Novel preparation method of amorphous alloy catalyst
A technology of amorphous alloy and catalyst, which is applied in the field of preparation of amorphous alloy catalyst, can solve the problems of poor repeatability, high preparation cost, low yield of amorphous alloy catalyst and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~19
[0029] These examples illustrate the preparation of unsupported NiB amorphous alloy catalysts.
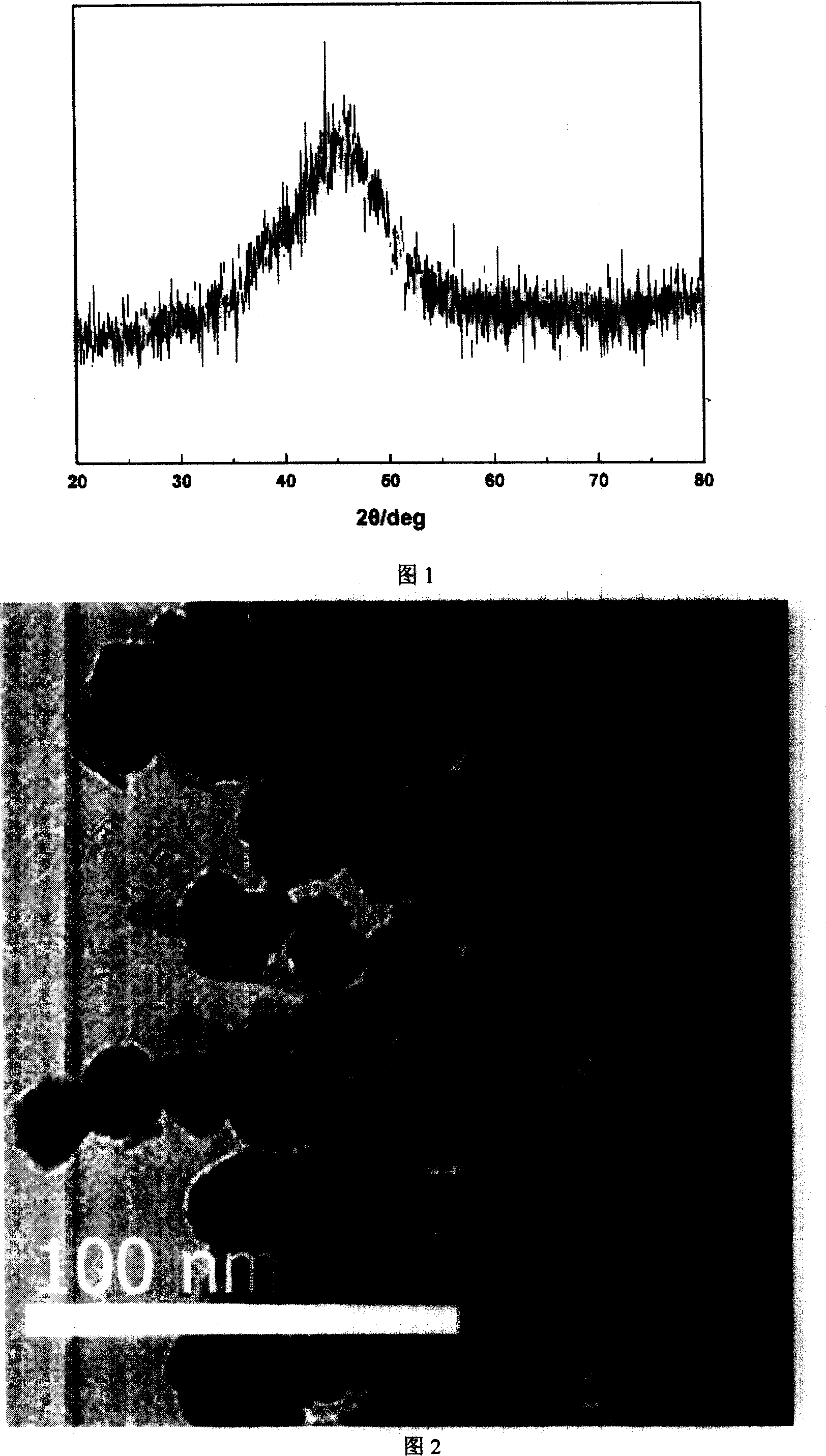
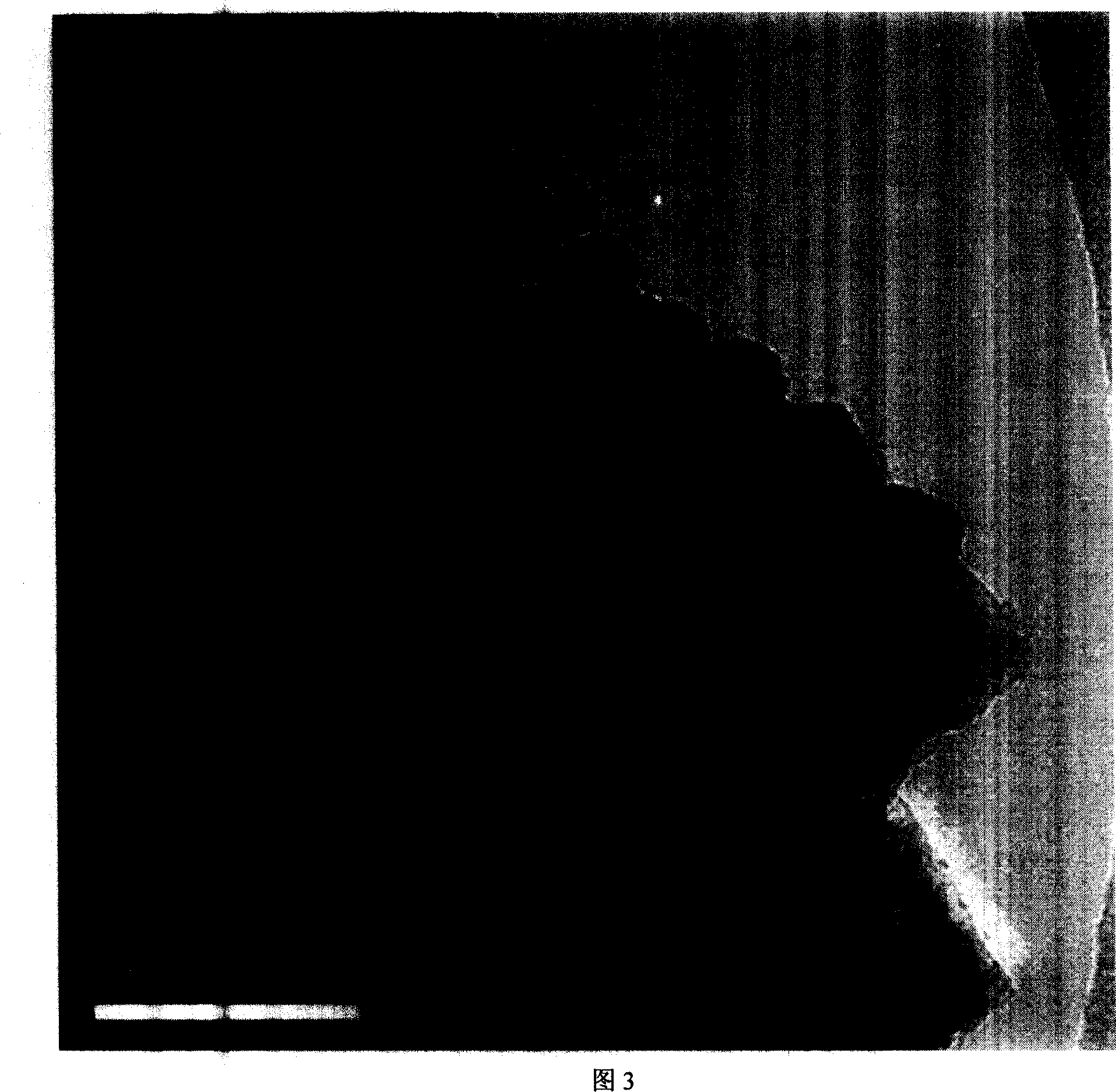
[0030] Configure three parts of mixed solutions of 0.1mol / L nickel sulfate and ethylenediamine respectively, A1 is Ni: ethylenediamine=1:0.5, A2 is Ni:ethylenediamine=1:1.5, A3 is Ni:ethylenediamine= 1:2.0, then add NaOH to adjust the pH to 12.0, 13.2 and 13.9 respectively, add KBH 4solution (B:Ni=2.0, atomic ratio), adding AgNO at 60 °C 3 solution (Ag accounts for 1% by weight of the catalyst), stirred and reacted until no bubbles are generated; after the catalyst is washed to be neutral, it can be stored in water or in ethanol. The XRD of samples A1-A3 have the characteristics of FIG. 1 . The TEM image of sample A2 has the characteristics of FIG. 2 .
[0031] Same as the preparation process of catalyst A1, change the main salt of nickel sulfate to nickel nitrate, nickel chloride and nickel acetate and keep the metal salt concentration constant to obtain catalysts A4-A6.
[00...
Embodiment 20~34
[0039] These examples illustrate the preparation of unsupported CoB amorphous alloy catalysts.
[0040] Configure three parts of mixed solutions of 0.1mol / L cobalt chloride and potassium sodium tartrate respectively, B1 is Co: potassium sodium tartrate=1:0.1, B2 is Ni: potassium sodium tartrate=1:1.0, B3 is Ni: potassium sodium tartrate =1:2.0, then add NaOH to adjust the pH to 13.0, 13.5 and 13.9 respectively, add KBH 4 solution (B:Co=2.0, atomic ratio), adding AgNO at 50 °C 3 solution (Ag accounts for 1% by weight of the catalyst), stirred and reacted until no bubbles are generated; after the catalyst is washed to be neutral, it can be stored in water or in ethanol. The XRDs of samples B1-B3 have the characteristics of FIG. 1 .
[0041] Same as the preparation process of the catalyst B2, the main salt cobalt chloride was changed to cobalt sulfate to obtain the catalyst B4.
[0042] Same as the preparation process of catalyst B2, potassium sodium tartrate was changed into ...
Embodiment 35~49
[0049] These examples illustrate the preparation of unsupported NiCoB amorphous alloy catalysts.
[0050] Dissolve the soluble nickel salt in ethylenediamine solution (nickel concentration is 0.1mol / L, Ni: ethylenediamine=1.5, atomic ratio), and then add a certain amount of potassium sodium tartrate solution of cobalt chloride (Co: potassium sodium tartrate =0.5, atomic ratio), control Co:Ni=0.5 (atomic ratio), drop NaOH solution to control pH to be 13.2, add KBH 4 solution (B:(Ni+Co)=2.0, atomic ratio), adding AgNO at 60°C 3 solution (Ag accounts for 1% by weight of the catalyst), stirred and reacted until no bubbles are generated; after the catalyst is washed to be neutral, it can be stored in water or in ethanol. The XRD of sample C1 has the characteristics of FIG. 1 .
[0051] Same as the preparation process of catalyst C1, changing the atomic ratio of Ni:ethylenediamine to 0.5 and 2.0 to obtain catalysts C2 and C3.
[0052] Same as the preparation process of the cataly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com