Ocean actinomycete fermentation extract, composite thereof, and application in biofouling resistance
A technology of marine actinomycetes and extracts, applied in the direction of chemicals, applications, biocides for biological control, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the marine environment, high toxicity of chemicals, low efficiency of physical removal methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Inoculate marine actinomycetes (Salinispora pacifica) SCSIO 00013 into two sterilized 500mL shake flasks. Starch 10~30g, K 2 HPO 4 0.5~1g, KNO 3 0.5~1.0g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5~1.0g, sea salt 1.5%~3%,), temperature 28 ℃ on the shaker, speed 40 rpm, after culturing for 3 days, transfer to 10 seed bottles respectively, after being in Gaoshi No. 1 medium medium, temperature 28°C, speed 40 rpm, after 7 days of cultivation, transfer the actinomycetes from 20 seed bottles to 500mL shake flasks, and the shake flasks are filled with 150mL Gaoshi No. 1 medium, and the culture conditions are temperature 28°C, speed 40 rpm, culture for 10 days, after a large amount of actinomycetes are fermented, use a large centrifuge to separate mycelia and fermentation broth. The fermentation broth was extracted three times with an equal volume of ethyl acetate, and the extracts were combined to obtain extract 1. The mycelium was ultrasonically treated, and then extracted three times with ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2: Example 1 extract antibacterial and antifouling biological larva attachment activity test
[0022] Antibacterial activity was determined by the agar diffusion method. A sterile paper piece (5 mmi.d.) soaked with 50 μg of the target extract was placed on the agar plate coated with bacteria, and the size unit of the inhibition zone was expressed in mm. The disc soaked with the same volume of DMSO was used as blank control, and the disc added with rifampicin (3-[[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)imino]methyl]-rifamycin) was used as positive control. After incubation at room temperature for 24 hours, the size of the inhibition zone was measured. Antibacterial results are shown in Table 1.
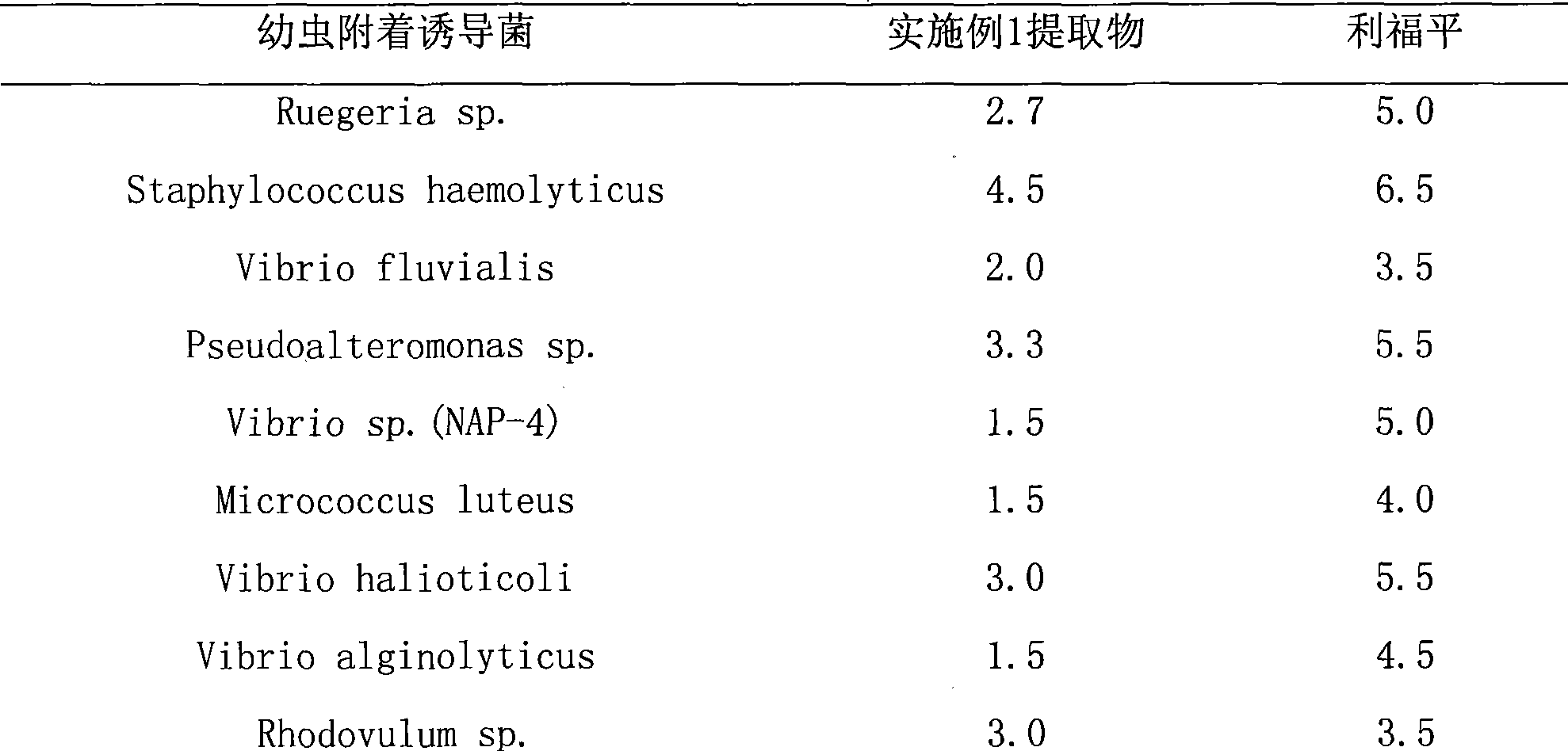
[0023] Table 1 Antibacterial activity of the target extract and rifampicin (the size unit of the inhibition zone L, mm; the content of each tablet, 50 μg / disc)
[0024]
[0025] The size of the inhibition zone L in Table 1 is measured by a vernier caliper, and the inhibition ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Embodiment 3: Anti-fouling biological larva adhesion test of the extract of embodiment 1
[0027] The anti-barnacle larvae attachment activity of the extracts from Example 1 were measured using 24-well plates. 1 mL of culture solution containing 10-15 mature barnacle larvae was added to each plate well, and the extract from Example 1 was dissolved in DMSO, and then diluted with sterilized seawater to different concentrations. Three parallels were performed for each concentration, and sterile seawater was used as a blank control. The culture plate was cultured at room temperature for 24 hours, and the number of attached larvae was counted under a dissecting microscope, and statistical analysis was performed with SPSS program. The statistical results are shown in Table 2:
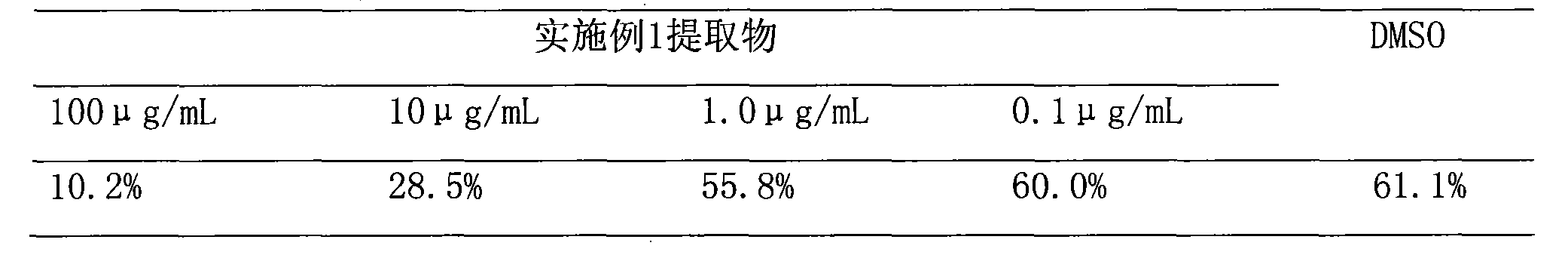
[0028] Table 2 The attachment rate (%) of the barnacle larvae at different concentrations of the extract of Example 1
[0029]
[0030] It can be seen from Table 2 that compared with the DMSO contr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com