Solid phase micro-extraction stainless steel fiber and preparation method thereof
A technology of stainless steel and stainless steel wire, which is applied in the field of new solid phase microextraction fiber and its preparation, can solve the problems of easy fiber breakage, high cost, and easy bending of fiber, and achieve high enrichment efficiency, simple method and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (a) Put the water bath in a well-ventilated fume hood and heat to a constant temperature of 40°C;
[0032] (b) in the polytetrafluoroethylene container, add the hydrofluoric acid of mass concentration 40%, it is put into (a) in the water bath constant temperature;
[0033] (c) A 304 stainless steel wire with a diameter of 300 μm is vertically fixed on the upper end of the polytetrafluoroethylene container in (b), so that about 4 cm of the stainless steel wire is immersed in hydrofluoric acid. React for 10-15 minutes;
[0034] (d) The corroded stainless steel wire is taken out, and the residual hydrofluoric acid on the stainless steel wire is carefully rinsed off with clear water;
[0035] (e) Insert the stainless steel wire in (d) into the gas phase injection port and age at 320° C. for 4 h under the protection of nitrogen to obtain the stainless steel fiber for solid phase microextraction.
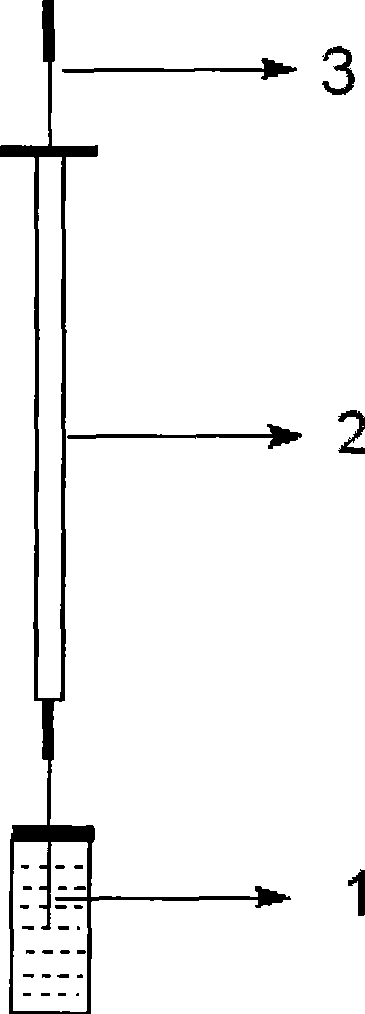
[0036] The prepared solid-phase microextraction stainless steel fiber 1 is l...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (a) Put the water bath in a well-ventilated fume hood and heat to a constant temperature of 25°C;
[0039] (b) in the polytetrafluoroethylene container, add the hydrofluoric acid of mass concentration 40%, it is put into (a) in the water bath constant temperature;
[0040] (c) Fix a 304 stainless steel wire with a diameter of 300 μm vertically on the upper end of the polytetrafluoroethylene container in (b), so that about 4 cm (or any length between 3 and 6 cm) of the stainless steel wire is immersed in hydrofluoric acid. Reaction about 1h;
[0041] (d) The corroded stainless steel wire is taken out, and the residual hydrofluoric acid on the stainless steel wire is carefully rinsed off with clear water;
[0042] (e) Pack the stainless steel wire in (d) into a micro-injector to make a solid-phase microextraction device. The prepared solid phase microextraction fiber was inserted into the gas phase injection port and aged at 280°C for 4h under the protection of nitrogen...
Embodiment 3
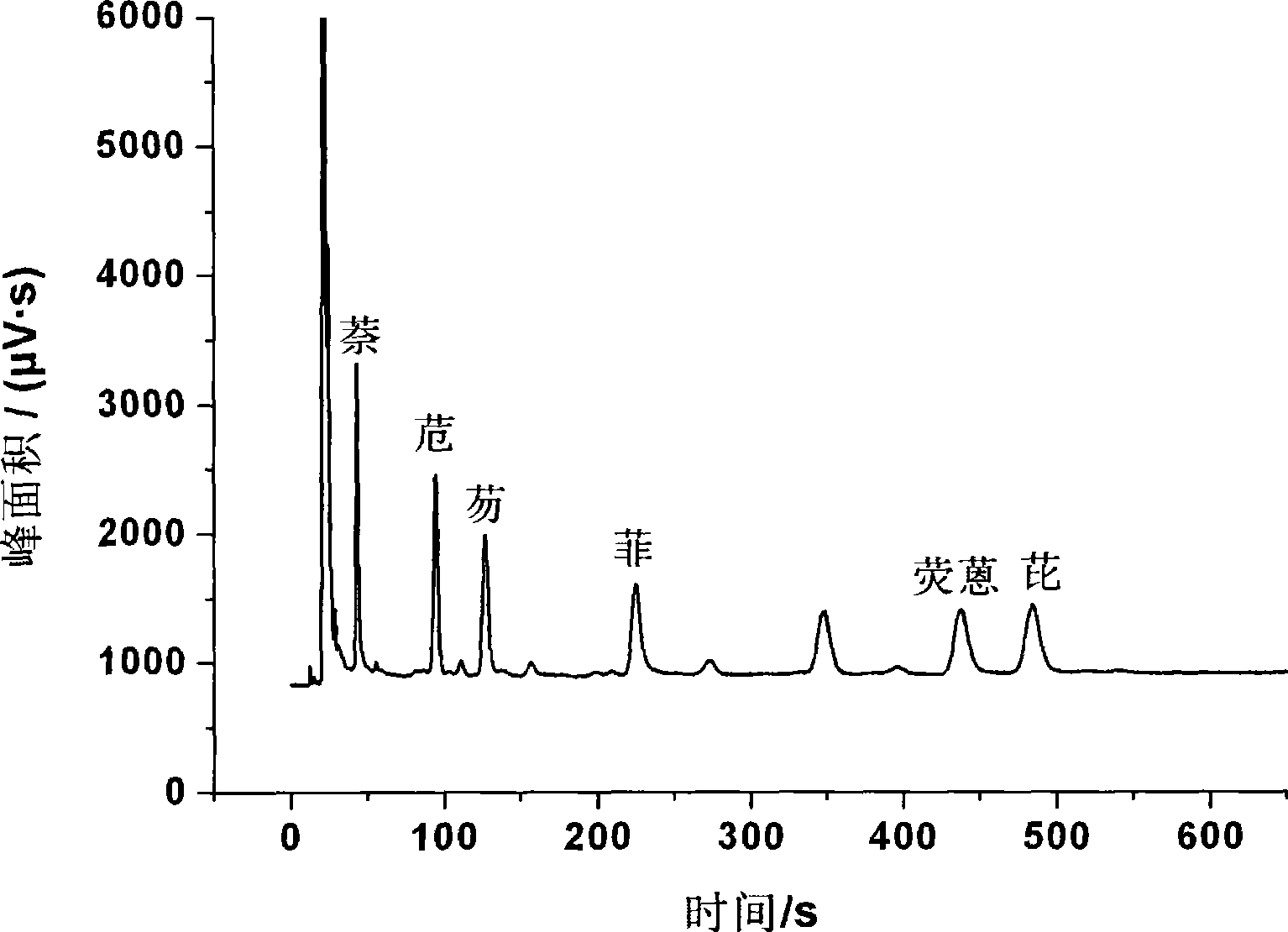
[0044] The solid-phase microextraction stainless steel fiber that embodiment 2 is made is used for the pre-enrichment of six kinds of EPA-PAHs of naphthalene, acenaphthene, fluorene, phenanthrene, fluoranthene, pyrene in the determination water sample (see appendix figure 2 , the concentration of each analyte is 10ppb), and the sensitivity of the detection limit obtained after the enrichment is 2630-3570 times higher than that before the enrichment. The detection limit is 0.24-0.63ppb. Tested repeatedly, its relative standard deviation is less than 6.0%. After the extraction fiber is used 250 times, the enrichment effect basically does not change.
[0045] GC-FID operating conditions: SE-54 capillary quartz column (30m×0.53mm.×1.0μm), heating program: 180°C for 1.5min, 4°Cmin -1 Raise the temperature to 220°C and keep it for 5min. Injection port temperature: 320°C, detector temperature: 320°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com