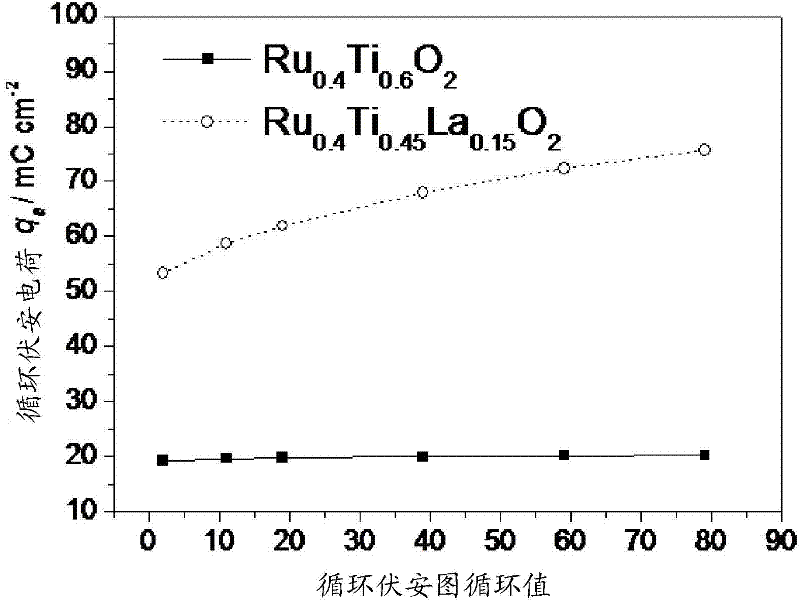
Electrode for producing chlorine through electrolysis
An electrode, conductivity technology, applied in the field of new electrodes, can solve problems such as low stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] A titanium plate with a diameter of 15 mm (thickness 2 mm) was blasted to clean and roughen the surface, followed by pickling (2 h) in 10% oxalic acid at 80 °C, followed by cleaning with isopropanol and Dry in a stream of nitrogen.
[0093] To make the coating solution, 99.6 mg of ruthenium acetylacetonate (Ru(acac) 3 ), 207.2 μl of titanium isopropoxide (Ti(i-OPr) 4 ) and 13.3 mg of vanadyl acetylacetonate (VO(acac) 2 ) were each dissolved in 1.45 ml of isopropanol and 1.45 ml of propionic acid and heated at reflux for 30 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, the three solutions were mixed to produce a homogeneous and clear solution with a wine red color. 50 μl of this coating solution was applied to the titanium substrate by micropipette, followed by air drying. The layer was first sintered in air at 250° C. for 10 minutes and then at 450° C. for 10 minutes. These steps (coating solution application, drying, sintering) were repeated 8 times. After the nint...
Embodiment 1b
[0095] Embodiment 1b (comparative example)
[0096] The titanium substrate was pretreated in a manner similar to Example 1.
[0097] To fabricate a coating by thermal decomposition, fabricate containing 2.00 g of ruthenium(III) chloride hydrate (Ru content = 40.5 wt%), 21.56 g of n-butanol, 0.94 g of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 5.93 g of tetrabutyltitanium Salt Ti-(O-Bu) 4 ) coating solution. A portion of the coating solution was applied to a small titanium plate by brush. It was dried in air at 80°C for 10 minutes and then treated in air at 470°C for 10 minutes. This step (solution application, drying, heat treatment) was carried out a total of 8 times. The plate was then treated in air at 520° C. for 1 hour. Ruthenium loading per unit area calculated from coating solution consumption is 16 g / m 2 , equivalent to 31 mol% RuO 2 and 69 mol% TiO 2 The total coating loading is 49.2 g / m at the composition of 2 (calculated as oxides).
[0098] The chlorine evolut...
Embodiment 2
[0100] The titanium substrate was pretreated in a manner similar to Example 1.
[0101] 60 mg of ruthenium acetylacetonate (Ru(acac) 3 ), 236.8 μl of titanium isopropoxide (Ti(i-OPr) 4 ) and 13.3 mg of vanadyl acetylacetonate (VO(acac) 2 ) were each dissolved in 1.45 ml of isopropanol and 1.45 ml of propionic acid, followed by heating (with stirring) at 150° C. under reflux for 30 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, the three solutions were mixed to produce a homogeneous and clear solution with a wine red color. The coating and sintering steps were performed as described in Example 1.
[0102] This yielded a sample with a composition of 15 mol% Ru / 80 mol% Ti / 5 mol% V based on the metal constituents. Based on metal content, this equates to 3.9 g / m 2 ruthenium loading. This corresponds to 22.7 g / m 2 The total coating loading (oxide RuO 2 、TiO 2 , V 2 o 2 Sum).
[0103] The chlorine evolution potential of this sample (measured in a similar manner to Example 1)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com