Application of rhein or compound of rhein compound and arginine in preparation of medicine for treating diabetic complications
A technology for rhein and diabetes, which is applied to the application field of rhein or a compound of rhein compound and arginine in the preparation of a drug for treating diabetic complications, and can solve problems such as male sexual dysfunction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
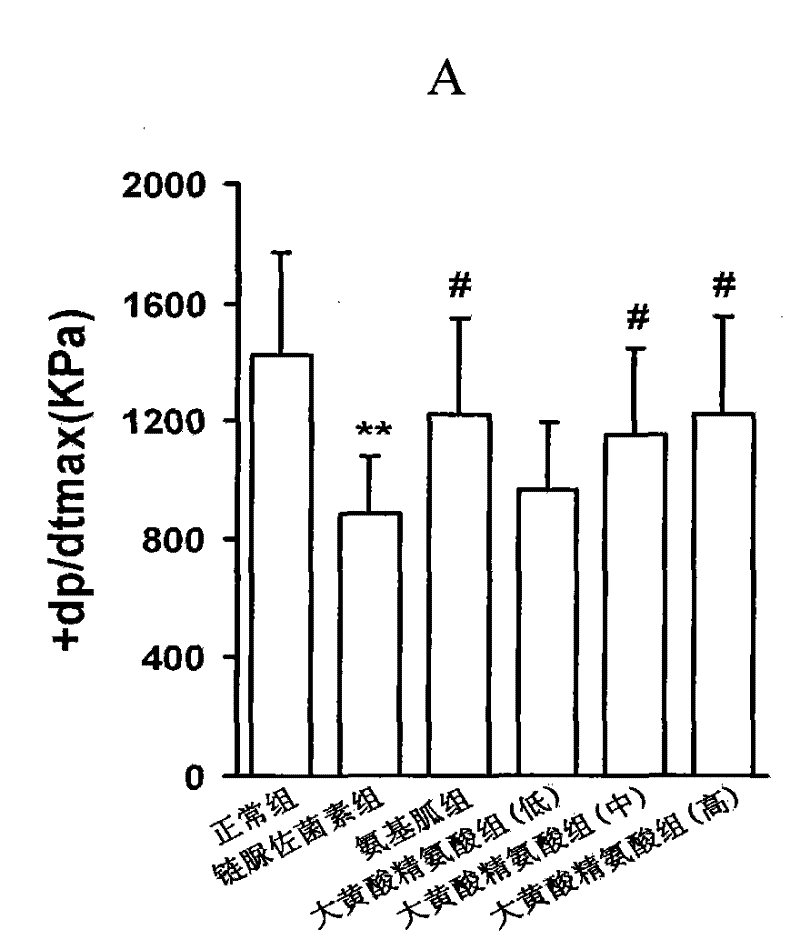
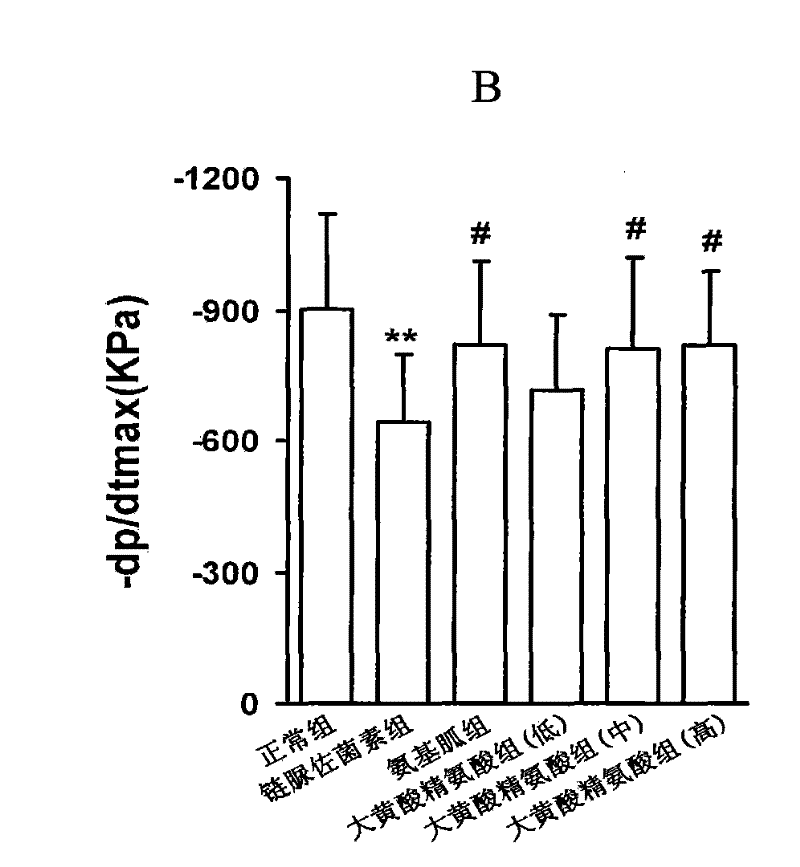
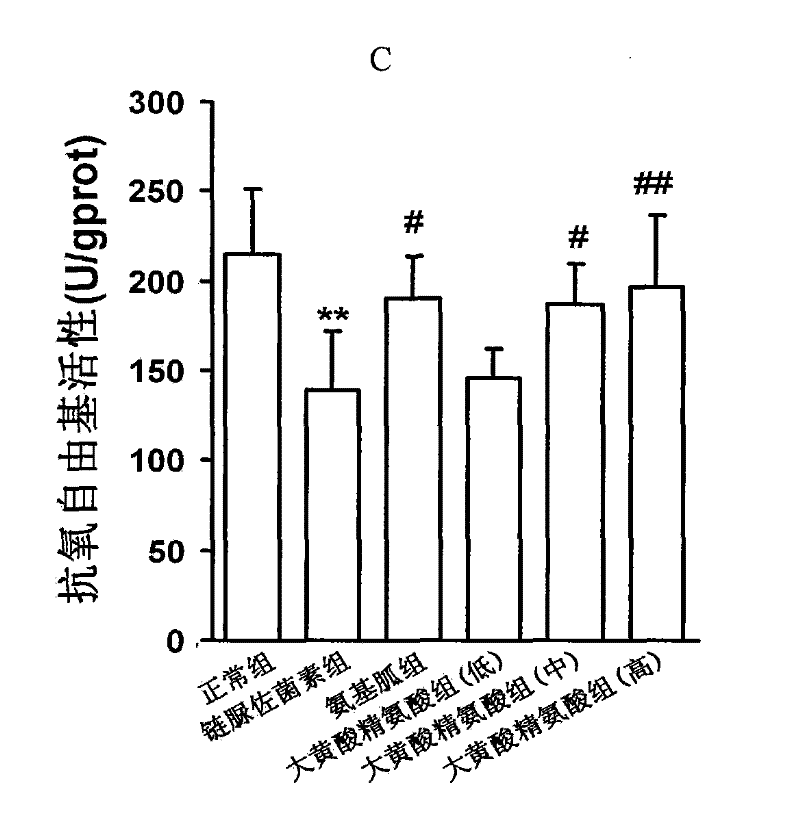
[0094] Example 1, the compound of rhein and arginine (macroarginic acid) treats diabetic cardiomyopathy.
[0095] Diabetes was induced in rats by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin 65mg / kg. Blood sugar was as high as 25mM and maintained for 8 weeks. After 4 weeks, diabetic complications had appeared. The untreated group continued to develop. The treatment group was administered in the last 4 weeks (mg / kg, intragastric administration): positive drug aminoguanidine 100, and 3 doses of sarginic acid: 50 mg / kg, 100 mg / kg, 200 mg / kg. Although the untreated diabetic group did not receive medication, they controlled their food intake and were given dietary control treatments to obtain appropriate treatment.
[0096] Pharmacodynamic observation: It consists of macroscopic main pharmacodynamic indicators, expression of important bioactive molecules (mRNA, and protein) in diseased cells and other indicators.
[0097] Sarginic acid restored the above indicators to the normal...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2, the treatment of diabetic macroangiopathy with sarginic acid. Basically the same as Example 1,
[0100] Diabetes was induced in rats by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin 65mg / kg. Blood sugar up to 25mM, maintained for 8 weeks. After 4 weeks, diabetic complications had appeared. The untreated group continued to develop. The treatment group was administered in the last 4 weeks (mg / kg, intragastric administration): positive drug aminoguanidine 100, and 3 doses of sarginic acid: 50 mg / kg, 100 mg / kg, 200 mg / kg. Although the untreated diabetic group did not receive medication, they controlled their food intake and were given dietary control treatments to obtain appropriate treatment.
[0101] The vasodilation function and NO bioavailability were restored after 4 weeks of treatment with sarginic acid and aminoguanidine. At the same time, the molecular biological targets abnormally expressed in the blood vessel wall are basically restored to the normal...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Example 3, the treatment of diabetic nephropathy with macrospermic acid.
[0104] Diabetes was induced in rats by intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin 65mg / kg. Blood sugar was as high as 25mM and maintained for 8 weeks. After 4 weeks, diabetic complications had appeared. The untreated group continued to develop. The treatment group was administered in the last 4 weeks (mg / kg, intragastric administration): positive drug aminoguanidine 100, and 3 doses of sarginic acid: 50 mg / kg, 100 mg / kg, 200 mg / kg. Although the untreated diabetic group did not receive medication, they controlled their food intake and were given dietary control treatments to obtain appropriate treatment.
[0105]The trace protein in 24h urine of rats with diabetic nephropathy increased significantly, and the creatinine and non-protein nitrogen in blood increased, suggesting: diabetic nephropathy. At the same time, the molecular biological indicators: the gene and protein expression of PPARα i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com