Extraction method of mouse liver sinusoidal endothelial cells
A technology of endothelial cells and extraction methods, which is applied in the field of extraction of mouse liver cells, can solve the problems of insufficient purity and poor cell viability, and achieve the stable effect of high cell purity, low cost, complete protection and activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0034] The steps for extracting hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells from mice are as follows:
[0035] 1) Select normal male KM mice, about 9-10 weeks old, weighing between 20-25g, and inject 0.1-0.2ml of gadolinium chloride solution (about 10mg-20mg / 25g) into the tail vein for two consecutive days before surgery. Fasting the day before, no water restriction;
[0036] 2) Disinfect instruments and animal workbenches, pre-irradiate the experimental bench with ultraviolet light for 1 hour, pre-warm D-hanks at 37°C, 1640 culture medium, and collagenase IV solution with a mass concentration of 0.05%;
[0037] 3) Take a mouse for intraperitoneal injection of 0.1ml of pentobarbital sodium solution with a mass concentration of 1% (10mg / ml), about 40mg / kg, and 0.2ml of heparin sodium solution with a concentration of 200U / ml, about 40U / ml only;
[0038] 4) After the mice were completely anesthetized, they were fixed on the animal operating table, and the abdomen of the mice was disin...
experiment example 1
[0059] Experimental example 1: microscope observation
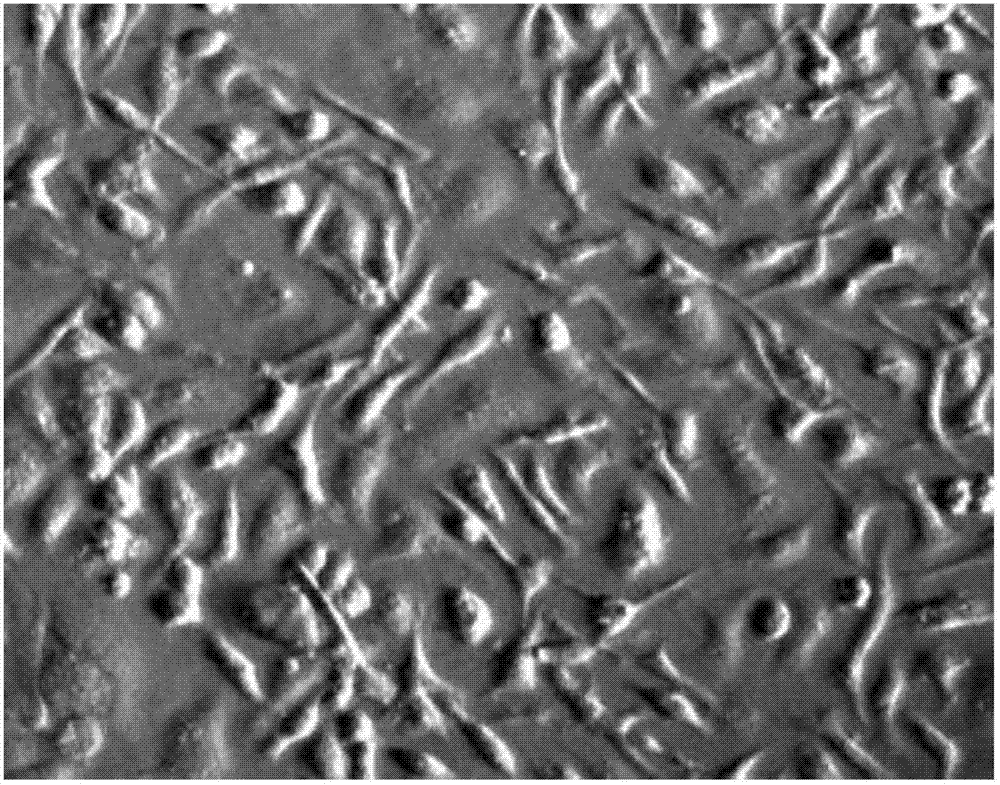
[0060] Obtained mouse hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells were observed under an inverted microscope. Under a low magnification microscope, the living cells were bright, round, plump, with good transparency and clear nuclei ( figure 1 ), evaluating each mouse can obtain about 2×10 6 liver sinusoidal endothelial cells.
experiment example 2
[0061] Experimental Example 2: Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observation
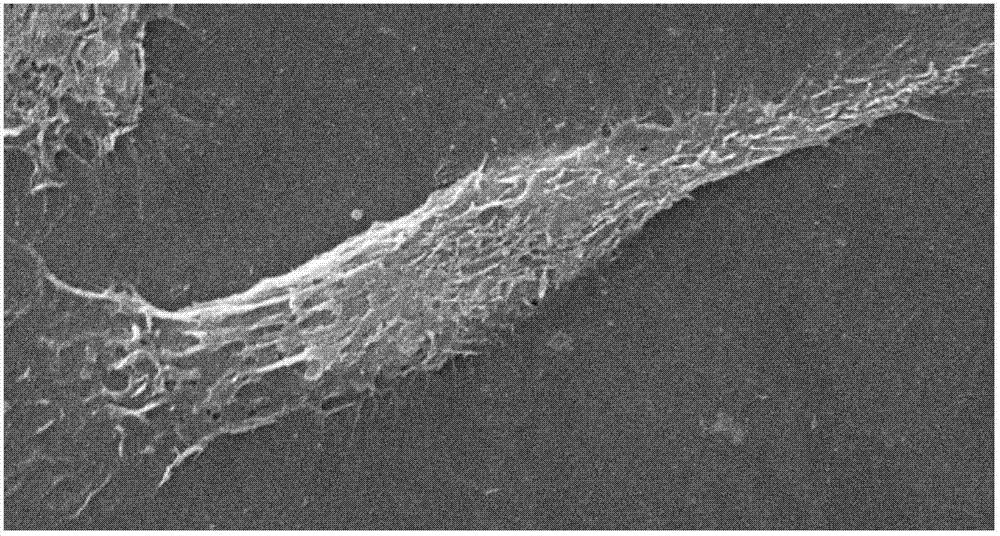
[0062] The hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells obtained in Example 1 were inoculated on cell slides pre-coated with rat tail collagen type I, fixed with glutaraldehyde at 4°C overnight, and dehydrated with 30%-100% alcohol gradients, with a gradient of 10%, each gradient About 2 hours, after the dehydration is completed, vacuum-dry and spray gold on the environmental scanning electron microscope ( figure 2 ), it can be seen that the cells are spindle-shaped, the nucleus is large, and the periphery is thin, and the fenestration structure of different sizes can be seen.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com