Technique for extracting and separating tea polyphenol from tea-leaf
A technology of tea polyphenols and a new process is applied in the field of extraction and separation of tea polyphenols, which can solve the problems of high waste water treatment cost, destruction of effective components, and high operating energy consumption, and achieves the reduction of energy consumption, the improvement of product quality, and the low energy consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: A new process for extracting and separating tea polyphenols from tea leaves
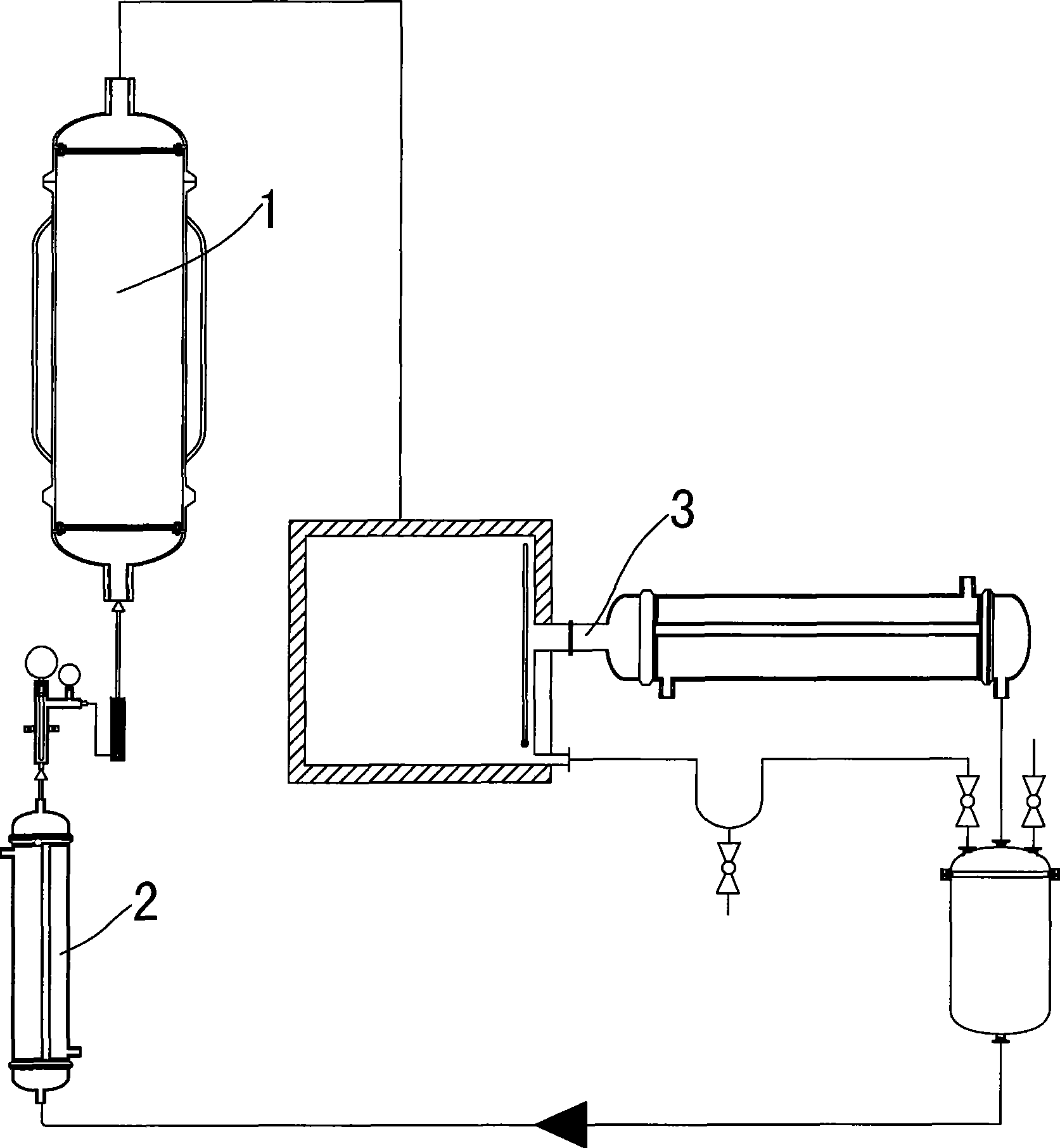
[0030] as attached figure 1 As shown, 1Kg of tea leaves, after being treated with the treatment steps, is wetted with 500ml of water, placed in the percolation tank 1, and the ethyl acetate is heated to 50°C by the preheater 2 at a flow rate of 4L / h through a peristaltic pump. Then it is sent into the percolation tank to extract tea polyphenols by percolation, and the continuous effluent passes through the plate falling film concentrator 3 to recover the solvent, and the recovered solvent obtained continues to be used for percolation extraction. Randomly detect EGCG (TLC method) at the outlet of the percolation tank during the process, until no EGCG spots appear, collect the concentrated solution and place it in a 3000ml stirring tank to recover the solvent until it is clean, add 500ml of n-hexane and stir to extract and remove the fat-soluble substances. Get tea polyphenol product...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: A new process for extracting and separating tea polyphenols from tea leaves
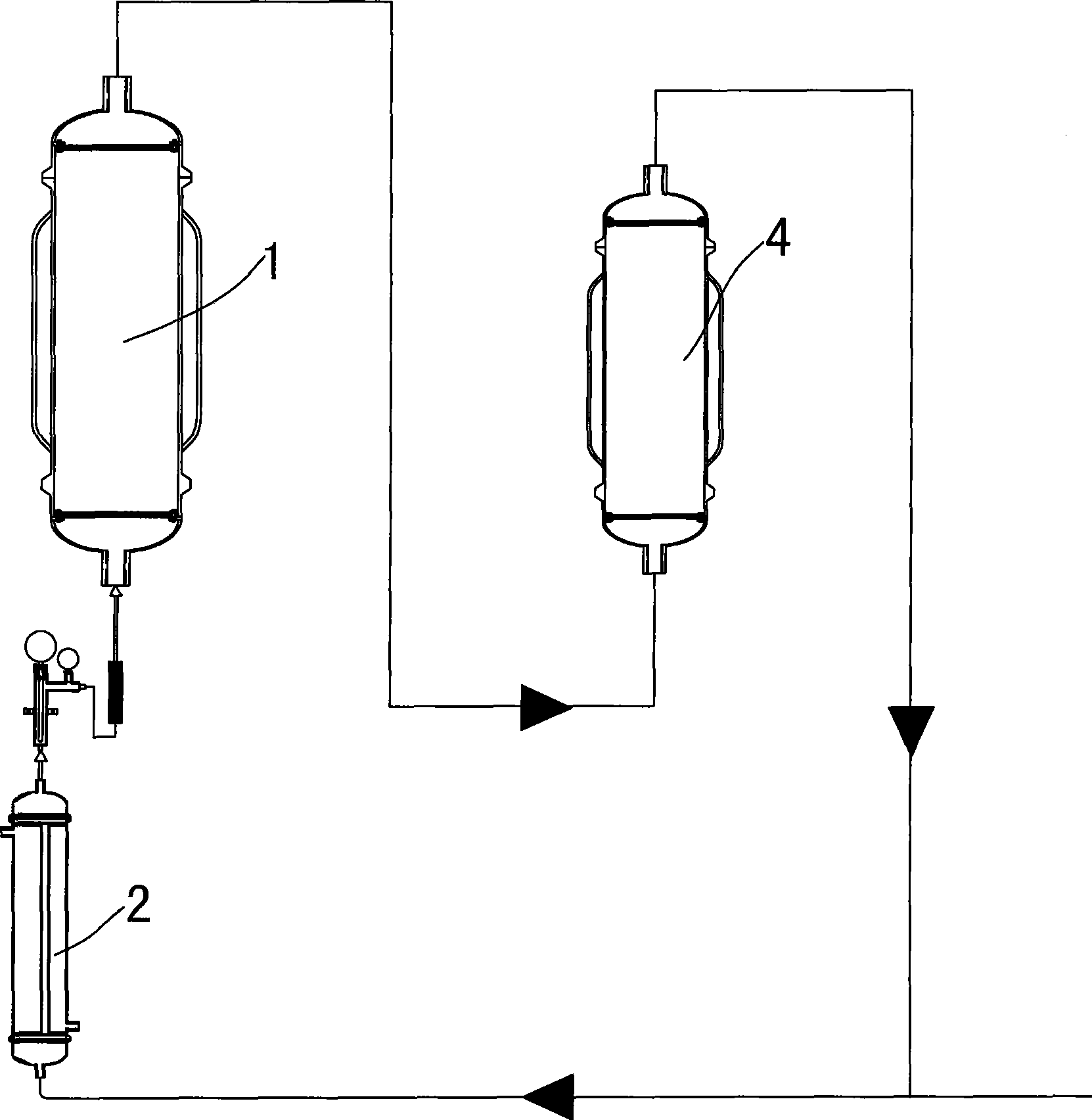
[0032] as attached figure 2 As shown, 1Kg of tea leaves is wetted with 1000ml of water, placed in the percolation tank 1, and the ethyl acetate containing n-hexane with a volume concentration of 15% is heated to At 50°C, enter the percolation tank to extract tea polyphenols by percolation, the extract flows through the adsorption column 4, and the polyamide absorbs tea polyphenols, and the effluent returns to the percolation tank to form a circular extraction. During the process, randomly detect EGCG at the outlet of the percolation tank (TLC method), and stop the cycle operation until there are no EGCG spots. Continuously inject water from the bottom of the adsorption column 4, about 5 times the column volume, until there is no caffeine and ethyl acetate-petroleum ether (extractant) residue in the effluent, drain the water, analyze and concentrate with 95% ethanol to obtain tea p...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3: A new process for extracting and separating tea polyphenols from tea leaves
[0034] Wet 1Kg of tea leaves with 200ml of water, place them in a percolation tank, and heat 10% ethyl acetate containing n-hexane through a peristaltic pump to 50°C through a preheater at a flow rate of 4L / h, and then send Enter the percolation tank to extract tea polyphenols by percolation, and the continuous effluent recovers the solvent through the plate falling film concentrator, and the recovered solvent is continued to be used for percolation extraction. Randomly detect EGCG (TLC method) at the outlet of the percolation tank during the process, until no EGCG spots appear, collect the concentrated solution and place it in a 3000ml stirring tank to recover the solvent until it is clean, add 500ml of petroleum ether and stir to remove the fat-soluble substances, to obtain Tea polyphenol products.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com