Lactic acid bacteria for producing bile salt hydrolase as well as screening method and application thereof
A technology for enzymolytic lactic acid bacteria and screening method, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, applications, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient sensitivity, and achieve the effects of high sensitivity, small workload and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1 produces the qualitative screening method of bile salt hydrolase
[0026] 1. Starting strain
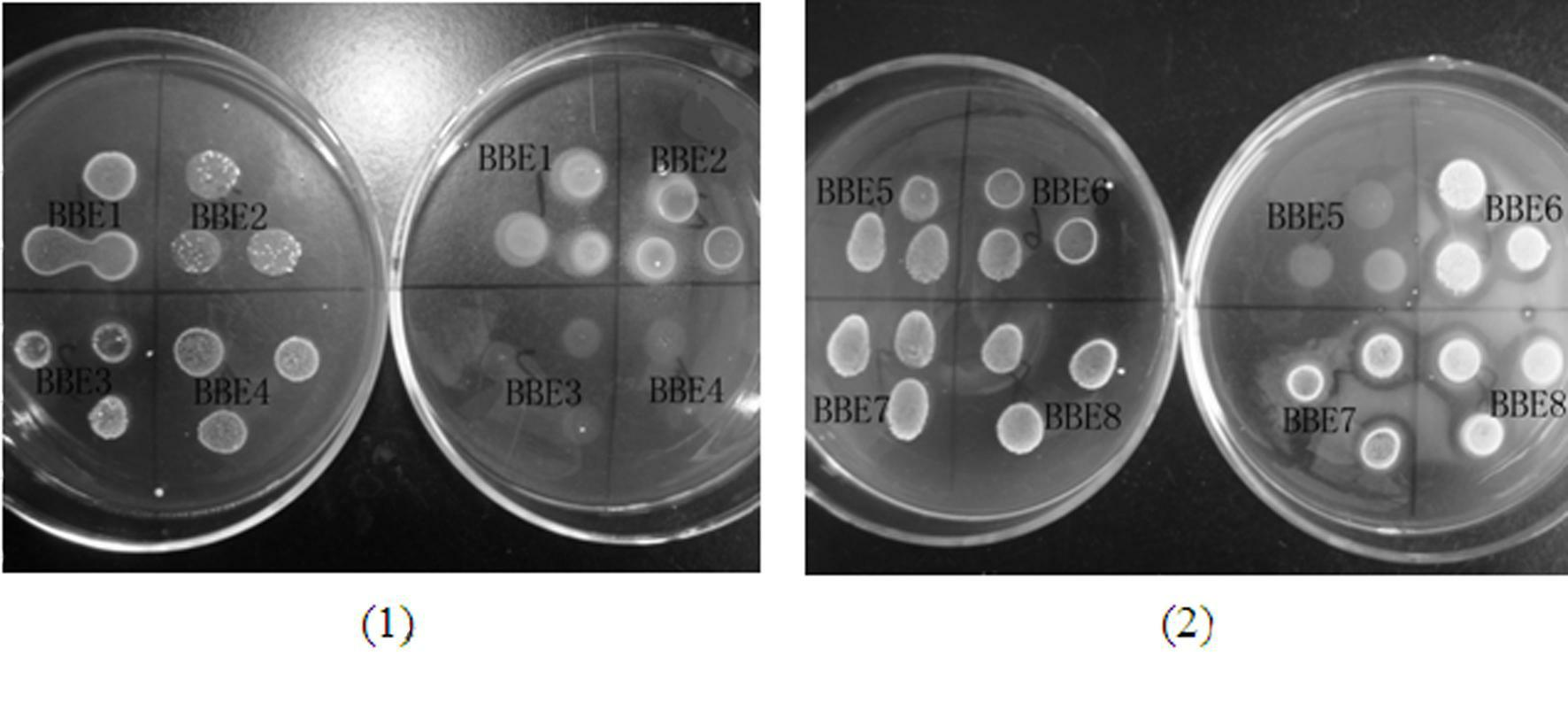
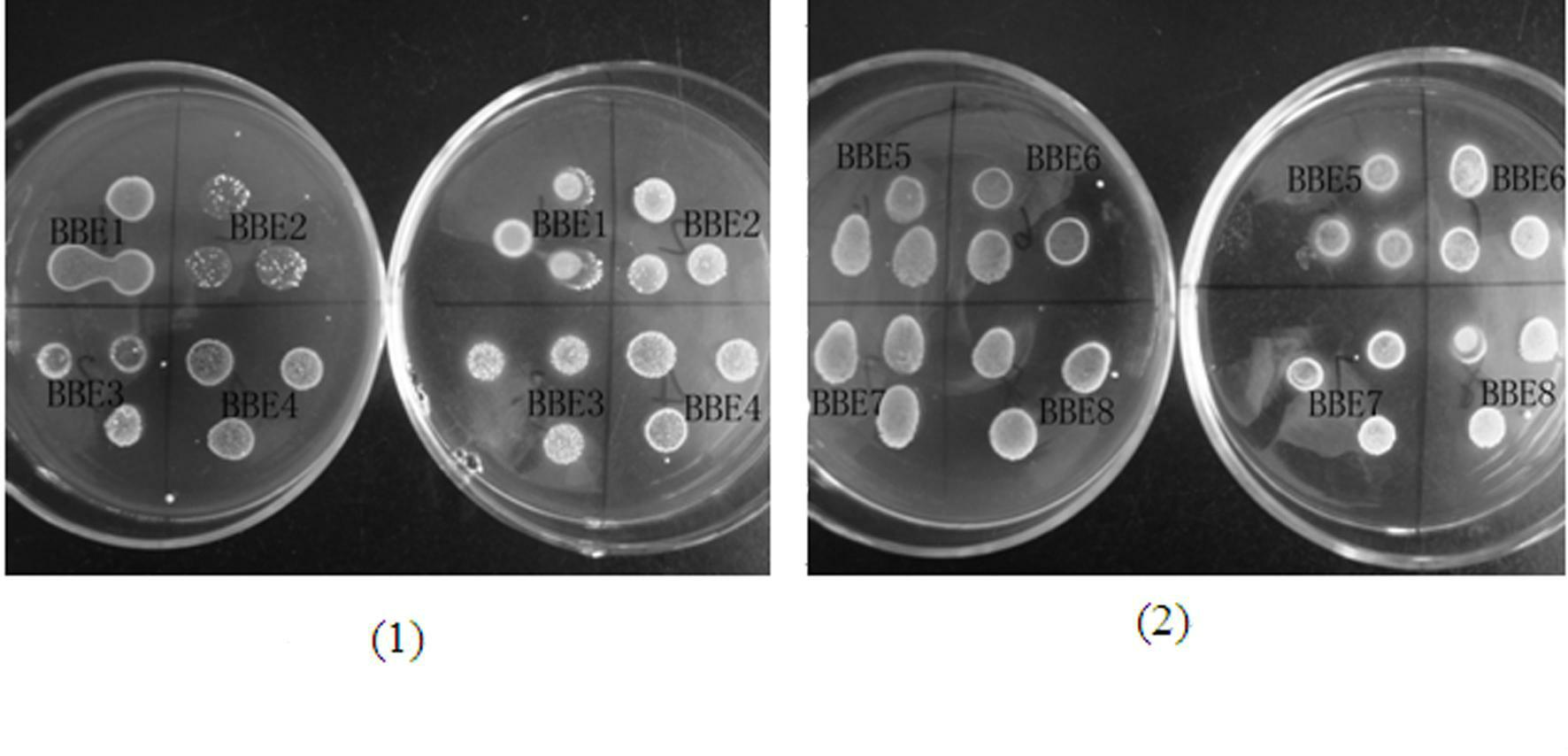
[0027] The starting strains are existing strains in the laboratory, including strains BBE1, BBE2, BBE3, BBE4, BBE5, BBE6, BBE7, BBE8, BBE10-211, BBE10-212, BBE10-215, BBE Kefir, Lactobacillus caseiZhang (LB.Z), Lactobacillus casei ATCC334, Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC4356 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC7469, among which the first 12 strains were screened in this experiment, BBE10-212 screened from kimchi was identified and named as Lactobacillus casei BBE10-212, and has applied for a Chinese patent with the application number 201010238658.8 ; Lactobacillus casei Zhang (LB.Z) was screened from sour kumiss by Inner Mongolia Agricultural University; Lactobacillus caseiATCC334, Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC4356 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC7469 were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC).
[0028] 2. Screening method
[0029] (1) Activation of...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: the quantitative screening method of the lactic acid bacteria that produces bile salt hydrolase (ninhydrin method measures enzyme activity)
[0041] (1) Ninhydrin Chromogenic Solution
[0042] Dissolve ninhydrin at a ratio of 1% in 0.5M citric acid buffer (pH 5.5), take 0.5 mL of the above mixture and add 1.2 mL of glycerin and 0.2 mL of 0.5 M citric acid buffer (pH 5.5).
[0043] (2) Enzyme activity assay method
[0044] (1) Activation of bacteria
[0045] Lactic acid bacteria preserved in glycerol tubes at -70°C were inoculated with 1% inoculum into test tubes containing 2mL of MRS medium, and cultured at 37°C for 20 hours.
[0046] (2) shake flask culture
[0047] The above-mentioned activated bacterial solution was transferred to a 50mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 20mL MRS medium according to the inoculum amount of 1%, and cultured statically at 37°C until the stationary phase.
[0048] (3) Determination of enzyme activity
[0049] The above ferme...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3: the effect of lactic acid bacteria removing cholesterol in vitro
[0067] (1) Cholesterol-containing MRS liquid medium
[0068] First prepare a concentration of 10mg mL with absolute ethanol -1 After filtering and sterilizing the cholesterol solution with a microporous membrane with a pore size of 0.45 μm, it was added to sterilized MRS containing 0.30% sodium taurocholate, so that the final concentration of cholesterol was 100 μg mL -1 .
[0069] (2) Preparation of fermentation broth
[0070] The test bacteria were continuously passed for 3 generations in the MRS medium, and the 3rd generation culture was 5000r min -1 Centrifuge for 10 min, discard the supernatant, wash the bacteria with sterilized physiological saline for 3 times, adjust the concentration of the bacterial suspension to 3×10 9 CFU mL -1 . Inoculate into cholesterol-containing MRS liquid medium according to 2% inoculum amount, and incubate anaerobically at 37°C for 24h. At the same ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com