Tissue engineered cornea epithelial transplantation membrane and preparation method and use thereof
A tissue engineering, corneal epithelial cell technology, applied in the fields of bioengineering and clinical medicine, to avoid immune rejection, good histocompatibility, and eliminate the effect of original antigenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
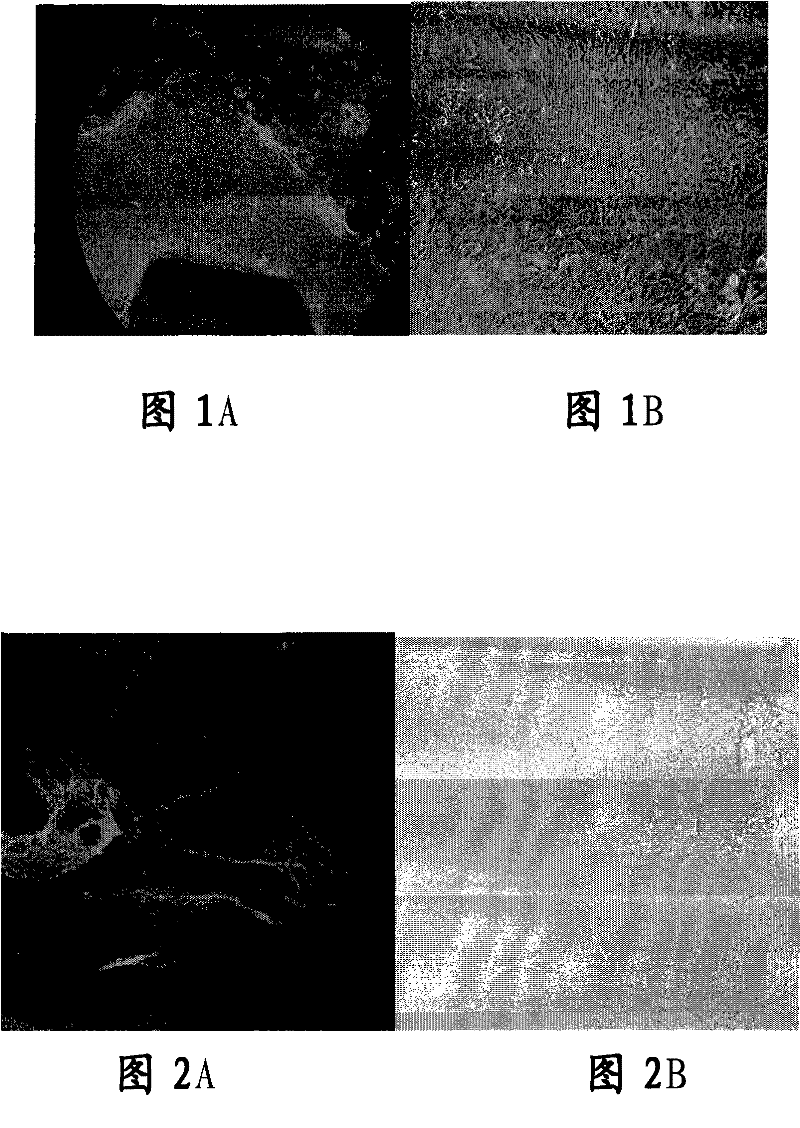
[0054] Embodiment 1, limbal tissue culture of human corneal epithelial cells in vitro
[0055] 1. In vitro primary and subculture corneal epithelial cells from corneal limbal tissue blocks
[0056] Primary culture: Disinfect human conjunctival sac and ocular surface with 10% povidone iodine, retrobulbar anesthesia with 2% lidocaine, use cataract phacoemulsification incision knife (Alcon, U.S.A.) to take a size of about 2.0mmX2.0mm in human corneal limbus The limbal tissue block with a thickness of about 200 μm was washed 3 times with D-PBS buffer containing 1% penicillin-streptomycin, then placed in 1.2U / ml dispase II digestion solution and kept overnight in the refrigerator at 4°C, after taking out the D- Wash with PBS buffer three times, and then treat with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA at 37°C for 10 minutes, and neutralize trypsin in DMEM medium containing 10% FBS. Place the limbal tissue pieces in a 60mm petri dish, dry naturally at room temperature in an ultra-clean bench, and adh...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Embodiment 2. Tissue engineered corneal stent material
[0078] 1. Carrier selection:
[0079] There are currently many kinds of carriers for constructing tissue-engineered corneal epithelial transplantation membranes, among which amniotic membranes, collagen membranes and hydrophilic gel membranes are mostly used, but these membranes all have a common disadvantage, that is, they lack a certain thickness to resist tension, compression and refraction. Therefore, its application is limited. Heterogeneous acellular matrix, especially porcine acellular matrix, is easy to obtain and has no antigenicity after enzymatic digestion of porcine corneal stromal cells, and has the structural characteristics that cornea should have.
[0080] 2. Preparation of porcine acellular corneal stroma:
[0081] Such as Figure 14 As shown, fresh pig eyeballs were soaked in 0.125% chloramphenicol solution for 1 hour, soaked in 75% ethanol for 0.15 hours, scraped off the epithelium with a ra...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3: Preparation of Tissue-Engineered Corneal Epithelial Graft Membrane in Vitro
[0083] 1. Preparation of acellular porcine corneal stroma:
[0084] The corneal stroma prepared in Example 2 was soaked in fetal bovine serum for 24 hours and then placed in DMEM culture medium for future use.
[0085] 2. The corneal epithelial cells were subcultured in vitro and digested with 0.25% trypsin to make cell suspension.
[0086] 3. Place the decellularized porcine corneal stromal epithelium face up and place it in a culture dish to dry naturally for several minutes. 3 / mm 2 Inoculate on the decellularized porcine corneal stroma and wait for the cells to adhere to the wall in an ultra-clean bench, during which the culture solution is continuously dripped to avoid excessive drying of the cells. After the completion of wall attachment, a small amount of fetal bovine serum was added and placed in a 5% carbon dioxide incubator at 37°C for 24 hours. After 24 hours, an appro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com