Preparation method of chimonanthus inhibited acetylcholinesterase active part and application thereof
A technology of acetylcholinesterase and active site is applied in the field of preparation of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory active site, and achieves the effects of easy industrialization, reasonable preparation process and abundant sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
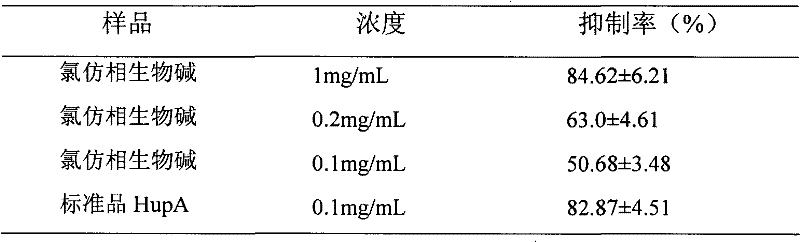
[0020] 1. Preparation of alkaloids from active parts of Chimonanthus
[0021] a. Weigh the Chimonanthus leaves as the raw material, dry, pulverize, and extract 3 times with a 60% volume percent ethanol solution. The quality of the ethanol solution used for each time is 10 times, 8 times and the quality of the raw material of the Chimonanthus leaves. 8 times, 10 hours each time, filter the three extracts with gauze and combine;
[0022] b. The above-mentioned combined extracts are concentrated under reduced pressure at a temperature of 45°C to recover the ethanol until there is no alcohol taste to obtain an ethanol extract, which is dried at 40°C to form an extract for later use;
[0023] c. Weigh 250 g of Chimonanthus praecox extract, disperse it with 10% acetic acid aqueous solution, and extract with ethyl acetate, 500 mL each time, extract 10 times, collect acid water phase, ethyl acetate phase and insoluble precipitate.
[0024] d. The above acid aqueous phase is alkalized with sod...
Embodiment 2
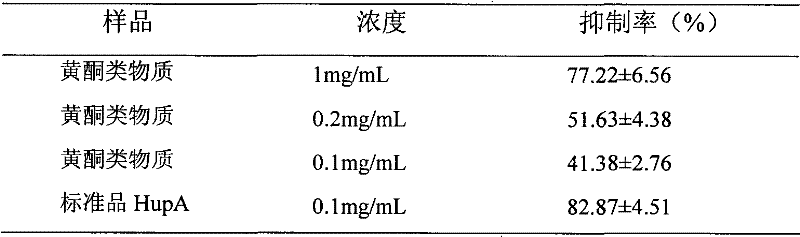
[0038] 1. Preparation of flavonoids from active parts of Chimonanthus
[0039] The processing of the leaves of Chimonanthus plant and the extraction of the extract are the same as the preparation steps a, b, and c of the active site alkaloids in Example 1. The subsequent preparation steps are as follows;
[0040] d. Extract the ethyl acetate phase with 10% sodium carbonate aqueous solution, 500 mL each time, extract 8 times, and collect the alkaline aqueous layer;
[0041] e. Acidify the collected alkaline water layer with hydrochloric acid to a solution pH of 6.0. After acidification, a large amount of precipitate will precipitate, centrifuge and collect the precipitate;
[0042] f. Take the precipitate and dissolve it in ethanol, develop it by TLC (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 7: 3), spray aluminum trichloride solution, it will show yellow fluorescence under ultraviolet long wave, and it is preliminarily determined that the precipitate is a flavonoid.
[0043] 2. Determination of ...
Embodiment 3
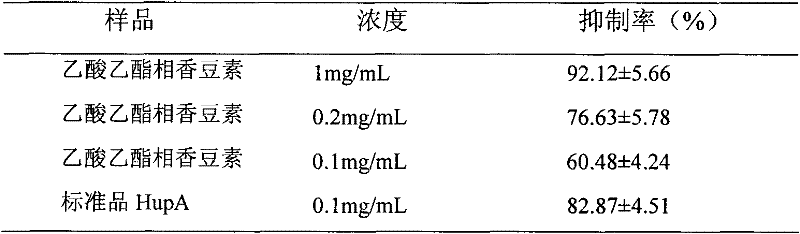
[0051] 1. Preparation steps of coumarins from the active part of Chimonanthus
[0052] The processing of the leaves of Chimonanthus plant and the extraction of the extract are the same as the preparation steps a, b, c, d of the active site alkaloids in Example 1. The subsequent preparation steps are as follows;
[0053] e. Acidify the collected alkaline aqueous layer with hydrochloric acid to a solution pH of 6.0. After acidification, a large amount of precipitation will precipitate. Centrifuge to collect the supernatant. The supernatant is extracted with ethyl acetate, 500 mL each time, 6 times, and ethyl acetate is collected phase;
[0054] f. After the ethyl acetate phase is developed by TLC (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate=6:4), spray 5% potassium hydroxide ethanol solution, the blue fluorescence enhancement phenomenon appears under ultraviolet, confirm the ethyl acetate phase is fragrant Legumes;
[0055] 2. Determination of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of coumarins i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com