapy of the multiple myeloma.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Application of tns11 in preparation of products for diagnosis and treatment of endometrial cancer
ActiveCN106119357BProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTreatment targetsUterus
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
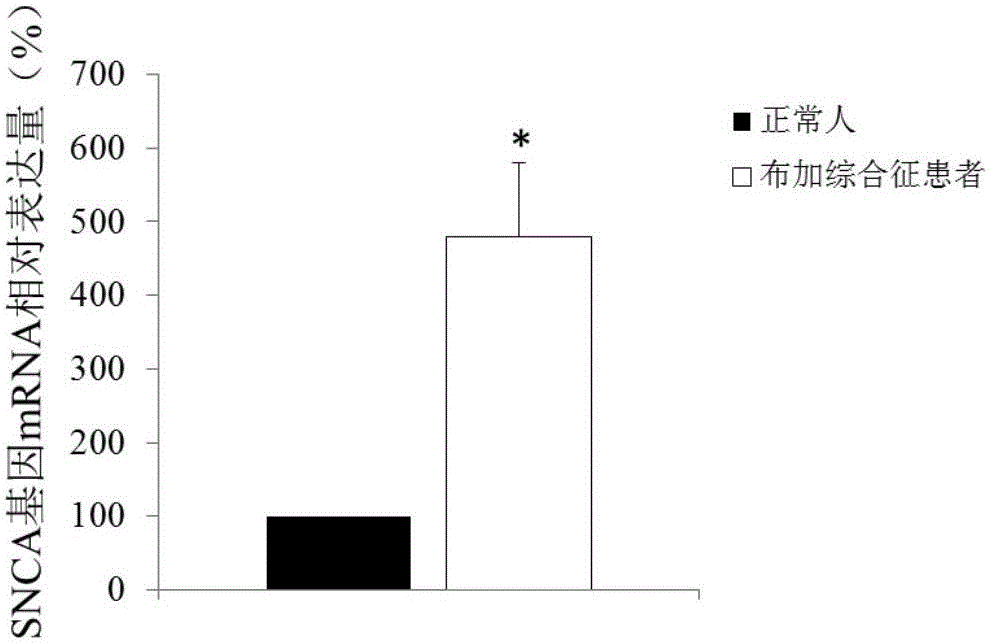
Budd-Chiari syndrome diagnosis marker
ActiveCN106435010AProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAlpha-synucleinBudd–Chiari syndrome
The invention discloses Budd-Chiari syndrome diagnosis marker-SNCA (Alpha-synuclein) gene; by detecting SNCA gene expression product content in blood of a subject, it is possible to judge whether the subject suffers from Budd-Chiari syndrome, or diagnose whether the subject has the risk of suffering from Budd-Chiari syndrome, or judge whether subject experiences recurrence or judge prognosis conditions of the subject. Based on research results of the invention, the invention also discloses a kit for diagnosing Budd-Chiari syndrome, the kit is suitable for the diagnosis of early Budd-Chiari syndrome and is easy to popularize and use clinically.
Owner:北京微未来科技有限公司
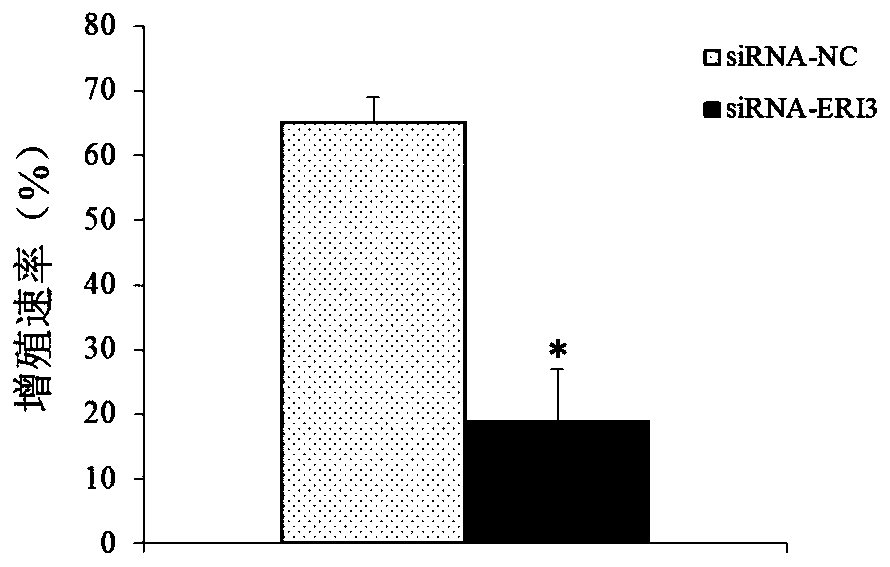
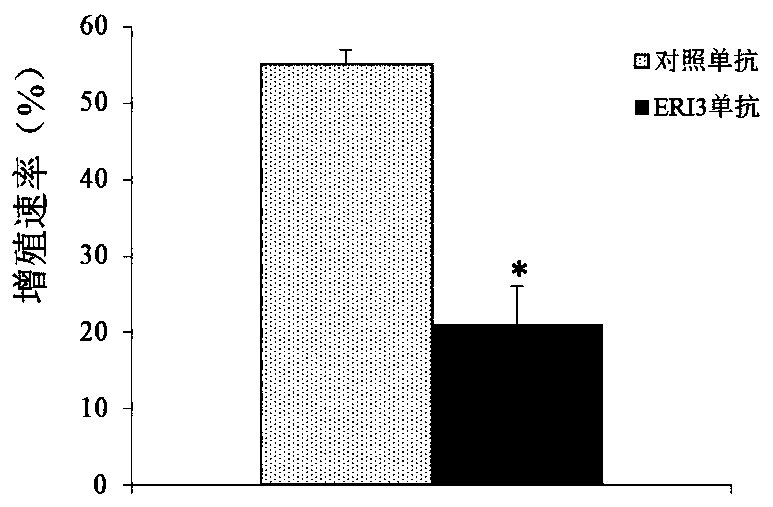
Multiple myeloma diagnosis and treatment markers and their application
ActiveCN106011288BProvide survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiagnosis methodsCancer research
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and discloses an ERI3 gene and new use of a code thereof. Studies prove that the ERI3 gene and encoded protein thereof not only can be taken as a molecular marker for diagnosing the multiple myeloma, but also can be used as a molecular target for treating the multiple myeloma. Based on the study results, the invention provides a new diagnosis method and treatment means for clinically.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com