Method for preparing molybdenum-copper alloy
A molybdenum-copper alloy and molybdenum-copper technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy, can solve the problems of reducing the electrical and thermal conductivity of molybdenum-copper alloys, and achieve the effects of lower sintering temperature, better powder uniformity, and shorter sintering time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1) Copper nitrate solution (Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O content 76g) and complexing agent citric acid solution (citric acid content 50g) join ammonium molybdate solution (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O content 147g), then adjust the pH of the solution=1, heat in a water bath at 80°C under stirring conditions to form a sol, then dry at 120°C to form a gel, and finally heat and decompose at 500°C in air to form a molybdenum-copper composite oxide powder;
[0022] 2) The molybdenum-copper composite oxide powder is reduced in two steps under a hydrogen atmosphere, the first reduction temperature is 500°C, the holding time is 90min, the second step reduction temperature is 700°C, and the holding time is 90min;
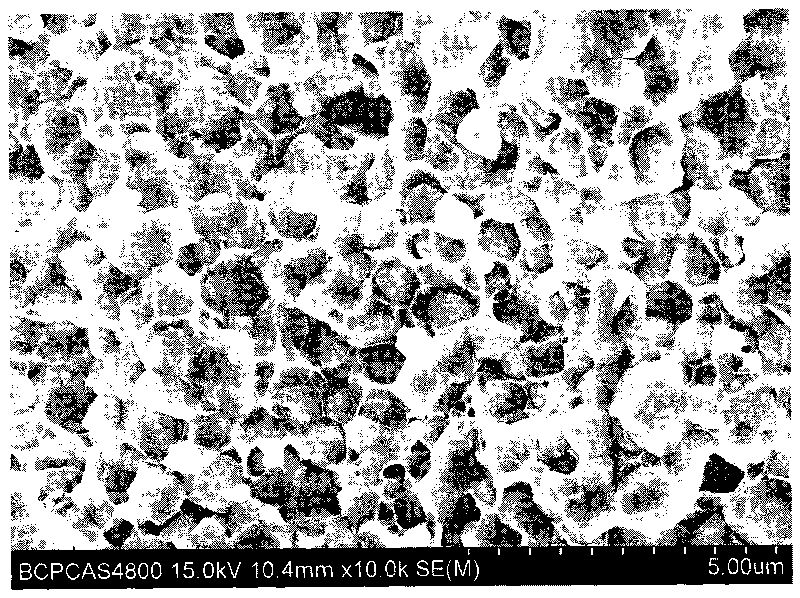
[0023] 3) After compacting the molybdenum-copper composite powder in a graphite grinding tool, heat it in a spark plasma sintering device at 1200°C and 30Mpa for 2 minutes to obtain molybdenum with a density of 98.4% and an average molybdenum grain size of 0.8um copper al...
Embodiment 2
[0025] 1) with step 1) among the embodiment 1;
[0026] 2) with step 2) in embodiment 1;
[0027] 3) After compacting the molybdenum-copper composite powder in a graphite abrasive tool, heat it in a discharge plasma sintering device at 1200°C and 50Mpa for 2 minutes to obtain molybdenum with a density of 99.6% and an average molybdenum grain size of 0.9um copper alloy.
Embodiment 3
[0029] 1) Copper nitrate solution (Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O content 76g) and complexing agent citric acid solution (citric acid content 50g) join ammonium molybdate solution (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O content 147g), then adjust the pH of the solution=1, heat in a water bath at 90°C under stirring conditions to form a sol, then dry at 120°C to form a gel, and finally heat and decompose at 500°C in air to form a molybdenum-copper composite oxide powder;
[0030] 2) with step 2) in embodiment 1;
[0031] 3) After compacting the molybdenum-copper composite powder in a graphite grinding tool, heat it in a spark plasma sintering device at 1150°C and 50Mpa for 0min to obtain molybdenum with a density of 95.2% and an average molybdenum grain size of 0.5um copper alloy.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com