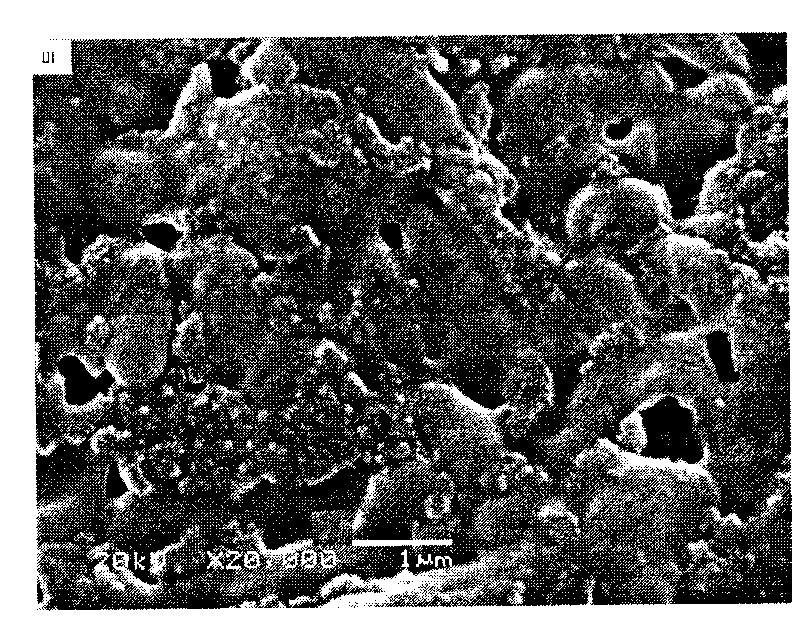
Composite material containing microelement for hard tissue repair and reconstruction and preparation method thereof
A technology of trace elements and composite materials, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as difficult degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Add 456g of sodium phosphate into 2 liters of distilled water, heat to 40°C-60°C, add 345g of calcium sulfate dihydrate and 0.2g of sodium bicarbonate (molar ratio Ca / P=1.67 / 1), stir for 2 hours and then add 0.21g strontium nitrate (molar ratio Sr / Ca=0.05%), stirred for 1 hour, and precipitated at room temperature for 48 hours. Remove the filtrate with a suction filter, and wash the filter cake 5 times with distilled water to obtain molar strontium and calcium. Calcium-phosphorus ceramic slurry with a ratio of 0.05%, the slurry is dried at 180° C., and ground through a 120-mesh sieve to obtain strontium-containing calcium-phosphorus ceramic powder with a molar ratio of strontium to calcium of 0.05%.
[0027] Take 105.25g, 4.45g, 4.95g, 4.6g, 5g, and 3g of 6-aminocaproic acid, alanine, phenylalanine, proline, hydroxyproline, and lysine, respectively, and add them to a 250ml three-neck bottle Add 50ml of distilled water, heat up to 200°C under electric stirring, and prote...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Add 456g of sodium phosphate into 2 liters of distilled water, heat to 40°C-60°C, add 345g of calcium sulfate dihydrate and 0.2g of sodium bicarbonate (molar ratio Ca / P=1.67 / 1), stir for 2 hours and then add 0.24 g of copper nitrate (molar ratio Cu / Ca=0.05%) was stirred for another 1 hour, and precipitated at room temperature for 48 hours. Remove the filtrate with a suction filter, wash the filter cake 5 times with distilled water, and obtain a calcium-phosphorus ceramic slurry with a copper-calcium molar ratio of 0.05%, dry the slurry at 180° C., and grind it through a 120-mesh sieve. A copper-containing calcium-phosphorus ceramic powder with a molar ratio of copper to calcium of 0.05% is obtained.
[0031] Take 105.25g, 4.45g, 4.95g, 4.6g, 5g, and 3g of 6-aminocaproic acid, alanine, phenylalanine, proline, hydroxyproline, and lysine, respectively, and add them to a 250ml three-neck bottle Add 50ml of distilled water, raise the temperature to 200°C under electric stir...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Add 456g of sodium phosphate into 2 liters of distilled water, heat to 40°C-60°C, add 345g of calcium sulfate dihydrate and 0.2g of sodium bicarbonate (molar ratio Ca / P=1.67 / 1), stir for 2 hours and then add 0.3 g of zinc nitrate (molar ratio Zn / Ca=0.05%), stirred for 1 hour, and precipitated at room temperature for 48 hours. Remove the filtrate with a suction filter, wash the filter cake 5 times with distilled water to obtain a calcium-phosphorus ceramic slurry with a zinc-to-calcium molar ratio of 0.05%, dry the slurry at 180°C, and grind it through a 120-mesh sieve. A zinc-containing calcium-phosphorus ceramic powder with a molar ratio of zinc to calcium of 0.05% is obtained.
[0034] Take 105.25g, 4.45g, 4.95g, 4.6g, 5g, and 3g of 6-aminocaproic acid, alanine, phenylalanine, proline, hydroxyproline, and lysine, respectively, and add them to a 250ml three-neck bottle Add 50ml of distilled water, heat up to 200°C under electric stirring, and protect it with nitrogen ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com