Process for producing tea extract
A technology for extracts and teas, applied in the field of tea extracts, to achieve the effects of improved operability, improved yield and shortened time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
reference example 1
[0054] Reference Example 1 Determination of polygalacturonase activity (Somogyi-Nelson method (ソモギーニルスン method): refer to J. Biol. Chem. 153, 375-380, 1994)
[0055] To 0.9 ml of 50 mM acetate buffer (pH 4.5) containing 1% polygalacturonic acid was added 0.1 ml of an appropriate (proper) dilution of the enzyme solution. The above mixed solution was reacted at 45°C for an appropriate (proper) time, then heated in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes to inactivate the enzyme, and ice-cooled to prepare a reaction solution. Add 0.3ml of Somogyi copper reagent to 0.3ml of the reaction solution, heat in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes, ice-cool, add 0.3ml of Nelson reagent, stir thoroughly with a test tube mixer, further add 3ml of ion-exchanged water, and mix with a test tube Mixer thoroughly. The solution was treated with a centrifuge at 9000 rpm for 3 minutes, and the absorbance (Abs.) at 500 nm of the supernatant was measured. On the other hand, using a solution obtained by...
reference example 2
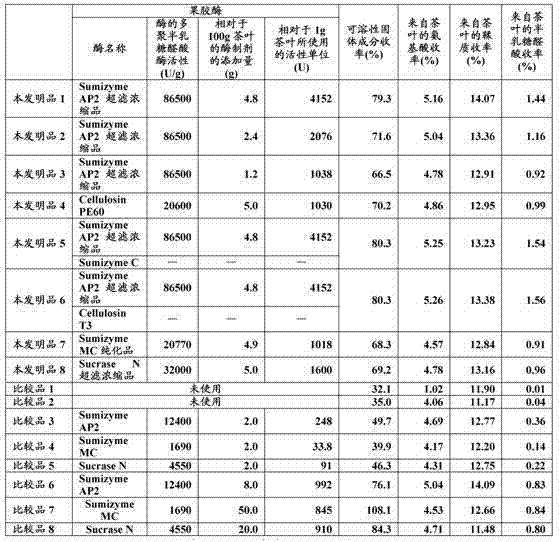
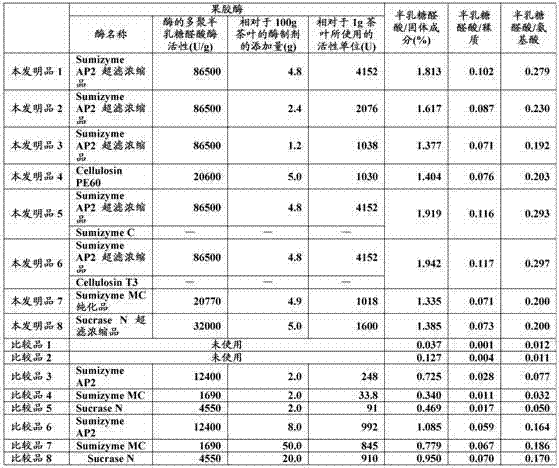
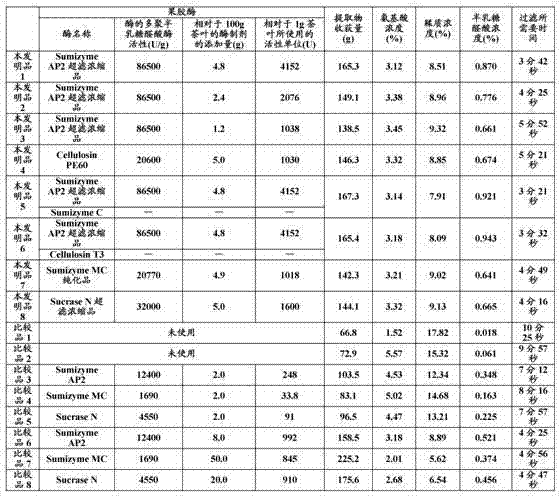
[0062] Dissolve 100 g of Sumizyme AP2 (manufactured by Shin Nippon Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) (polygalacturonase activity obtained by the above measurement: 12,400 U / g) in 1,000 g of ion-exchanged water, and use Vivaflow (ビバフロー) (registered trademark) 50VF05P2 (Separation molecular weight: 30,000: manufactured by Sartorius Co., Ltd. (Zaltorius Corporation)) was concentrated by ultrafiltration, and 30 ml of the fraction that failed to pass through was recovered, and further freeze-dried to obtain reference product 2 (12.0 g: the polysemi- Lacturonidase activity: 86500U / g).
Embodiment 1
[0064] To a solution obtained by dissolving 0.6 g of sodium ascorbate in 900 g of demineralized water, 100 g of green tea leaves (made in China by steaming green leaves) were added, sterilized at 80°C for 5 minutes, and cooled to 45°C. 1 g of tannase (manufactured by Mitsubishi-Kagaku Foods Corporation: 500 U / g) was added thereto, followed by stirring for 15 minutes. Then, 1 g of protease M (manufactured by Amano Enzyme Inc.: 5500 U / g) and 4.8 g of reference product 2 (polygalacturonase activity obtained by the above measurement with respect to 1 g of tea leaves) were added. 4152U / g), after dissolving, carry out enzyme treatment at 40°C for 8 hours.
[0065] After the enzyme treatment, sterilize at 90°C for 10 minutes, then cool to 30°C, remove the tea residue solids with a dry cloth, and then use a No. 2 filter paper (8cm) pre-coated with 10g of cellulose powder. , carry out suction filtration under certain pressure (degree of reduced pressure 13.33KPa), obtain the extract o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com