Method for manufacturing conductive polyaniline/cellulose composite biosensor
A conductive polyaniline and biosensor technology, which is applied in instruments, scientific instruments, and material analysis through electromagnetic means, can solve the problems of high cost, limit the wide application of sensors, limit the wide application of biosensors, etc., and achieve low production cost, Renewable and low cost, easy to industrialize the effect of production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
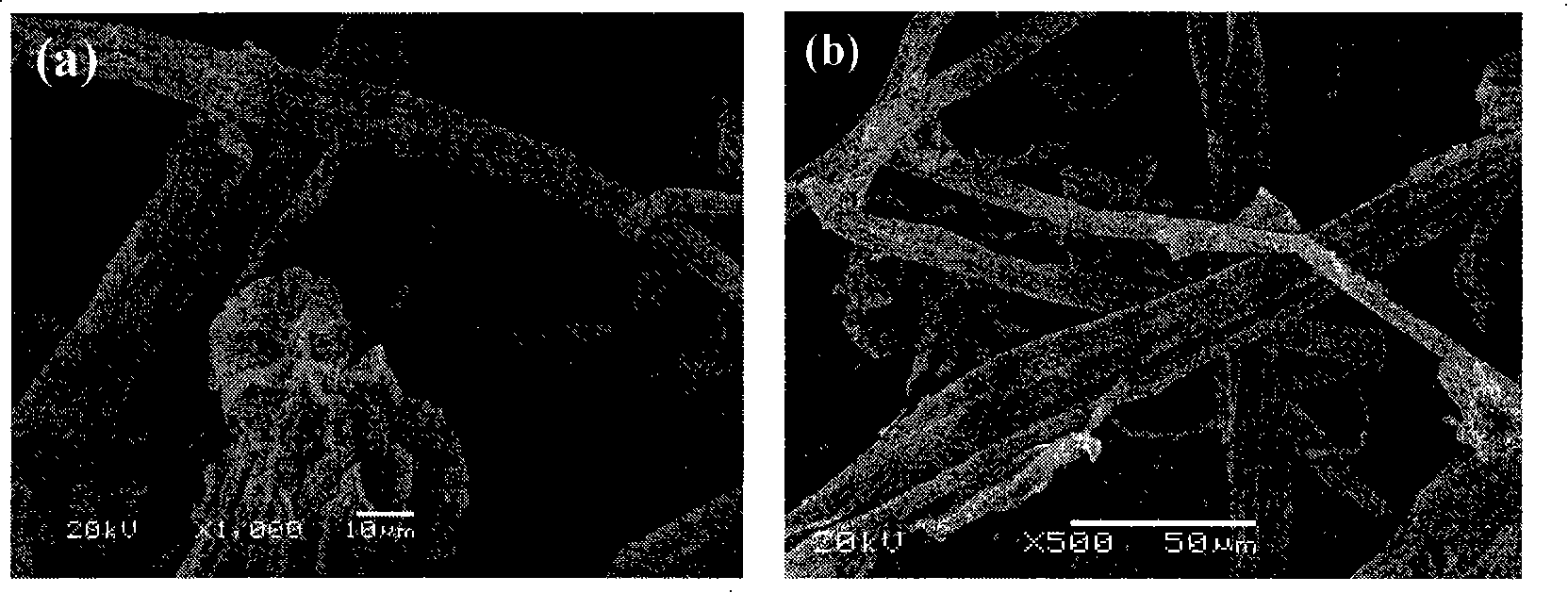
[0026](1) Preparation of cellulose: After crushing corn stalks into 20-100 mesh powders, dissolve them in a nitric acid solution with 15 times the weight of corn stalks and a concentration of 8%, distill at 110°C for 2 hours under magnetic stirring, and then Add 7 times the weight of corn stalks and 3% sodium hydroxide solution, continue distillation for 1.5 hours, cool the reaction mixture to room temperature, wash with distilled water until it is colorless, and then wash with ethanol several times to remove residual Oligosaccharides. Finally, it was dried in a drying oven at 40° C. for 5 hours. The cellulose is light yellow and appears as a ribbon or flat rod under the microscope. This structure is conducive to the attachment of aniline monomers.
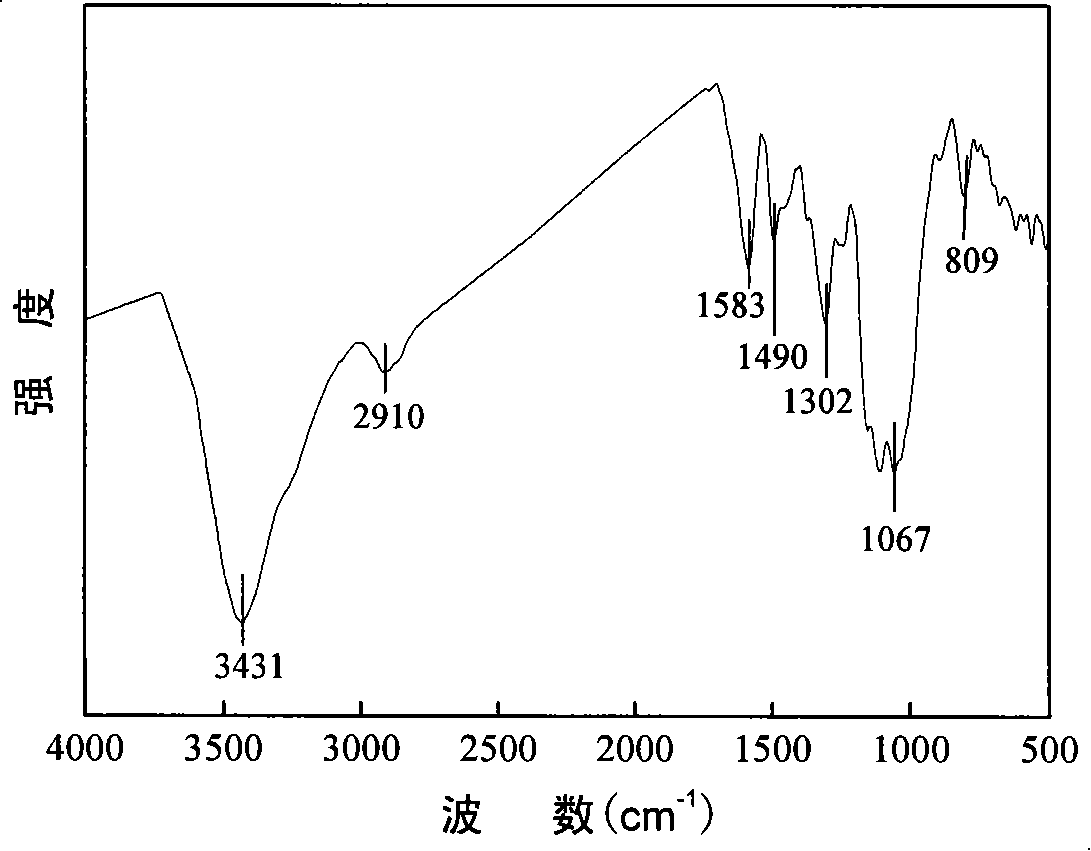
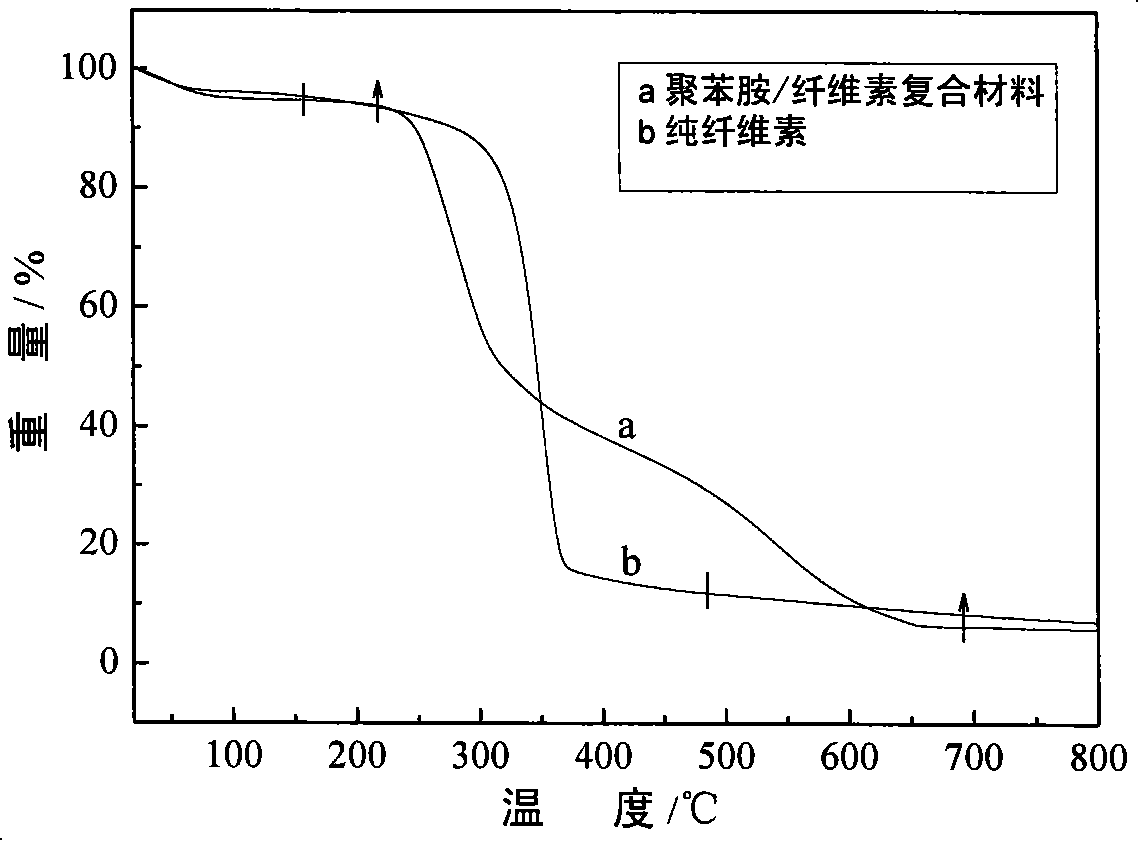
[0027] (2) Preparation of conductive polyaniline / cellulose conductive composite material: first dissolve aniline monomer in hydrochloric acid solution at room temperature, and continue to stir until aniline hydrochloride is compl...
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Preparation of cellulose: after crushing wheat straw into 20-100 mesh powder, dissolve it in a nitric acid solution with 20 times the weight of the straw and a concentration of 6%, distill at 100°C for 2.5 hours under magnetic stirring, and then add 10 times the weight of corn stalks and a concentration of 5% sodium hydroxide solution, after continuing to distill for 1 hour, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, washed with distilled water until it was colorless, and then washed with ethanol several times to remove residual low polysaccharides. Finally, it was dried in a drying oven at 40° C. for 5 hours. The cellulose is light yellow and appears as a ribbon or flat rod under the microscope. This structure is conducive to the attachment of aniline monomers.
[0032] (2) Preparation of conductive polyaniline / cellulose conductive composite material: Dissolve aniline monomer in hydrochloric acid solution at room temperature, and keep stirring until anil...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Preparation of cellulose: After crushing corn stalks into 20-100 mesh powders, dissolve them in a nitric acid solution with 18 times the weight of corn stalks and a concentration of 5%, distill at 120°C for 2.5 hours with magnetic stirring, and then Add 10 times the mass of corn stalks and a 4% sodium hydroxide solution, continue distillation for 1.5 h, then cool the reaction mixture to room temperature, wash with distilled water until it is colorless, and then wash with ethanol several times to remove residual Oligosaccharides. Finally, it was dried in a drying oven at 40 °C for 5 h. The cellulose is pale yellow and appears as a band or flat rod under the microscope.
[0037] (2) Preparation of conductive polyaniline / cellulose conductive composite material: Dissolve aniline monomer in hydrochloric acid solution at room temperature, and keep stirring until aniline hydrochloride is completely dissolved; then dissolve cellulose with 2.5 times the mass of aniline mono...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com