Organic radical-modified cellulose derivative, as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of cellulose derivatives and free radicals, applied in electrical components, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the performance of polymer organic free radical batteries, polymers are difficult to degrade, and the concentration of free radicals cannot be achieved. The battery capacity is not easy to decay, the battery cycle stability is good, and the output is abundant.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
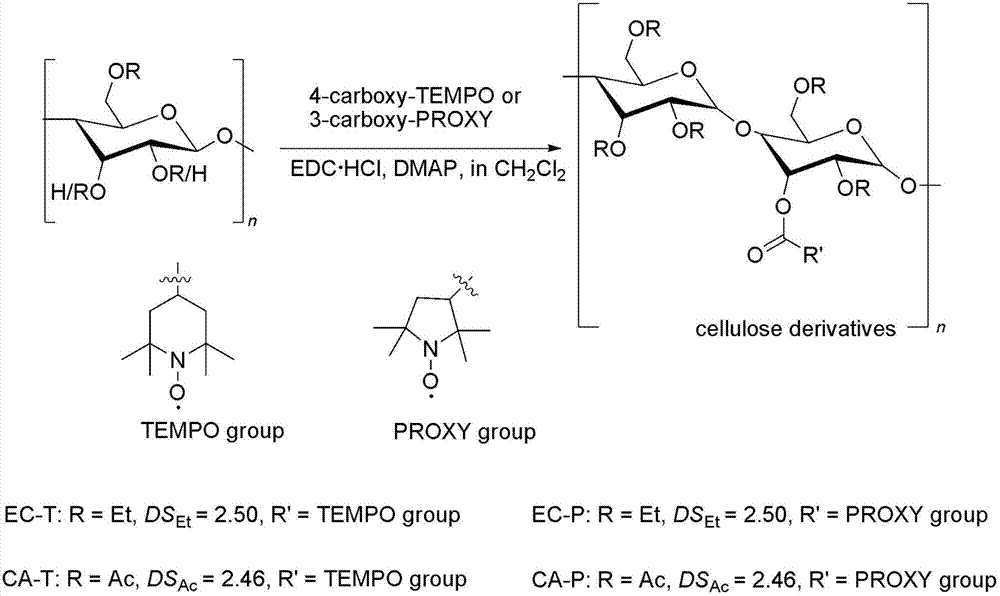
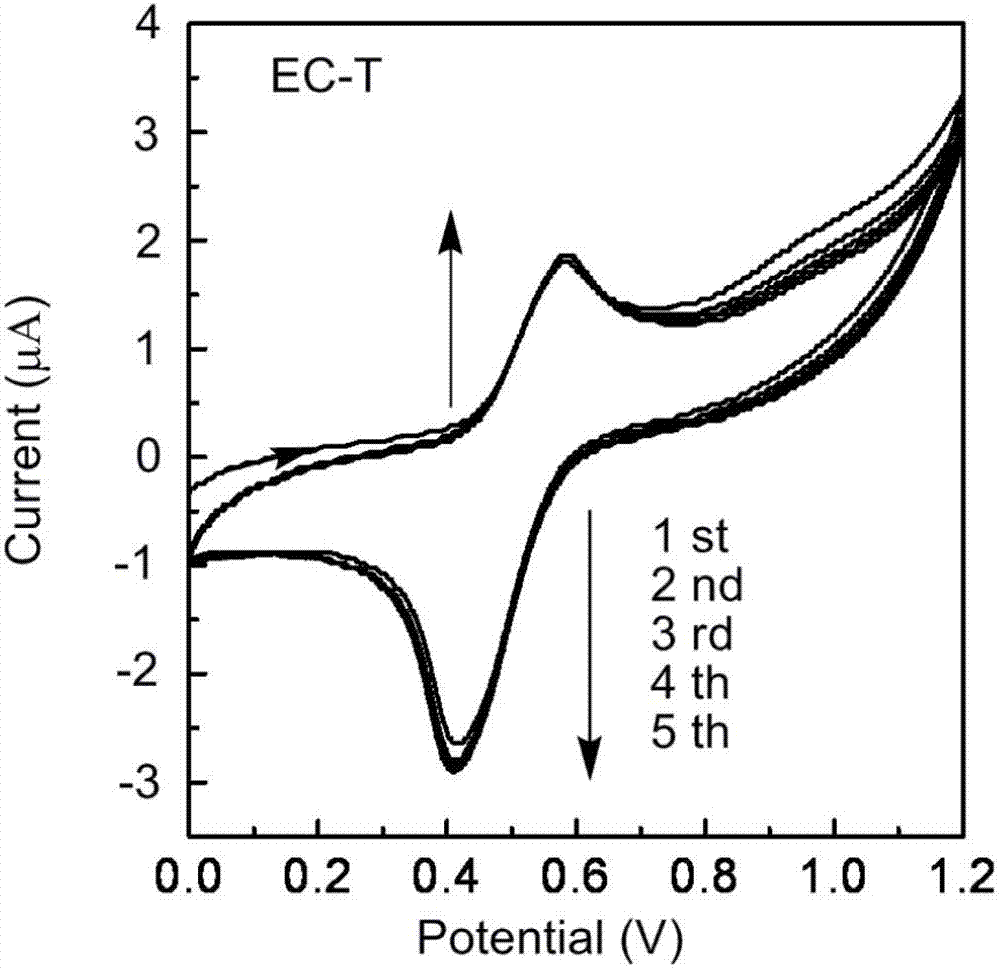
[0040] (1) Polymer preparation: 500 mg of 4-carboxy-TEMPO (2.90 mmol) was added to ethyl cellulose (ethyl substitution degree 2.50) solution in an ice-water bath (1 gram of ethyl cellulose was dissolved in 30 ml of dichloromethane containing 2.22mmol hydroxyl groups), start magnetic stirring, add catalyst EDC.HCl (581mg, 3.04mmol) and DMAP (37mg, 0.30mmol), react at room temperature for 48h, filter the product, wash twice with deionized water, and then use Concentrate to 10ml with a rotary evaporator, precipitate in 500ml methanol, and dry the insoluble matter to obtain a light red solid (EC-T), with a yield of 85%; see the attached figure 1 .
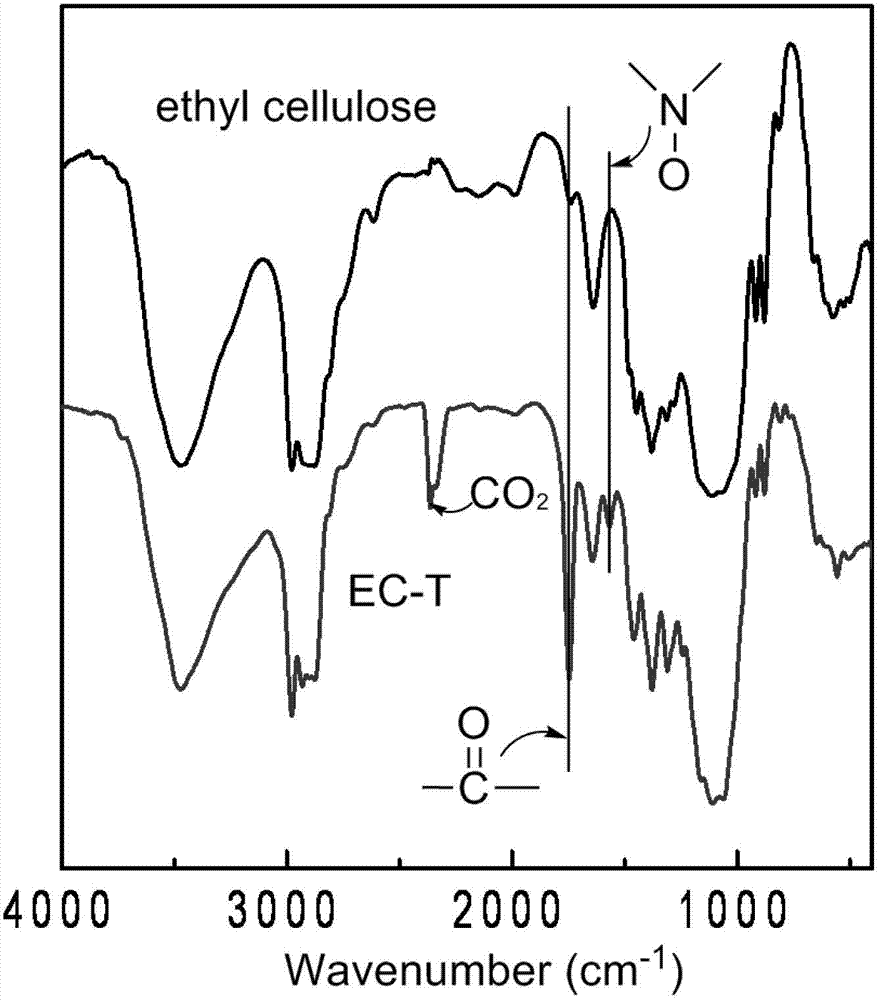
[0041] (2) Polymer structure and properties: The infrared spectrum of organic radical modified cellulose derivative EC-T is shown in the attached figure 2 shown at 3460cm -1 and 1550cm -1 is the characteristic peak of the NO group of the free radical TEMPO, at 1744cm -1 The characteristic peaks of the ester carbonyl groups are at ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Polymer preparation: 500 mg of 3-carboxy PROXYL (2.44 mmol) was added to ethyl cellulose (ethyl substitution degree 2.50) solution (1 gram was dissolved in 30 ml of dichloromethane, containing 2.22 mmol of hydroxyl groups) in an ice-water bath ), start magnetic stirring, add catalyst EDC.HCl (581mg, 3.04mmol) and DMAP (37mg, 0.30mmol), react at room temperature for 48h, filter, wash twice with deionized water, and then concentrate to 10ml with a rotary evaporator, Precipitate in 500ml of methanol, and dry the insoluble matter to obtain a light yellow solid (EC-P), with a yield of 88%; see the attached figure 1 ;
[0046] (2) Polymer structure and properties: as shown in the infrared spectrum of organic radical modified cellulose derivative EC-P, at 3460cm -1 and 1550cm -1 is the characteristic peak of the NO group of the free radical PROXYL, at 1745cm -1 The characteristic peaks of ester carbonyl groups are at the peaks, which do not appear in the infrared spectr...
Embodiment 3
[0050] (1) Polymer preparation: Add 500 mg of 4-acyl chloride TEMPO (4.44 mmol) to a solution of cellulose acetate (acetate substitution degree 2.46) in an ice-water bath (dissolved in 30 ml of dichloromethane, containing 2.22 mmol of hydroxyl ), start magnetic stirring, add catalyst triethylamine (307.3mg, 3.04mmol), react at room temperature for 48h, filter, wash twice with deionized water, then concentrate to 10ml with rotary evaporator, precipitate in 500ml methanol, insoluble The product was dried to obtain a cellulose derivative containing organic free radicals (AC-T) containing TEMPO, a light red solid, and the yield was 84%; the preparation process is shown in the attached figure 1 ;
[0051] (2) Polymer structure and properties: The infrared spectrum of organic radical modified cellulose derivative AC-T shows that at 3455cm -1 and 1554cm -1 is the characteristic peak of the NO group of the free radical TEMPO, at 1740cm -1 These peaks are characteristic peaks of ester...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal degradation temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal degradation temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com