Preparation of tin dioxide nano line array electrode for lithium battery
A nanowire array, tin dioxide technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of short nanowire length, low first charge and discharge efficiency of batteries, disordered arrangement, etc. Electrode charge adsorption amount and electrode stability, simple effect of equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
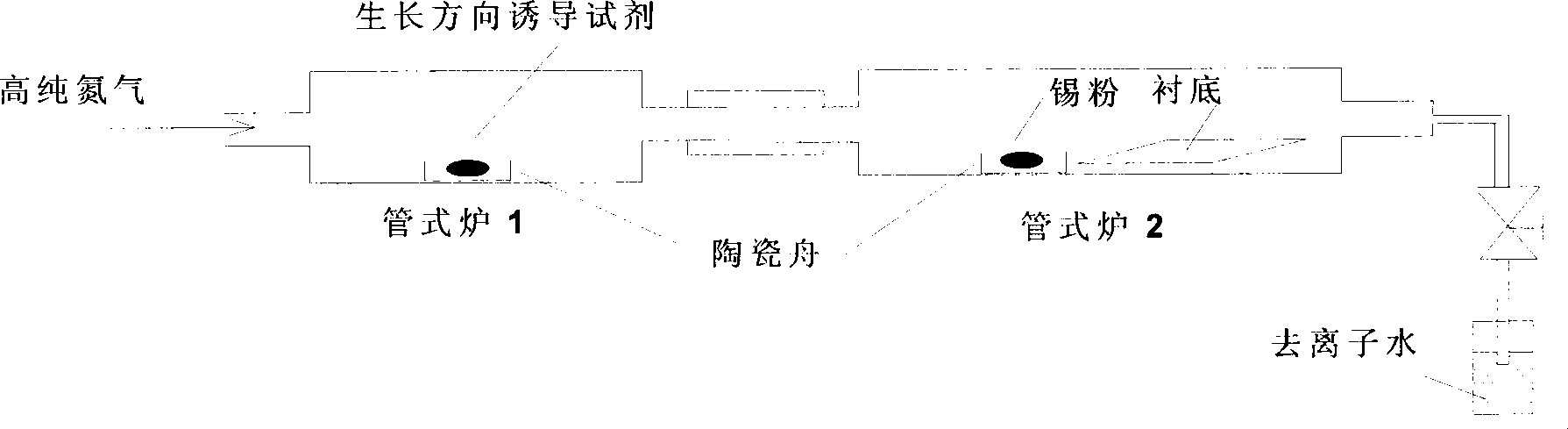
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, the second tube furnaces 1 and 2 are both one-stage constant temperature resistance heating quartz tubes, and the ceramic boat is ensured to be placed at the thermocouple of the tube furnace during the reaction process.
[0027] Weigh 2g of tin powder and put it into a ceramic boat, place it in the middle of the first tube furnace 2, and place a silicon wafer of a noble metal Au catalyst with a thickness of about 100nm by magnetron sputtering at a distance of 1cm downwind of the ceramic boat. Weigh 100 mg of sulfur powder and selenium (mass ratio 9:1) into a ceramic boat, and place the ceramic boat in the middle of the second tube furnace 1 . The closed system continuously feeds high-purity nitrogen with a flow rate of 20 sccm. After the time of passing nitrogen gas for one hour, raise the temperature of the first tube furnace 2 to 800°C at a heating rate of 50°C / min. After the tube temperature reaches 800°C, raise the temperature of the seco...
Embodiment 2
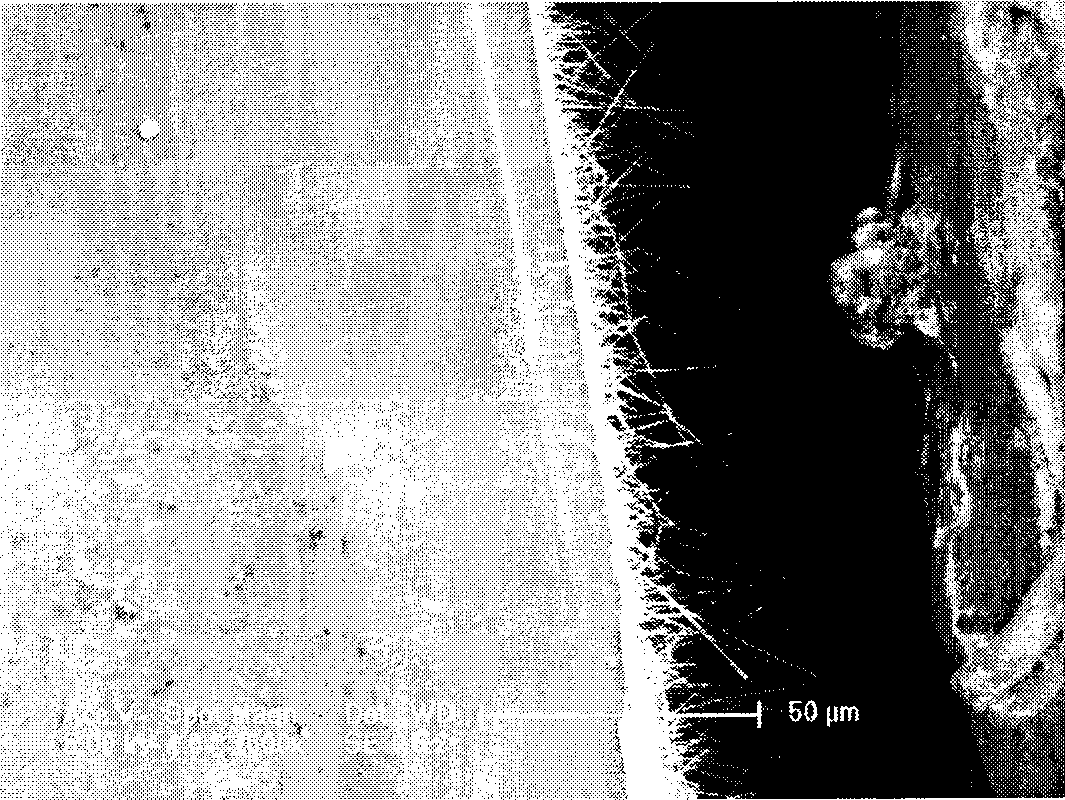
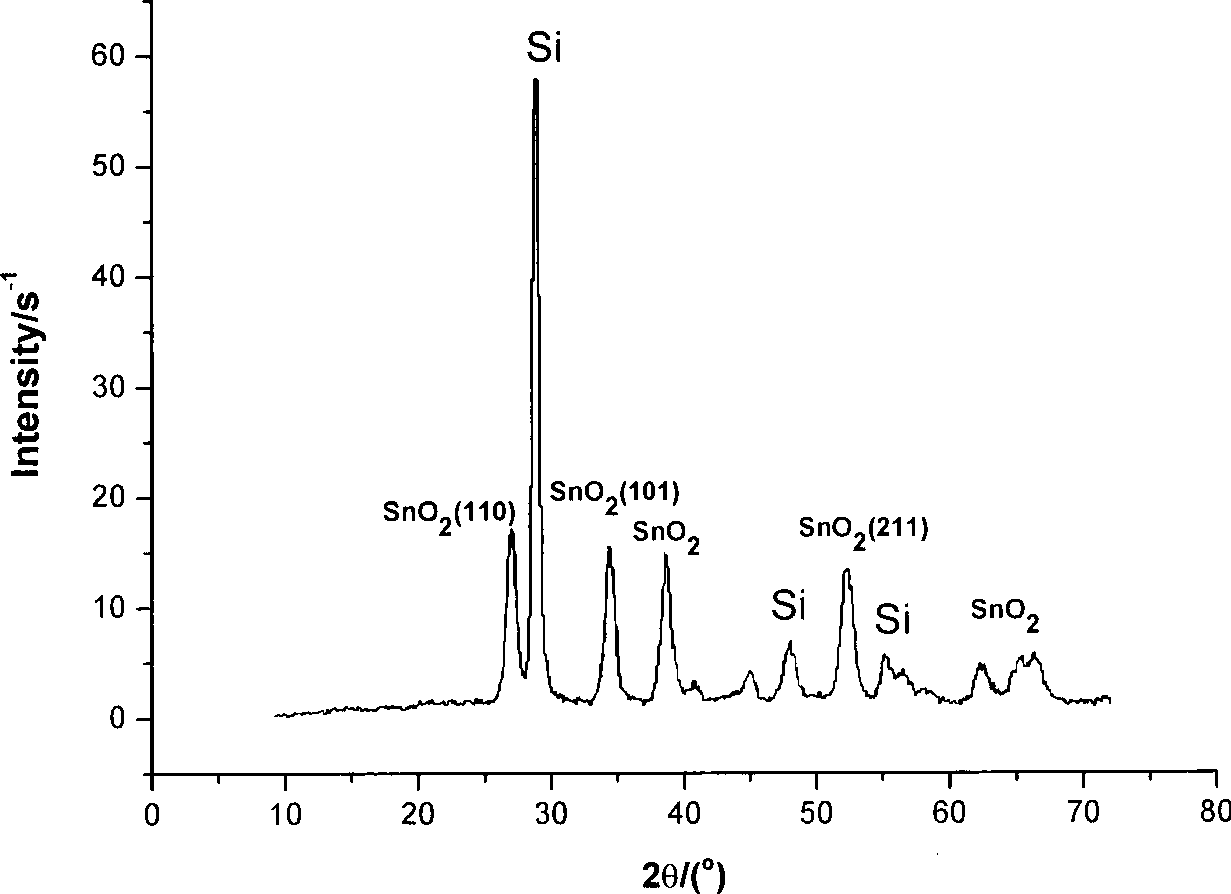
[0030] Weigh 5g of tin powder and put it into a ceramic boat, place it in the middle of the first tube furnace 2, and place a silicon wafer of a noble metal Au catalyst with a thickness of about 100nm by magnetron sputtering at a distance of 3cm downwind of the ceramic boat. Weigh 1000 mg of sulfur powder and selenium (mass ratio 9:1) into a ceramic boat, and place the ceramic boat in the middle of the second tube furnace 1 . Closed system, continuously fed high-purity nitrogen with a flow rate of 300 sccm. After the nitrogen flow time reaches one hour, raise the temperature of the first tube furnace 2 to 1300°C at a heating rate of 30°C / min. The temperature of tube furnace 1 is up to 300°C. The second tube furnace 1 was kept at 300° C. for 5 minutes and then cooled down naturally. The first tube furnace 2 was kept at 1300° C. for 30 minutes, then cooled down naturally, and the ventilation valve was closed. After cooling to room temperature, a similar figure 2 The tin dio...
Embodiment 3
[0032]Weigh 3.5g of tin powder and put it into a ceramic boat, place it in the middle of the first tube furnace 2, and place a silicon wafer of a noble metal Au catalyst with a thickness of about 100nm by magnetron sputtering at a distance of 2cm downwind of the ceramic boat. Weigh 500mg of sulfur powder and put it into a ceramic boat, which is placed in the middle of the second tube furnace 1 . The closed system continuously feeds high-purity argon with a flow rate of 160 sccm. After the nitrogen gas flow time reaches one hour, raise the temperature of the first tube furnace 2 to 1050°C at a heating rate of 40°C / min. The temperature of tube furnace 1 is up to 200°C. The second tube furnace 1 was kept at 200° C. for 12 minutes and then cooled down naturally. The first tube furnace 2 was kept at 1300° C. for 45 minutes, then cooled down naturally, and the ventilation valve was closed. After cooling to room temperature, a similar figure 2 The tin dioxide nanowire array elec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com