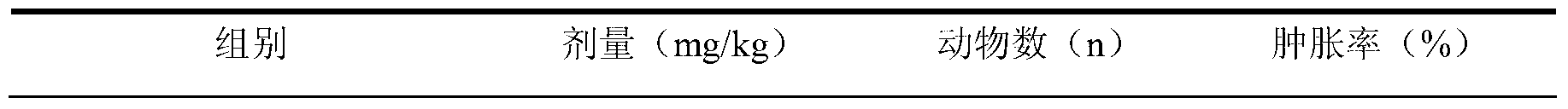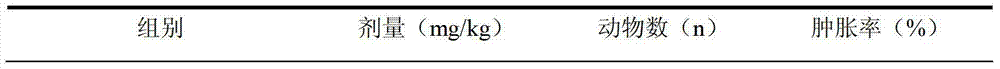Patents
Literature
37 results about "Proteus penneri" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Proteus penneri is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It is an invasive pathogen and a cause of nosocomial infections of the urinary tract or open wounds. Pathogens have been isolated mainly from the urine of patients with abnormalities in the urinary tract, and from stool. P. penneri strains are naturally resistant to numerous antibiotics, including penicillin G, amoxicillin, cephalosporins, oxacillin, and most macrolides, but are naturally sensitive to aminoglycosides, carbapenems, aztreonam, quinolones, sulphamethoxazole, and co-trimoxazole. Isolates of P. penneri have been found to be multiple drug-resistant (MDR) with resistance to six to eight drugs. β-lactamase production has also been identified in some isolates.
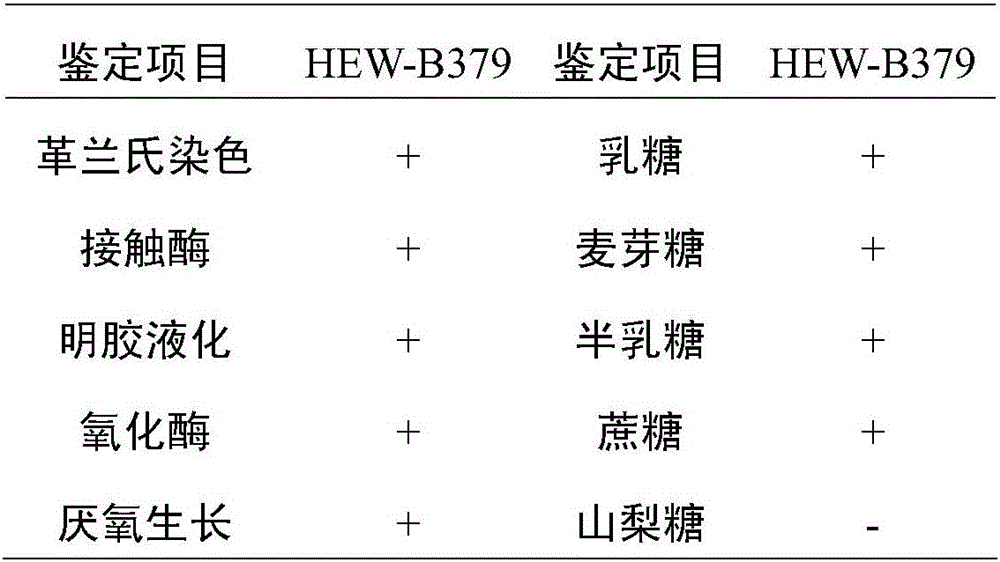
Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 with probiotic effect, and application thereof
ActiveCN106011036AStrong heat resistanceStrong fermentation abilityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliFeed conversion ratio
The invention provides a Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 with a probiotic effect. The above strain is named as HEW-B379, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.12553. The Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 has a substantial probiotic property, and can effectively inhibit growth breeding of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi, salmonella, Shigella, Proteus species, Shewanella putrefaciens and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 has strong stress resistance, can resist high temperature and simulated gastric juice and simulate bile salt environment, can keep the survival rate of 99-100%, and can effectively adjust microbial balance of animal intestinal tracts, inhibit growth of harmful microbes, promote nutrition absorption of animals, improve the conversion rate of a feed and improve the productivity of the animals.
Owner:BEIJING HESWOF BIOTECH CO LTD
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20070009947A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090053702A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStreptococcus pyogenes
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090047671A1Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
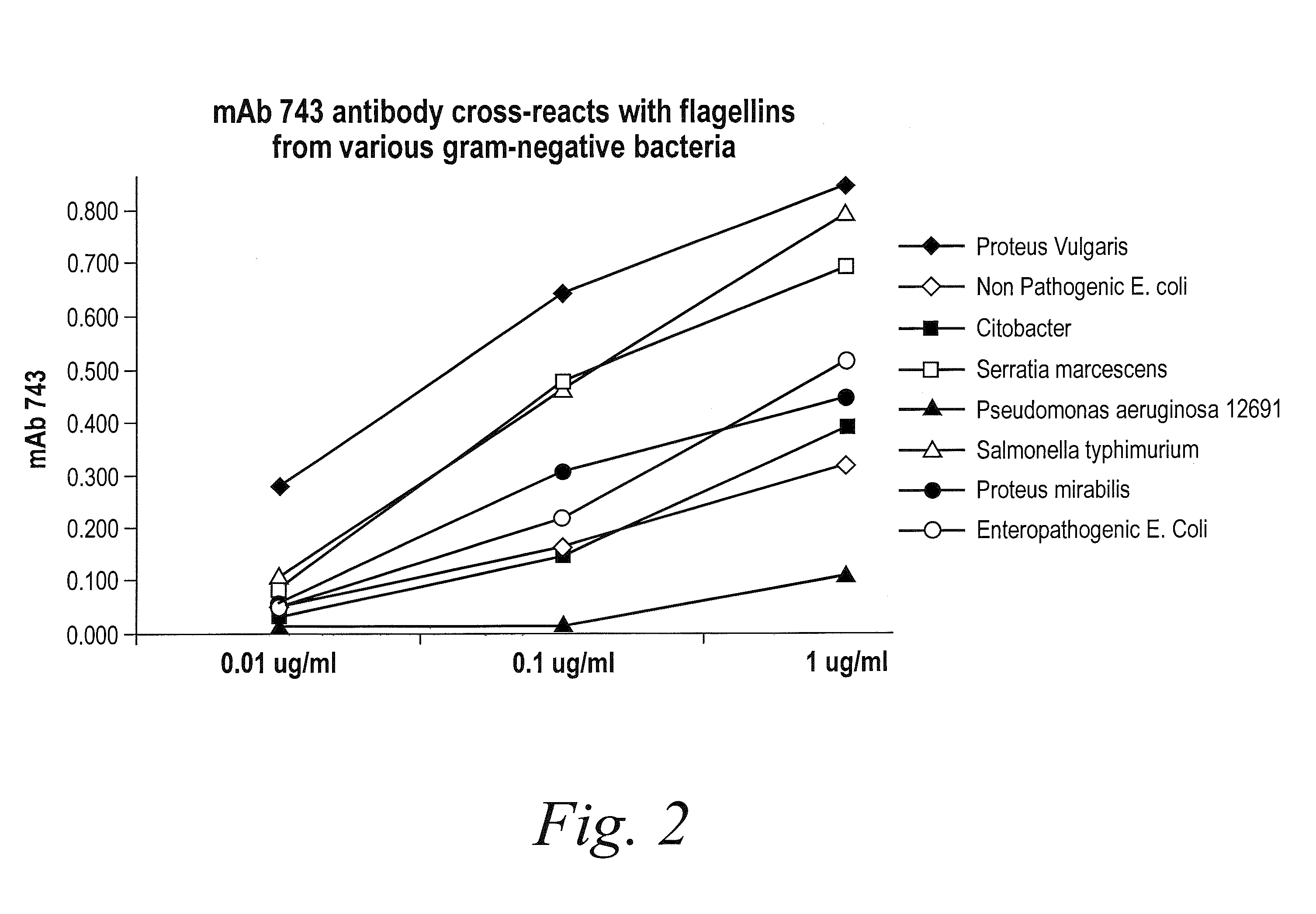
Antibodies against flagellin and uses thereof
The present invention provides a novel class of monoclonal antibodies which have a high affinity, broad spectrum neutralizing reactivity to flagellin from various Gram-negative bacteria including, but not limited to, E. coli, Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Campylobacter and Pseudomonas. The present invention further provides methods of treating infections and diseases using anti-flagellin antibodies in humans, other animals and birds.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
Antibodies against flagellin and uses thereof
The present invention provides a novel class of monoclonal antibodies which have a high affinity, broad spectrum neutralizing reactivity to flagellin from various Gram-negative bacteria including, but not limited to, E. coli, Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Campylobacter and Pseudomonas. The present invention further provides methods of treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and methods of treating enterobacterial infections using anti-flagellin antibodies in humans, other animals and birds.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
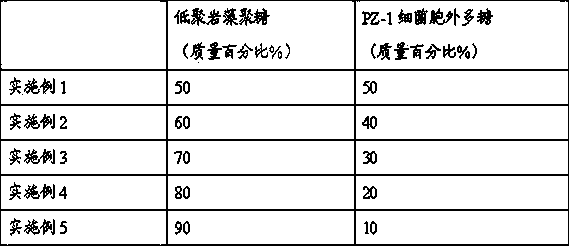
Polysaccharide compound for preventing and treating porcine diarrhea and application thereof
ActiveCN103432158AEffective controlGood effectOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemBacteroidesOligomer
The invention provides a polysaccharide compound for preventing and treating porcine diarrhea and application thereof. The polysaccharide compound is composed of 50-90 wt% of oligomer fucosan and 10-50 wt% of PZ-1 bacterial extracellular polysaccharide, wherein the PZ-1 bacterial extracellular polysaccharide is prepared by fermenting Proteus penneri PZ-1 and performing extraction and purification; and the oligomer fucosan is prepared by the following steps: extracting from Laminaria digitata powder, hydrolyzing and separating with a hyperfiltration membrane. The oligomer fucosan and the PZ-1 bacterial extracellular polysaccharide are crudely mixed proportionally by a progressive mixing method, and finally mixed uniformly to obtain the polysaccharide compound. The polysaccharide compound provided by the invention can reduce the consumption of antibiotic medicines in the pig breeding process, provides safe and green pork products for consumers, and effectively prevents and treats porcine diarrhoea. The polysaccharide compound can be used as a substitute of an antibiotic medicine for treating porcine diarrhea. The polysaccharide compound has better effect than the single oligomer fucosan or PZ-1 bacterial extracellular polysaccharide, and much better than the simple addition of the oligomer fucosan and PZ-1 bacterial extracellular polysaccharide.
Owner:福建九为生物技术有限公司
Nucleotide specific to ITS of Balcillus proteus mirabilis and use thereof
ActiveCN101469326AQuick checkSensitive detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSocial benefitsNucleotide
The invention relates to nucleotide special to an Internal transcribed spacer (ITS for short) of a 16S rRNA-23S rRNA gene in Proteus mirabilis, in particular to oligonucleotide special to the ITS in the Proteus mirabilis and application thereof. The invention also provides a PCR detection reagent taking an oligonucleotide pair as a primer and a detection method thereof. The detection method utilizes the PCR reagent to detect the Proteus mirabilis in human body and the environment, is simple, convenient and quick, has good specificity and high sensitivity, can be used in the fields of supervision and detection of food and clinical samples, detection of pathogen in the food, microbial classification and epidemiological investigation and so on, and has deep social benefit and large economic benefit.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Antibodies against flagellin and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090191208A1Avoid loweringIncrease intakeSnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEscherichia coliCitrobacter
The present invention provides a novel class of monoclonal antibodies which have a high affinity, broad spectrum neutralizing reactivity to flagellin from various Gram-negative bacteria including, but not limited to, E. coli, Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Campylobacter and Pseudomonas. The present invention further provides methods of treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and methods of treating enterobacterial infections using anti-flagellin antibodies in humans, other animals and birds.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
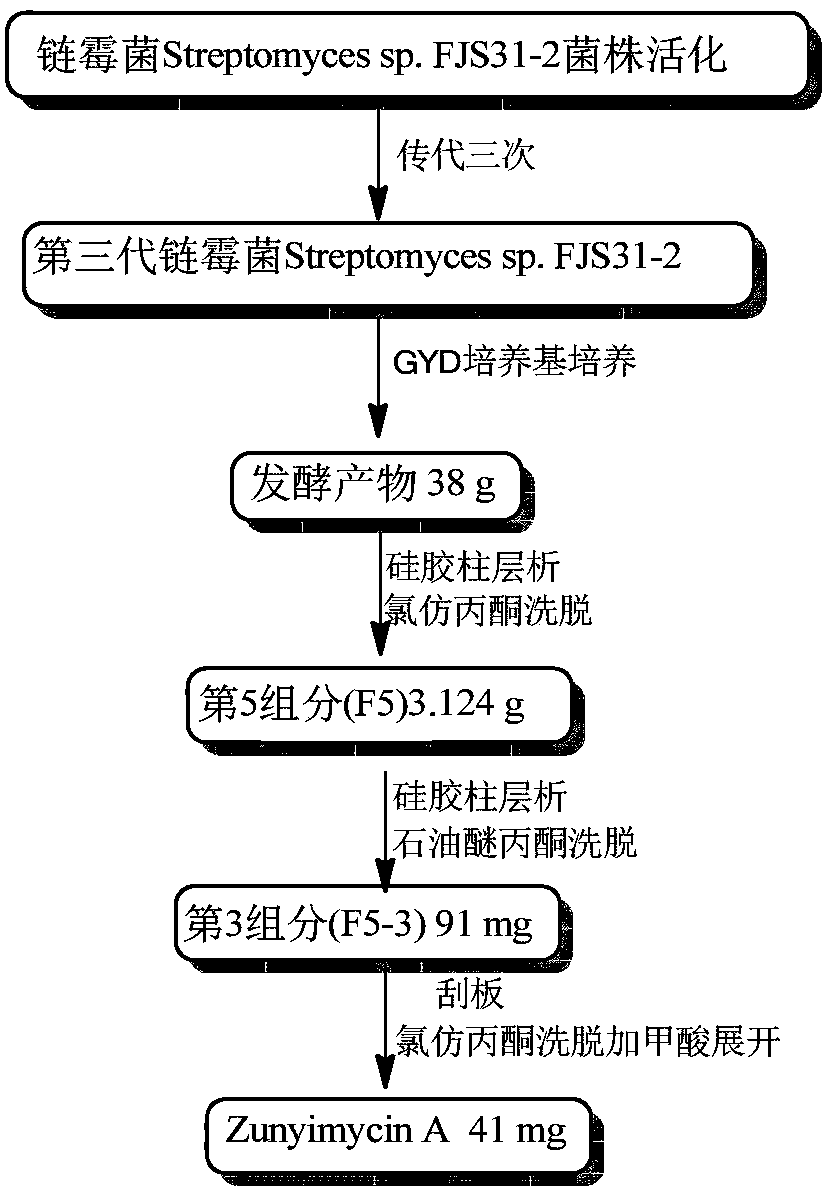
Preparation method for dichloro substituted II-type halogenated polyketone compound and antibacterial activity application
ActiveCN107937453AImprove reproductive performanceTo promote metabolismAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCandida famata
The invention discloses a preparation method for a dichloro substituted II-type halogenated polyketone compound zunyimycin A, wherein the compound is derived from a secondary metabolite of a streptomyces sp.FJS31-2 strain (with the strain preservation number of CGMCC4.7321), and finally, a structure is identified and determined after strain activation, expansion culture and isolation. The compoundcan be used in treatment of diseases infected by gram-positive bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and drug-resistant bacteria thereof, staphylococcus epidermidis, bacillus subtilis and thelike, is used in treatment of diseases infected by gram-negative bacteria such as super-spectrum beta-lactamase escherichia coli (ESBL), proteusbacillus vulgaris, bacterium burgeri and the like, andis used for treatment of diseases infected by fungi, such as candida albicans.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Pediococcus pentosaceus NHB-PpA9601 and application thereof
ActiveCN113388551AGood antibacterial effectIncrease acidityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyVibrio parahaemolyticus
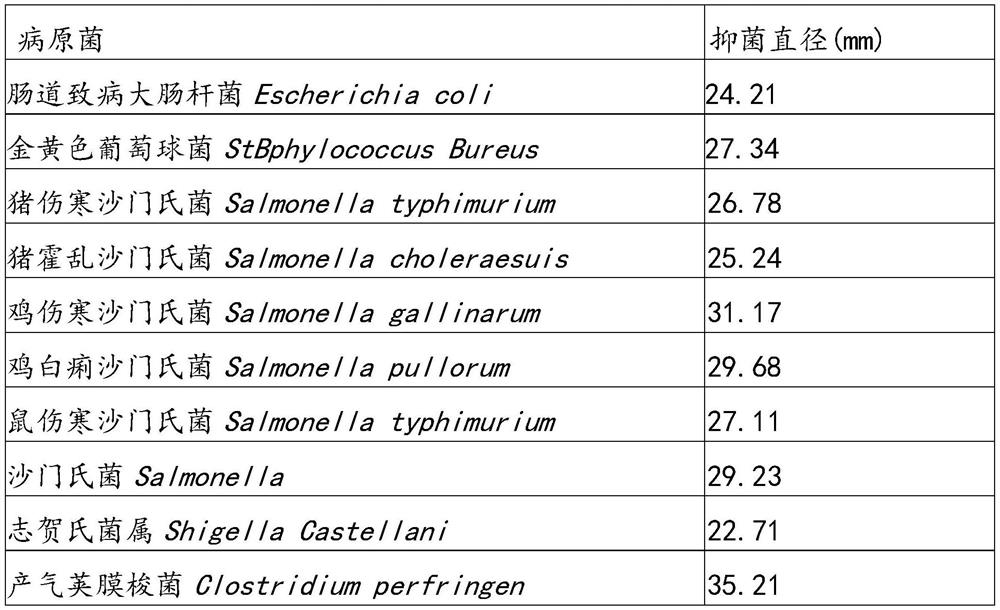
The invention provides a pediococcus pentosaceus NHB-PpA9601. The pediococcus pentosaceus NHB-PpA9601 is separated from intestinal tracts of white feather broilers, and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short, the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3 #, 1 # yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the postal code is 100101), the preservation number is CGMCC NO.22646, and the preservation date is May 31, 2021. The pediococcus pentosaceus NHB-PpA9601 has the advantages that the obvious probiotic property is realized, the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria such as intestinal pathogenic escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella suis, salmonella choleraesuis, salmonella gallinarum, salmonella pullorum, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella, shigella, bacillus perfringens, proteus penneri, aeromonas hydrophila and vibrio parahaemolyticus can be effectively inhibited; the pediococcus pentosaceus NHB-PpA9601 can be used for producing a wet-based fermented feed, and can be used for effectively improving intestinal health and increasing economic benefits.
Owner:NEW HOPE LIUHE +2
Bacillus subtilis, its combination preparation and method for preparing combination preparation
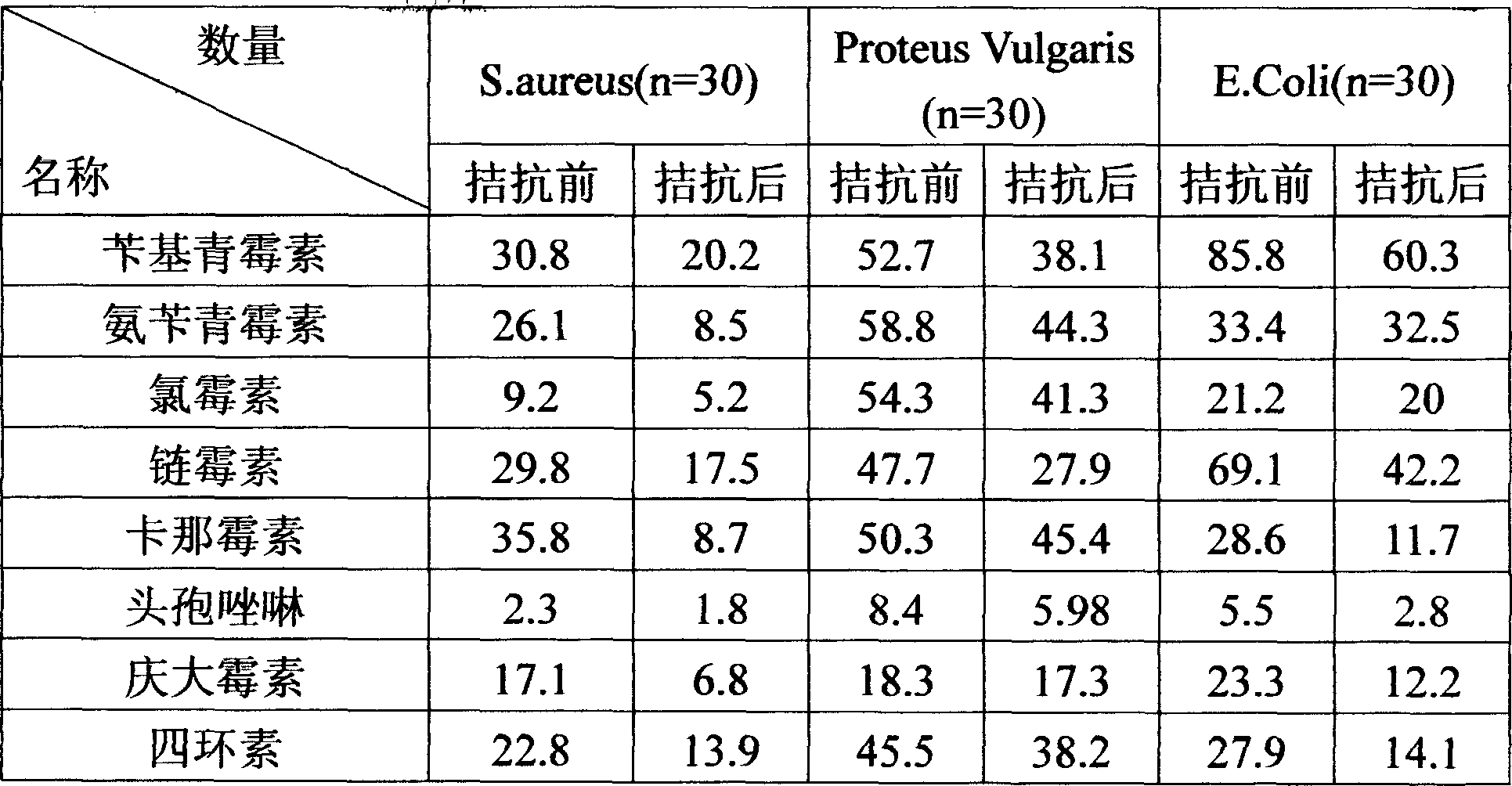
The invention relates to a bacilli, its compound preparation and the preparing method for the compound preparation. Its name is Bacillus subtilis LY-35, which is preserved in the general microbe center of Micro Germ conservation Management committee of China, and its conservation number is:CGMCC N0.1222. The preparation is a mixture of lambda phage of culture of bacilli and staphylococcus, streptococcus, colibacillus, bacillus proteus, pseudomonad, salmonella, pasteurella and klebsiella, can cure and prevent all kinds of illness caused by conditional pathogen,is a micro biological preparation which can be used by being mixed with antibiotics or replace antibiotics without any remainder and pollution, with good curative effect and safety.
Owner:烟台绿云生物工程研究院有限公司
Detection, identification and differentiation of Proteus species using the spacer region
InactiveUS20050176048A1Rapid and reliable hybridizationRapid and reliable methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementP. mirabilisSpecific detection
The present invention relates to new nucleic acid sequences derived from the ITS region, between the 16S and 23S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) or rRNA genes, to be used for the specific detection and / or identification of Proteus species, in particular of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris and / or Proteus penneri in a biological sample. The present invention relates also to a method for the specific detection and / or identification of Proteus species, in particular Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris and / or Proteus penneri, using said new nucleic acid sequences derived from the ITS (Internal Transcribed Spacer) region. It relates also to nucleic acid primers to be used for the amplification of said spacer region of Proteus species in a sample.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV (NL) +1
Primers, probes, kit and method for detecting proteus mirabilis
ActiveCN106566889AAccurate detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
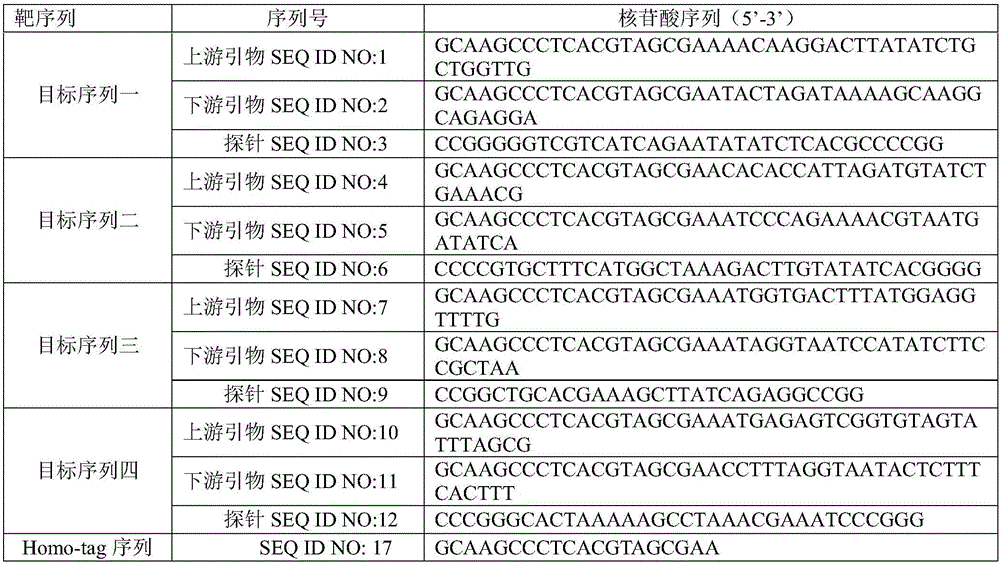
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbiological detection, and in particular, relates to primers, probes, a kit and a method for detecting proteus mirabilis. The invention discloses a set of primers and probes for detecting the proteus mirabilis, wherein the set of primers and probes comprise primers and probes for detecting four target sequences. The kit for detecting the proteus mirabilis comprises the primers and probes for detecting the proteus mirabilis. The primers and probes provided by the invention can accurately detect the proteus mirabilis, have good specificity and high sensitivity, and avoid generation of false positives; and the kit is low in cost, easy to use, and suitable for rapid screening for the proteus mirabilis.
Owner:SHENZHEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
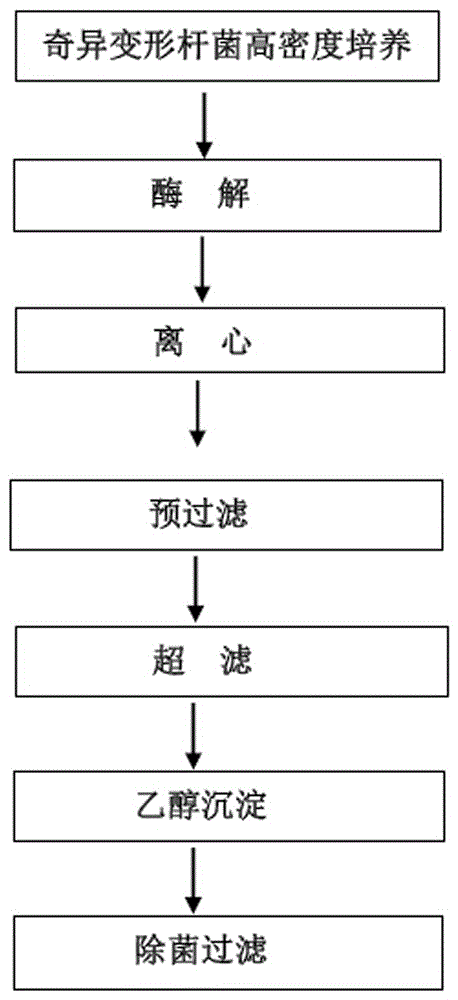
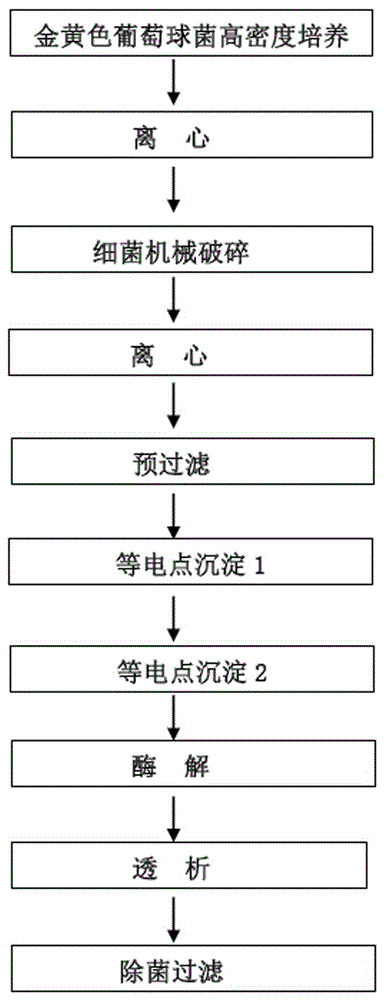
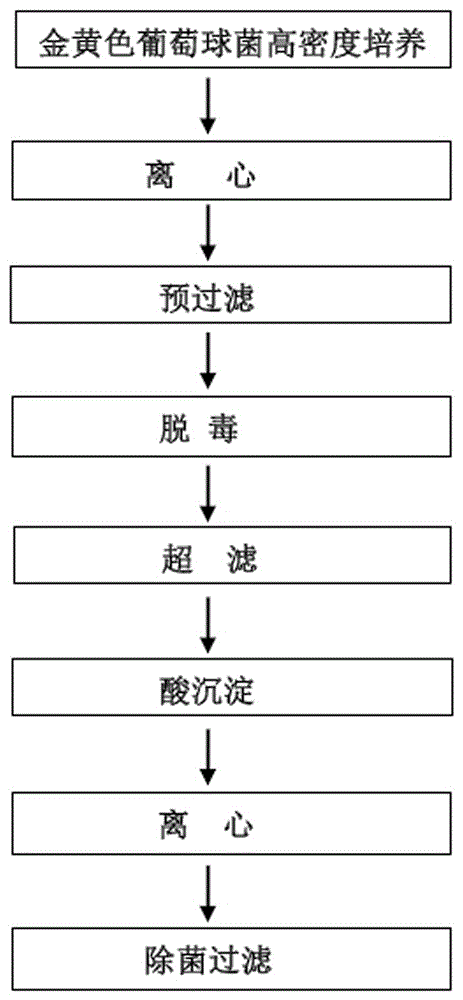
Method for preparing proteus mirabilis-staphylococcus aureus-pseudomonas aeruginosa adsorption combined vaccine
InactiveCN105709218ARich varietySimple processAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for preparing a proteus mirabilis-staphylococcus aureus-pseudomonas aeruginosa adsorption combined vaccine. The method includes the steps that firstly, a proteus mirabilis culture solution is subjected to in-situ digestion, high-speed centrifugation, pre-filtering, ultrafiltration and precipitation, and a proper proteus mirabilis cell membrane soluble antigen raw solution is obtained; secondly, a staphylococcus aureus bacterium suspension is subjected to centrifugation, smashing, re-centrifugation, filtering, precipitation, enzymolysis and dialysis, and a proper staphylococcus aureus cytoplast antigen raw solution is obtained; thirdly, a staphylococcus aureus and pseudomonas aeruginosa culture solution is subjected to centrifugation and pre-filtering, formalin is added for detoxification, then purification is conducted, and a proper inactivated staphylococcus aureus and pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin raw solution is obtained. The vaccine is used for preventing burn, scalding and infection caused by one or more of conditioned pathogens including proteus mirabilis, staphylococcus aureus and pseudomonas aeruginosa before and after operations in an intramuscular deep injection mode.
Owner:LIAONING CHENGDA BIOTECH
Detection, identification and differentiation of proteus species using the spacer region
InactiveUS20090098558A1Rapid and reliable methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenus AmoebobacterSpecific detection
The present invention relates to new nucleic acid sequences derived from the ITS region, between the 16S and 23S ribosomal ribionucleic acid (rRNA) or rRNA genes, to be used for the specific detection and / or identification of Proteus species, in particular of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris and / or Proteus penneri in a biological sample.The present invention relates also to a method for the specific detection and / or identification of Proteus species, in particular Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris and / or Proteus penneri, using said new nucleic acid sequences derived from the ITS (Internal Transcribed Spacer) region.It relates also to nucleic acid primers to be used for the amplification of said spacer region of Proteus species in a sample.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV +1
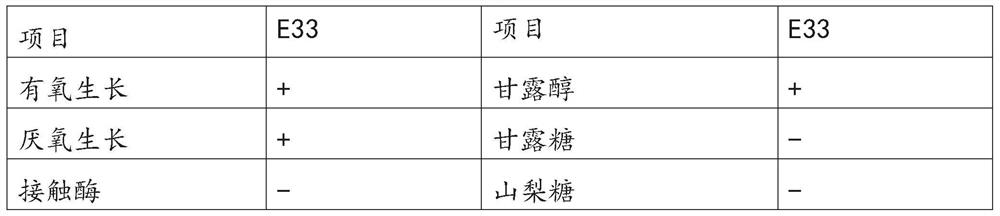
Lactobacillus salivarius NHE-LsE33 and application thereof
ActiveCN113388550AGood antibacterial effectIncrease acidityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyLactobacillus salivarius
The invention provides Lactobacillus salivarius NHE-LsE33. The Lactobacillus salivarius NHE-LsE33 is used for separating intestinal tracts of piglets and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short, the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, No.1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the postal code is 100101), the preservation number is CGMCC NO.22510, and the preservation date is May 12, 2021. The lactobacillus salivarius NHE-LsE33 has remarkable prebiotics, and can be used for effectively inhibiting growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria such as intestinal pathogenic escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella choleraesuis, salmonella, shigella, bacillus perfringens, proteus penneri, aeromonas hydrophila and vibrio parahaemolyticus. The lactobacillus salivarius NHE-LsE33 can be prepared into a micro-ecological preparation to be applied to animal breeding, and the strain of the micro-ecological preparation for feed is widened.
Owner:NEW HOPE LIUHE +2
Suppository for treating bacterial vaginitis
InactiveCN100340263CTo achieve the effect of treating both symptoms and root causesGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsSuppositories deliveryEscherichia coliBacteroides
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Bacillus subtilis, composite preparation, and method for preparing the composite preparation
InactiveCN1796542AIncreased sensitivityNo side effectsBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsEscherichia coliDisease
This invention describes a bacillus subtilis and the process for preparing its compound pharmaceutics. The bacillus subtilis is conserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms, the name is: Bacillus subtilis LY-35 and the conservation number is: CGMCC No. 1222. The pharmaceutics is a compound of the bacteriophages of such pathogens as bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus, Streptocoaus, colibacillus, proteus, pseudomonas, salmonella, shigella, pasteurella and klebsiella. The pharmaceutics can prevent and treat the diseases caused by pathogens, and can be a non-polluted, high therapeutic effectiveness and safe substitute for antibiotics.
Owner:烟台绿云生物工程研究院有限公司
Combined bacterin for treating allergic disease and preparation method
The present invention relates to a combined bacterial vaccine for curing allergic diseases of allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, various bronchitis and asthma and deafness resulted from medicine with good therapeutic effect. Said combined bacterial vaccine is formed from diplococcus pneumoniae, alpha-hemolytic streptococcus, beta-hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococuus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis and others.
Owner:天津市长征医院
Combined bacterin for treating allergic disease and preparation method
The present invention relates to a combined bacterial vaccine for curing allergic diseases of allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, various bronchitis and asthma and deafness resulted from medicine with good therapeutic effect. Said combined bacterial vaccine is formed from diplococcus pneumoniae, alpha-hemolytic streptococcus, beta-hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococuus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis and others.
Owner:天津市长征医院
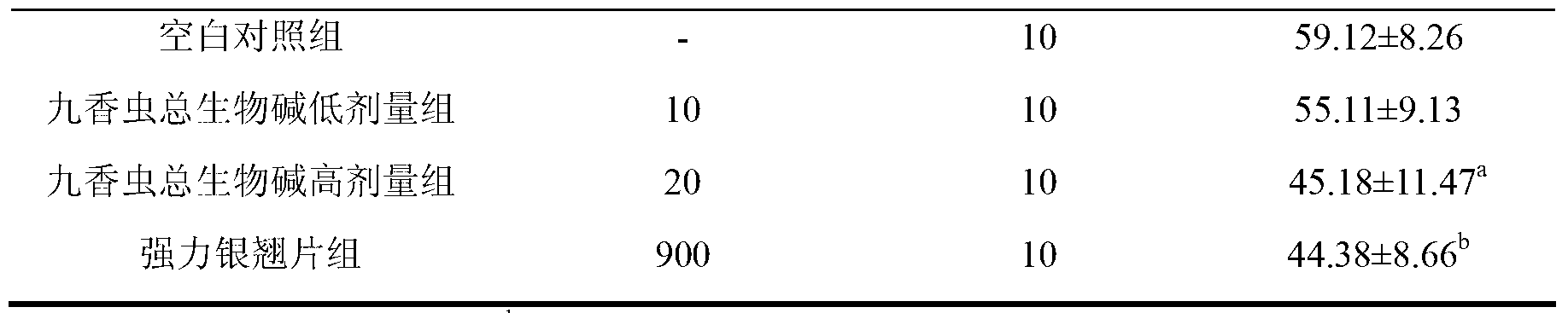
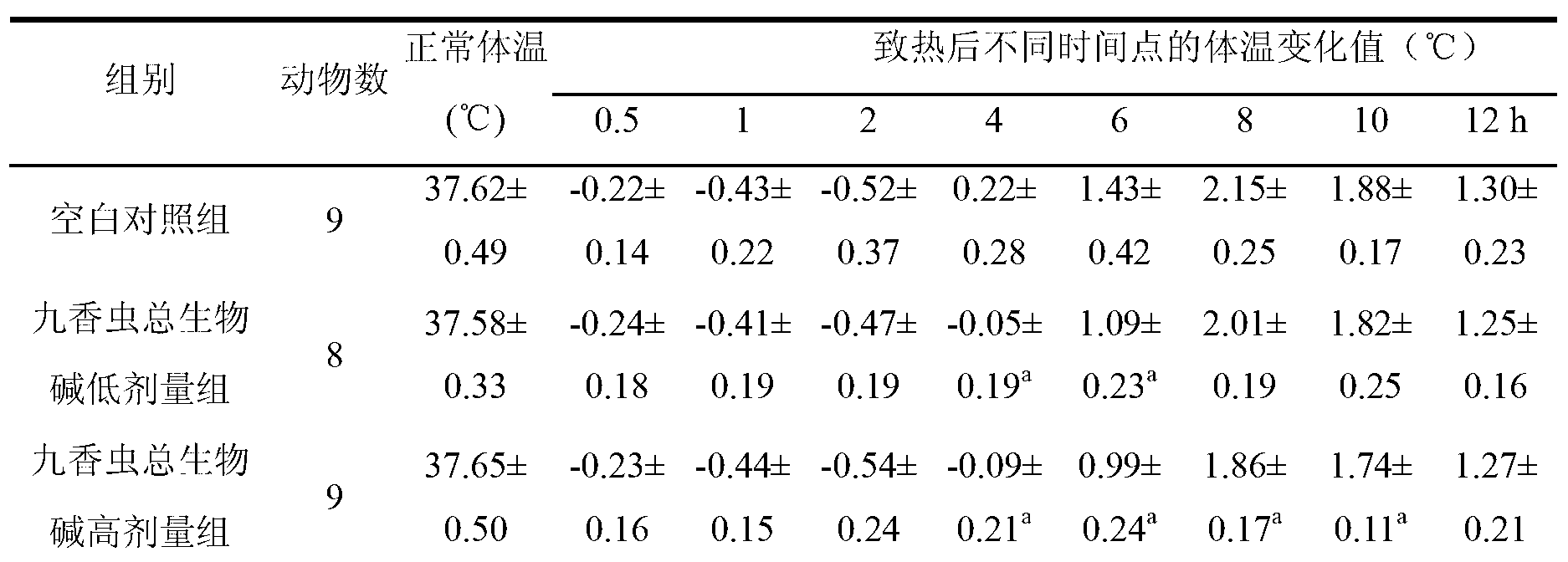
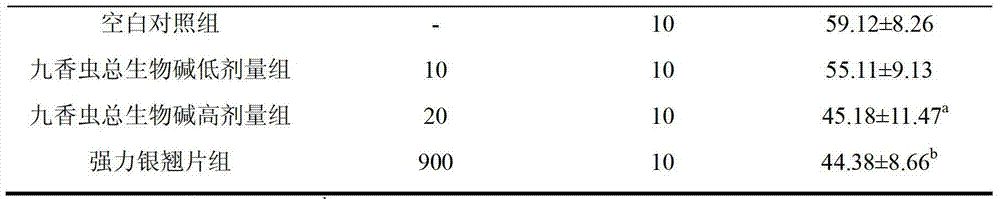
Application of aspongopus total alkaloids in preparation of medicines or health care products with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and immunological enhancement functions
InactiveCN103301160AHigh market valueClarify the material basis of medicinal effectAntibacterial agentsAnthropod material medical ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
The invention discloses application of aspongopus total alkaloids in preparation of medicines or health care products with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and immunological enhancement functions. The biological activity detection result of the aspongopus total alkaloids proves that the aspongopus total alkaloids have the inhibition effects of different degrees on diplococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, type A streptococcus pyogens, type B streptococcus pyogens and proteusbacillus vulgaris, have obvious inhibition effects on the diplococcus pneumoniae and staphylococcus aureus, have the obvious anti-inflammatory effect on ear swell of mice caused by dimethylbenzene and have the obvious antipyretic effect on exothermic reaction of rats caused by dried yeasts, the phagocytic function of the reticuloendothelial system of the mice can be obviously enhanced, and the aspongopus total alkaloids have the immunological enhancement function and are low in toxicity and safe to use.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
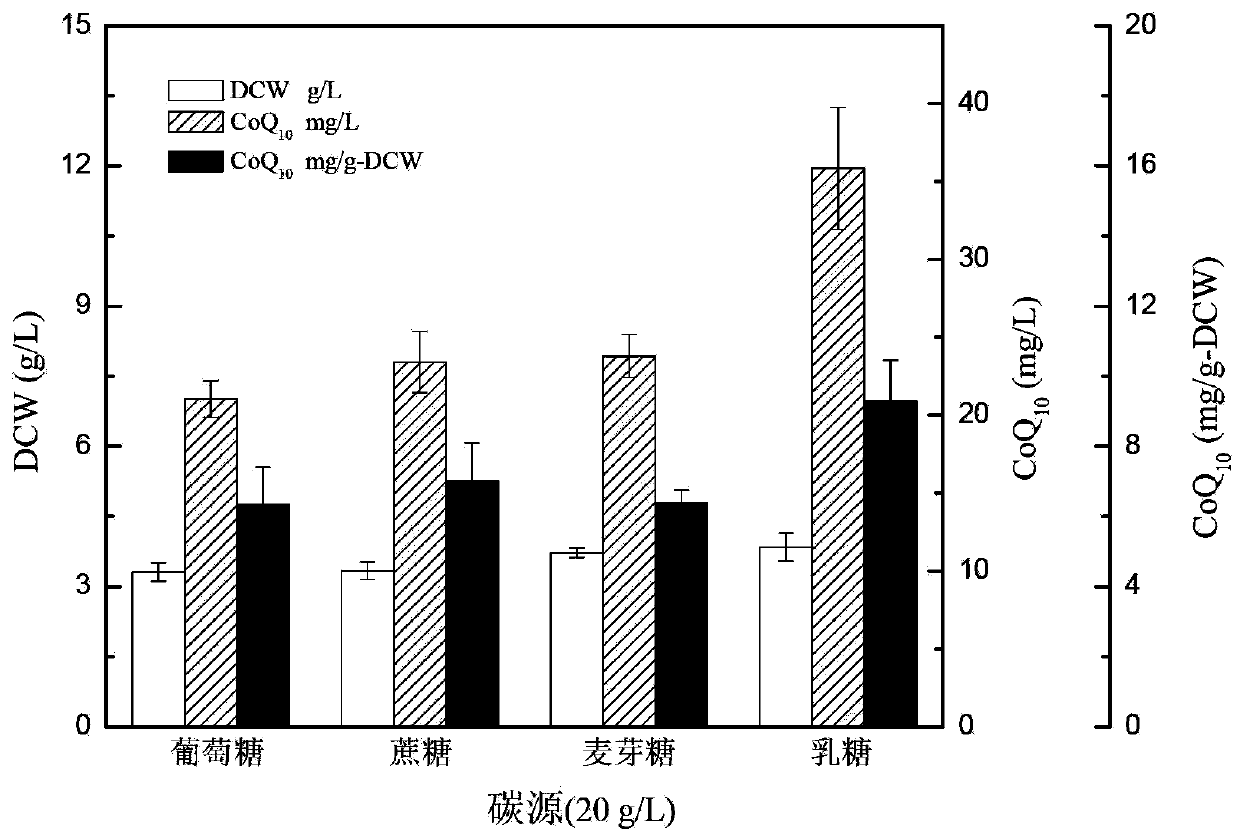
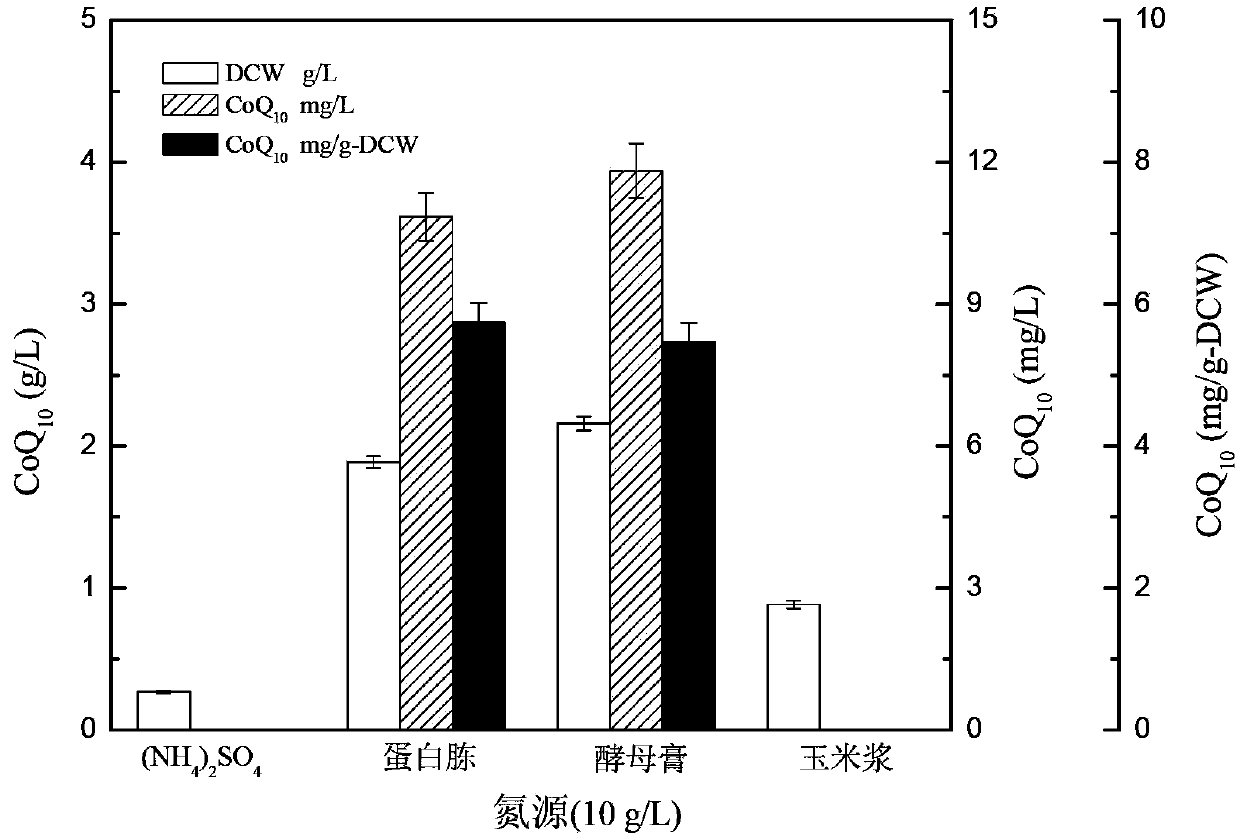
New bacterial strain-proteus penneri CA8 for generating coenzyme Q10 and applications thereof
ActiveCN102994409BIncrease productionSubsequent extraction method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention provides a new bacterial strain-proteus penneri CA8 for generating coenzyme Q10 and applications of the proteus penneri CA8 in preparation of the coenzyme Q10 by microbial fermentation. The bacterial strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, the address is 430072, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, the preservation number is CCTCC No: M2012208, and the preservation date is June 10, 2012. The new bacterial strain-proteus penneri CA8 for generating the coenzyme Q10 has the following main beneficial effects: the new coenzyme Q10 producing strain is provided, and the coenzyme Q10 is prepared by utilizing the microbial fermentation of the strain, so that yield is high, the subsequent extraction method is simple, and the industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:浙江中科宏寿医药科技有限公司
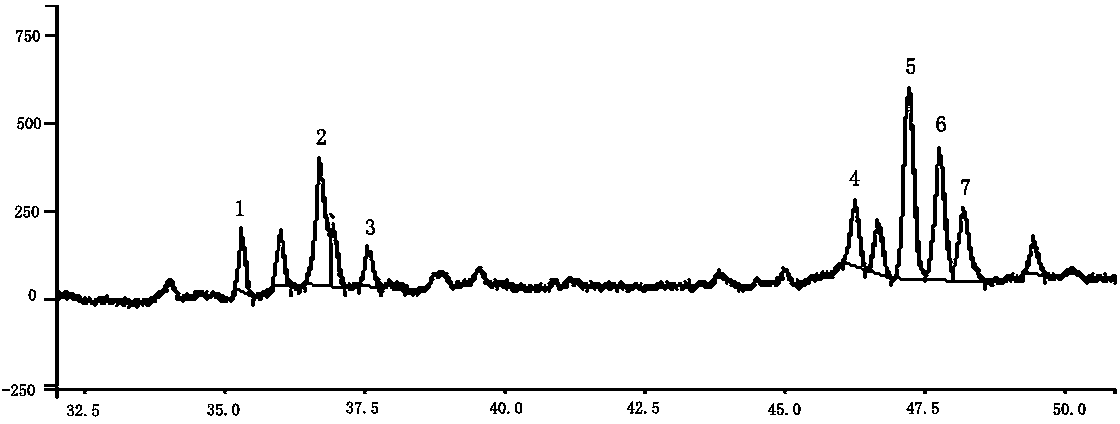
Fermentation production method and application of high-yield exopolysaccharide strain and amylase thereof
ActiveCN101654664BImprove disease resistanceSignificant immune enhancementPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAmylase
The invention relates to an amylase, in particular to a fermentation production method and an application of a high-yield exopolysaccharide strain and an amylase thereof. The strain is a proteus penneri PZ-1. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating a culture medium with the roteus penneri PZ-1; fermenting the culture medium to obtain fermentation culture fluid; cooling and centrifuging the fermentation culture fluid to remove a strain body; getting supernatant fluid; precipitating the supernatant fluid with industrial alcohol; standing still precipitate liquid is obtained; centrifuging the precipitate liquid and taking out a precipitate to obtain crude amylase; and purifying the crude amylase to obtain exopolysaccharide. Proved by a series of experiments, the strain has the proteus characteristics, is used for producing the exopolysaccharide with high yield, and has obvious effects on improving immunity and capability to resist diseases; and the exopolysaccharide producedby fermentation can be used for preparing veterinary injecta, veterinary powder, feed additives, an immunologic adjuvant and functional raw material of healthcare foods.
Owner:厦门百拓生物工程有限公司
Application of aspongopus total alkaloids in preparation of medicines or health care products with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and immunological enhancement functions
InactiveCN103301160BAntibacterial agentsAnthropod material medical ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses application of aspongopus total alkaloids in preparation of medicines or health care products with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and immunological enhancement functions. The biological activity detection result of the aspongopus total alkaloids proves that the aspongopus total alkaloids have the inhibition effects of different degrees on diplococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, type A streptococcus pyogens, type B streptococcus pyogens and proteusbacillus vulgaris, have obvious inhibition effects on the diplococcus pneumoniae and staphylococcus aureus, have the obvious anti-inflammatory effect on ear swell of mice caused by dimethylbenzene and have the obvious antipyretic effect on exothermic reaction of rats caused by dried yeasts, the phagocytic function of the reticuloendothelial system of the mice can be obviously enhanced, and the aspongopus total alkaloids have the immunological enhancement function and are low in toxicity and safe to use.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
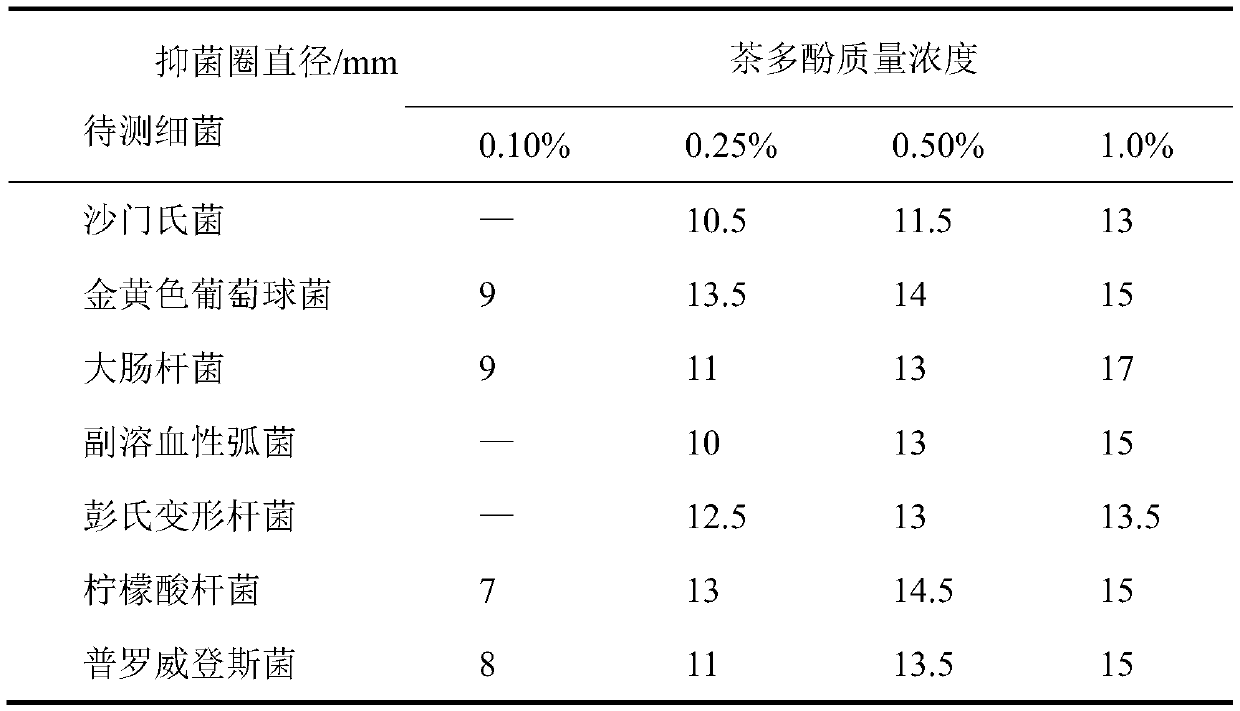
Composite biological preservative and application thereof
ActiveCN110915887ABroaden the antimicrobial spectrumSolution rangeMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsFood ingredient for microbe protectionBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
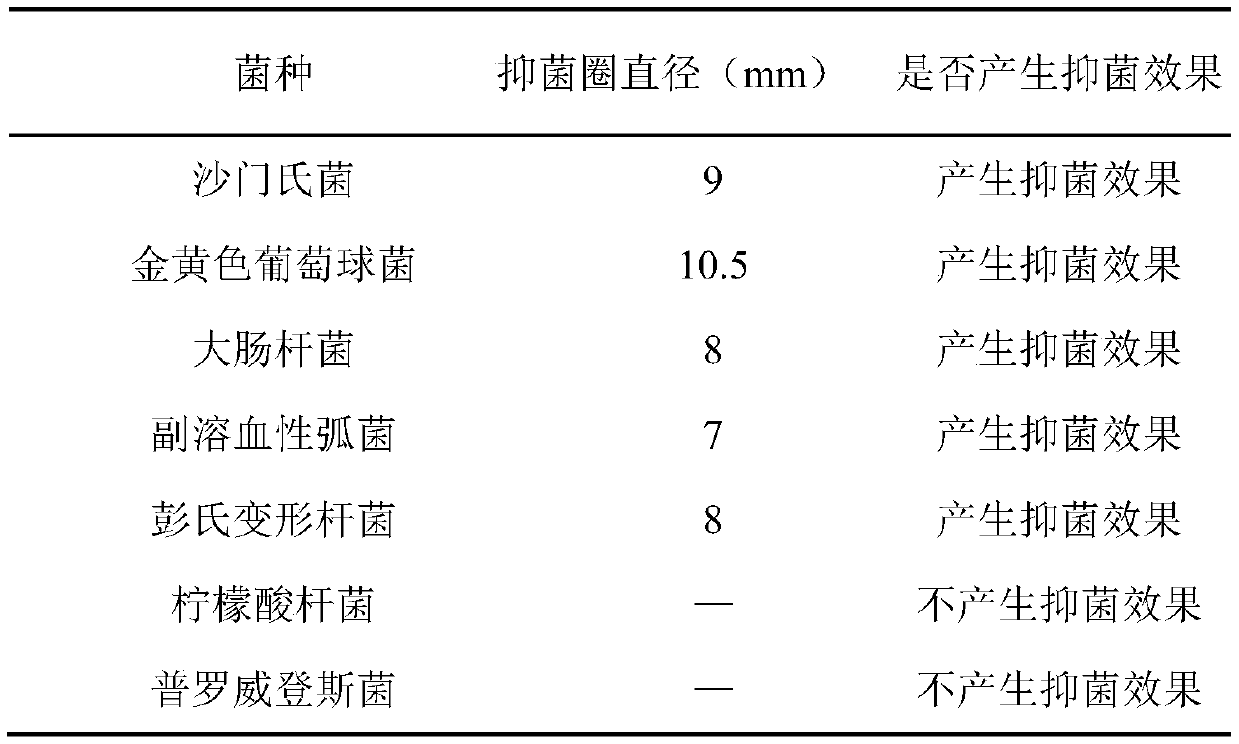
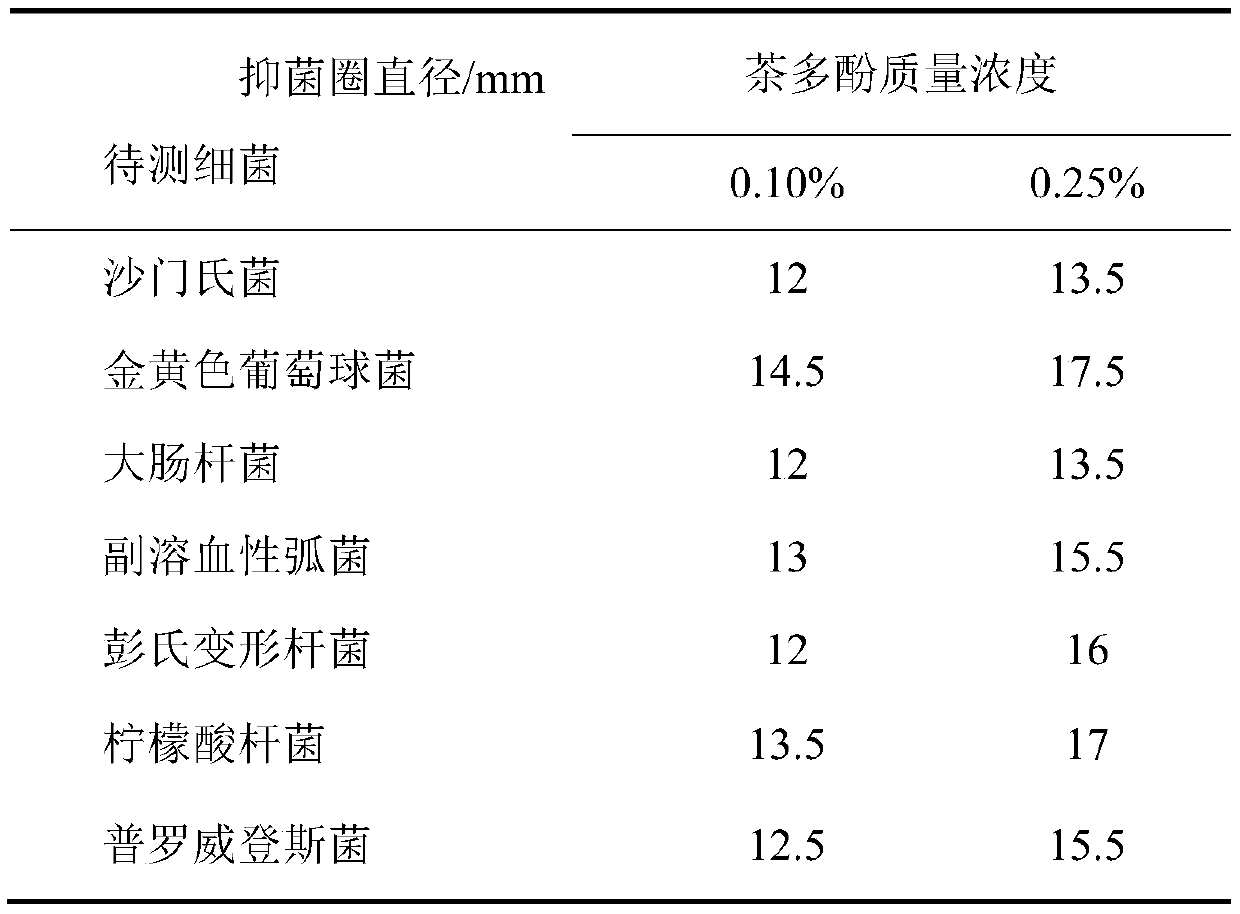
The invention provides a composite biological preservative and application thereof. The invention firstly provides a composite biological preservative which comprises lactobacillus rhamnosus and tea polyphenol, wherein the mass concentration of the tea polyphenol is 0.01%-2.0%. The low-concentration tea polyphenol and lactobacillus rhamnosus in the composite biological preservative have a synergistic interaction effect when being compounded, have a remarkable inhibition effect on escherichia coli, salmonella, staphylococcus aureus, vibrio parahaemolyticus, Proteus penneri, citrobacter and Providencia, and are wide in antibacterial spectrum; the composite biological preservative can significantly reduce the total number of colonies of animal products and aquatic products and the decomposition rate of proteins to maintain the content of the proteins and ensure bright red, glossy, tight and firm meat and the flavor of the aquatic products, and can further significantly prolong the shelf lives of the animal products and the aquatic products when the combined storage temperature of the composite biological fresh-keeping agent is 4 DEG C or lower. Great popularization and application values are realized.
Owner:味燃食品生物科技(深圳)有限公司
Bacillus subtilis, composite preparation, and method for preparing the composite preparation
InactiveCN100352915CImprove antagonistic abilityBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsDiseaseEscherichia coli
This invention describes a bacillus subtilis and the process for preparing its compound pharmaceutics. The bacillus subtilis is conserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms, the name is: Bacillus subtilis LY-35 and the conservation number is: CGMCC No. 1222. The pharmaceutics is a compound of the bacteriophages of such pathogens as bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus, Streptocoaus, colibacillus, proteus, pseudomonas, salmonella, shigella, pasteurella and klebsiella. The pharmaceutics can prevent and treat the diseases caused by pathogens, and can be a non-polluted, high therapeutic effectiveness and safe substitute for antibiotics.
Owner:烟台绿云生物工程研究院有限公司
Screening and identification method of electricigen enzyme
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
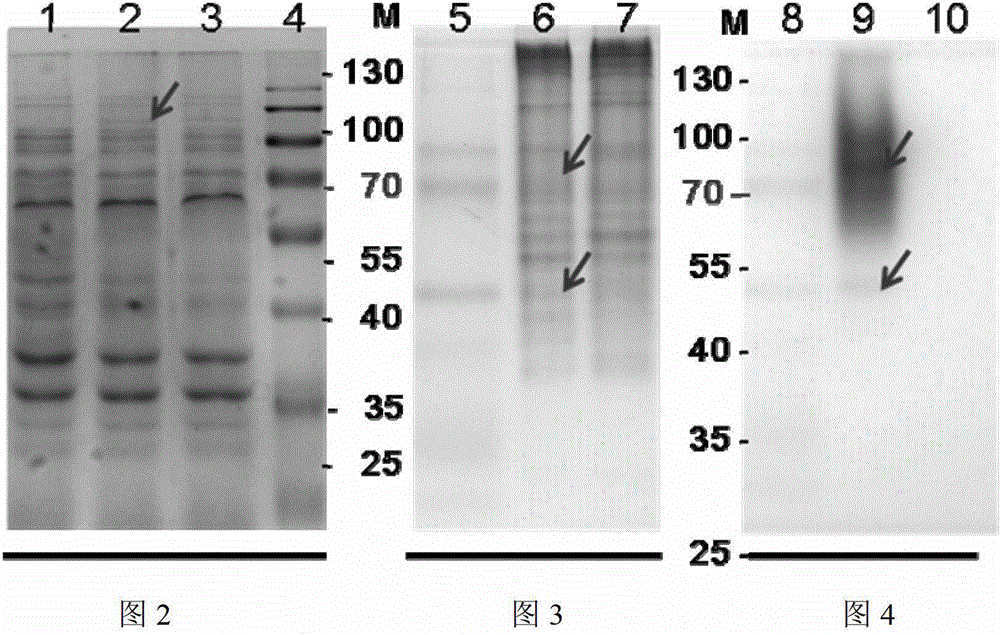
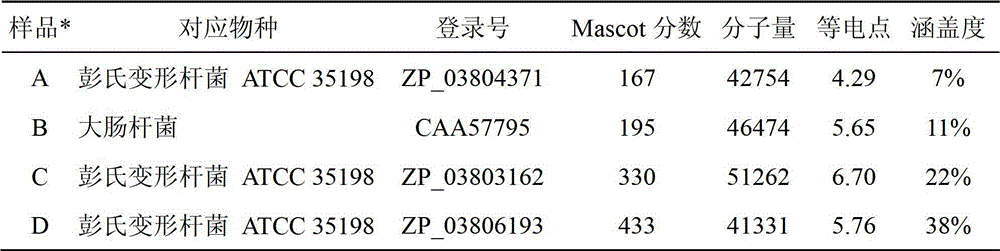
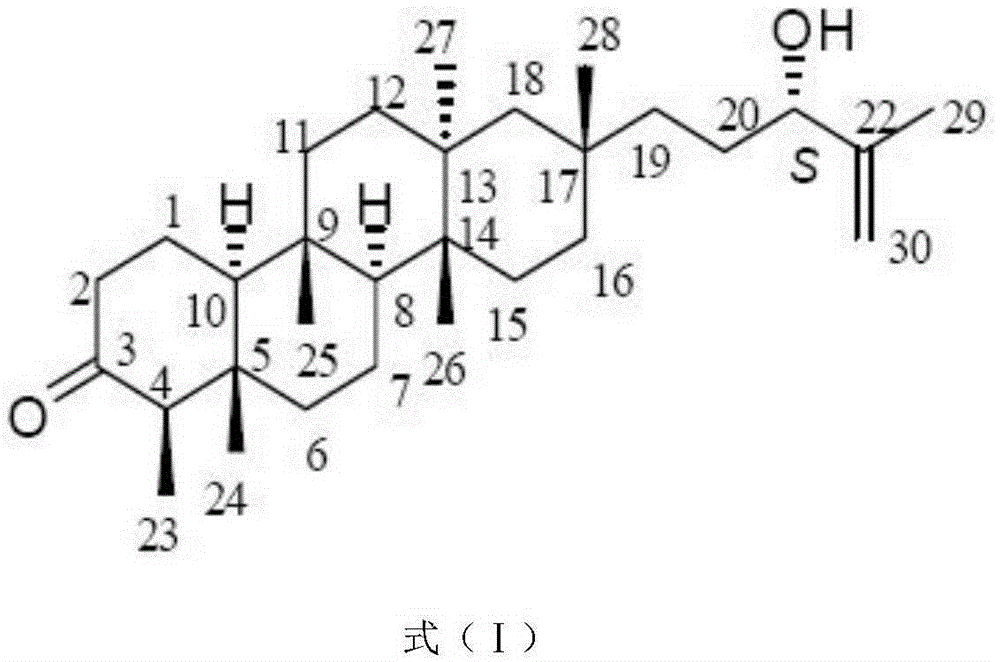
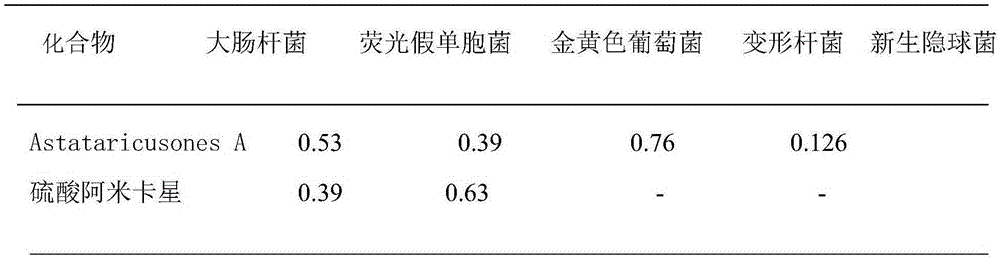
Application of Astataricusones A in preparation of antibacterial drugs
InactiveCN105395559AStrong inhibitory activityHighlight substantive featuresAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention relates to application of Astataricusones A in preparation of antibacterial drugs. Astataricusones A has strong inhibitory effect on escherichia coli, pseudomonas fluorescens, Staphylococcus aurous, proteus species and cryptococcus neoformans, can serve as an antibacterial compound, and the features are disclosed for the first time. Also due to strong bacteriostatic activity, Astataricusones A has outstanding substantive characteristics, and at the same time has remarkable progress in prevention and treatment of bacterial infection.
Owner:ZIBO DINGLI PATENT INFORMATION CONSULTING CO LTD
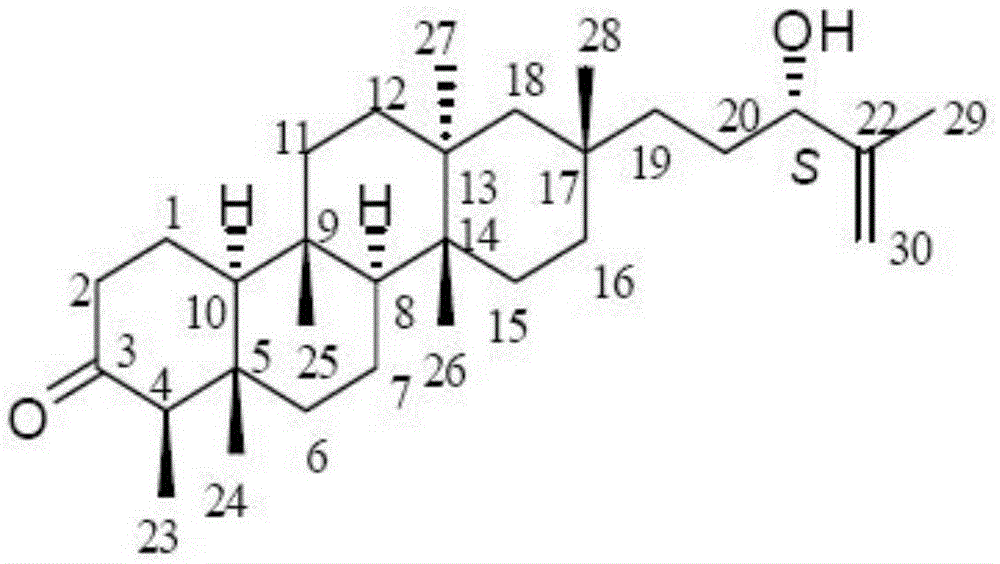
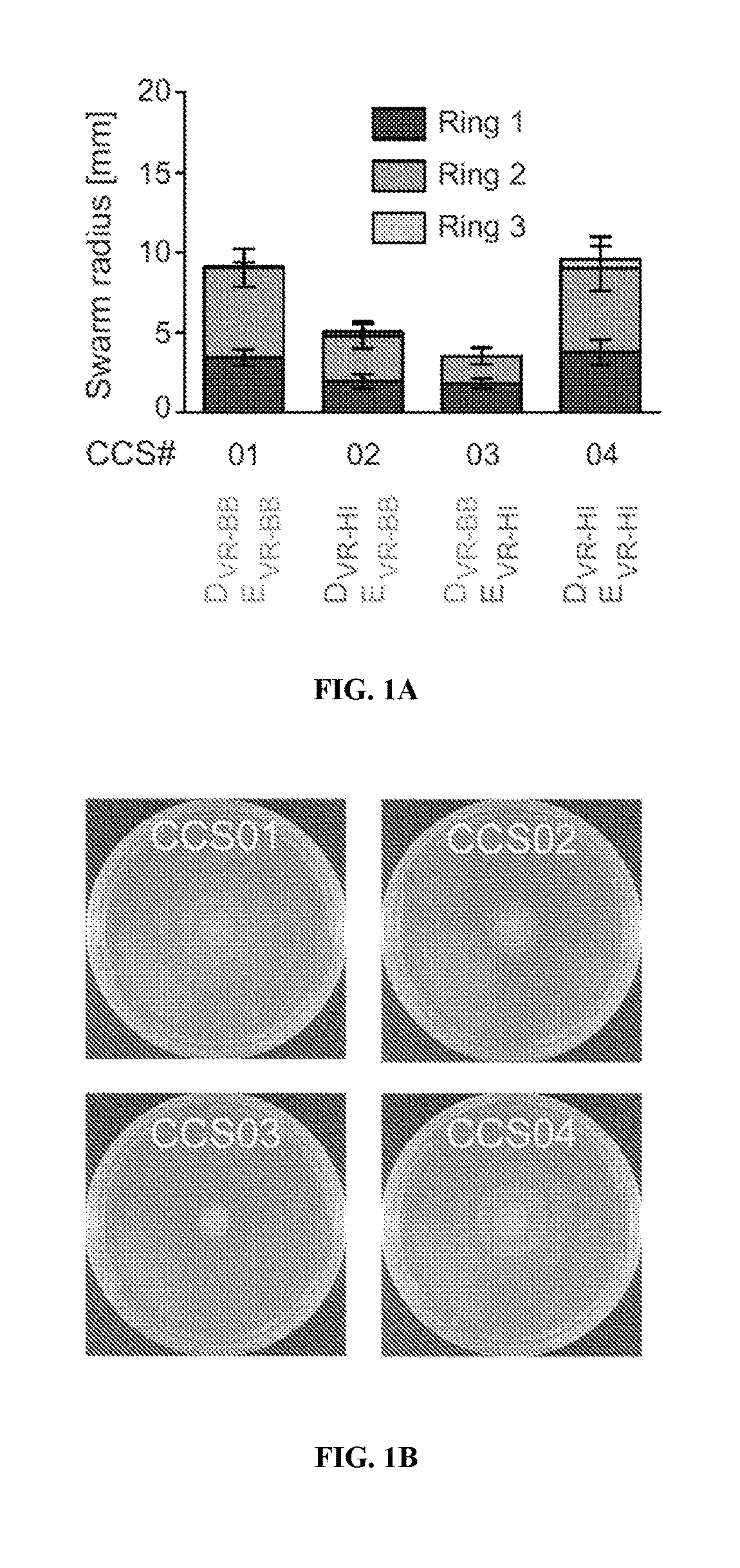
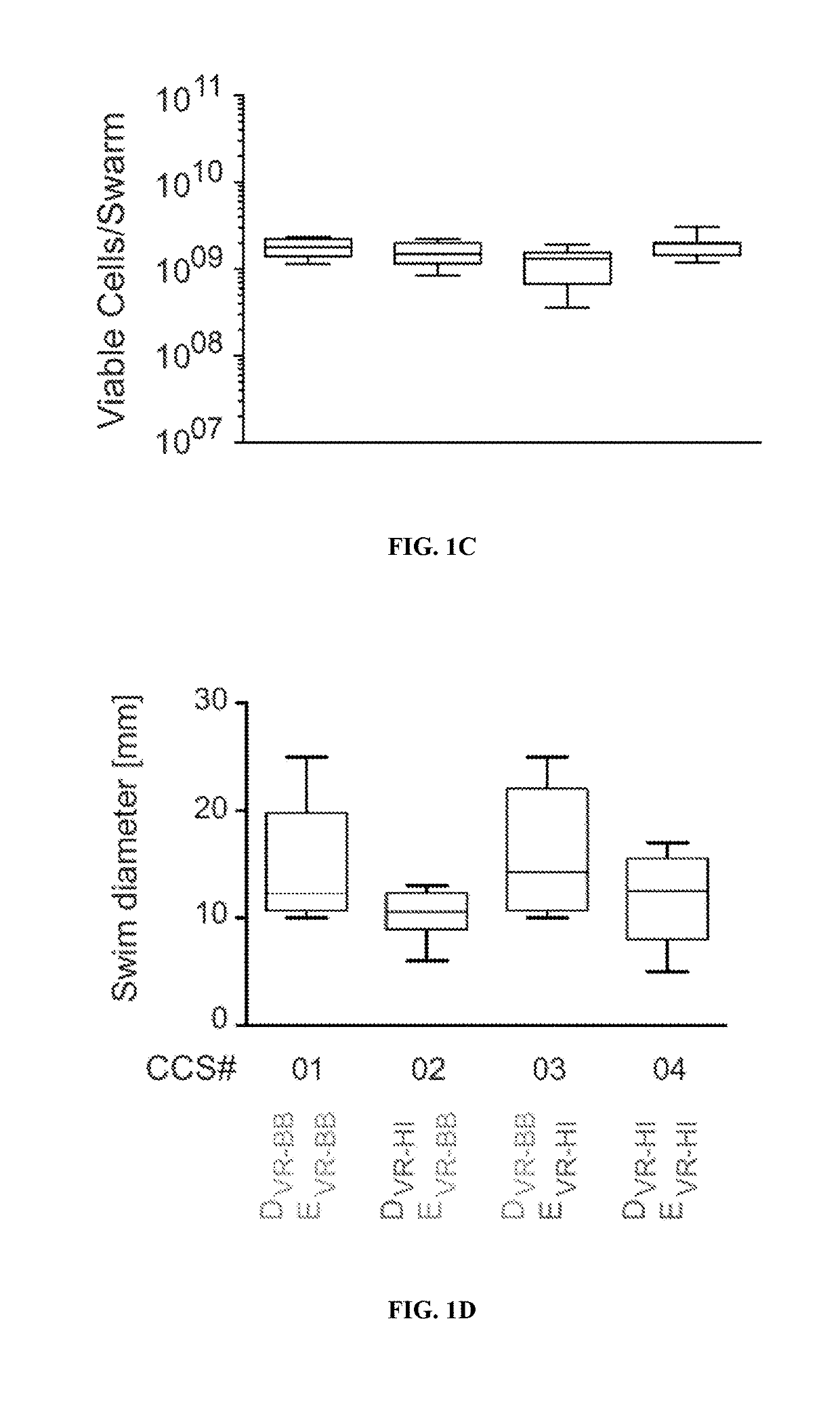
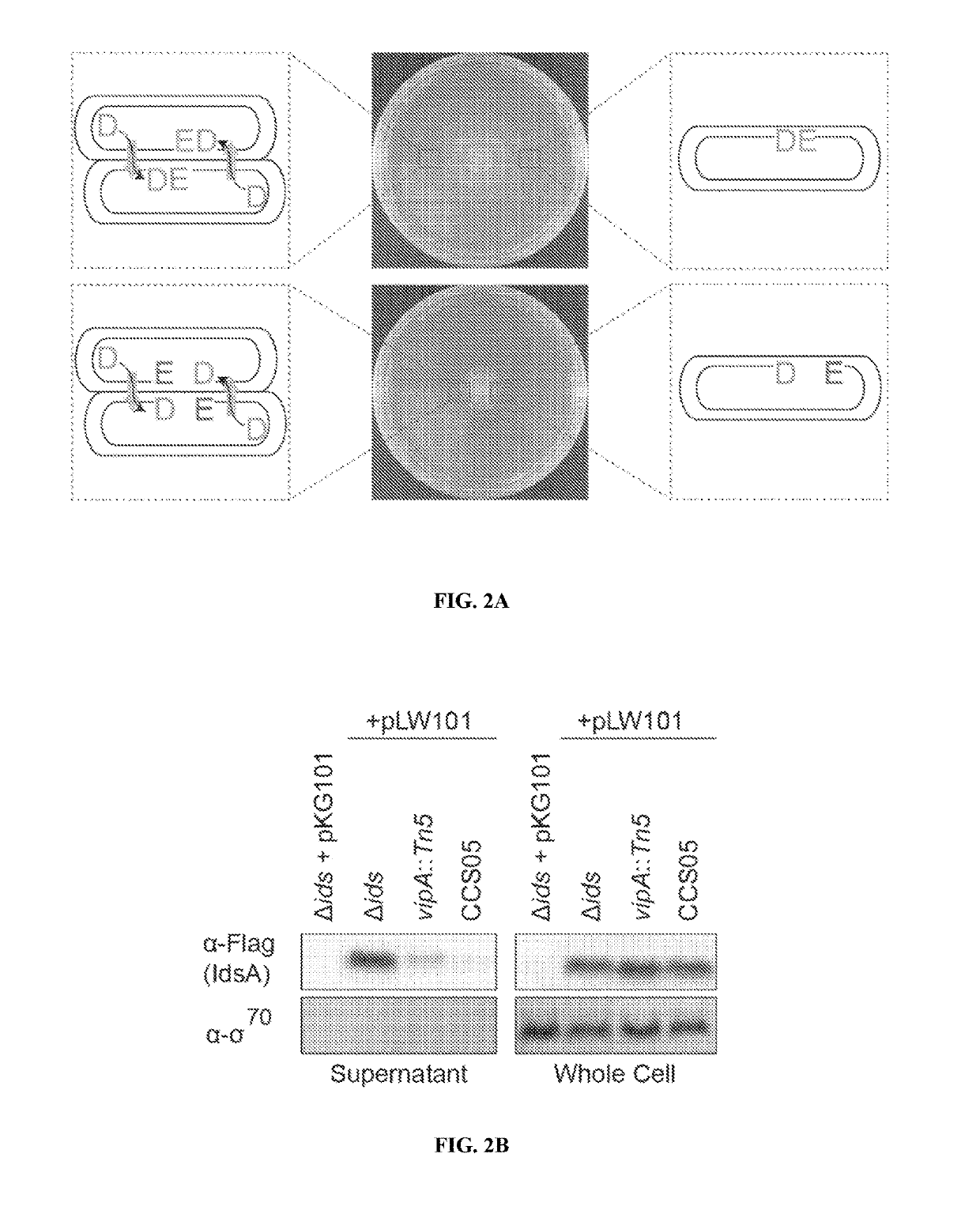
Treating infections using idsd from proteus mirabilis
ActiveUS20190201479A1Reduce bacterial growthReducing swarmingAntibacterial agentsBiocideUpper urinary tract infectionMedicine
The present disclosure provides, in some embodiments, compositions, kits, systems, and methods for reducing bacteria on a surface (e.g., a medical device) and preventing and / or treating a bacterial infection (e.g., urinary tract infection) in a subject using IdsD protein or a fragment thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com