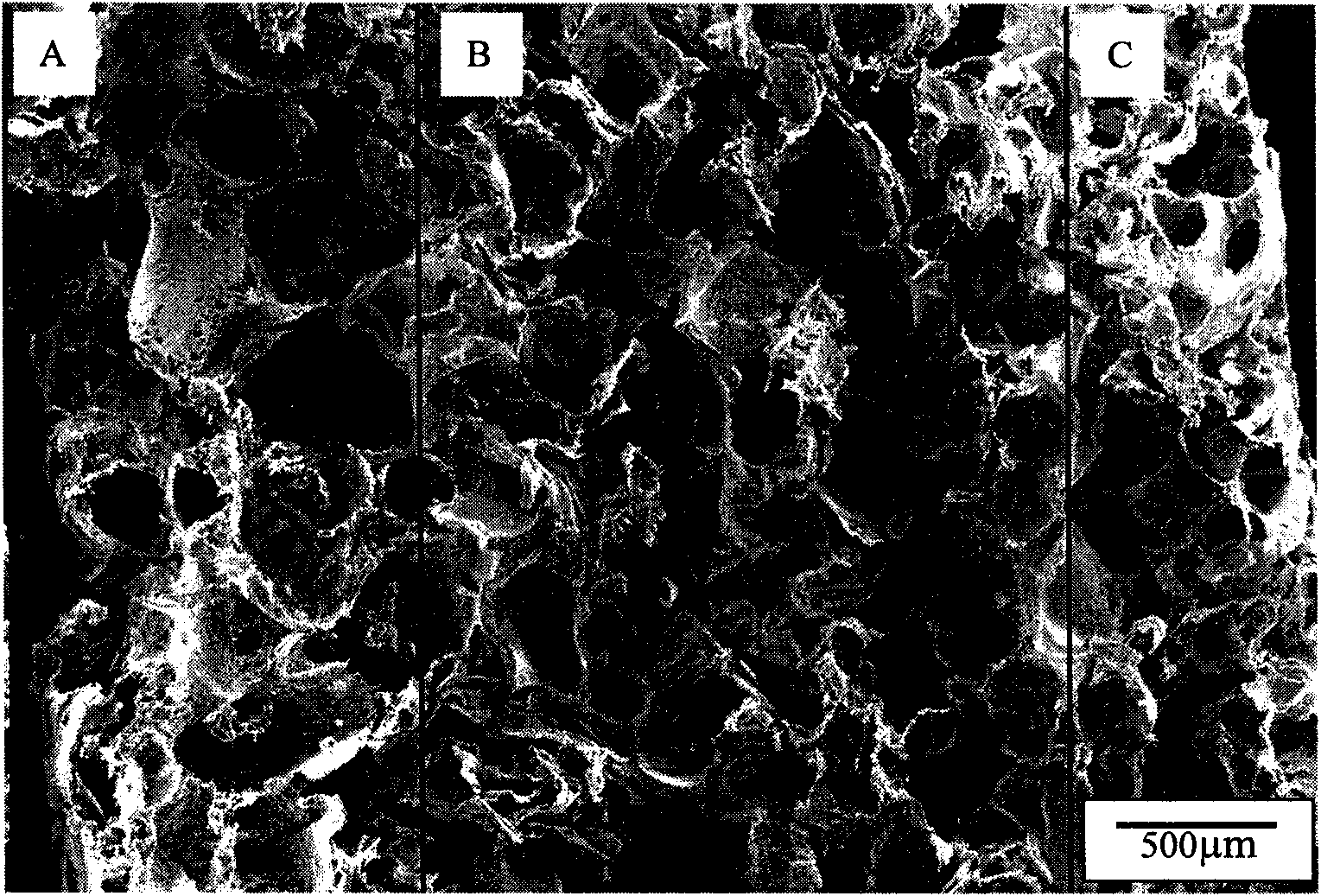
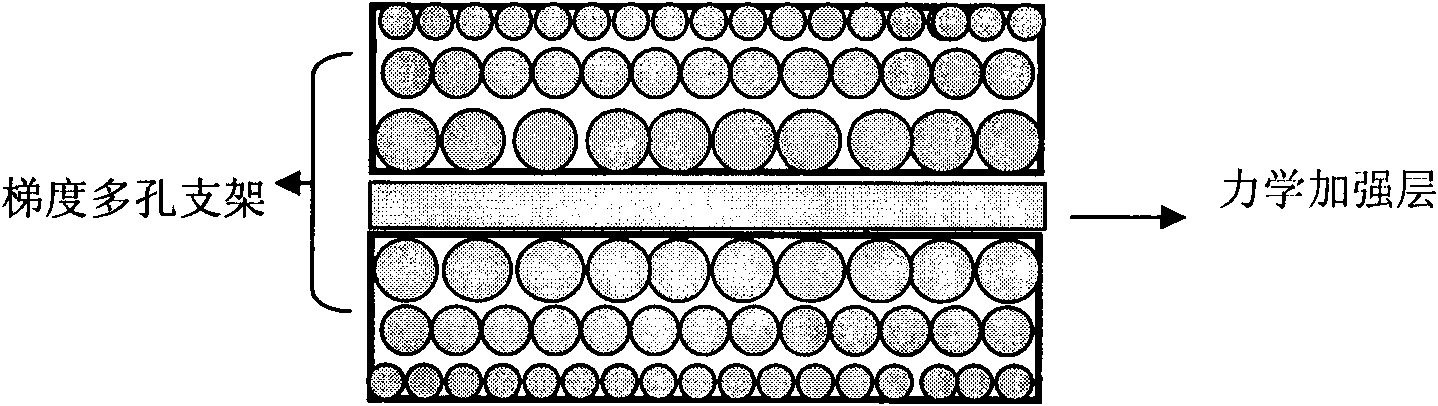
Method for preparing high-strength rib grads multi-aperture bracket
A gradient porous, high-strength technology, applied in the field of polymer materials and biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of increasing the suffering of patients, achieve the effects of improving biocompatibility, increasing mechanical strength, and simplifying the preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] a. Use a standard sieve to sieve 7.2g of 125-224μm, 21.6g of 224-300μm, and 7.2g of 300-340μm sodium chloride respectively.
[0042] b. Weigh 0.8g, 2.4g, 0.8g of polymers with a mass ratio of polylactic acid and polycaprolactone of 7:3, respectively, and place them in three beakers, add 10ml, 30ml, and 10ml of chloroform, and stir magnetically Dissolving, the polylactic acid and polycaprolactone are dissolved to form a polymer blend solution.
[0043]c. Weigh 0.032g, 0.096g, and 0.032g of nano-hydroxyapatite respectively, add them to the polymer solution obtained in the previous step, stir magnetically for half an hour, and then vibrate ultrasonically for half an hour, so that the hydroxyapatite is evenly dispersed in the in the polymer solution.
[0044] d. Add 7.2g of 125-224μm, 21.6g of 224-300μm, and 7.2g of 300-340μm sodium chloride obtained in step a to the blend obtained in step c, and stir with a glass rod to disperse the salt evenly A pasty mixture with certa...
Embodiment 2
[0051] a. Sieve 18g of 125-224μm, 54g of 224-300μm, and 18g of 300-340μm potassium chloride with a standard sieve respectively.
[0052] b. Weigh 2g, 6g, and 2g of polylactic acid and place them in three beakers respectively, add 20ml, 60ml, and 20ml of dichloromethane respectively, stir and dissolve with magnetic force, and dissolve the polylactic acid to form a polymer solution.
[0053] c. Weigh 0.16g, 0.48g, and 0.16g of nano-hydroxyapatite respectively, add them to the polylactic acid solution obtained in the previous step, stir magnetically for half an hour, and then oscillate ultrasonically for 1 hour, so that the hydroxyapatite is evenly dispersed in the in polylactic acid solution.
[0054] d. Add 18g of 125-224μm, 54g of 224-300μm, and 18g of 300-340μm potassium chloride obtained in step a to the blend obtained in step c, and stir with a glass rod to disperse the salt evenly in the solution A pasty mixture with certain fluidity containing porogens with different par...
Embodiment 3
[0061] a. Use a standard sieve to sieve 7.2g of 125-224μm, 21.6g of 224-300μm, and 7.2g of 300-340μm sodium chloride respectively.
[0062] b. Weigh 0.8g, 2.4g, 0.8g of polymerized monomers with a molar ratio of LA:Cl of 7:3 copolymer PLCL respectively in three beakers, add 10ml, 30ml, 10ml of chloroform, magnetically Stir to dissolve, so that the copolymer PLCL dissolves to form a polymer solution.
[0063] c. Weigh 0.032g, 0.096g, and 0.032g of calcium silicate, respectively, and add them to the polymer solution obtained in the previous step, stir magnetically for half an hour, then ultrasonically shake for half an hour, so that the calcium silicate is evenly dispersed in the polymer solution middle.
[0064] d. Add 7.2g of 125-224μm, 21.6g of 224-300μm, and 7.2g of 300-340μm sodium chloride obtained in step a to the blend obtained in step c, and stir with a glass rod to disperse the salt evenly A pasty mixture with certain fluidity containing porogens with different parti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com