Method for producing acetic acid by carbonylation of methanol as well as special catalyst and preparation method thereof
A methanol carbonylation and catalyst technology, which is applied to the preparation of carboxylic acid by carbon monoxide reaction, physical/chemical process catalyst, organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, etc. Selective, highly adaptive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1, the preparation of catalyst
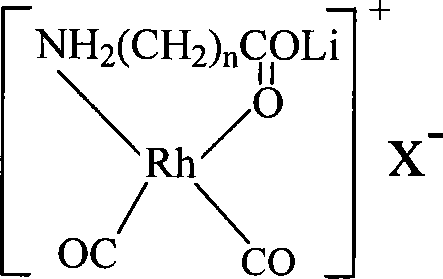
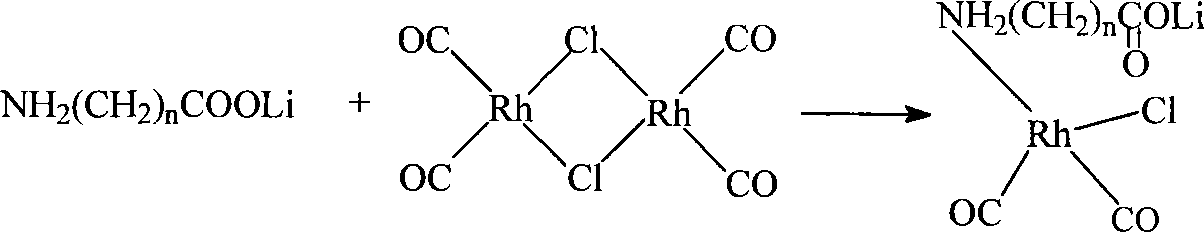
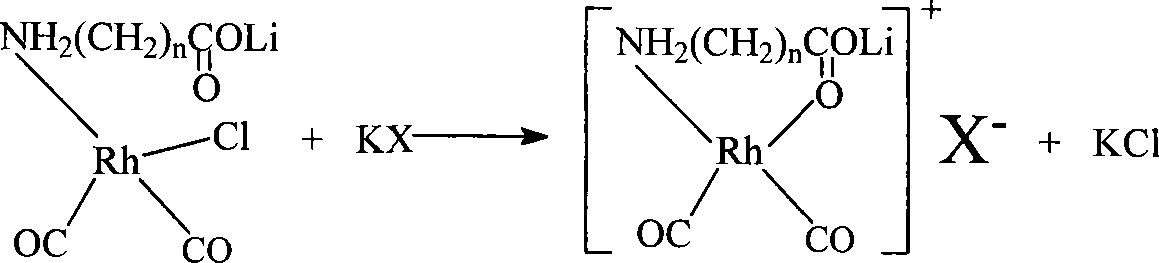
[0064] Dissolve 0.01 mole of allanine and 0.01 mole of lithium hydroxide in 100ml of methanol, stir at 30°C for 30 minutes at high speed to form a methanol solution of lithium allanate; dissolve 0.005 mole of dirhodium tetracarbonyl dichloride In 50ml of methanol, slowly add the methanol solution of lithium allanylpropionate under stirring, and continue to stir for 40 minutes at 40°C to form a lithium-rhodium aminopropionate complex; dissolve 0.01 mole of potassium iodide in 50ml of methanol, and stir Add it into the above-mentioned complex solution at 40° C. and continue to stir for 30 minutes to obtain the catalyst solution to be prepared, which is designated as catalyst (I).
[0065] Dissolve 0.01 mole of aminobutyric acid and 0.01 mole of lithium hydroxide in 100ml of methanol, stir at 40°C for 40 minutes at high speed to form a methanol solution of lithium aminobutyrate; dissolve 0.005 mole of dirhodium tetracarbonyl dich...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Embodiment 2, catalytic reaction
[0070] The catalyst used is the catalyst (I) prepared in Example 1. The batch test is carried out in a 250ml zirconium autoclave, and different reaction results can be obtained by controlling the composition of different reaction systems. The performance of the catalyst is discussed below through the reaction data in Table 1. The yield of acetic acid refers to the percentage of acetic acid produced from raw material methanol.
[0071] Methanol is the raw material of reaction, and the addition of methyl acetate is mainly in order to regulate the water content of medium in the reaction process, and the higher the addition of methyl acetate, the lower actual water content in the reaction. The remainder of the reaction medium is acetic acid. The content of the rhodium complex catalyst of lithium aminocarboxylate (prepared in Example 1) is calculated by the mass fraction (ppm) of rhodium in the reaction system. The reactor pressure of t...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Embodiment 3, catalytic reaction
[0076] The catalyst used is the catalyst (II) prepared in Example 1. The continuous use performance of the methanol carbonylation catalyst was evaluated using a batch model test device. In this device, the catalytic reaction is carried out in a 250ml reactor. After a period of time, the reaction mother liquid is discharged and enters a glass multistage rectification device. After a certain amount of mother liquid (mainly methyl iodide and acetic acid) is steamed, the remaining Catalyst mother liquid together with a certain amount of methyl iodide enters a stainless steel high-pressure tank, and is pressed into the reactor by high-pressure carbon monoxide gas, and the temperature rises to start a new reaction, and the cycle repeats. The activity of the reaction can be calculated by the absorption rate of carbon monoxide and the amount of acetic acid product in the reaction, the selectivity of the reaction can be calculated by analyzing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com