Separation method of LED (light emitting diode) epitaxy chip
A separation method and epitaxial wafer technology, applied in laser welding equipment, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of dust pollution, low efficiency, long time consumption, etc., to simplify separation operations, improve separation efficiency, and reduce production costs. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
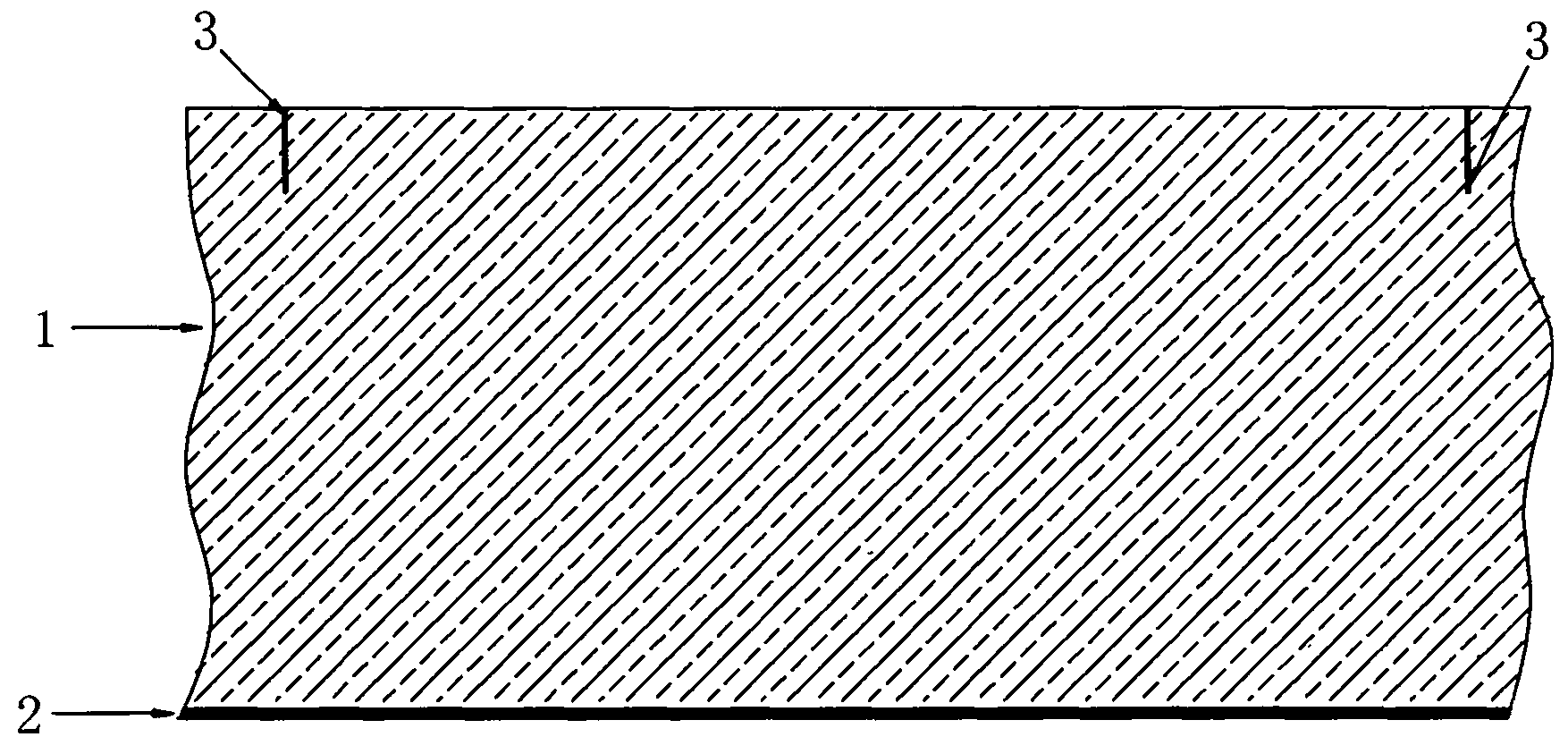
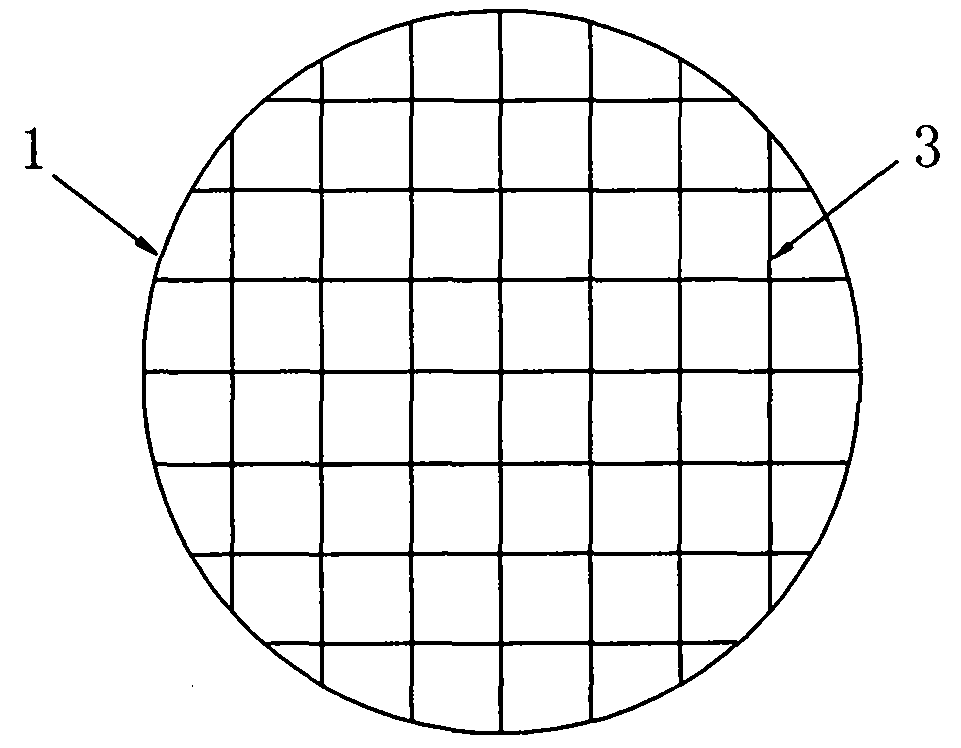
[0035] Example 1 please refer to Figures 1 to 2 , this embodiment involves the separation process of a GaN-based LED epitaxial chip with a sapphire crystal as a substrate, the epitaxial chip includes a 2-inch sapphire substrate 1 with a thickness of about 430 μm, and a GaN-based LED with a thickness of about 7 μm grown on the front side of the substrate. Epitaxial wafer layer 2.
[0036] The operation of separating the GaN-based LED epitaxial chip with the sapphire substrate is performed by a laser scribing process, which includes the following steps:
[0037] The LED epitaxial structure is cut and grown by a laser beam with a suitable wavelength (see "Laser Scribing Process of Sapphire Crystal Substrate for LEDs", "China Lighting Appliances", No. 3, 2010, and the invention patent with publication number CN100407461C, etc.) The backside of the sapphire substrate is formed with a number of trenches 3 with a depth of more than 43 μm, and the trenches correspond to predetermine...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2 This embodiment involves the separation of a GaN-based LED epitaxial chip with a sapphire crystal as a substrate. The epitaxial chip includes a 4-inch sapphire substrate with a thickness of about 650 μm, and a sapphire substrate with a thickness of about 8 μm grown on the front surface of the substrate. GaN epitaxial wafer layers.
[0041] The operation of separating the GaN-based LED epitaxial chip with the sapphire substrate is performed by a laser scribing process, which includes the following steps:
[0042] The LED epitaxial structure is cut and grown by a laser beam with a suitable wavelength (see "Laser Scribing Process of Sapphire Crystal Substrate for LEDs", "China Lighting Appliances", No. 3, 2010, and the invention patent with publication number CN100407461C, etc.) The backside of the sapphire substrate is formed with several grooves with a depth of more than 65 μm, and the grooves correspond to the predetermined dividing positions between the ch...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Horizontal size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com