Culture system and method for propagation of human blastocyst-derived stem cells
A culture system and cell technology, applied in the field of culture systems for proliferating human blastocyst-derived stem cells, can solve the problems of a lot of man-hours, laboratory space, low compatibility, reproducibility, and negative effects of standardization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0151] Culture of human foreskin fibroblast feeder cells and use as feeder cell layer
[0152] Commercially available hFFs were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (CRL-2429 ATCC, Manassas, VA) and cultured in a medium supplemented with 10% FBS (Invitrogen) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Iscove's DMEM (Gibco Invitrogen Corporation, Paisley, Scotland; http: / / www.invitrogen.com). Cells were passaged periodically (weekly) using trypsin-EDTA (Invitrogen) at a split ratio between 1:2 and 1:8. Confluent monolayers of hFF were treated with mitomycin-C (Sigma) (10 μg / ml, 2.5 hours) and incubated in VitroHES supplemented with 4 ng / ml human recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor (hrbFGF, Invitrogen). TM 70,000-80,000 cells / cm in medium 2 at a density of 0.1% gelatin (Sigma) coated IVF dishes. hFF cells were used as feeder cells between passage 4 and passage 12.
Embodiment 2
[0154] Culture of human embryonic fibroblasts and use as feeder cell layer
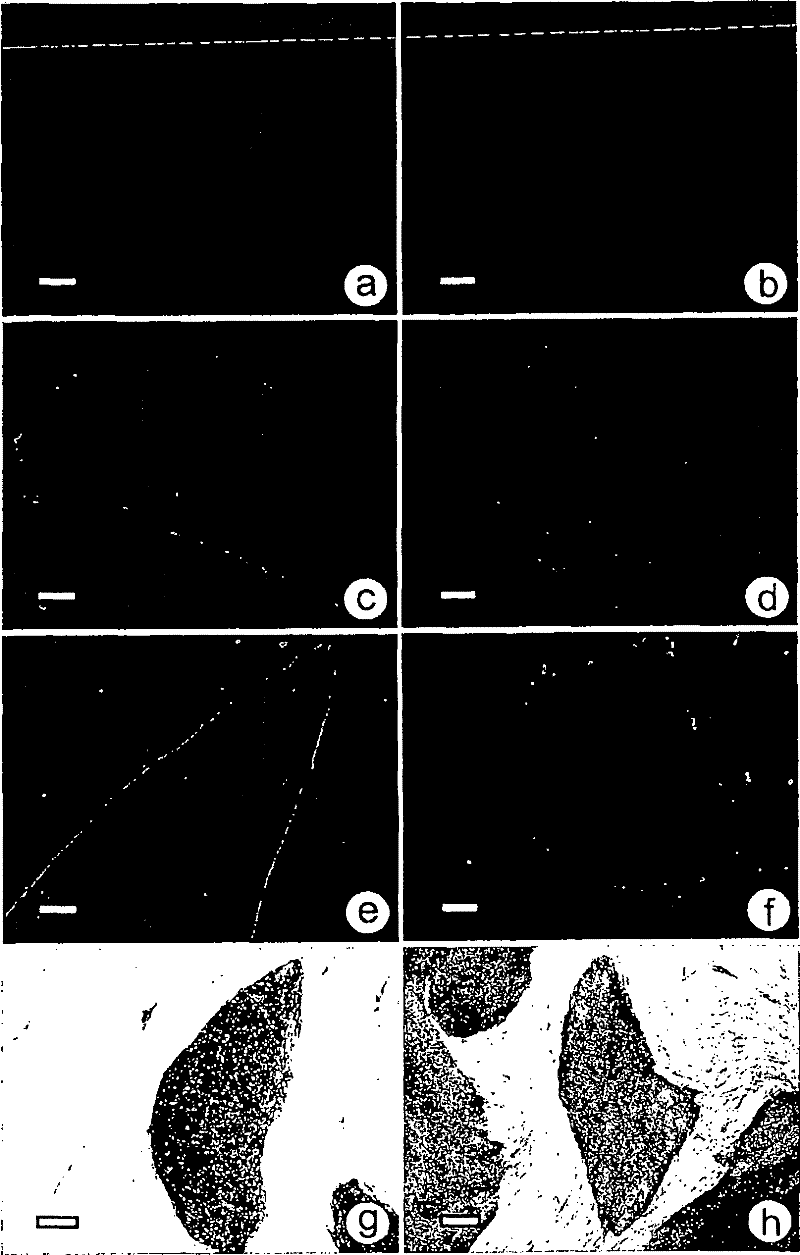
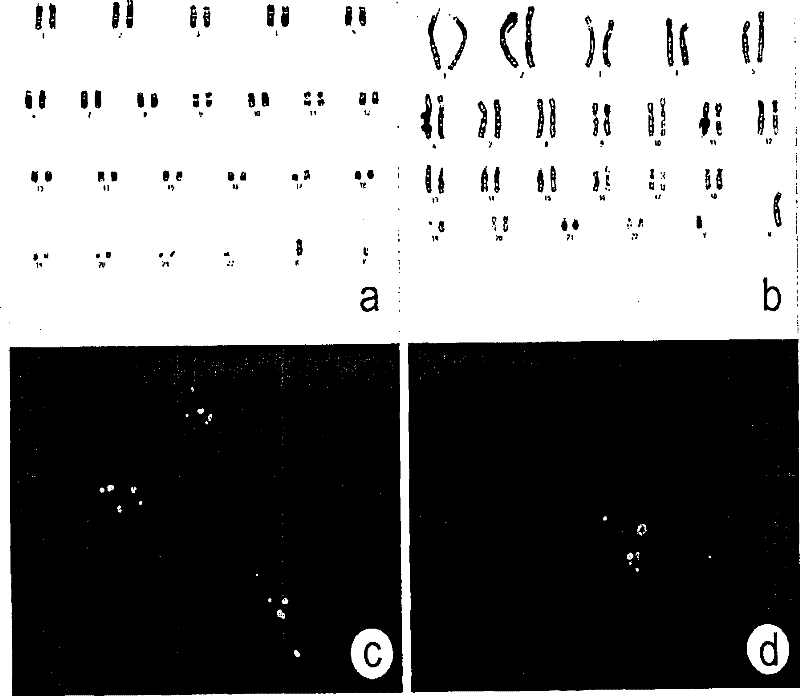
[0155] Commercially available human embryonic fibroblasts were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (CCL-110 ATCC, Manassas, VA) and cultured in Iscove's supplemented with 10% FBS (Invitrogen) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. DMEM (Gibco Invitrogen Corporation, Paisley, Scotland; http: / / www.invitrogen.com). Cells were passaged periodically (weekly) using trypsin-EDTA (Invitrogen) at a split ratio between 1:2 and 1:8. Confluent monolayers of human embryonic fibroblasts were treated with mitomycin-C (Sigma) (10 μg / ml, 2.5 hours) and treated with 4 ng / ml human recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor (hrbFGF, Invitrogen ) VitroHES TM 70,000-80,000 cells / cm in medium 2 at a density of 0.1% gelatin (Sigma) coated IVF dishes. Human embryonic fibroblasts were used as feeder cells between passage 4 and passage 12, Figure 8 .
Embodiment 3
[0157] Establishment of human foreskin fibroblast feeder cell lines (e.g. cell line hFF003)
[0158]Human foreskin samples from circumcised 8-week-old boys were aseptically collected in sterile IMDM (Invitrogen) containing 2X gentamicin. Skin explants were placed in 25 cm2 primary tissue culture flasks (Becton Dickinson) containing IMDM medium (Invitrogen), 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco Invitrogen Corporation) and 10% human serum. After about 10 days, a confluent monolayer was established. Use TrypLE TM Cells were serially passaged with Select (Invitrogen). After expansion, for a standard panel of human pathogens (mycoplasma, HIV types 1 and 2, hepatitis B and C, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, Epstein-Barr virus, human papillomavirus) They were tested and all came back negative.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| separation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com