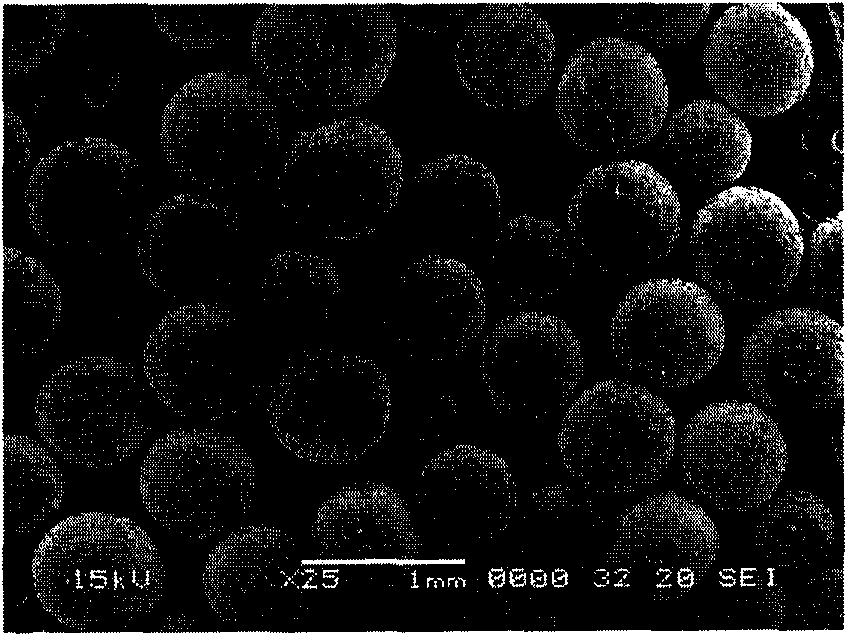Preparation method of phenolic resin polymer microspheres
A technology of phenolic resin and polymer, which is applied in the field of preparing spherical phenolic resin polymer by one-pot one-step method, which can solve the problems of difficult control of particle size, high labor intensity, poor sphericity, etc., and achieve uniform particle size distribution, surface Smooth, highly spherical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Example 1: 0.5 g of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, 27.74 g of ethylene glycol monophenyl ether, 61.00 g of formic acid, and 70.42 g of formaldehyde were mixed uniformly, and then 14.67 g of concentrated sulfuric acid was slowly added dropwise at room temperature. After the dropwise addition, heat to 70 degrees Celsius and stir for 6 hours; filter out the polymer microspheres, soak the solution with 5% sodium hydroxide for 5 hours, wash with water until neutral, and dry.
[0013] The scanning electron micrograph of gained phenolic resin type polymer microsphere is as follows figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0014] Example 2: 2.59 grams of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, 27.74 grams of ethylene glycol monophenyl ether, 61.00 grams of formic acid, and 70.42 grams of formaldehyde were mixed uniformly, and then 14.67 grams of concentrated sulfuric acid was slowly added dropwise at room temperature. After the dropwise addition, heat to 70 degrees Celsius and stir for 6 hours; filter out the polymer microspheres, soak the solution with 5% sodium hydroxide for 5 hours, wash with water until neutral, and dry.
[0015] Gained phenolic resin type polymer microsphere particle size distribution is as follows Figure 4 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0016] Example 3: 0.79 g of carboxymethylmethyl cellulose, 27.74 g of ethylene glycol monophenyl ether, 61.00 g of formic acid, and 35.55 g of formaldehyde were mixed uniformly, and then 14.67 g of concentrated sulfuric acid was slowly added dropwise at room temperature. After the dropwise addition, it was heated to 70 degrees Celsius and stirred for 6 hours; the polymer microspheres were filtered out, soaked in 5% sodium hydroxide solution for 5 hours, washed with water until neutral, and dried.
[0017] The scanning electron micrograph of gained phenolic resin type polymer microsphere is as follows figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com