Thermostable chitosanase-producing engineered yeast strain and production method of thermostable chitosanase
A technology of chitosan enzyme and production method, applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering, can solve the problems of insufficient thermal stability to meet the requirements of industrialization, reduced enzyme activity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
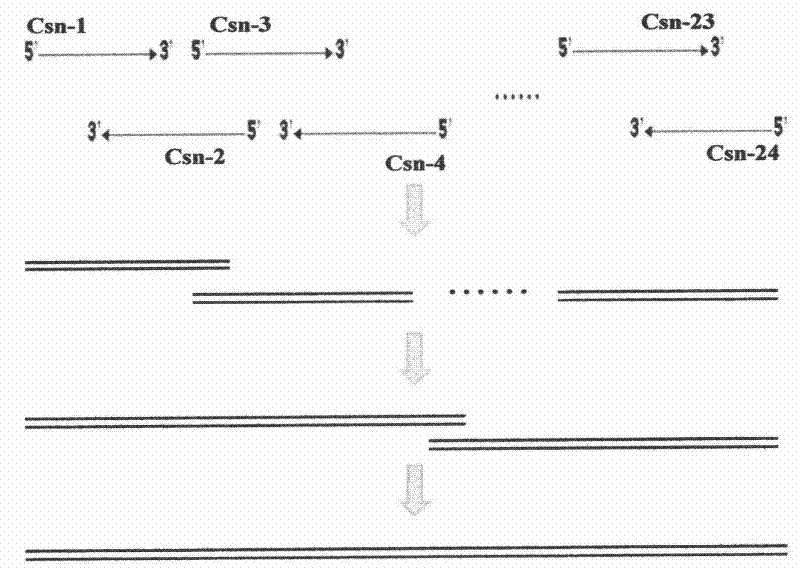
[0041] Example 1: Synthesis of a full-length gene encoding chitosanase and construction of Pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacteria using nested PCR method.
[0042] 1. Synthesize the full-length gene encoding chitosanase by nested PCR method. From the amino acid sequence of chitosanase reported from Aspergillus fumigatus (GenBank TM accession number AY190324), the gene encoding chitosanase was optimized according to the codon bias of Pichia pastoris. The optimized sequence is shown in Sequence List 1, and the primers (see Table 1) were designed. Except that hbcsn-1 is 26bp and hbcsn-24 is 55bp, the length of each primer is 50, and there is a gap of about 20bp between two adjacent primers. Overlapping sequences with Tm values of 58-62°C. Then the full-length chitosanase gene was synthesized by nested PCR method.
[0043] Table 1 Primers for the synthesis of full-length chitosanase gene by nested PCR
[0044]
[0045] hbcsn-20
5'AGTGAAACCAATAAACAAA...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Pichia pastoris genetically engineered strain HBCSN was cultured in a shake flask to prepare chitosanase.
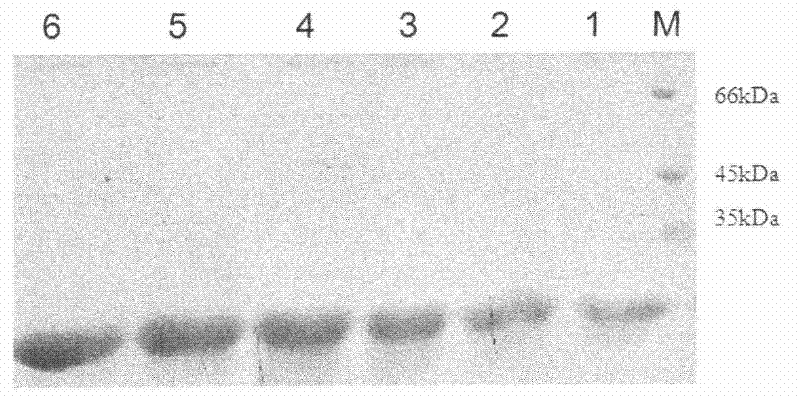
[0052] The genetically engineered bacterium HBCSN is colonized into the BMGY medium, cultured at 28°C-30°C for 46-48 hours, centrifuged, and then the bacteria are transferred into BMM for induced expression. 100% methanol was added to the medium every 24 hours to a final methanol concentration of 1%. After six days of induction, the fermentation liquid was centrifuged, and the supernatant was the crude enzyme liquid containing chitosanase. Samples were taken every 24 hours to detect protein expression by SDS-PAGE, and the results were as follows image 3 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Preparation of Chitosanase by Scale-Up Culture of Pichia pastoris Genetic Engineering Bacteria HBCSN in a Fermenter.
[0054] 1. Seed preparation is as follows: a single colony is placed in BMGY medium, and cultured at 28°C-30°C for 46-48 hours.
[0055] 2. Inoculation: Add the seed medium into the fermenter at a ratio of 5% (volume of the seed medium / volume of the initial medium in the fermenter). The initial medium in the fermentor was BMGY.
[0056] 3. The whole fermentation process is divided into two stages:
[0057] A. The first stage is the long biomass stage, that is, the cell growth stage. The fermentation parameters are: temperature 28°C, pH 5.8, ventilation rate 0.5vvm, stirring speed 250-700 rpm, dissolved oxygen 30%. After 10-14 hours from the start of inoculation, the glycerol in the fermenter was consumed, and at this time, a 50% glycerol (W / V) mixture was added (that is, 12 mL of PTM1 was contained in every liter of 50% glycerol), when the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com