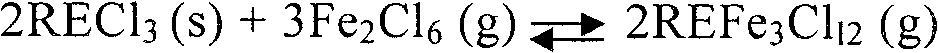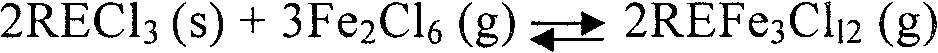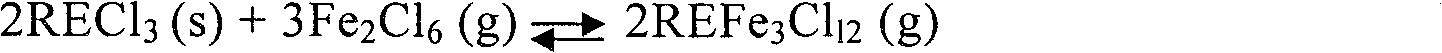Method for recovering mixed rare earth chlorides from neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material scraps
A technology of rare earth chlorides and permanent magnet materials, applied in rare earth metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, iron halides, etc., can solve the problems of large consumption of chemical raw materials, high production costs, and many solid and liquid wastes, and achieve reduction Emissions, Effects of Reducing Species and Quantities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for recovering mixed rare earth chlorides from NdFeB permanent magnet material waste, characterized in that: the method is carried out according to the following steps:
[0029] (1) Waste gas recovery: 100g of NdFeB permanent magnet material waste is ground into a 200-mesh powder material in an inert gas environment, and 8g of carbon powder is mixed into the powder material (the weight ratio of waste material to carbon powder is 1: 0.08), Place in a tubular quartz reactor and pass dry chlorine gas at 450°C for 2.5 hours for chlorination reaction to generate carbon dioxide, rare earth chlorides such as rare earth neodymium, terbium, dysprosium, ferric chloride and other chloride mixtures; Absorb the carbon dioxide and excess chlorine generated by the reaction with ammonia water to obtain a mixture of ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium chloride that can be reused after concentration and crystallization;
[0030] (2) Recovery of mixed rare earth chlorides: the rare...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for recovering mixed rare earth chlorides from NdFeB permanent magnet material waste, characterized in that: the method is carried out according to the following steps:
[0037] (1) Waste gas recovery: Grind 100g of NdFeB permanent magnet material waste into a 200-mesh powder material in an inert gas environment, and mix 10g of carbon powder into the powder material (the weight ratio of waste material to carbon powder is 1: 0.1), Place in a tubular quartz reactor and pass dry chlorine gas at 500°C for 2.5 hours for chlorination reaction to generate carbon dioxide, rare earth chlorides such as rare earth neodymium, terbium, dysprosium, ferric chloride and other chloride mixtures; Absorb the carbon dioxide and excess chlorine generated by the reaction with ammonia water to obtain a mixture of ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium chloride that can be reused after concentration and crystallization;
[0038] (2) Recovery of mixed rare earth chlorides: the rare earth ch...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A method for recovering mixed rare earth chlorides from NdFeB permanent magnet material waste, characterized in that: the method is carried out according to the following steps:
[0045] (1) Recovery of waste gas: 100g of NdFeB permanent magnet material waste is ground into 400 mesh powder material in an inert gas environment, and 10g of carbon powder is mixed into the powder material (the weight ratio of waste material to carbon powder is 1: 0.1), Place in a tubular quartz reactor and pass dry chlorine gas at 450°C for 2.5 hours for chlorination reaction to generate carbon dioxide, rare earth chlorides such as rare earth neodymium, terbium, dysprosium, ferric chloride and other chloride mixtures; Absorb the carbon dioxide and excess chlorine generated by the reaction with ammonia water to obtain a mixture of ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium chloride that can be reused after concentration and crystallization;
[0046] (2) Recovery of mixed rare earth chlorides: the rar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com