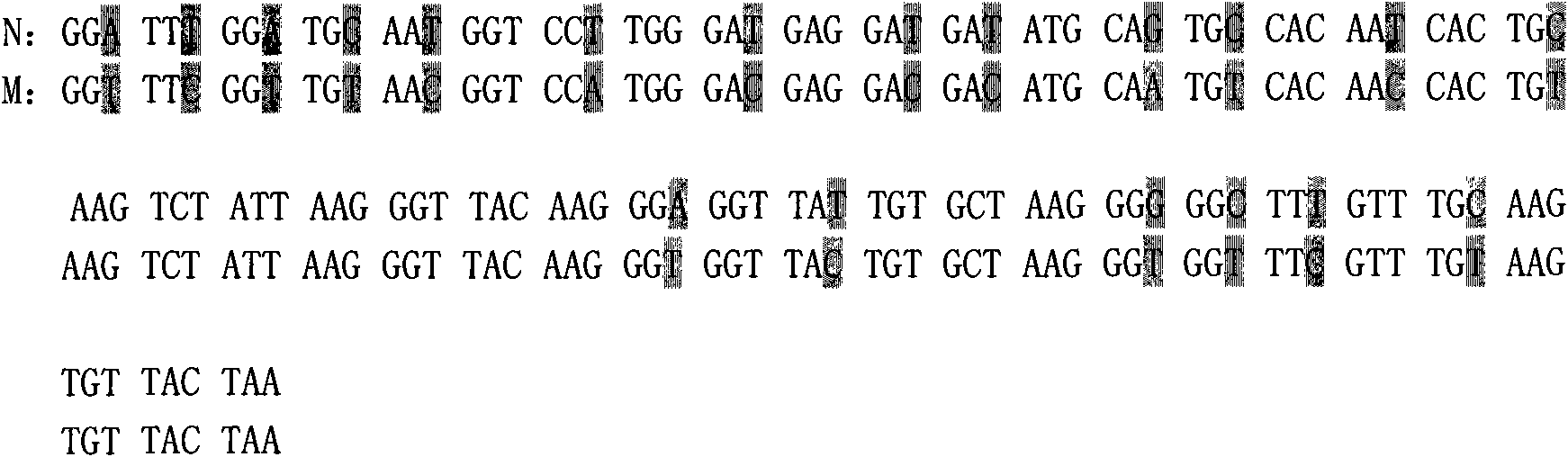Method for expressing pseudoplectania nigrella mature peptide in recombinant pichia pastoris
A mature polypeptide, Pichia pastoris technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of plasmid instability, few people use, easy to lose, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
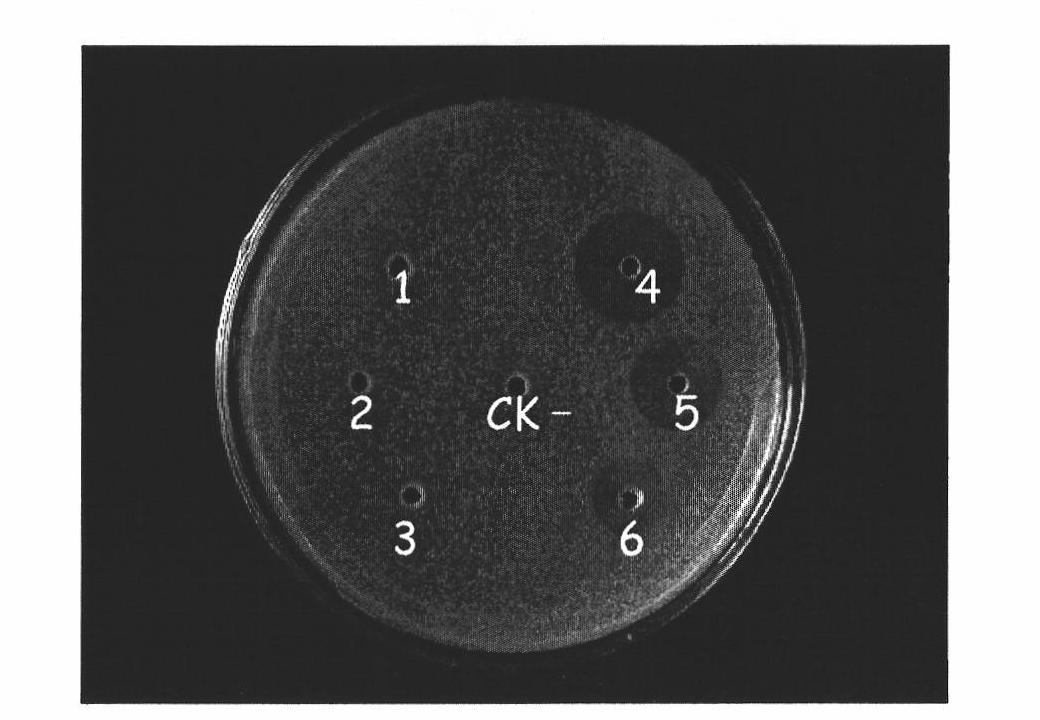
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The artificial synthesis of the mature polypeptide gene of embodiment 1 pseudosigladenin
[0050] According to the known full-length gene sequence (GenBank: AJ964941) of Pseudomycin, according to the codons preferred by Pichia pastoris, without changing the amino acid sequence, artificially synthesized the gene encoding the mature polypeptide of Pseudomycin , the synthetic mature polypeptide gene has a full length of 123bp (including the stop codon), encodes a total of 40 amino acid residues (see SEQ ID NO: 1), and has a molecular weight of about 4.4KDa. During the process of artificially synthesizing the polypeptide nucleotide coding sequence, a restriction enzyme site XhoI and a yeast Kex2 gene expression product cleavage recognition sequence were synthesized and added before the first codon GGT at the 5' end of the gene CTCGAGAAAAAGA (see SEQ ID NO: 2); a restriction enzyme cutting site Not I was added after the stop codon TAA at the 3' end of the gene. 19 nucleoti...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The cloning of embodiment 2 pseudosigladenin mature polypeptide gene
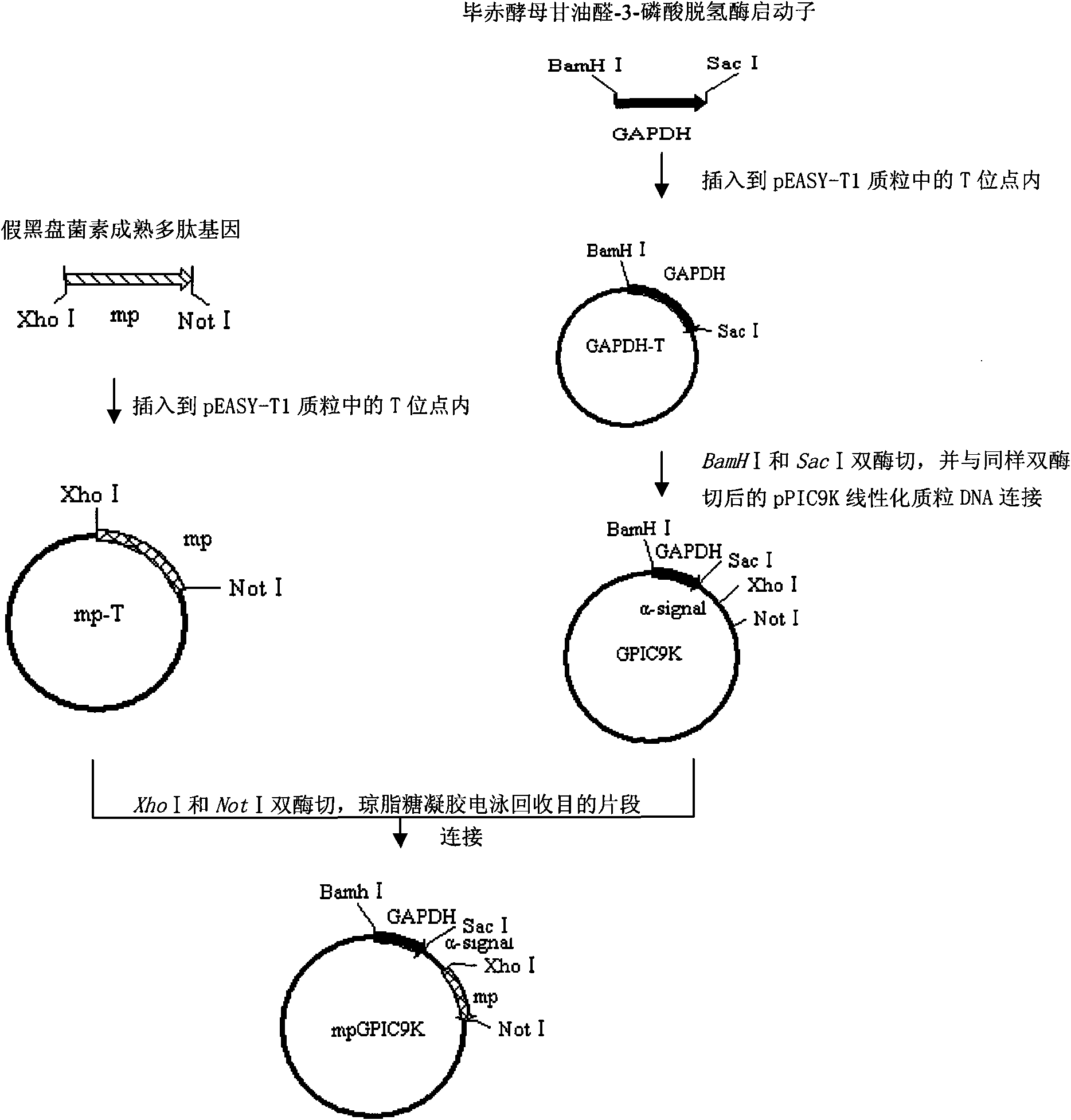
[0052] The above-mentioned artificially synthesized pseudosigalcin mature polypeptide gene fragment was directly inserted into the T site of the pEASY-T1 (purchased from Beijing TransGenic Company) plasmid to obtain a bacterial clone containing the plasmid vector mp-T, and then, through DNA Sequencing to determine the correctness and completeness of the mature pseudosigladin gene contained in it (DNA sequencing was completed by Beijing Biaokai Technology Co., Ltd.).
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Cloning of Pichia pastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter
[0054] According to the known Pichia glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter sequence (GenBank: U62648.1), synthesize primers F and R located at both ends of the promoter, wherein F is 5'-AT GGATCC TTTTTTGTAGAAATGTCTTGGTGTCC-3' (the underline is the BamH I cleavage site), R is 5'-AT GAGCTC TGTGTTTTGATAGTTGTTCAATTGATTG-3' (the underline is the Sac I cleavage site), using Pichia pastoris genomic DNA as a template (for the genome extraction method, see "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide, Third Edition"), using F and R as primers, amplified by PCR. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter sequence (GAPDH, whose sequence is shown in SEQID NO: 3) was obtained by increasing, and the amplified fragment was directly inserted into the T site of the pEASY-T1 plasmid to obtain an intermediate plasmid containing Bacterial clones vectoring GAPDH-T were then analyzed by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com