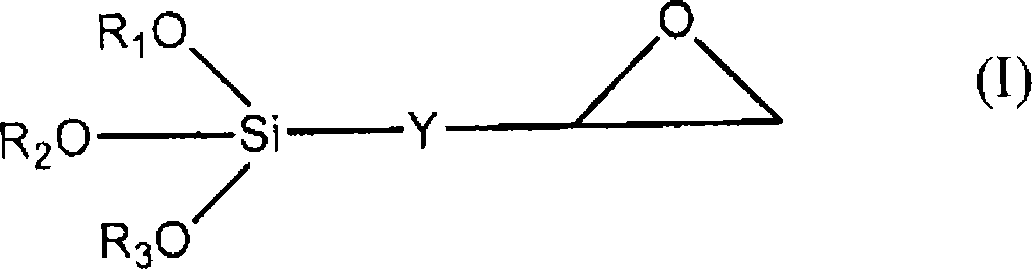Sol-gel process for the functionalisation of a surface of a solid substrate
A solid matrix, sol technology, applied in the sol-gel field, can solve problems such as very complex development, and achieve the effects of limited duration, reduced cost, and reduced energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0159] In this example, epoxy-functional and A thick layer around 100 nm in thickness, where the matrix was cleaned and prepared by washing (or stripping) in sodium hydroxide (Brown method).
[0160] A solution of (5,6-epoxyhexyl)triethoxysilane (EHTEOS) in ethanol in the presence of triethylamine (TEA) and water was deposited on the substrate.
[0161] The content of EHTEOS in the solution was 2.5% by weight. The ratio of the contents of water and ethanol was 0.18% by weight (water / ethanol).
[0162] The relative amounts of ingredients are specified by two parameters: H=[H 2 O] / [EHTEOS]=1 and T=[TEA] / [EHTEOS]=1, where [X] represents the molar concentration of the bulk X.
[0163] The solution was matured for at least 3 days at 22°C with gentle agitation.
[0164] Deposition is performed by spin coating at ambient temperature (at a rate of 200 to 3000 rpm, eg 700 rpm) to produce a wet layer. The contact time between the matrix and the liquid solution is 1 to several secon...
Embodiment 2
[0168] In this example, thick layers with a thickness of about 100 nm and containing aldehyde functional groups were prepared on a glass substrate (thin flakes of commercially available float glass) by the sol-gel method according to the invention.
[0169] Substrates prepared as in Example 1 (set with a Thick layer of epoxy functional group) in order to open the epoxy ring and form diol, then use NaIO 4 The diol was oxidatively sheared (stirred at ambient temperature for 1 hour, rinsed with deionized water for 5 minutes, then centrifuged dry) to generate aldehyde functional groups.
Embodiment 3
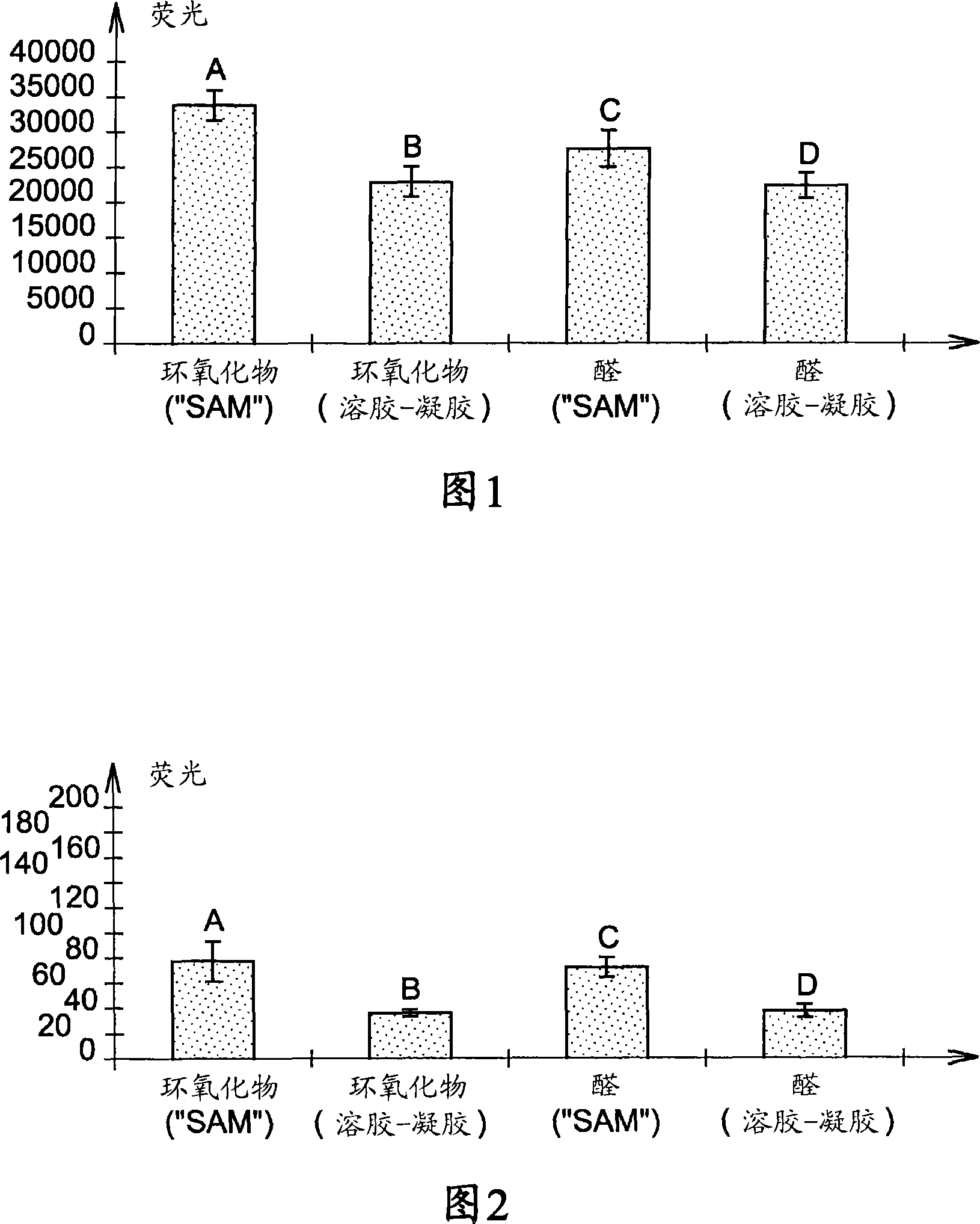
[0171] Will NH 2 Modified oligonucleotides (20 bases (20mers)) were deposited and immobilized on the support prepared in Example 1. Through a pressure-type automatic device in an aqueous solution (0.3MNa 2 HPO 4 ) for deposition.
[0172] The resulting oligonucleotide probes were hybridized to a complementary target labeled with the CY3 fluorophore. Fluorescence measurements were performed with an Axon Genepix scanner.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com