Method for preparing modified coatings of imitating cell outer-layer membrane structure
A technology imitating the outer membrane and coating of cells, which is applied in the fields of polymer chemistry and physics and biomedical materials, can solve problems such as the instability of amphiphilic polymer coatings, and achieve good blood compatibility and stability, Strong hydrophilicity and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
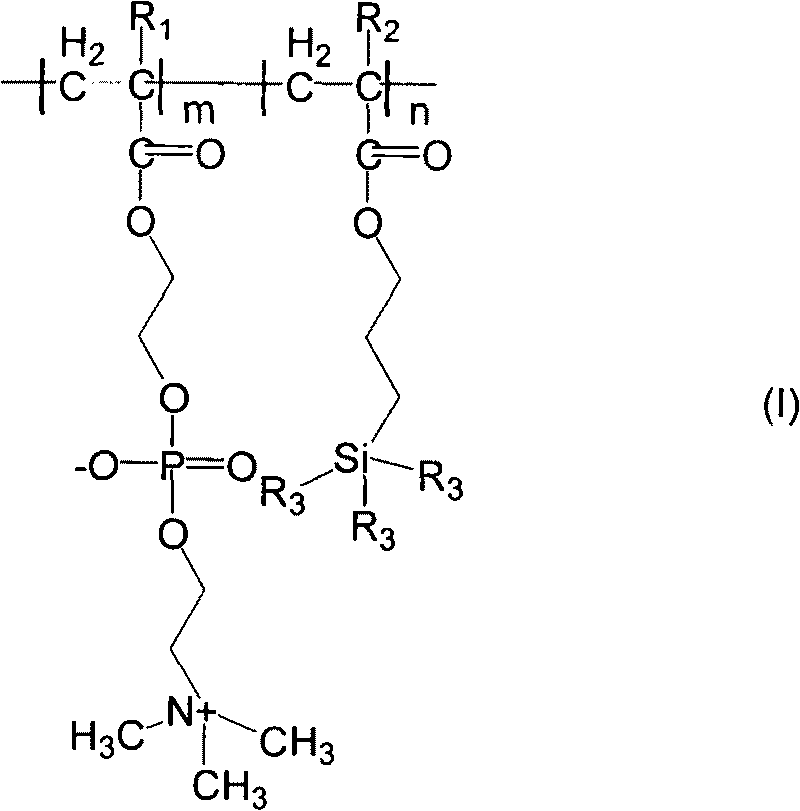
[0019] Take the monomer 2-methacryloyloxyethylphosphorylcholine (MPC) and γ-methacryloyloxypropyltrimethoxysilicon (TSMA) according to a certain ratio, dissolve them in isopropanol, and weigh the monomers The initiator azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) with a total mass of 1% was dissolved with a small amount of THF, mixed with the monomer solution, and loaded into a dropping funnel. in N 2 Under protection and stirring at a constant temperature of 80°C, the mixture of monomer and initiator was added dropwise, and the drop was completed within 3 hours. After the dropwise addition was completed, the system was sealed for reaction. After the reaction was carried out for 10 hours, a THF solution of 0.02% of the total monomer mass was added, and the heating and stirring was stopped after the reaction was carried out for 24 hours. Reaction solution in N 2 Filtrated under protection, the filtrate was concentrated by rotary evaporation and precipitated with cold anhydrous ether, the pr...
Embodiment 2
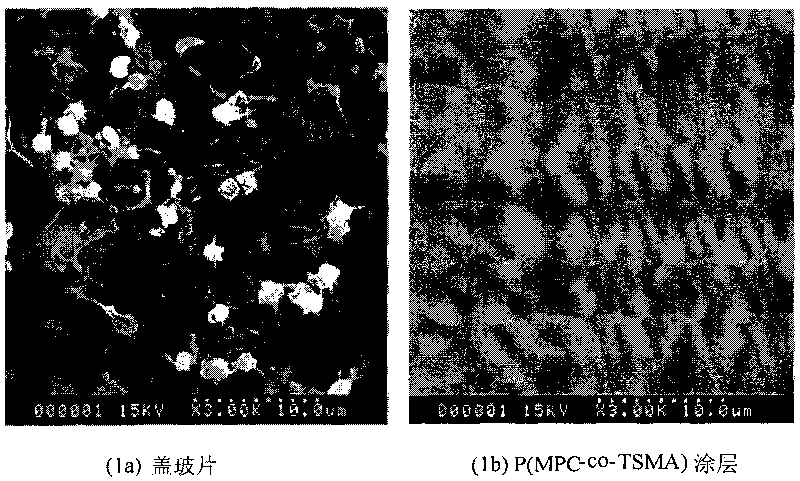
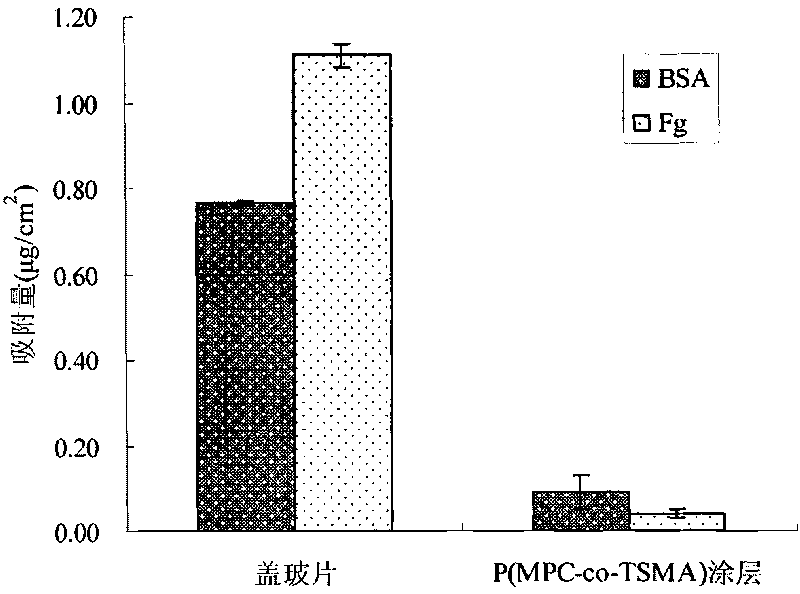
[0021] The cross-linkable polymer synthesized in Example 1 with a ratio of MPC and TSMA of 80:20 was prepared into a 1 mg / mL acetonitrile solution. The solution was sprayed or dipped onto a dry and clean cover glass surface, and after vacuum drying, it was treated in a saturated atmosphere of 2% triethylamine aqueous solution at 90°C for 1 hour to obtain a water-insoluble cross-linked coating. With pure water as the wetting medium, the test temperature is 20°C, the test speed of the advancing angle and the receding angle are both 0.05mm / s, the surface tension measurement threshold is 5.00mg, the immersion depth is 10.00mm, and the test point frequency is 5.00Hz. The angle is 45±2°, and the receding angle is 5±1°.
[0022] In the comparison test, after vacuum drying, the coating was still dissolved in a saturated atmosphere of pure water at 90°C for 1 hour, indicating that the crosslinking was not complete. After treatment at 120°C for 1 hour, the coating no longer dissolves, ...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Take the cross-linkable polymer synthesized in Example 1 with a ratio of 90:10 between MPC and TSMA, and prepare a 2 mg / mL isopropanol solution. The solution was dip-coated on a dry and clean cover glass surface, and after vacuum drying, it was treated in a saturated atmosphere of 0.8% trimethylamine aqueous solution for 10 h at 50° C. to obtain a cross-linked coating imitating the membrane structure of the outer layer of cells. With pure water as the wetting medium, the test temperature is 20°C, the test speed of the advancing angle and the receding angle are both 0.05mm / s, the surface tension measurement threshold is 5.00mg, the immersion depth is 10.00mm, and the test point frequency is 5.00Hz. The angle is 41±2°, and the receding angle is 4±2°.
[0025] In the comparison test, after vacuum drying, the coating was still dissolved in a saturated atmosphere of pure water at 50°C for 10 hours, indicating that the crosslinking was not complete. After treatment at 100°C ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com