Advanced treatment method for printing and dyeing wastewater
A technology for advanced treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater, applied in water/sewage multi-stage treatment, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. Achieve the effect of low operating cost, small footprint and no secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] (1) Preparation of coal filler: the filler is composed of anthracite and pulverized coal with particle size less than 2mm. When preparing the filler, the anthracite is first crushed, and then the pulverized coal with the required particle size is obtained by using a drum sieve with an aperture of 2mm.
[0021] (2) Static adsorption: fill the filler into the adsorption bed, and the ratio of filler to waste water is preferably 1:2.5 to 1:5.
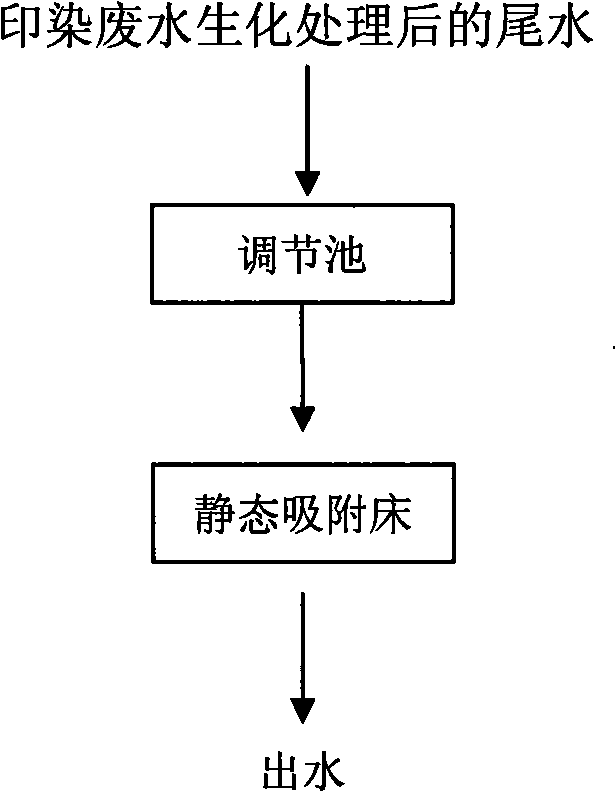
[0022] (3) Process flow: such as figure 1 As shown, the tail water after biochemical treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater is pumped into the static adsorption bed by the water pump after being uniformly adjusted in the water quality and quantity in the adjustment tank, where it is statically adsorbed in the reaction bed for 2 hours, and finally discharged through the outlet pipe at the bottom.
[0023] (4) Process conditions and process parameters: the intermittent operation mode is adopted, and the tail water after biochemic...
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) Preparation of coal filler: the filler is composed of anthracite and pulverized coal with particle size less than 2mm. When preparing the filler, the anthracite is first crushed, and then the pulverized coal with the required particle size is obtained by using a drum sieve with an aperture of 2 mm.
[0027] (2) Static adsorption: fill the filler into the adsorption bed, and the ratio of filler to waste water is preferably 1:2.5 to 1:5.
[0028] (3) Process flow: such as figure 1 As shown, the tail water after biochemical treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater is pumped into the static adsorption bed by the water pump after being uniformly adjusted in the water quality and quantity in the adjustment tank, where it is statically adsorbed in the reaction bed for 2 hours, and finally discharged through the outlet pipe at the bottom.
[0029] (4) Process conditions and process parameters: the intermittent operation mode is adopted, and the tail water after biochemi...
Embodiment 3
[0032] (1) Preparation of coal filler: the filler is composed of anthracite and pulverized coal with particle size less than 2mm. When preparing the filler, the anthracite is first crushed, and then the pulverized coal with the required particle size is obtained by using a drum sieve with an aperture of 2 mm.
[0033] (2) Static adsorption: fill the filler into the adsorption bed, and the ratio of filler to waste water is preferably 1:2.5 to 1:5.
[0034] (3) Process flow: such as figure 1 As shown, the tail water after biochemical treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater is pumped into the static adsorption bed by the water pump after being uniformly adjusted in the water quality and quantity in the adjustment tank, where it is statically adsorbed in the reaction bed for 2 hours, and finally discharged through the outlet pipe at the bottom.
[0035] (4) Process conditions and process parameters: the intermittent operation mode is adopted, and the tail water after biochemi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com