Method for processing heavy metal industrial waste water with low concentration
A technology for industrial wastewater and heavy metals, which can solve the problems of unsuitable heavy metal wastewater, pollution transfer, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing the risk of environmental secondary pollution, saving costs, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
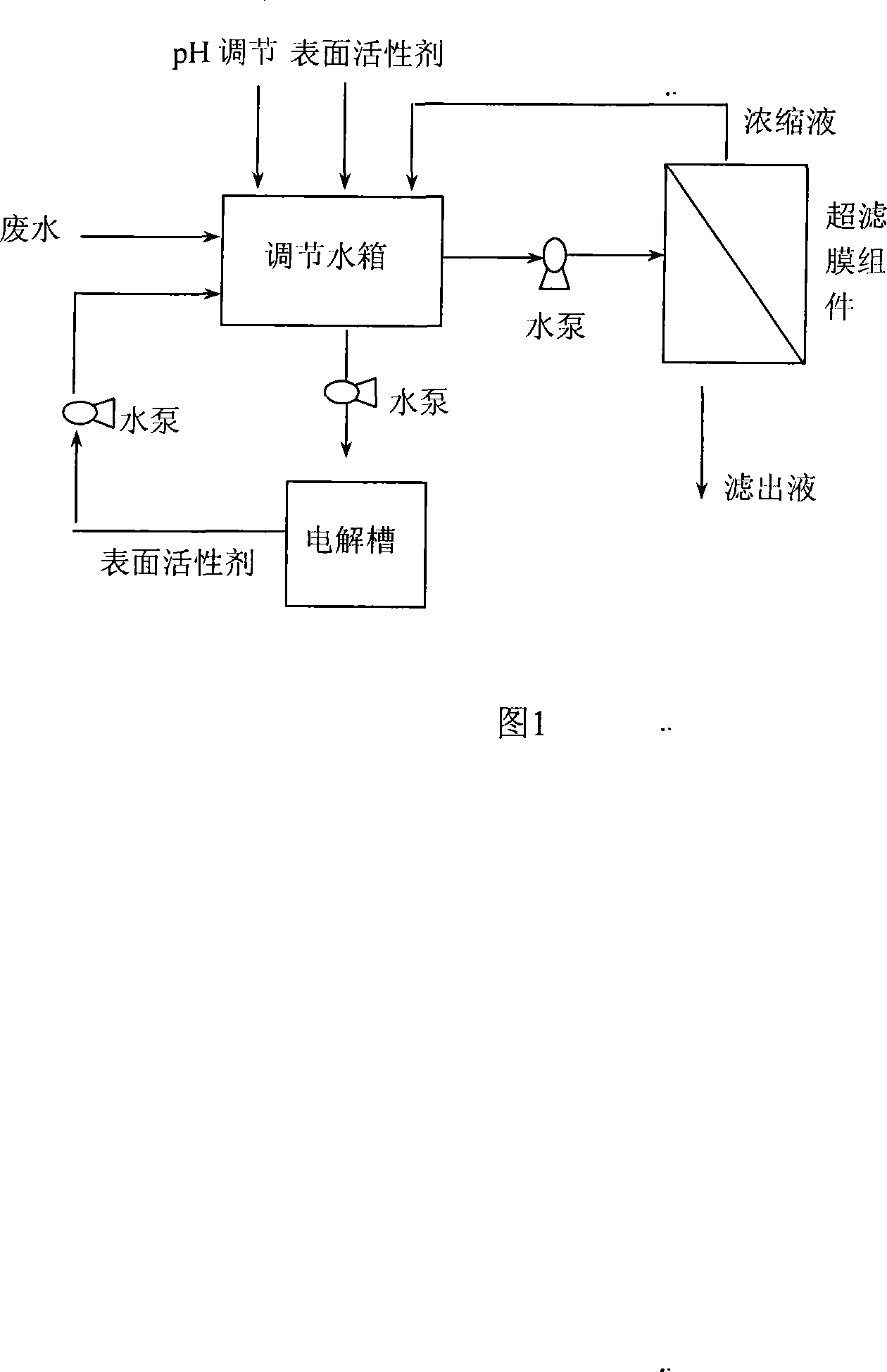
[0021] A method for recovery and treatment of industrial waste water with a lower concentration of heavy metals, the specific steps of the treatment method:
[0022] Step 1: collect the electroplating wastewater containing copper ions with a concentration of 12.8mg / L into the adjustment water tank, add lye NaOH, and adjust the pH to 6.
[0023] In step 2, 8.5 mM sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic surfactant, is added to the wastewater to reach its critical micelle concentration.
[0024] Step 3, turn on the water pump between the water tank and the ultrafiltration membrane module, filter under a pressure of 0.15MPa with a polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 8kDa, and a tangential flow rate of 1.1m / s. The chelate is intercepted by the ultrafiltration membrane, and the formed concentrated solution flows back to the regulating water tank along with the tangential flow. The removal rate of copper ions in the filtrate of the ultrafiltration...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Concrete steps of this embodiment:
[0029] Step 1: Collect industrial wastewater containing cadmium ion concentration of 10 mg / L and lead ion concentration of 15 mg / L into the adjustment water tank, add lye NaOH, and adjust the pH to 11.
[0030] In step 2, 8.5 mM sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), an anionic surfactant, is added to the wastewater to reach its critical micelle concentration.
[0031] Step 3, turn on the water pump between the adjustment water tank and the ultrafiltration membrane module, use an inorganic tubular ceramic membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 20kDa to filter under a pressure of 0.1MPa, a tangential flow rate of 2m / s, sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS) The chelate with copper ions is intercepted by the ultrafiltration membrane, and the formed concentrated solution flows back to the regulating water tank along with the tangential flow. The removal rates of cadmium ions and lead ions in the filtrate of the ultrafiltration membr...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Concrete steps of this embodiment:
[0036] Step 1, the chromate (CrO 4 2- 、HCrO 4 - ) The industrial wastewater with a concentration of 100mg / L is collected into the adjustment water tank. The pH of the original wastewater is 6.5, and there is no need to add lye for further adjustment.
[0037] In step 2, 10 mM of cationic surfactant cetylpyridinium chloride (CPCl) is added to the wastewater to reach its critical micelle concentration.
[0038] Step 3, turn on the water pump between the water tank and the ultrafiltration membrane module, use a polysulfone membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 10kDa to filter under a pressure of 0.07MPa, a tangential flow rate of 1m / s, cetylpyridinium chloride (CPCl) and chromic acid The salt chelate is intercepted by the ultrafiltration membrane, and the formed concentrated solution returns to the regulating water tank along with the tangential flow. The chromate removal rate of the ultrafiltration membrane filtrate reaches 9...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com