Fermentation production method and application of high-yield exopolysaccharide strain and amylase thereof
A technology of extracellular polysaccharides and production methods, applied in the field of polysaccharides, to achieve the effects of enhancing immunity and low production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Identification of a high-production exopolysaccharide strain
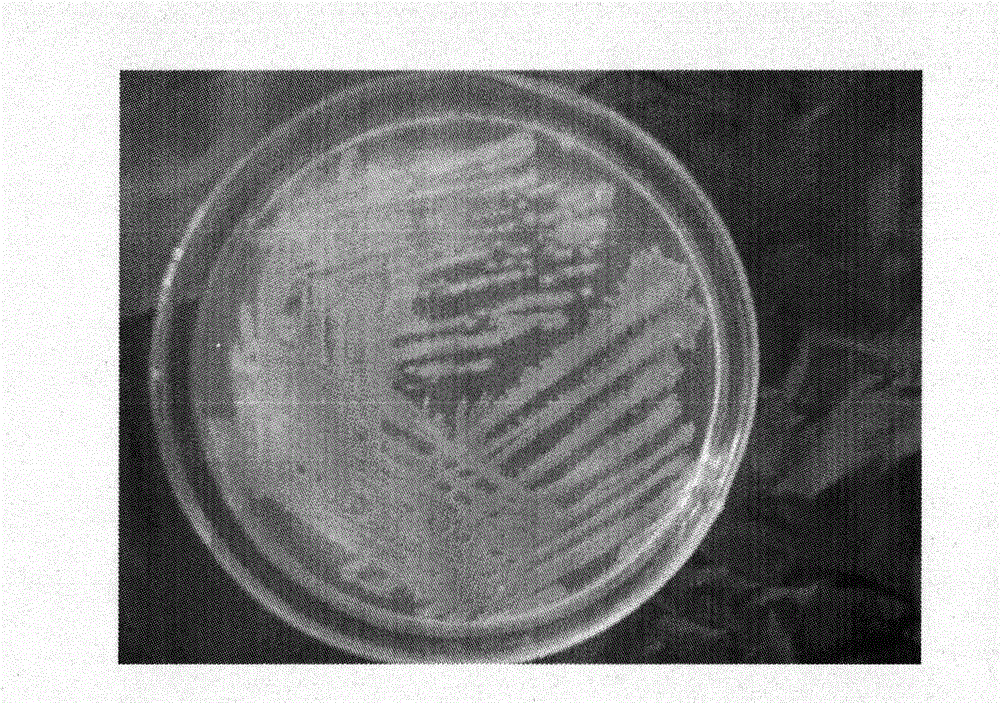
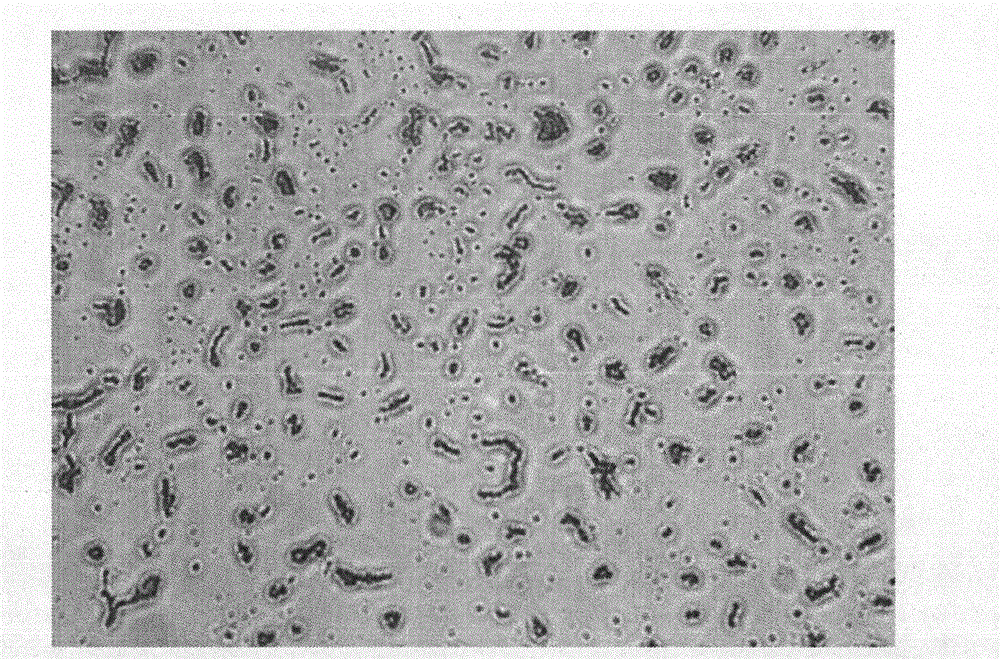
[0031] Classical microbial biochemical tests show that the obtained high-yield exopolysaccharide strain has the characteristics of Proteus, a kind of Proteus penninii, Gram staining is negative, and the size is (0.4~0.6)μm×(1~3) μm, has obvious pleomorphism, is filamentous, has complete cell wall, no capsule, and there are flagella all over the body in young cultures; it grows diffusely on solid medium, forming alternating thickness with the inoculation site as the center, Concentric circular layers of wavy lawns. see figure 1 with 2 .
[0032] Biochemical profile:
[0033] This strain does not ferment lactose, but can produce urease, which decomposes urea and releases ammonia. Indole negative, oxidase negative. Catalase test was positive. Can break down collagen. It can ferment glucose to produce gas, but does not ferment lactose, citric acid and malonic acid. Methyl red staining is posi...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: A production process for the production of exopolysaccharides by fermentation of exopolysaccharide strains
[0035] 1) culture medium
[0036] Take the preparation of 1L medium stock solution as the seed solution, the inoculum size is 1:50, and the seed tank is 50L as an example.
[0037] Recipe: peptone 10g, KH 2 PO 4 5g, inorganic salt 25ml (MgSO 4 0.5g / L, MnSO 4 0.18g / L, FeSO 4 7H 2 (00.1g / L).
[0038] After preparation, use NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 7.2-7.4, and then pack it separately.
[0039] 2) Sterilization
[0040] Put the aliquoted medium stock solution into a high-pressure steam sterilizer for sterilization. The sterilization temperature is 121°C and the time is 20 minutes.
[0041] 3) Vaccination
[0042] After cooling the sterilized medium stock solution, inoculate the bacteria on the aseptic operation table, and pay attention to prevent bacterial contamination during the operation.
[0043] 4) Shaker culture
[0044] After ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: A method for measuring the content of exopolysaccharide produced by the exopolysaccharide strain
[0060] 1) Reagent
[0061] Water is distilled water. Concentrated sulfuric acid (GR), 95% ethanol and anhydrous glucose are commercially available analytically pure.
[0062] Phenol reagent: Take 200g of phenol (CP), add 0.2g of aluminum flakes and 0.1g of sodium bicarbonate, distill and collect the distillate at about 180°C. Make freshly distilled phenol into a solution with a concentration of 50g / L, put it into a brown bottle, and store it in the refrigerator for later use.
[0063] 2) Instrument
[0064] 722 spectrophotometer, BECKMAN low temperature refrigerated centrifuge, vacuum freeze dryer, constant temperature box, rotary evaporator.
[0065] 3) Operation method
[0066] 3.1 Determination of glucose standard curve: Accurately weigh 20 mg of standard glucose dried to constant weight at 105°C and dissolve in 100 ml of double-distilled water respectiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com