Branch type dry strength agent and preparation method thereof
A dry strength agent and branched chain technology, applied in the direction of reinforcing agent addition, can solve the problems of gelation, explosion, high local concentration, etc., to achieve the effect of preventing gelation, good effect, and increasing the dry strength of paper
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
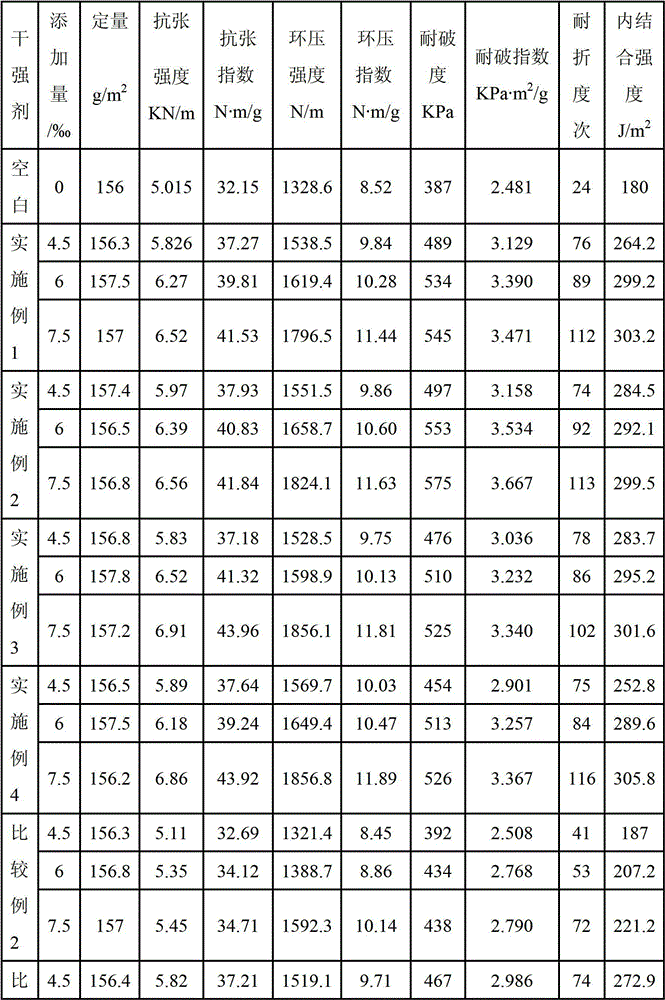
Embodiment 1
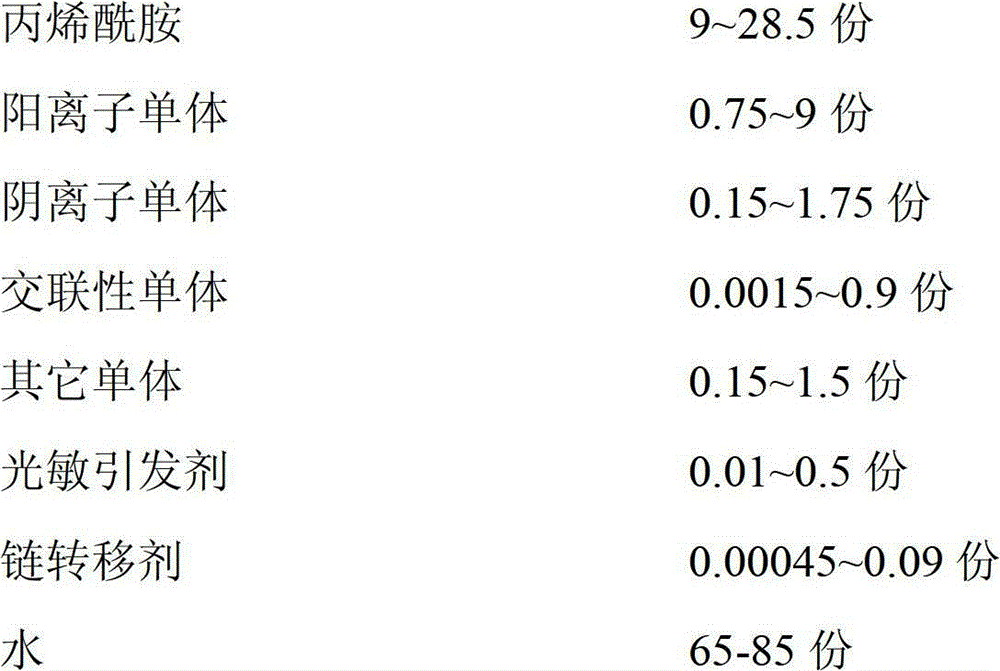
[0034] Mix 355g of water, 118g of acrylamide, 2g of itaconic acid, 16g of methacryloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride, 0.08g of methylenebisacrylamide, 4g of hydroxypropyl acrylate, 2g of ethyl acrylate and diphenyl Stir and mix 1 g of ketone evenly, repeatedly evacuate and pass high-purity nitrogen to drive oxygen 3 times to obtain solution A;
[0035] Stir and dissolve 1 g of sodium allyl sulfonate and 50 g of water evenly, and repeatedly evacuate and pass high-purity nitrogen to drive oxygen 3 times to obtain solution B;
[0036] Add 50% of solution A and 30% of solution B into the reaction kettle washed with high-purity nitrogen to drive oxygen, raise the temperature to 75°C, turn on the ultraviolet light to irradiate the reaction kettle, and carry out photoinitiated polymerization for 60 minutes;
[0037] Continue to add 25% of solution A and 25% of solution B in the reactor to carry out photoinitiated polymerization for 30 minutes;
[0038] Continue to add 25% of soluti...
Embodiment 2
[0041].Water 350g, acrylamide 110g, maleic anhydride 2g, dimethylaminoethyl (meth)acrylate 10g, dimethylacrylamide 0.9g, hydroxypropyl methacrylate 15g, styrene 5g and benzophenone 0.7g was stirred and mixed evenly, and the high-purity nitrogen was repeatedly evacuated to drive oxygen 3 times to obtain solution A; 0.6g sodium allyl sulfonate and 60g water were stirred and dissolved evenly, and the high-purity nitrogen was repeatedly evacuated to drive oxygen 3 times. Obtain solution B; add 50% of solution A and 30% of solution B into the reaction kettle washed with high-purity nitrogen to drive oxygen, heat up to 80°C, turn on the ultraviolet light to irradiate the reaction kettle, and carry out photoinitiated polymerization for 55 minutes ; Continue to add 25% of solution A and 25% of solution B in the reactor for photoinitiated polymerization for 25 minutes; continue to add 25% of solution A and 45% of solution B in the reactor for photoinitiated polymerization until the visc...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Mix 450g of water, 82g of acrylamide, 1g of maleic acid, 10g of methacryloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride, 0.5g of dimethylacrylamide, 2g of styrene, 1g of hydroxypropyl acrylate, and 5g of ethyl acrylate Stir and mix with 0.7 g of eosin, and repeatedly vacuumize and pass high-purity nitrogen to drive oxygen twice to obtain solution A; stir and dissolve 0.005 g of mercaptoacetic acid and 120 g of water evenly, and repeatedly pump high-purity nitrogen to drive oxygen twice to obtain Solution B: add 40% of solution A and 25% of solution B into the reaction kettle rinsed with high-purity nitrogen to drive oxygen, heat up to 85°C, turn on the ultraviolet light to irradiate the reaction kettle, and carry out photoinitiated polymerization for 70 minutes; Continue to add 35% of solution A and 35% of solution B to the reactor for photoinitiated polymerization for 25 minutes; continue to add 25% of solution A and 40% of solution B to the reactor for photoinitiated polymerizatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com