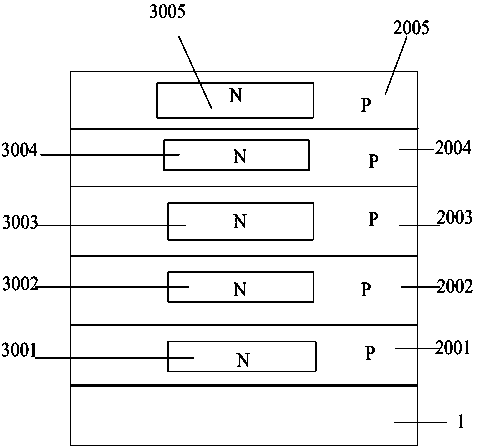
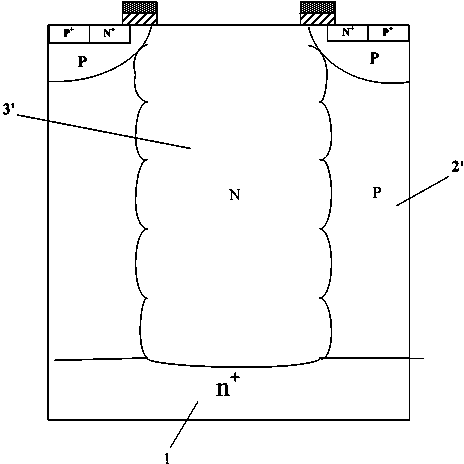
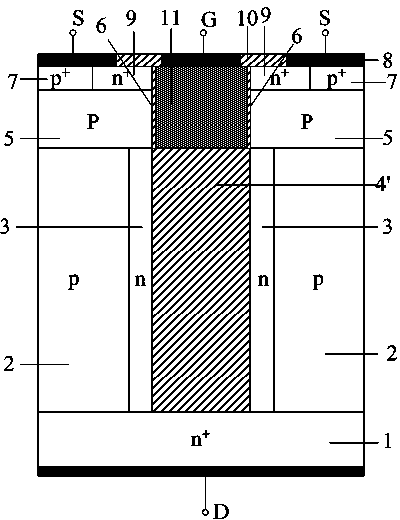
Manufacturing method for groove type semiconductor power device
A technology for power devices and manufacturing methods, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problem that the bottom of the trench gate and the lower interface of the body region cannot be guaranteed to be flush or lower than the lower interface of the body region, affecting the body region. , the body contact area and active area, and the implantation angle need to be precisely controlled to avoid lattice damage, reduce difficulty and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the present invention discloses a method for manufacturing a trench-type semiconductor power device, which includes the following steps:
[0070] a. By epitaxial growth, a p-type first semiconductor region 2 is formed on the semiconductor substrate, such as Figure 5a shown;
[0071] b. Thermally oxidize and grow an oxide layer on the top of the first semiconductor region 2, and then deposit Si 3 N 4 , and perform photolithography; then etch from the top of the first semiconductor region to the semiconductor substrate until the semiconductor substrate 1, forming grooves, and then removing the photoresist; Figure 5b shown. Dry etching such as reactive ion etching may be used, or wet etching may be used. The aspect ratio of the trench can be accurately controlled by dry etching, and the formed trench is basically U-shaped; the trench formed by wet etching can be trapezoidal or V-shaped.
[0072] c. Use anisotropic ...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The manufacturing process of the semiconductor device of the present invention described in Embodiment 1 is preferably applied to a MOS control vertical device, so as to alleviate the contradictory relationship among withstand voltage, on-resistance and switching loss. used for Figure 6a with 6b It is a schematic diagram of the structure of an IGBT manufactured based on the manufacturing method of the present invention. Based on the manufacturing method of the present invention, the difference from Example 1 is that the initial semiconductor material substrate 1 is P + A semiconductor substrate 101, and a buffer layer 12 of the same conductivity type as that of the second semiconductor region is formed on the semiconductor substrate, and the buffer layer can improve the electrical characteristics of the IGBT. Epitaxially forming a first semiconductor region on the semiconductor buffer layer, and partially etching the first semiconductor region from the top to the sem...
Embodiment 3
[0086] The manufacturing process of the semiconductor device of the present invention described in Embodiment 1 can be applied to control vertical devices of N-channel MOS, and can also be applied to control vertical devices of P-channel MOS. P-channel DMOS as Figure 7a with 7b shown. When used in the manufacture of P-channel DMOS, the corresponding conductivity types of the semiconductor substrate 1, the semiconductor layer 2 of the first semiconductor region, the second semiconductor region 3, the active region 5, the body contact region 7, and the source region 9 are related to N The conductivity type of the corresponding region of the channel MOS control vertical device is opposite. Its key steps are as Figure 7c , Figure 7d with Figure 7e As shown, the subsequent steps are exactly the same as in Example 1. In Embodiment 1, an N-channel DMOS is manufactured, and the second semiconductor region 3 is formed by carving grooves on the epitaxial P-type semiconductor, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com