Polylactic acid degrading enzyme with protein degrading activity
A technology for degrading active polylactic acid, which can be used in peptide/protein components, hydrolase, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., and can solve the problems of limited separation and purification and property research.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Screening of degrading strains
[0041] Spot or spread activated Amycolatopsis orientalis strains (strain bank, commercially available) and environmental sample enrichment solution on PLA emulsified plates, culture them upside down in a 30°C incubator, and observe the strains for 15-30 days The growth and the formation of the transparent hydrolysis circle were selected, and the bacterial strains that could grow on the plate and form an obvious transparent hydrolysis circle were screened. To prevent moisture from evaporating, replenish water regularly and maintain a humid environment. Screening media components and production methods are as follows:
[0042] Basic medium: 250mg yeast extract, 1g (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 100mg NaCl, 200mg MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 20mgCaCl 2 2H 2 O, 10mg FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.5 mg Na 2 MoO 4 2H 2 O, 0.5 mg Na 2 WO 4 , 0.5 mg MnSO 4 , 1.6g K 2 HPO 4 , 0.2g KH 2 PO 4 Distilled water to 1L, natural pH.
[0043] Preparation of PLA em...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2 Purification of Enzymes
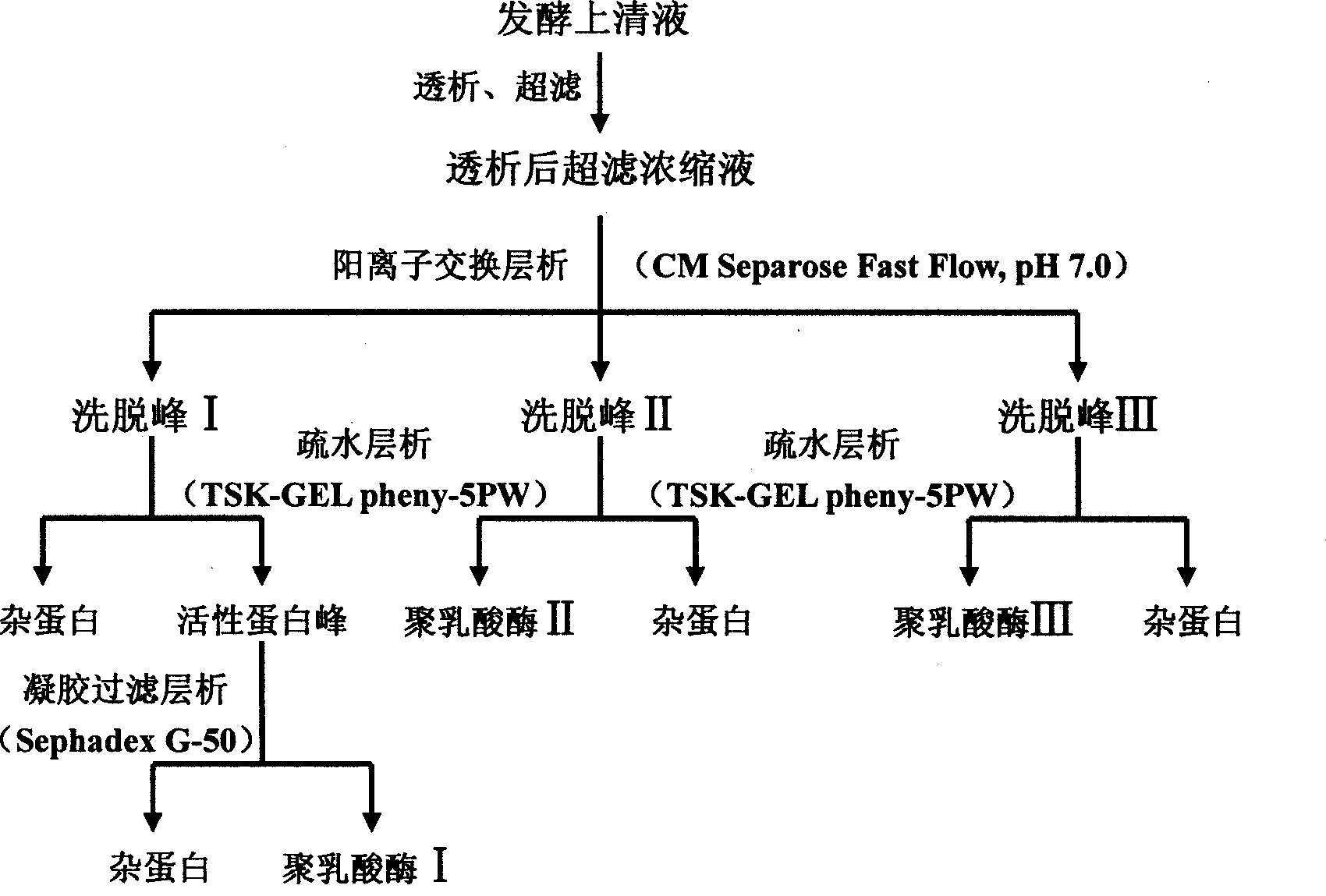
[0046] Amycolatopsis orientalis was fermented and cultured in a 3L GBCS-5 biological fermenter. The medium was 10g gelatin, 10g glucose, 2g yeast extract, 5g NaCl, 1.6g K2HPO4, 0.2g KH2PO4, 0.5g MgSO4 and dilute to 1L distilled water. The crude enzyme liquid obtained by centrifuging the supernatant from the fermentation broth was concentrated by ultrafiltration, and then separated and purified by CM SepharoseFast Flow cation exchange chromatography, TSK-gel phenyl-5PW hydrophobic chromatography, and Sephadex G-50 fine molecular sieve chromatography. Specifically, the concentrated crude enzyme solution was dialyzed with 20mM phosphate buffer containing 10mM NaCl, pH 7.0 to remove salt, and then subjected to CM Sepharose Fast Flow chromatography. The electrophoresis results showed that the obtained enzyme components were not yet purified, and the three elution peaks collected separately and proceed to the next step of separation. Ammon...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 Determination of Enzyme Characteristics
[0049] 1. Determination of Enzyme Molecular Weight
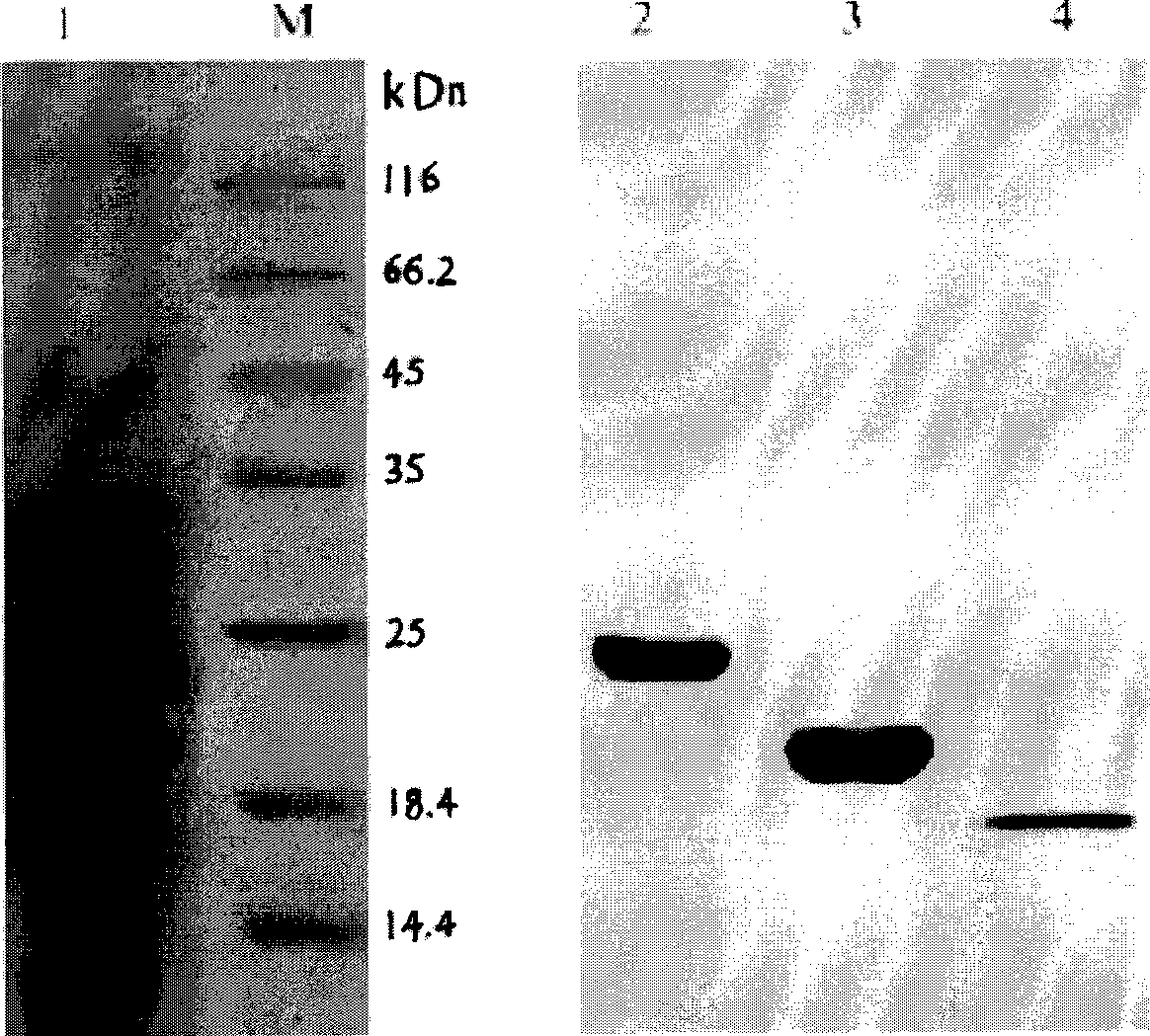
[0050] The purified degrading enzyme components were analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the molecular weights of polylactic acid degrading enzymes I, II and III were calculated as 24.0, 19.5 and 18.0 kDa by mobility calculation.
[0051] 2. Determination of isoelectric point
[0052] The isoelectric points of the three polylactic acid degrading enzymes were measured by isoelectric focusing electrophoresis. After electrophoresis, the gel was cut to measure the pH gradient, and the isoelectric point of the protein was estimated. At the same time, lysozyme with a pI of about 11 was used as a control. Based on the pH gradient measurement results of gel cutting and electrophoretic patterns, it can be speculated that the isoelectric points of the three isolated polylactic acid degrading enzymes I, II and III are all greater than 10, so these three enzymes are all basic protein...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com